
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
1
Orthopaedic Examination
Of A Patient
Compiled by dr sreekanth r

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
2
CONTENTS
Chapter
Page number
1.
Examination of a patient
3
2.
Characteristics of pain
5
3.
General examination
6
4.
Examination of a diseased bone
7
5.
Examination of a swelling/lump
11
6.
Examination of pathological joints
14
7.
Examination of hip joint
18
8.
Examination of peripheral nerves
21
9.
Examination of shoulder joint
27
10.
Examination of elbow joint
29
11.
Measurement of limb length
31
12.
Examination of wrist and hand
32
13.
Examination of knee joint
35
14.
Examination of ankle and foot
39
15.
Examination of CTEV
41
16.
Examination of spine
44
17.
Examination of peripheral
vascular disease and gangrene
53
18.
Evaluation of rotation of lower limb 56
19.
Developmental milestones
58
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
3
1.EXAMINATION OF A PATIENT
1.
Always stand on right side of patient
2.
Always introduce yourself to patient
3.
Always explain the procedure to patient
4.
Demonstrate first on normal side
5.
Reassure the patient
6.
Always call the patient mr.X/ms.Y
HISTORY
Age Sex Place occupation
Informer-reliable/not
Presenting complaints
History of presenting complaints
Past H
Personal H
Treatment H
Prenatal, natal, postnatal H
Developmental H
Drugs H
Immunization H
Socioeconomic H
ALWAYS ASK FOR DISABILITIES
Grade 0
normal
Grade 1
Limited recreational
Grade 2
Limited professional
Grade 3
Self-care restriction
Grade 4
Bedridden
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
4
ALL CASES OF LOWER LIMBS-
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
6.
taking food
7.
washing face ;
8.
brushing teeth
9.
drying hairs
10.
donning of clothes
11.
writing
12.
jumping
13.
holding & carrying objects in hand
Footwear examination
-Unusual wear and tear
-Any modification
VASCULAR PULSE
5+
abnormal pulse with aneurysm
4+
normal good volume pulse
3+
good with suboptimal volume
2+
feeble but without interobsever dispute
+
very feeble with interobsever dispute
ANY DEFORMITY
-
FIXED OR DYNAMIC
-
GRADE
o
Grade I FULLY CORRECTABLE & CAN BE FORCED
TO OPPOSITE DEFORMITY
o
Grade II ONLY FULLY CORRECTABLE
o
Grade III NOT FULLY CORRECTABLE
EXAMINATION OF SKIN &
NAILS
FOR TROPHIC CHANGES

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
5
2.Characteristics of PAIN
1.
site of pain
2.
mode of onset
3.
severity of pain
4.
nature of pain
-
vague aching
-
burning (tractopathy)
-
throbbing
-
scalding
-
pins & needles
-
shooting
-
stabbing
-
constricting
5.
progression of pain
6.
duration of pain
7.
movement of pain
-
radiation of pain( pain at original site persists )
-
referred pain ( no pain at original site )
-
shifting , migration of pain
8.
special time of occurrence
9.
periodicity of pain
10.
precipitating / aggravating factors
11.
relieving factors
12.
associated symptoms
13.
H/o Tuberculosis
14.
spasm of muscles
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
6
3.GENERAL EXAMINATION
1.Vital index
2.HEAD TO FOOT
•
Craniofacial anomaly, dysmorphism, crowding of teeth, maxillary
hypoplasia, hypertelorism ( canthal index = inner cantal distance/outer
canthal distance x 100 ; 38 males & 38.5 females); teeth ( dentigenous
imperfecta) , tongue ( storage disorder & hypothyroidism)
Plagiocephaly = asymmetrical head
Scaphocephaly= elongated boat shaped head
Oxycephaly = tower or high skull
Clover leaf skull = premature suture fusion
Caput quadratum = narrow based head
•
Chest- pegion chest, pectus carinatum, excavatum, kyphoscoliosis,
spinabifida occulta.
•
Café-au –lait spots ( post pubertal
>6 in number & each >1.5 cm in diameter
Prepubertal >5 in number of each> 0.5 cm )
•
Extremities-hyperelasticity,congenital deformities.
•
Small joint nodules, rheumatoid nodules
•
Neurocutaneous markers
•
Genitourinary abnormalities
•
Sexual development
•
Dentition
•
Hypothyroidism-muscle tone,fasciculation, tremor, nystagmus
•
Weight, armspan, US/LS ratio
•
Dwarfism/gigantism
Short stature-rhizomelic
Mesomelic
Acromelic
micromelic

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
7
HEIGHT
WEIGHT
3-12 months ( 9 + A)/2 kgs
1-6 yrs 2A + 8 kgs
7-12 yrs (7A-5)/2 kgs
ARM SPAN
<5 yrs H-2 cm
5-9 yrs H-1 cm
10 yrs H cm
adults H + 2 cm
WYNE DAVIES CRITERIA FOR HYPERELASTICITY
A.
flexion of the thumb to touch the forearm
B.
dorsiflexion of the fingers parallel to forearm
C.
hyperextension of elbow 15
0
or more
D.
hyperextension of knee 15
0
or more
E.
dorsiflexion of ankle 60
0
or more
US/LS ratio =
1.7 at birth
1 at birth
0.8 after 10 years
Riser sign
Turner index of maturity
Peak height velocity-
8.0 cm in females
9.5 cms in males
1-3 mon 3cm/mon
4-6 mon 2cm/mon
7-12 mon 1.6cm/mon
13-24 mon 1 cm/mon
2-12 yrs (weech formula) 6A + 77 cms
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
8
TANNER SEXAL MATURITY RATING
TANNER SMR GIRLS
STAGE PUBIC STAGE
BREASTS
1
Preadolescent
Preadolescent
2
Sparse,lightly
pigmented
strsight,mediaal border of labia
Breast papilla elevated as
small mound, areola diameter
increased
3
Darker,
beginning
to
curl,increased amount
Breast and areola enlarged,no
contour separation
4
Coarse ,curly, abundant but
amount less than adult
Areola and papilla form
secondary mound
5
Adult feminine triangle , spread
to medial side of thigh
Mature, nipple projects,areola
part of general contour
TANNER SMR boys
STAGE PUBIC hair
PENIS
TESTES
1
NONE
Preadolescent Preadolescent
length<2.5 cm
2
Scanty,
long,
slightly
pigmented
Slight
enlargement
Enlarged
scrotum,pink,texturealtered
lengh >2.5 cm
3
Darker starts to
curl,
small
amount
Longer
Larger length 3.3-4 cm
4
Resembles adult
type, but less in
amount
Larger, glans
and
breath
increase
in
size
Larger
scrotum
darkens
length 4-4.5 cm
5
Adult
distribution
spread to medial
surface of thighs
Adult size
Adult

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
9
4. EXAMINATION OF A DISEASED BONE
HISTORY
1.
Age
2.
onset & progress
3.
pain
4.
duration
5.
fever
6.
sinuses-passage of pieces of bone
7.
any similar disease, other bones
8.
past history-DM,TYPHOID, TUBERCULOSIS,ACTINOMYCOSIS,
h/o open fractures, surgeries, implant insitu
9.
family history- sickle cell disease
GENERAL EXAMINATION
General condition
Cachexia
Neurocuteneous markers; café-au-lait spots
, hemangioma etc
LOCAL EXAMINATION
INSPECTION
1.
attitude & deformity
2.
Swelling
3.
skin over the swelling; sinuses
scar
dilated veins
inflammatory signs
4.
pressure effects distal neurovascular deficit
5.
neighbouring joints
6.
muscle wasting
7.
shortening or lengthening of limb
PALPATION
1.
Local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness – entire bone
-
joint line
3.
swelling
4.
bony irregularity
5.
thickening of bone
6.
bowing
7.
steps on bone
8.
ulcers & sinuses- fixity to bone
9.
presence of fracture
10.
neighbouring structures
•
muscles
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
10
•
nerves
•
vessels
PERCUSSION
AUSCULTATION- BRUIT
MEASUREMENTS
1.
LENGTH of bone/limb
2.
circumference of limb
LOOK FOR
1.
NEIGHBOURING JOINTS
2.
LYMPH NODES
3.
PRESSURE EFFECTS
DON`T MISS
1.
DISTAL – NEUROVASCULAR DEFICIT
2.
PROXIMAL- LYMPHATICS
3.
RULE OF TWO
ALL SWELLING ARISING FROM BONE WILL BE FIXED TO IT
ANY JOINT LOOK FOR ANY SURROUDING MASS ( MYOSITIS)

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
11
5.EXAMINATION OF A SWELLING/LUMP
HISTORY
1.
duration
2.
mode of onset
3.
other symptoms
4.
pain-
-
site
-
time of onset
-
nature
5.
progress of swelling
6.
exact site
7.
fever & other constitutional symptoms
8.
presence of other lumps
9.
secondary changes
-
softening
-
fungation
-
ulceration
-
inflammatory changes
10.
impairment of function
11.
recurrence of swelling
12.
loss of body weight
13.
past history
-
similar history
-
recurrence
-
tuberculosis
-
syphilis
-
leprosy
14.
personal history
15.
family history
-
similar swelling in family members
-
history of malignancy
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
6.
taking food
7.
washing face ;
8.
brushing teeth
9.
drying hairs
10.
donning of clothes
11.
writing
12.
jumping
13.
holding & carrying objects in
hand

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
12
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
GENERAL EXAMINATION
1.
features of cachexia
2.
attitude of limb
3.
pallor/jaundice /cyanosis/clubbing/ pedal edema/ generalized lymphadenopathy
LOCAL EXAMINATION
INSPECTION
1.
Attitude of limbs
2.
gait
3.
situation
4.
colour
5.
shape
6.
size
7.
surface
8.
edge
9.
number
10.
plane of swelling
11.
pulsation
12.
movement with
a.
respiration
b.
deglutition
c.
protrusion of tongue
d.
movt of adj joints,muscle contraction etc
e.
direction of movts
13.
peristalsis
14.
impulse on coughing
15.
skin over the swelling
a.
sinuses
b.
scar ( primary or secondary intention healing)
c.
inflammatory changes
d.
engorged veins
PALPATION
1.
INSPECTORY FINDINGS CONFIRMED
2.
local rise in temperature
3.
tenderness
4.
size,shape,extend
5.
surface
6.
edge-ill/well defined
7.
consistency uniform/variable, soft/firm/hard/bony hard
8.
fluctuation
9.
fluid trill
10.
pulsation

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
13
11.
mobility/fixity- fixity to skin/pinch ability of skin
1.
fixed to surrounding structures
2.
direction of mobility ,structure to which fixed
12.
translucency
13.
impulse on coughing
14.
reducibility
15.
compressibility
16.
pulsations
17.
fixity to overlying skin-skin pinchable or not
18.
relation to surrounding structures
19.
palpable thrill
RELATIVE PROMINENCE OF SWELLING W.R.T DIFFERENT POSITION OF JOINT
PERCUSSION
AUSCULTATION – bruit
MEASUREMENT
-
LENGTH OF LIMB
-
SEGMENTAL LENGTH OF LIMB
EXAMINATION OF NEIGHBOURING JONTS
-RESTRICTION OF MOVTS
- Effusion
EXAMINATION OF DISTAL NEUROVASTULARITY
EXAMINATION OF PROXIMAL LYMPH NODES
EXAMINATION OF PRESSURE EFFECTS ON
-
SURROUNDING & DISTAL STRUCTURES
EXAMINATION OF CHEST
EXAMINATION OF THYROID,BREAST, PROSTATE ETC AND PRIMARY AREA OF
MALIGNANCY.

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
14
6.EXAMINATION OF PATHOOGICAL JOINTS
HISTORY
1.
Age,sex
2.
occupation
3.
mode of onset & progress
4.
pain-
-
site
-
character
-
night cry
-
relation to activities
-
aggravating & relieving factors
5.
locking
6.
deformity
7.
past history
-
leprosy
-
tuberculosis
-
gonorrhoea
-
syhphilis
-
typhoid
-
constitutional symptoms
-
arthritis symptoms
-
psoriasis
-
urethritis
-
rheumatic fever
8.
TREATMENT HISTORY
9.
FAMILY HISTORY
-
hemophilia
-
blood dyscrasisa
-
tuberculosis
-
gout
-
leprosy
-
syhpyilis
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
6.
taking food
7.
washing face ;
8.
brushing teeth
9.
drying hairs
10.
donning of clothes
11.
writing
12.
jumping, running
13.
holding & carrying objects in hand
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
15
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
GENERAL EXAMINATION
1.
toxemia
2.
cachexia
3.
pyrexia
LOCAL EXAMINATION
FULLY EXPOSE BOTH JOINTS & PLACE IN SAME POSITION
INSPECT FROM ALL SIDES
1.
GAIT
2.
attitude & deformity
3.
swelling – generalized (effusuion)
-
localized
4.
skin over the joint
-
sinuses, scar,ulcers,engorged veins,inflammatory signs
5.
muscle wasting
6.
signs of skin lesions -- café au lait spots, psoriasis, hemangiomas
PALPATION
1.
local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness—joint line & other structures
3.
palpation of bones
•
swelling
•
irregularities
•
crepitus
•
deformity
4.
swelling – take form of the joint = effusion
•
synovial thickening
•
effusion—fluctuation , tap
5.
muscle wasting
6.
signs of hyper elasticity
Position of ease
1.
hip -- flexion abduction external rotation
2.
shoulder—flexion adduction internal rotation
3.
elbow—semiflexion pronation
4.
knee—slight flexion
5.
wrist—slight flexion
6.
ankle—slight plantar flexion inversion
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
16
WYNE DAVIES CRITERIA FOR HYPERELASTICITY
A.
flexion of the thumb to touch the forearm
B.
dorsiflexion of the fingers parallel to
forearm
C.
hyperextension of elbow 15
0
or more
D.
hyperextension of knee 15
0
or more
E.
dorsiflexion of ankle 60
0
or more
7.
TESTS FOR INSTABILITY
MOVEMENTS & DEFORMITY
1.
FIXED DEFORMITIES
2.
reveal concealed deformities
3.
both active & passive movements
4.
both jonts to examined
5.
movement
—
range of motion
—
arc of motion
—
axis deviation
—
movement in different planes
—
restriction of movements (all or specific)
—
gear stick phenomenon
—
pain spasm crepitus
—
abnormal movements
MEASUREMENTS
APPARENT LENGTH – KEEP BOTH LIMBS PARALLELL
TRUE LENGTH—SQUARE THE PELVIS
-- KEEP NORMAL LIMB IN SAME POSITION AS THAT OF AFFECTED
LIMB
BRAYANTS `S TRIANGLE —SQUARE THE PELVIS
-- KEEP NORMAL LIMB IN SAME POSITION AS THAT OF AFFECTED
LIMB

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
17
1.Length of limb
1. Upper limb -
•
- angle of acromion
•
Lateral epicondyle
•
Radial styloid
2. Lower limb
•
ASIS
•
Medial joint line of knee
•
Medial malleolus
2.Circumference of the limb
3.Special measurements
EXAMINATION OF SPINE & ALL OTHER JOINTS
CHEST EXPANSION
STRAIGHT WALL TEST
EXAMIATION OF GENITALIA
EXAMINATION OF DISTAL VASCULARITY
EXAMINATION OF PROXIMAL LYMPHNODES
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
o
MOTOR
1.
BULK OF muscles
2.
tone of muscles
3.
power of muscles ( test against gravity first)
4.
reflexes
5.
coordination
o
SENSORY
o
Autonomous nervous system

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
18
7.EXAMINATION OF HIP JOINT
History
1.
Pain
2.
Inability to walk
3.
Stiffness
4.
Drug intake, STERIODS
5.
Childhood problems
6.
Alcohol intake, SMOKING
7.
Other joint involvement
8.
bleeding disorders
9.
storage disorders
10.
evening rise of temperature
11.
spine disease
12.
shoe modification
13.
use of brace or canes
14.
deep sea diving
15.
endocrine diseases
16.
storage disoder
17.
Instability
18.
LLD
19.
Limp
20.
Injury
21.
h/o small joint disease
22.
h/o pain opposite hip
23.
surgery around hip
24.
major trauma to hip
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
GENERAL INSPECTION
1.
small joint disease
2.
cushingoid features
3.
short stature US/LS RATIO
4.
features of cerebral palsy
5.
endocrine disease
6.
bleeding diseases
7.
storage disorder
8.
steroid treating disease
9.
features
of
chronic
alchoholism
10.
rheumatoid nodules
11.
features of skeletal dysplasia
LOCAL EXAMINATION
INSPECTION
GAIT
ANTERIORLY
-
attitude & deformity
-
level of shoulders , nipple , umbilicus
-
trunk furrows
-
external iliac fossa
-
level of ASIS
-
position of patella
-
level of medial malleolus & heel
-
apparent shortening

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
19
-
scarpas triangle –fullness
-swelling
- mass
- pulsations
- sinus
- scar
- creases in inguinal region & thigh
- visible pulastions
- engorged veins
- wasting of muscles
- broadened perineum
- cold abscess areas
LATERALLY
-
kyphosis
-
lumbar lordosis
-
protrubent abdomen
-
position of trochanter
-
fullness, prominence
- Sinus, scar, pulsations, engorged veins
POSTERIORLY
-
scoliosis, rib hump
-
level of scapulae
-
gluteal folds ( symmetric/asymmetric)
-
atrophy of gluteal muscles- g.maximus.g.medii & minimii
-
atrophy of calf muscles
-
sinus, scar, pulsations, engorged veins
EXAMINATION IN SITTING POSITION ON A STOOL
SEE FOR OBLITERATION OF SCOLIOSIS, LORDOSIS
EXAMINATION IN LYING DOWN POSITION
Prone
Supine
Lateral

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
20
PALPATION
IN LYING DOWN POSITION
ANTERIORLY
-
local rise in temperature
-
anterior joint line tenderness
-
level of asis
-
scarpas triangle
-
normalresistance
-
femoral pulsation
-
fullness , mass
-
hernial orifices
-
cold abscess areas
-
palpation of proximal femur
-
any myositic mass
-
LATERALLY
-
greater trochanter
-
tenderness local & joint
-
level elevaed/depressed
-
Thickened
-
any myositic mass
-
POSTERIORLY
-
any bony mass
-
tenderness
-
oher mass
-
any myositic mass
-
PROXIMAL FEMUR
MOVEMENT & DEFORMITIES
FIXED FLEXION, ABDUCTION, ADDUCTION & ROTATIONAL DEFORMITIES
FURTHER MOVEMENTS POSSIBLE ( active then passive)
EACH MOVEMENT – EXAGGERATED
- RESTRICTED BY PAIN & SPASM
- ASSOCIATED CREPITUS
- AXIS DEVIATION
BOTH ACTIVE & PASSIVE MOVEMENTS
NORMAL LIMB
AFFECTED LIMB
FLEXION
120
0
EXTENSION
15
0
ABDUCTION
40
0
ADDUCTION
30
0
INTERNAL ROTATION
30
0
EXTERNAL ROTATION
45
0

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
21
MEASUREMENT
APPARENT LENGTH ---- KEEP LIMBS PARALLEL & IN LINE WITH TRUNK
TRUE LENGTH -- SQUARE THE PELVIS & KEEP NORMAL LIMB IN POSITION AS
AFFECTED ONE
NORMAL
AFFECTED
APPARENT
TRUE
SUPRATROCHANTERIC
BRAYANTS METHOD
NELATON`S LINE
THIGH
LEG
SCHOEMAKER’S LINE
MORRIS’ BITROCHANTERIC TEST
CHIENE’S TEST
KOTHARIS LINE
MEASUREMENT OF GIRTH
THIGH
LEG
STABILITY TESTS
TELESCOPY
TRENDELENBERG TEST ( CONVENTIONAL; DELAYED ; STRESS)
ORTOLANI TEST
BARLOW TEST
SPECIAL TESTS
GAUVAIN`S TEST
PATERIC (FABER) TEST
CRAIG TEST (RYDER METHOD OF VERSION OF FEMUR)
GALEAZZI TEST FOR THIGH
ALLIS TEST FOR LEG
ELY`S PRONE RECTUS FEMORIS CONTRACTURE TEST
NOBLE COMPRESSION TEST
OBER TEST
ERICHSON`S TEST
HART`S SIGN
OBER TEST

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
22
PER RECTAL DIGITAL EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION OF LYMPH NODES
EXAMINATION OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
EXAMINATION OF OPPOSITEHIP, KNEES, SPINE
CHEST EXPANSION
EXAMINATION OF GENITALIA
EXAMINATION OF FOOT WEAR
EXAMINATION OF SACROILIAC JOINTS
1.
GENSELEN`S TEST
2.
GILLES TEST
3.
PUMP HANDLE TEST
4.
ACTIVE SLRT
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
23
8.EXAMINATION OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
HISTORY
1.
age,sex
2.
occupation ( painter; industrial worker ; fireexposive worker etc)
3.
numbness, parasthesia
4.
diabetes mellitus
5.
leprosy, syphilis
6.
seizure disorder
7.
loosening of slippers
8.
able get up from squatting position
9.
able get things over head
10.
areas of skin that is dry always
11.
varizella zoster infection
12.
arthritis
13.
skin lesions –SLE,other autoimmune disorders
14.
neurocutaneous markers café au lait spots
15.
poliomyelitis,cerebral palsy
16.
FAMILY HISTORY of neurological illness
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
6.
taking food
7.
washing face ;
8.
brushing teeth
9.
drying hairs
10.
donning of clothes
11.
writing
12.
jumping
13.
holding & carrying objects in hand
14.
SEXUAL FUNCTION
15.
BOWEL BLADDER FUNCTION
INSPECTION
1.
attitude & deformity
( wrist drop,winging of scapula,claw hand,ape thumb,pointing index,foot drop)
2.
wasting of muscles
3.
skin
•
dry glossy, smooth
•
disappearance of cutaneous folds & subcutaneous fat
•
causalgia
•
vasomotor changes –pallor,cyanosis
•
tropic changes of nails
•
trophic ulcers
4.
scar s, or wounds

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
24
PALPATION
1.
TEMPERATURE
2.
MUSCLES – wasted soft flabby
3.
skin – aneasthesia
4.
scar
5.
any myositic mass
6.
thickening of nerves
-
ulnar nerve at elbow
-
CPN at fibula neck
-
Supratrochlear nerves
-
Facial nerve
MUSCLE POWER
1.
ACCESORY NERVE – trapezius
2.
hypoglossal nerve- muscles of tongue
3.
long thoracic nerve- serratus anterior
4.
axillary nerve- deltoid
5.
radial nerve
-
brachioradialis
-
triceps
-
ext. digitorum communis
-
extensors of wrist
6.
medial nerve
-
FPL
-
FDS,FDP( LATERAL HALF) oschsners clasping test
-
Abductor pollicis brevis (PEN TEST)
-
Opponens pollicis
7.
ulnar nerve
-
FCU
-
FIRST DORSAL INTEROSSEUS & ADDUCTOR POLLICIS – FORMET`S
SIGN
-
INTEROSSEII
-
--ABDUCTION OF FINGERS
-
CARD TEST
-
EGAWA TEST( PITRES-TESTUT SIGN)
-
EXTENSION OF PIP DIP JOINTS
7.
SCIATIC NERVE- CPN; TIBIAL NERVE
8.
FEMORAL NEVE – QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
25
SENSATION
1.
tactile sensitivity
2.
pain
3.
temperature (cold & hot)
4.
steriognosis
5.
position sense ( hold on sides of phalanx only)
6.
vibration sense (128 Hz)
REFLEXES
EXAMINATION OF NERVE AS A WHOLE- TINEL SIGN; thichening
AUTONOMOUS FUNCTION
1.
anhydrosis
2.
causalgia
3.
trophic changes ( ulcers, pulp atrophy, nail changes )
4.
oedema ( CRPS)
5.
atrophy of skin
ULNAR NERVE PALSY
1.
DUCHENNE SIGN – clawing of RF,LF
2.
loss of flexion of MCPJ
3.
BOUVIER`S MANEUVER- if hyperextension prevented by dorsal pressure EDC can
extend PIP DIP joints
4.
ANDRE-THOMAS SIGN- AN unconscious effort to extend the fingers by
tenodesing the extensor tendons with palmar flexion of wrist will only increase the
deformity
5.
CROSS YOUR FINGER TEST-inability to cross the flexed middle finger dorsally
over the index finger or index over the long finger(MF) when palm and finger are
placed on a flat surface
6.
PITRES-TESTUT SIGN== EGAWAS TEST
7.
LOSS OF INTEGRATION OF FLEXION OF MCP,DIP,PIP—FINGERS ROLL
ONTO PALM
8.
LOSS OF LATERAL OR KEY PINCH ( ADD POLLICIS PALSY
JEANNES`S SIGN –loss of key pinch with hyperextension of I MCP to 10-15
0
9.
MASSES`S SIGN – flattened metacarpal arch & loss of hypothenar eminence
10.
POLLOCK SIGN- loss of extrinsic power of ulnar inverted FDP with inability to flex
distal phalanges of RF & LF
11.
impairment of precision grip
12.
BUNNELL`S O SIGN- or NEWS PAPER SIGN-IP of thumb flexes to 80-90
0
as FPL
attempts to hold an object

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
26
MOVEMENTS
-
ACTIVE
-
PASSIVE
EXAMINATION OF TENDONS ELIGIBLE FOR TENDON TRANSFERS
-
PALMARIS LONGUS
-
PLANTARIS
-
ECRL & B
-
ECU
-
EDC
-
EI, EDM

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
27
9.EXAMINATION OF SHOULDER JOINT
HISTORY
1.
trauma
2.
dislocation
3.
pain
4.
diabetes mellitus
5.
cervical spine pain
6.
brachial plexus injury
7.
past history-
8.
birth injury
Disabilities
1.
taking food
2.
washing face ;
3.
brushing teeth
4.
drying hairs
5.
donning of clothes
6.
writing
7.
jumping
8.
holding & carrying objects in hand
INSPECTION ( anteriorly,laterally, superiorly, posteriorly )
1.
attitude & deformity
2.
DROOPNG OF SHOULDER
3.
contour of shoulder; abnormal prominence of acromion
4.
sulcus sign
5.
abnormal swelling
6.
skin – sinus , scar, engorged veins
7.
axilla
8.
winging of scapula
9.
sternoclavicular joint
10.
clavicle
11.
scapula ( level, borders and angles, spine, acromion)
12.
acromion ( size , shape )
13.
acromoclavicular joint
14.
axilla
PALPATION
1.
local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness
3.
three bony point relation
•
tip of corocoid
•
tip of acromion
•
greater tuberosity
4.
palpation of bones
•
thickening
•
irregularity
5.
CODMANN METHOD OF PALPATION
6.
swelling
7.
axilla – swelling,sinus scar etc
8.
sternoclavicular & acromioclavicular joints
9.
any myositic mass
10.
DOWBARN`S SIGN
DON`T MISS THE
AXILLA
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
28
MOVEMENTS
ABDUCTION - 180
0
ADDUCTION-50
0
FLEXION 90
0
EXTENSION -45
0
IN
FULL
ADDUCTION
IN
FULL
ABDUCTION
IN
FULL
EXTENSION
EXTERNAL
ROTAION
45
0
90
0
70
0
INTERNAL
ROTATION
45
0
70
0
70
0
PAIN SPASM CREPITUS WITH EACH MOVEMENT
MOVEMENTS OF SHOULDER GIRDLE
1.
ELEVATION
2.
DEPRESSION
3.
PROTRACTION
4.
RETRACTION
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
rotator cuff – NEER`s impingement
test & sign
2.
apprehension test
3.
jobes relocation test
4.
drawertest of gerber & ganz
5.
jerk test
6.
sulcus test
7.
sulcus test at 0
0
& 45
0
abduction
8.
shift and load test
9.
anterior apprehension test
10.
posterior clunk test
11.
speed`s test
12.
drop arm test
13.
yegarson`s test
14.
Hawkin`s test
15.
Dougas test
16.
Hamilton ruller test
17.
Andrew`s prone apprehension test
18.
callaway sign
19.
bryant test
( sulcus test 0
0
RC interval laxity & 45
0
inferior capsule
+ 1 < 1cm ; + 2 1-2 cm ; +3cm >2cm )
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
1.
AXILLARY NERVE – DELTOID
2.
SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE- SUPRA & INFRASPINATUS
3.
LONG THORACIC NERVE—WINGING OF SCAPULA
4.
BRACHIAL PLEXUS EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION OF CERVICAL SPINE
EXAMINATION OF AXILLARY LYPHNODES
EXAMINATION OF CHEST , ELBOW OPPOSITE SHOULDER ABDOMEN

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
29
10.EXAMINATION OF ELBOW JOINT
HISTORY
1.
TRAUMA; treatment history
2.
tuberculosis
3.
arthritis history
4.
urethritis
inspection
1.
attitude & deformity
2.
carrying angle
3.
swelling
-
para olecranon areas
-
anconeus soft spot
-
radicapitellar joint
-
general diffuse swelling - effusion
4.
skin
- sinus scar engorged veins
5.
muscle wasting
PALPATION
1.
local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness
3.
bony components esp radial head
-
irregularity
-
bowing
-
thickening
-
steps
4.
three bony points
•
olecranon
•
medial epicondyle
•
lateral epicondyle
5.
swelling
- effusion
6.
supratrochlear lymph nodes
- anterior to medial intermuscular septum I cm above medial condyle
7.
any myositis mass
8.
ulnar nerve dis/subluxable
9.
DRUJ
10.
radial head
11.
instability

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
30
MOVEMENTS
FLEXION 180
0
EXTENSION 0
0
HYPEREXTENSION
SUPINATION 90
0
PRONATION 90
0
MEASUREMENT
1.UPPER LIMB
2.ARM SEGMENT
3. FOREARM SEGMENT ( 7cm distal to medial epicondyle)
4. MUSLE WASTING
-
ARM
-
FOREARM
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
COZEN`S TEST
2.
MILLS MANUOVER
3.
YEAGARSONS TEST
4.
POSTEROLATERAL ROTATORY INSTABILITY TEST
5.
VALGUS TEST @
a.
FULL EXTENSION } FULL SUPINATED & FULL PRONATED
b.
30
0
FLEXION } END POINT SOFT/HARD
6.
VARUS INSTABILITY
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
SENSORY
MOTOR
EXAMINATION OF ULNAR NERVE -THICKENING & STATBILITY
EXAMINATION OF BRACHIAL ARTERY PULSE
EXAMINATION OF CERVICAL SPINE
EXAMINATION OF SHOULDER , WRIST, OPPOSITE ELBOW
POSTEROLATERAL INSTABILITY TEST
Pt supine shoulder 90
0
abducted and externally rotated. Forearm fully supinated and
axial and valgus force applied. Elbow is flexed from 0
0
flexion to 90
0
. At about
30
0
flexion the radial head subluxates and spontaneously relocates on further flexion
VALGUS INSTABILITY
AT FULL SUPINATION = MEDIAL OR LATERAL INSTABILITY
AT FULL PRONATION = ONLY DUE TO MEDIAL INSTABILITY
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
31
11.MEASUREMENT OF LIMB LENGTH
1.
upper limb has only one length i.e true length since pectoral girdle are not
interconnected to conceal the deformity
2.
lower limb has two lengths
3.
for true length both limbs to be kept in the same position and in lower limbs square the
pelvis also
4.
apparent length keep both limbs parallel to each other
APPARENT LENGTH – KEEP BOTH LIMBS PARALLEL
TRUE LENGTH—SQUARE THE PELVIS
-- KEEP NORMAL LIMB IN SAME POSITION AS THAT OF AFFECTED
LIMB
BRAYANTS `S TRIANGLE —SQUARE THE PELVIS
-- KEEP NORMAL LIMB IN SAME POSITION AS THAT OF AFFECTED
LIMB
segment
FROM
TO
1.
upper limb
Angle of acromion
Radial styloid
2.
arm
Angle of acromion
Lateral epicondyle
3.
fore arm
Lateral epicondyle
Radial styloid
4.
radial column
Lateral epicondyle
Radial styloid
5.
ulnar column
Medial epicondyle
Ulnar styloid
6.
lower limb
-
apparent
-
true
Xiphisternum
ASIS
Tip of Medial malleolus
Tip of Medial malleolus
7.
supratrochanteric
Base of Bryants triangle
8.
thigh
Tip of trochanter
Medial knee joint line
9.
leg
Medial knee joint line
Tip of Medial malleolus
10.
tibial column
Medial knee joint line
Tip of Medial malleolus
11.
fibular column
Lateral knee jont line
Tip of lateral malleolus
12.
foot
Tip of Medial malleolus
Tip of head of I metatarsal
13.
FOOT medial column
Tip of Medial malleolus
Tip of head of I metatarsal
14.
FOOT lateral column
Tip of lateral malleolus
Tip of head of V metatarsal
15.
HEEL VERTICAL
HEIGHT OF MEDIAL & LATERAL MALLEOLI FROM
SOLE
16.
HEEL TRANSVERSE
MEDIOLATERAL LENGTH
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
32
12.EXAMINATION OF WRIST AND HAND
HISTORY
1.
trauma
2.
arthritis
3.
autoimmune disorders
4.
leprosy
5.
tuberculosis
6.
nerve injuries
7.
cervical spine shoulder elbow diseases
8.
burns
9.
iv drug abuse
Disabilities
1.
taking food
2.
washing face ;
3.
brushing teeth
4.
drying hairs
5.
donning of clothes
6.
writing
7.
jumping
8.
holding & carrying objects in hand
INSPECTION
1.
attitude & deformity
2.
swelling
-
effusion of wrist joint
-
effusion of tenovaginal sheath
-
others
3.
skin
- sinus scar burns engorged veins
4.
web spaces maintained or contracted
5.
palmar arch
6.
trophic changes
7.
orientation of fingers to scaphoid
8.
wasting
-
forearm
-
thenar
-
hypothenar
PALPATION
1.
LOCAL RISE IN TEMPERATURE
2.
tenderness
•
I CMC J
•
UCL of IP thumb
•
Radiocarpal
•
DRUJ
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
33
•
EPL; EPB
•
Tendons
•
Anatomical snuff box
3.
swelling
4.
palpation of bones
-
deformities
-
thickening
-
irregularity
-
step
5.
styloid relation
6.
DRUJ
- instability ( piano key sign )
7.
volkman`s sign
8.
joint hypermobility
MOVEMENTS
1.
WRIST
•
Palmar flexion - 80
0
•
Dosiflexion - 70
0
•
Radial deviation -20
0
•
Ulnar deviation - 30
0
2.
pronation
3.
supination
FINGERS
FLEXION
EXTENSION
MCP
0
0
90
0
DIP
0
0
80
0
PIP
0
0
100
0
THUMB
ABDUCTION ADDUCTION FLEXION
EXTENSION
CMC
90
0
0
0
90
0
20
0
MCP
85
0
5
0
IP
80
0
20
0
OPPOSITION

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
34
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
FINKESTEIN TEST
2.
PHALEN`S & REVERSE PHALEN`S TEST
3.
TOURNIQUET TEST
4.
MEDIAN NERVE COMPRESSION TEST
5.
CARPAL INSTABILITY
-
WASTSON TEST ( SCAPHOID )
-
BALLOTEMENT TEST ( TRIQUETREAL )
6.
ALLEN TEST
7.
COZEN`S TEST
8.
MILLS MANOUER
EXAMINATION FOR ELIGILBLE TENDONS FOR TENDON TRANSFERS
EXAMINATION OF HAND FUNCTION
1.
POWER GRIP
-
CYLINDRICAL GRIP
-
SPHERICAL GRIP
-
HOOK GRIP
-
LATERAL PREHENSION
2.
PRECISION GRIP
-
PAD TO PAD PREHENSION
-
TIP TO TIP PREHENSION
-
PAD TO SIDE PREHENSION
EXAMINATION OF ELBOW HEAD OF RADIUS
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
35
13.EXAMINATION OF KNEE JOINT
HISTORY
1.
TRUAMA
-
twisting
-
contact
2.
swelling
3.
locking
4.
instability (giving way)
5.
pivot
6.
audible pop. click
7.
limp
8.
constitutional symptoms
9.
arthritis
10.
low back ache
11.
hip ankle problems
12.
other joints
13.
tuberculosis
14.
diabetes
15.
hemophilia
&
other
bleeding
diseases
16.
black urine
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
6.
BYCYCLING
INSPECTION
1.
GAIT
2.
attitude & deformity
-
flexion
-
triple deformity
-
genu varum/valgum/recurvatum
-
DEFORMITY INCRESE OR DECREASE ON FLEXION OF JOINT
3.
swelling
-
parapatellar
-
housemaids
-
clergyman
-
bakers cyst
-
semimembranous
-
bony
-
I STANDING POSITION
ANTERIORLY
POSTERIORLY
II
SITTING POSITION
III
SUPINE
IV
PRONE
DON’T MISS TO EXAMINE
THE POPLITEAL FOSSA

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
36
4.
postion of patella
5.
shape of patella
6.
muscle wasting
-
quadriceps – VMO
-
calf muscles
-
hamstrings
7.
skin – sinus scars engorged veins
PALPATION
1.
LOCAL RISE in temperature
2.
local tenderness
•
medial & lateral joint line – anterior/ middle / posterior
•
ligumentum patellae
•
poles of patella
•
bursal sites
3.
swelling
4.
effusion
-
stroke test
-
fluctuation
-
patellar tap
5.
synovial hypertrophy & plica
6.
popliteal fossa palpation
7.
palpation of bones
swelling
irregularities
thickening
step
8.
clicks
iliotibial band
menisci
medial plica
bicepsfemoris
9.
popliteal artery pulsation
10.
patella under surface
11.
retinaculum rent or tear
12.
palpable thud
13.
PATELLA
•
Size
•
Shape
•
Tracking
•
Glide test
•
Sliding
•
Alta/baja
•
Apprehension test

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
37
MOVEMENT
1.
Flexion
2.
Extension
-extensor lag
3.
abnormal movements – abduction/adduction/rotation
4.
patella tracking
MEASUREMENTS
1.
Leg length
2.
Femoral length
3.
Muscle bulk
-femoral
-calf
4.
Q angle
5.
Insal salvti index
6.
INTERMALLEOALAR DISTANCE
7.
INTERCONDYLAR DISTANCE
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
VARUS / VALGUS stress test @ 0
0
and 30
0
flexion
2.
lachman test
3.
anterior drawer test
4.
geodfrey`s sign ( posterior sag sign)
5.
posterior drawer test
6.
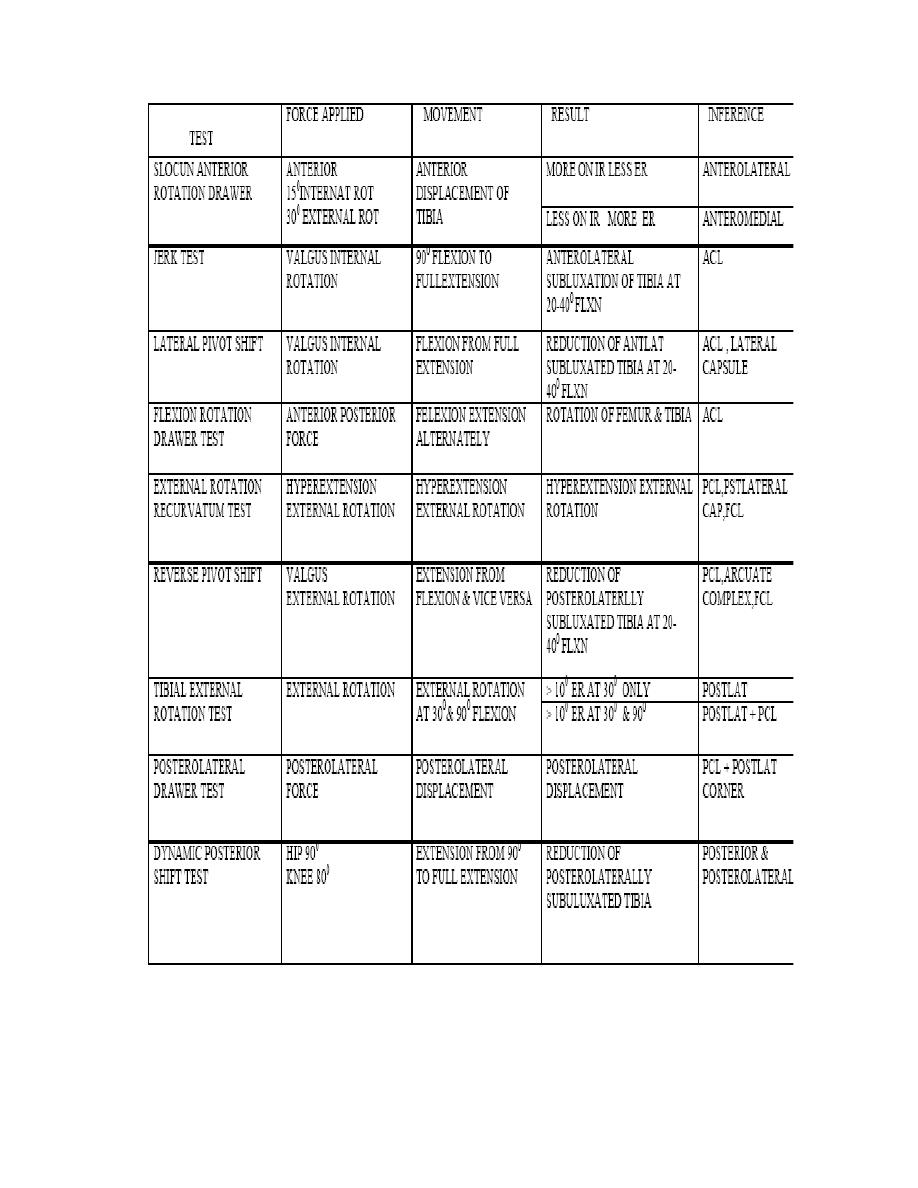
slocum anerior rotation drawer test
7.
jerk test of houghston
8.
lateral pivot test
9.
flexion rotation drawer test
10.
external rotation reccurvatum test
11.
reverse pivot test
12.
tibial external rotation test
13.
dymanic posterior shift test
14.
FAIBANK apprehension test
15.
Wilson test for ostch: dissecans ( like macmurray )
16.
appley frinding test
17.
appley distraction test
18.
pissani sign
EXAMINATION OF POLITEAL LYMPH NODES
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION OF SPINE HIP ANKLE OPPSITE KNEE
TESTS FOR ROTATORY INSTABILITY OF KNEE
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
38

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
39
14.EXAMINATION OF ANKLE AND FOOT
HISTORY
1.
diabetes mellitus
2.
peripheral neuropathy
3.
arthritis
4.
leprosy
5.
spine disease
6.
trauma & fracture
7.
myopathy
8.
gout,syphilis
9.
habit of shoe wearing
10.
wear & tear of shoe
Disabilities
1.
Walking (aided or unaided),
2.
side of using walking stick
3.
sitting cross-legged,
4.
squatting
5.
climbing stairs, coming down
INSPECTION
1.
ATTITUDE & DEFORMITY
2.
swelling
3.
skin
-
callocities
-
adventitious bursae
-
abnormal thickening of skin
-
sinus scar warts
4.
muscle wasting
5.
big toe & other toes
6.
arches of foot
7.
obliteration of arch on weight bearing
8.
gouty tophi
9.
abnormal creases
10.
deformities
11.
trophic changes in skin & nails
PALPATION
1.
local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness
3.
palpation of bones
4.
heel
5.
arches of foot
6.
manual forceful reduction of
deformity
7.
presence of tibia,tibial torsion
8.
palpation of sesamoids
9.
relation of malleoli
10.
anterior or posterior displacement of
foot
11.
forefoot-midfoot-hindfoot relation
MOVEMENTS
1.
ANKLE
-plantar flexion 35
0
-dorsiflexion 25
0
2.
SUBTALAR
i.
INVERSION

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
40
ii.
EVERSION
3.
TARSOMETATARSAL
-ABDUCTION
- ADDUCTION
4.
HEEL MOVEMENTS
5.
MOVEMENT OF BIG TOE AND OTHER TOES
6.
COMBINATION
i.
SUPINATION
ii.
PRONATION
MEASUREMENTS
a)
CALF WASTING
b)
MEDIAL & LATERAL COLUMNS OF FOOT
c)
HEEL MALLEOLI LENGTH
d)
HEEL
a.
VERTICAL
b.
TRANSVERSE
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
pendulum test ( tibial torsion )
2.
anterior drawer test
3.
posterior drawer test
4.
valgus/ varus stress test
5.
TESTS OT TENDO ACHHILLIS
a.
Thomson test for tendo Achilles
b.
OBRIEN`S needle test of TA
c.
Sphygmomanometer test
d.
Knee flexion test
6.
mulder`s test ( compression of metatarsals produce paresthesia in morton`s diseses)
7.
tarsal tunnel compression
-
dorsiflexion-exersion test of kinoshita
-
tourniquet test
EXAMINATION TIBIOFIBULAR JOINT
a)
SQUEEZE TEST OF HOPKINSON
b)
EXTERNAL ROTATION STRESS TEST ( KNEE & FOOT 90
0
; FOOT ER)
EXAMINATION OF DISTAL VASCULARITY
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
VIBRATION SENSE
EXAMINATION OF FOOT WEAR
EXAMINATION OF SPINE;HIPS;KNEE ; OPPOSITE ANKLE

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
41
15.EXAMINATION OF CTEV
HISTORY
1.
age sex
2.
antenatal history – drugs; diseases(TORCH)
3.
family h/o congenital anomalies
4.
symptoms suggestive of myopathy
5.
symptoms suggestive of neurological lesion
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Fully undress the patient
Inspect head to toe from all sides
HEAD TO TOE EXAMINATION
1.
general built
2.
café au lait spots
3.
craniofacial dysmorphism
4.
congenital anomalies of neck , ,genitalia,chest,abdomen, extremities
5.
features of terratogenicity
6.
SPINE –
•
Swelling
•
Tuft of hair
•
macules
7.
JOINT CONTRACTURES
LOCAL EXAMINATION
INSPECTION
1.
GAIT
2.
attitude & deformity
•
ankle equinus
•
heel varus
•
fore foot adduction
•
cavus
3.
deformities of toes
4.
other deformities
5.
skin creases thigh, leg, foot (posterior & medial aspects)
6.
joint contractures
7.
bilaterality
8.
skin callosities, adventitious bursea
9.
size of calf,leg,heel & foot
10.
tibial torsion
11.
high riding of calf muscles
12.
trophic changes in skin nails,ulcers
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
42
PALPATION
1.
local rise in temperature
2.
tenderness
3.
presence of tibia, bending
4.
tightness of tendoachillis;tibialis posterior ,other tendons
5.
retraction of triceps surae
6.
adduction & inversion of calcaneum
7.
postion of navicular bone
8.
position of cuboid
9.
palpation of cuniforms
10.
palpation of metatarsals
11.
resistance to reduction of each deformity by force
12.
Curvature of the lateral boarder (CLB)
13.
Medial crease (MC)
14.
.Uncovering of the lat. head of talus (LHT)
15.
.Posterior crease (PC)
16.
.Emptiness of heel (EH)
17.
VASULARITY ON FULL CORRECTION
18.
PLANTAR FASCIA TIGHTNESS
MEASUREMENT
1.
DEFORMITY( supple or fixed)
TRUE
REDUCIBLE TO
1.
EQUINUS
2.
HEEL VARUS
3.
FOREFOOT ADDUCTION
4.
CAVUS
2.
MOVENENTS
AFFECTED
NORMAL
1.
DORSIFLEXION
2.
PLANTAR FFLEXION
3.
INVERSION
4.
EVERSION
5.
FOREFOOT ABDUCTION
6.
FOREFOOT ADDUCTION
7.
SUPINATION
3.
LENGTH OF LEG, CALF CIRCUMFERENCE
4.
LENGTH OF MEDIAL & LATERAL COLUMN OF FOOT
5.
SIZE OF HEEL
a.
Transverse
b.
vertical

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
43
REDUCTION OF DEFORMITY BY SUPINATION & ABDUCTION OF FORE FOOT
-
reduction of heel varus, reduction of TCN joint
SPECIAL TESTS
1.
SILVERSKEOID TEST
2.
PENDULAR TEST ( TIBIAL TORSION)
EXAMINATION OF SPINE
TO rule out spina bifida; diastenomelia
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION OF DISTAL VASCULARITY
VASCULARITY ON FULL CORRECTION
EXAMINATION OF OTHER JOINTS
1.
HIPS
2.
KNEES

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
44
16
EXAMINATION OF SPINE
1.
Examination of vertebral column
2.
Examination of spinal cord
3.
Examination of spinal roots ( complete neurological examination is always better )
GENERAL EXAMINATION
1.
Squint
2.
Nystagmus
3.
TREMOURS ( pill rolling & intentional )
4.
Chorea; hemiballism & athetolic movements
EXAMINATION OF VERTEBRAL COLUMN
1.
GAIT and posture
2.
Altitude and deformity
INSPECTION
1.
Posteriorly
Position of head
Level of hair line
Length of neck
Level of shoulders
Level of scapulae
Spinous processes
Iliac crest
Paraspinal muscle spasm or not
Any swelling , cold abscess
Renal angle
Skin- dimple; hair tufts; nevus; scar; sinus; café-au- lait spots
Step
Abnormal trunk furrows
Apparent shortening of lower limbs
Pelvic obliquity
2.
Laterally
Spinal curves
3.
Anterilorly
Chest shape pectus carrinatum ; excavatum
Rib hump
Abdomen protution
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
45
PALPATION
1.
Local rise in temperature
2.
Tenderness ( occiput to coccyx)
a.
Direct pressure
b.
Twist tenderness
c.
Deep thrust tenderness
d.
Anvil test
3.
Step or deformity
4.
Any swelling
5.
Cold abscess
6.
Sacroiliac joint
7.
Trigger points
8.
Pelvic obliquity
PERCUSSION
-TENDERNESS
Abnormal curvatures of spinal column
1.
Torticollis
2.
Scoliosis
a.
Site
b.
Adam forward bending test
c.
Number of curves
d.
Convexity
e.
Associated kyphosis
f.
Chest rib hump(razor back)
g.
Rib iliac crest distance
h.
Facial asymmetry
i.
Squint
j.
Mobile or fixed
3.
Kyphosis
a.
Labile/fixed
b.
Fixed
i.
Knuckle
ii.
Angular
iii.
Round
4.
Lordosis
a.
Kyrtorhacchic
b.
Ophithotonus

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
46
MOVEMENTS
1.
Atlantoocciputal joint – nodding
2.
Atlantoaxial joint- rotation
3.
Cervical spine
a.
Flexion
b.
Extension
c.
Lateral bending
d.
Rotation
4.
Dorsal spine
a.
Practically nill
5.
Lumbar spine
a.
Forward bending – standing ( finger tip floor distance)
-sitting with fixed pelvis
b.
Back ward bending ( angle between axes of lower limb & body)
c.
Lateral bending ( distance between finger tip & floor)
6.
Segmental mobility
a.
Schober`s & modified schober`s test
7.
Sacroiliac stress tests
MEASUREMENTS
1.
Linear measurements
a.
From external occipital protrubence to tip of coccyx
b.
Iliocostal distance ( tip off last rib to iliac cest)
c.
Segmental measurement
d.
Acromiooccipital distance
e.
Schober`s test
f.
Otto test
2.
Chest expansion
3.
Limb length discrepancy
SPECIAL TESTS OF SPINE
1.
Stress test of spine( Lhermitte test)
2.
Cervical root stretch test
a.
Lateral stretch test
b.
Cervical compression test ( Spurling test)
3.
Distraction test
4.
Thoracic outlet test
a.
Adson` test
b.
Roos test
c.
Hyperabduction manoeure ( 90
0
abduction and full external rotation)
d.
Exaggerated military position test ( scapula fully depressed and retracted-
costoclavicular compression manoeure
e.
Halsted rest (45
0
shoulder abd + downward pull of upper limb with head turned
to opposite side)
5.
Lumbar root tension test
a.
Straight leg raising test

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
47
i.
SLRT ( LASEGUE TEST )
ii.
DISSAPEANCE OF PAIN BY LOWER LEG
iii.
FRAJARZTANZ TEST
iv.
BOWSTRING TEST
b.
Well leg SLRT
c.
Sitting root test
d.
FNST
6.
Test for pyriformiss syndrome
i.
FRIEBERG SIGN
ii.
PACE-NAGLE SIGN
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
1.
Higher mental function
2.
Cranial nerves
3.
Gait & posture
4.
Motor system
a.
Bulk of muscle ( wasting or hypertrophy)
b.
Tone of muscle
i.
Hypertonia
1.
Spasticity
2.
Rigidity
3.
gegenhalten
ii.
hypotonia
c.
Power of muscle
d.
Reflexes
5.
Sensory system
a.
Temperature
i.
Hot
ii.
cold
b.
Touch
i.
Deep
ii.
Crude
iii.
Light
c.
Posterior column sensations
i.
Two point discrimination
ii.
Vibration sense ( 128 Hz)
iii.
Position sense
iv.
stereognosis
6.
Visceral system
a.
Bowel
b.
Bladder functions
7.
Co ordination mechanism
a.
Straight line walking
b.
Finger to nose & finger test
c.
Heel to knee test
d.
Romberg sign
e.
Pastpointing
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
48
f.
Dysdidokinesia
g.
Rebound phenomenom
8.
Vasomotor changes & pressure sores
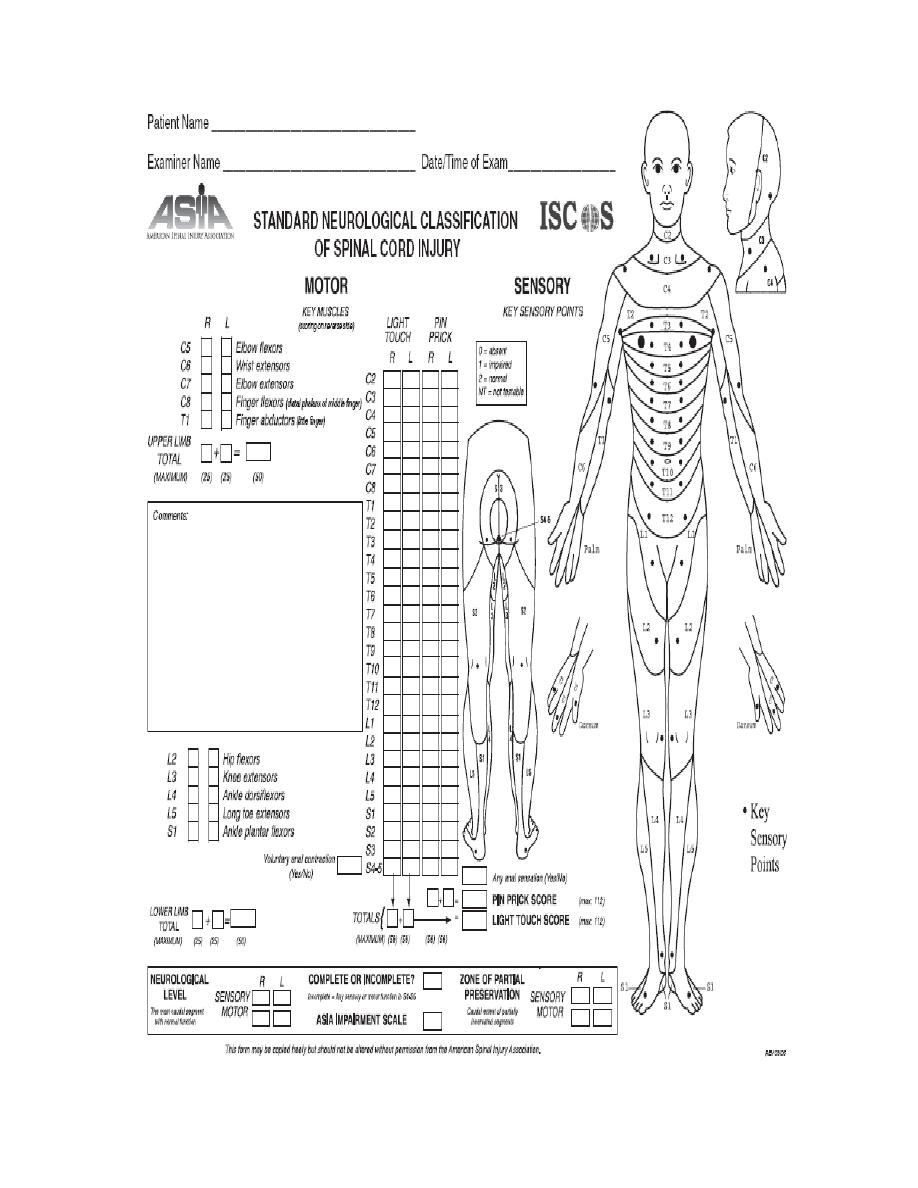
ASIA SORE FOR SPINAL CORD INJURY
A
Complete:
No sensory or motor function is preserved in sacral
segments S4-S5.
B
INCOMPLETE
Sensory, but not motor, function is preserved below the
neurologic level and extends through sacral segments S4-S5
C
INCOMPLETE
Motor function is preserved below the neurologic level,
and most key muscles below the neurologic level have
muscle grade <3.
D
INCOMPLETE
Motor function is preserved below the neurologic level,
and most key muscles below the neurologic level have
muscle grade greater than or equal to 3.
E
NORMAL
Sensory and motor functions are normal.
MUSCLE CHART
1
strnocleidomastoid
Hip flexors
2
Deltoid
Hip extensors
3
Biceps
Hip abductors
4
Triceps
Hip adductors
5
Brachioradialis
Quadriceps femoris
6
Wrist flexors
Hamstrings
7
Wrist extensors
Ankle dorsiflexors
8
Finger flexors
Ankle plantar flexors
9
MCP extensors
Foot inverters
10 Intrincic muscles
Foot everters
11 Adductor pollicis
Toe extensors
12 Opponens pollicis
Toe flexors
First dorsal interrosius
EHL
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
49
9.
REFLEXES
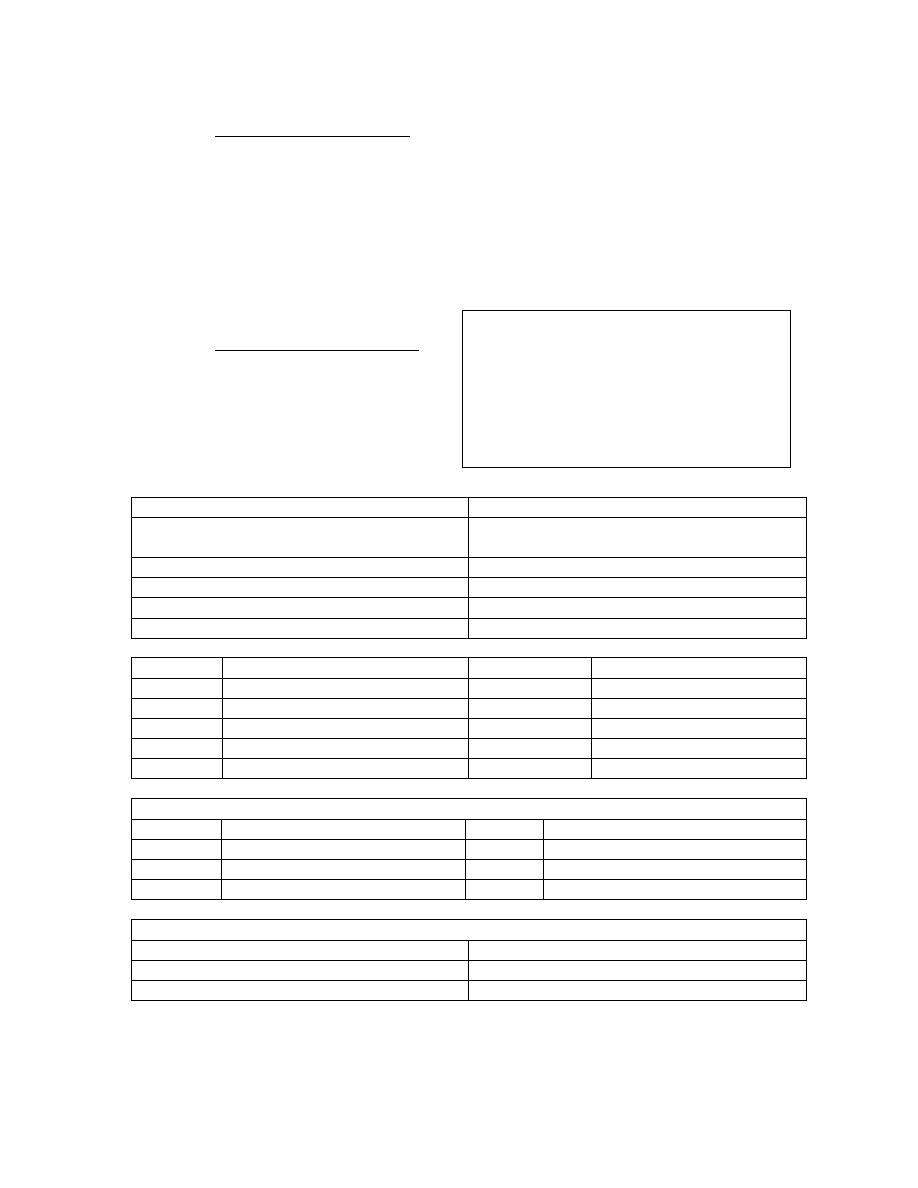
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
50
-
SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES
1.
PHARRYNGEAL
2.
LARYNGEAL
3.
ABDOMINAL ( ALL FOUR QUADRANTS & Beevor`s sign)
4.
CREMASTRIC REFLEX
5.
ANAL WINK
6.
BULBOCAVERNOUS REFLEX ( stimulation of glans or catheter pulling )
7.
PLANTAR REFLEX
8.
SCAPULAE REFLEX
-
DEEP TENDON REFLEXES
1.
JAW REFLEX -CN 5
2.
BICEPS REFLEX-C56
3.
SUPINATOR REFLEX-C56
4.
TRICEPS REFLEX C67
5.
KNEE REFLEX & CLONUS L234
6.
ANKLE REFLEX & CLONUS S12
SPINAL SEGMENT LEVELS
C1-C7
+1
T11
L3;L4
T1-T6
+2
T12
L5
T7-T9
+3
L1
S1-S5 ; CX
T10
L1;L2
L2
CAUDA EQUINA
SENSORY LEVELS
CLAVIVLE- C4-T2 AXIAL LINE
UMBLICUS T10
NIPPLE T4
INGUINAL LIG T12-L1
XHIPHISTERNUM T6
ANATOMICAL LAND MARKS
T2 STERNAL NOTCH
C1 BELOW & ANTERIOR TO
MASTIOD PROCESS
T3 BASE OF SPINE OF SCAPULA
C3
HYOID BONE
T4 ANGLE OF LOUIS
C4 THYROID CARTILAGE
T7 INFERIOR ANGLE OF SCAPULA
C6 CRICOID
L4 ILLIAC CREST
C7 V.PROMINENCES
S1 PSIS
ROOT
MUSCLE
ROOT
MUSCLE
C5
ELBOW FLEXION;DELTOID
L2
HIP FLEXION
C6
WRIST EXTENSORS
L3
QUADRICEPS
C7
TRICEPS
L4
ANKLE DORSIFLEXION
C8
FDP-MF
L5
EHL; GlU.MEDIUS
T1
FINGER ABDUCTION
S1
ANKLE PF; G.MAXIMUS
DEEP TENDON REFLEXES
Grade 0 absent
Grade +1
present (as ankle jerk)
Grade +2
brisk (as knee jerk)
Grade +3
very brisk
Grade +4
clonus
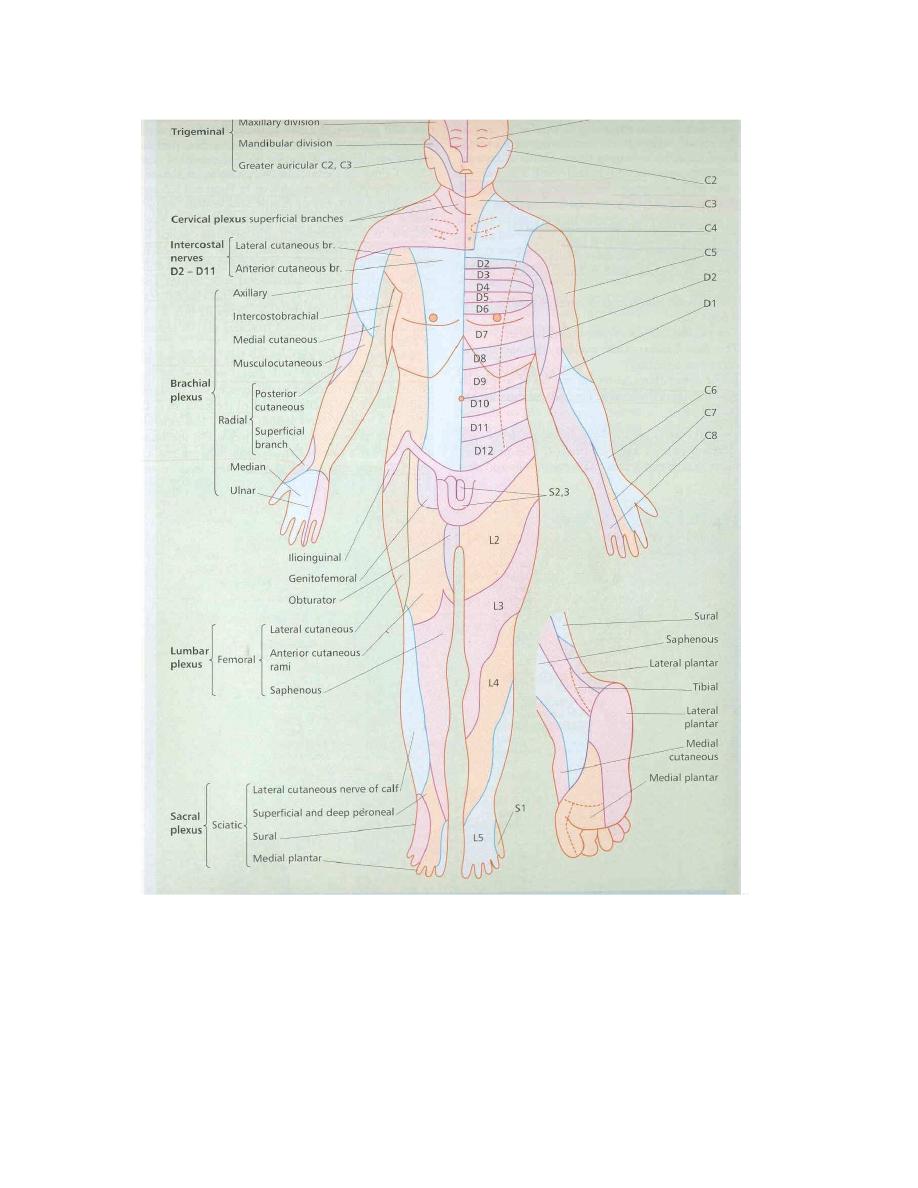
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
51
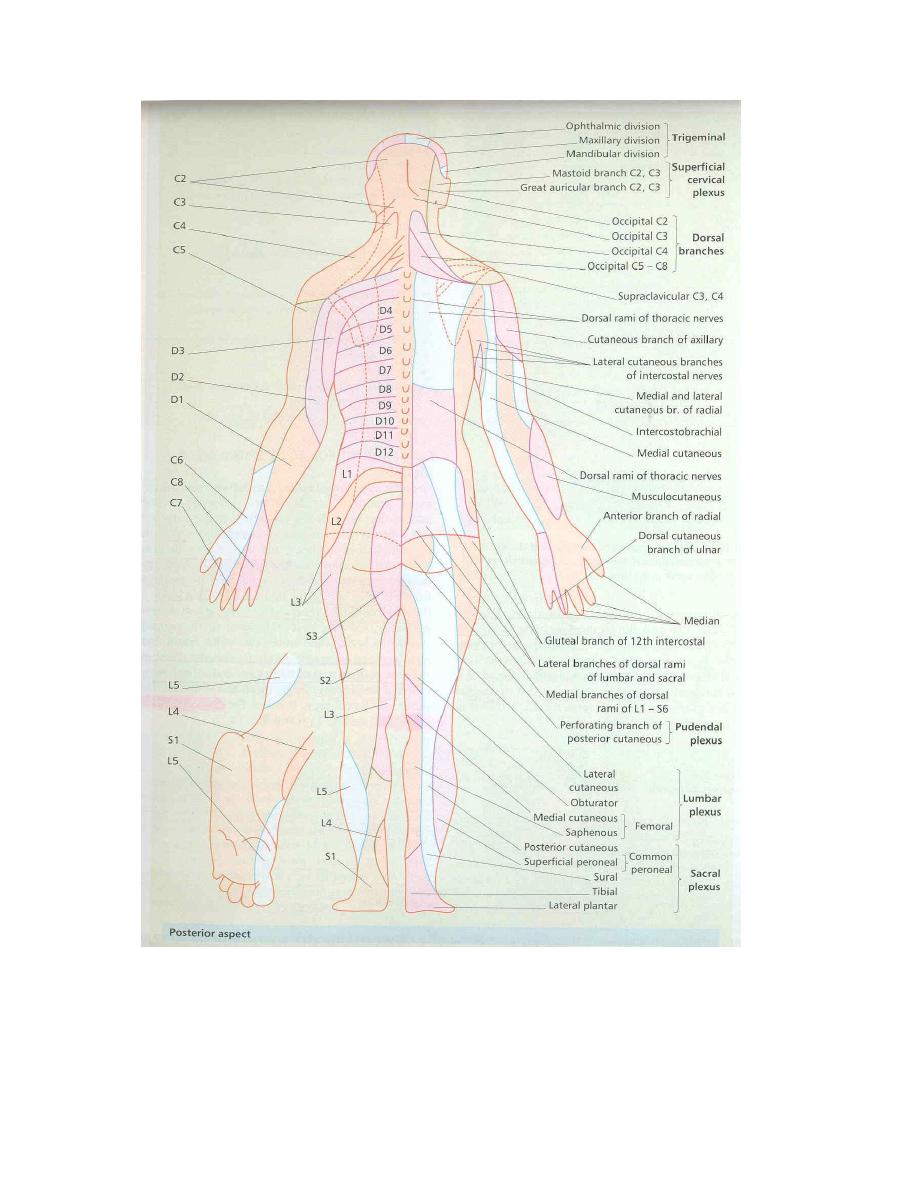
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
52

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
53
17 EXAMINATION OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
DISEASE AND GANGRENE
HISTORY
1.
Age and sex
2.
Limbs affected
3.
Bilateral or unilateral
4.
Mode of onset
5.
Pain
a.
Intermittent claudication
i.
Boyd`s classification
1.
Grade 1 pain dissapiared on continued walking
2.
Grade 2 pain present but can walk with pain
3.
Grade 3 cant walk with pain need to take rest
b.
Rest pain
6.
Effects of heat and cold ( reynauld`s phenomenon)
7.
Parasthesia
8.
h/o superficial throbophlebitis
9.
symptoms s/o macrovascular disease
(syncope; chest pain; blurred vision; abdominal pain)
10.
impotence
11.
past history
12.
personal history
a.
smoking
b.
alcoholism
13.
family history
LOCAL EXAMINATION
1.
INSPECTION
a.
CHANGE IN COLOUR
b.
Signs of ischemia
i.
Thinning of skin
ii.
Hair loss
iii.
Loss of subcutaneous fat
iv.
Nail changes
v.
ulcers
c.
Buerger`s angle (<30
0
indicates severe ischemia)
d.
Capillary filling time
e.
Venous refilling time
f.
Established gangrene
i.
Extent and color
ii.
Type –dry/wet
iii.
Line of demarcation

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
54
2.
PALPATION
a.
Skin temperature
b.
Capillary refilling
c.
Venous refilling
d.
Cold and warm water test
e.
Limb above gangrene
f.
Palpation of blood vessels
i.
Dorslais pedis & anterior tibial
ii.
Posterior tibial
iii.
Popliteal
iv.
Femoral
v.
Radia & ulnar
vi.
Brachial
vii.
Sublavian
viii.
Superificial temporal
ix.
Common carotid
3.
AUSCULTATION
a.
Bruit
4.
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF LIMB
PALPATION OF VESSEL
1.
Pulse volume
2.
Condition of vessel wall
3.
Thrombossed
4.
thrill

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
55
19.
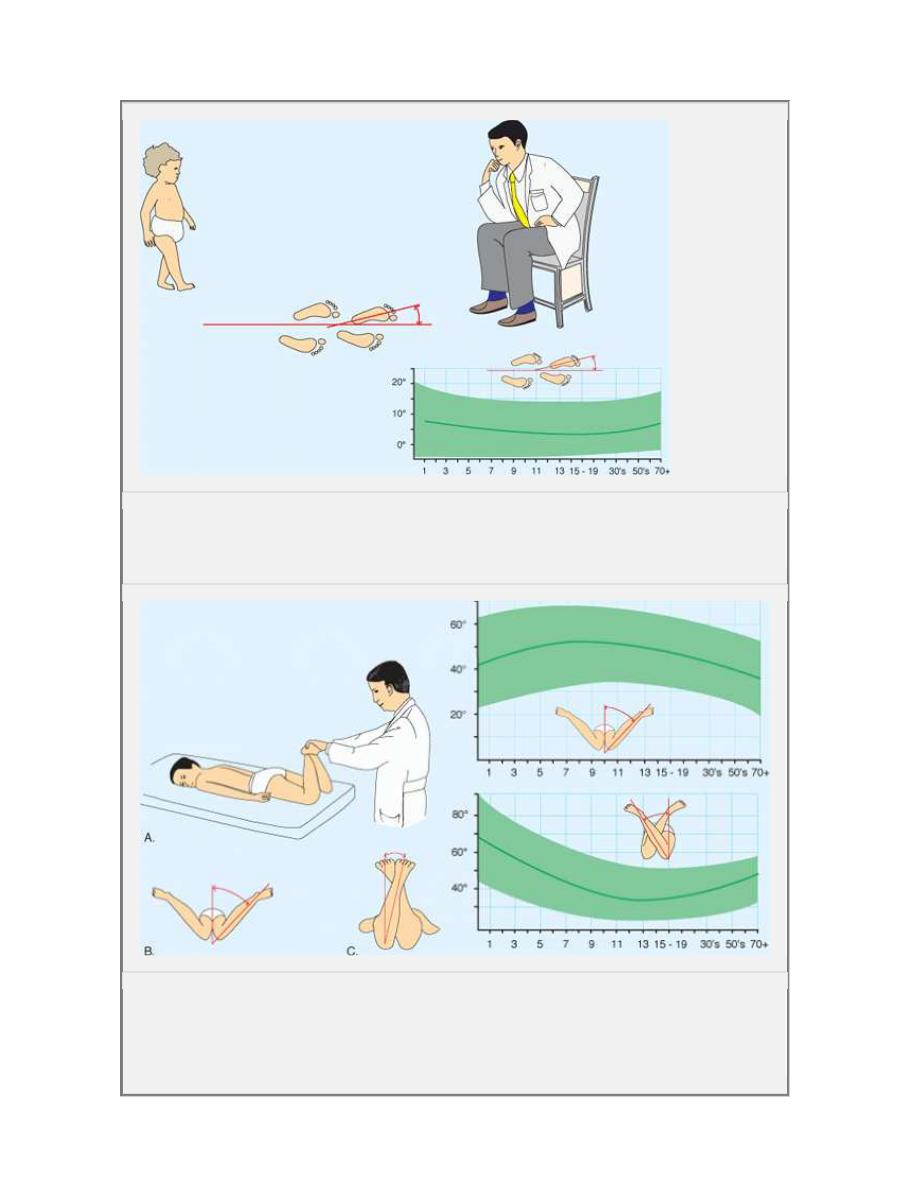
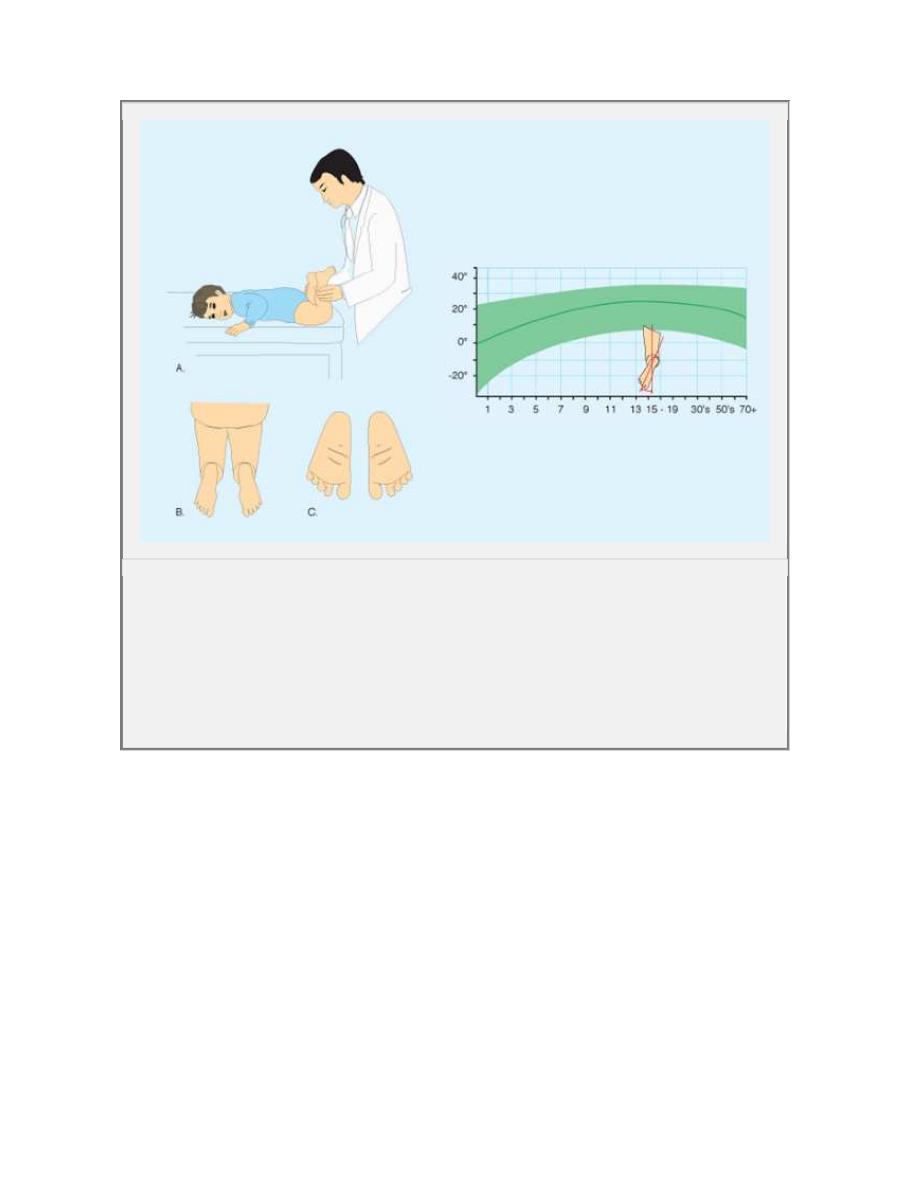
Evaluation of rotation of lower limb ( staheli)
.
History
1.
onset,
2.
severity,
3.
disability
4.
previous treatment
5.
developmental history.
6.
family history of a rotational
problem.
Screening examination
i.
hip dysplasia
ii.
cerebral palsy.
Rotational.. Evaluate in four steps:
1. Observe the child walking and r unning .
foot progres sion angle (FPA)
2.Assess femoral version
hip rotation external rotation (ER)
internal rotation (IR) with the child prone
3. Quantitate tibial vers ion
the thigh-foot angle (TFA)
TM A.
4.Assess the foot
forefoot adductus.
Intoeing
-5 ° to -10° mild
-10° to -15° moderate,
more than -15° severe
ROTATION ARC CHANGE TO
I.
Externally = retro torsion
II.
Internally = ante torsion
TMA GIVES TIBIAL TORSION
TFA-TMA = HIND FOOT TORSION
BECK`S HEEL BISECTOR METATRSUS
ADDUCTUS
Normal
= bisects 2 & 3
rd
toes
Mild
= bisects 3
rd
toe
Moderate
= bisects 3 & 4
th
toes
Severe
= bisects 4 & 5
th
toes
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
56
A Foot progress ion angle The f oot progres sion angle is estimated by
observing the child walking. The normal range is shown in green.
B Hip rotation Hip rotation is assessed with the child prone (A). Internal
rotation (B) and external rotation (C) are measured. Normal ranges are shown
in green.
Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
57
D Assess ing ro tation al s tatus of tibia a nd foo t T he ro tational status of the
tibia a nd fo ot are best ass essed by evalu at ing the ch ild in the prone
pos ition (A), allowin g t he fo ot to fall int o a natural resting posit ion. The
thigh-f oot axis (B ) a nd sha pe of the f oot (C) are readily dete rmine d. T he
rang e o f normal is s hown in g re en.

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
58
17.
DEVELOPMENTAL MILESTONES
1.
Cognitive Milestones
1.
Month 3-5: Attends to and Reaches for objects
2.
Month 4-8: Pulls string to secure a ring
3.
Month 8-15: Imitates patting doll
4.
Month 14-20: Finds Hidden Object
5.
Month 18-28: Completes simple puzzles
2.
Language Milestones
1.
Month 1.5-3: Squeals
2.
Month 3.5-8: Turns to locate a voice
3.
Month 9-13: Says Mama or Dada
4.
Month 14-24: Combines two different words
5.
Month 21-36: Uses plurals
3.
Social and Emotional Milestones
1.
Month 1.5-4: Smiles at others
2.
Month 4-9: Seeks primary caregiver
3.
Month 8-15: Stranger anxiety
4.
Month 10-15: Displays 2 or more recognizable emotions
5.
Month: 11-20: Exploratory play by self
6.
Month 21-36: Cooperative play in small groups
4.
Gross Motor Milestones
1.
Month 2-4.5: Rolls Over
2.
Month 5-8: Sits without support
3.
Month 10-14: Stands Alone
4.
Month 14-20: Walks up steps
5.
Month 21-28: Pedals tricycle
6.
Month 30-44: Balances on one foot
7.
By age 6: Rhythmic skipping
8.
By age 8.5: Alternates foot-hop in place
9.
By age 10: Holds tandem stance for 10 sec (eyes closed)
5.
Fine Motor Milestones
1.
Month 2.5-4: Grasps rattle
2.
Month 4.5-7: Transfers cube hand to hand
3.
Month 8-12: Has neat pincer grasp
4.
Month 15-20: Builds tower of four cubes
5.
Month 18-24: Imitates vertical line
6.
Month 28-36: Copies circle
7.
By age 5 years: Draws a square
8.
By age 5.5 years: Tripod pencil grasp
9.
By age 7 years: Draws diagonal line
10.
By age 9: Draws cross with same dimensions
11.
By age 12: Draws three dimensional cube
Frankenburg (1990) Denver II Developmental Screening

Orthopaedic Examination of a patient
59
