
1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
ع
م
ل
ي
د.ندى العلي
26/10/2015
NEUROLOGICAL EXAIMNATION IN PEDIATRIC
Don't take the developmental history during acute illnesses always ask the mother, (how
was the child developmental features before the illness).
When we face a patient with developmental delay in one are
there is a special cause
for this
we must find it.
When it is in more than one area
it is more likely to take it seriously
it is called (global
developmental delay).
Features of hypothyroidism in pediatric age group?
1. husy cry.
2. coarse facies.
3. constipation
4. obese (puffy).
5. pale
6. umbilical hernia.
7. jaundice at birth
8. mental retardation if it is NOT treated early.
Examination of CNS:
1. general appearance
2. tone
3. power
4. reflexes.
5. cranial nerves.
Notes:
we must measure OFC to determine wether this infant is microcephalic or NOT &
always before deciding
compare with the parents shape (may be familial
microcephaly).

2
in acute illnesses
weight is affected more then height ;; if height diminishes in
corresponding to the weight
it is chronic(OFC also will be affected).
If all small since birth
means intrauterine disease (Torchs).
squint normally is up to 6moths;; if remain
abnormal sign.
distended abdomen NOT always an ascites , sometimes it is an indication for hypotonia
& wasting.
weakness+hypotoniaLMN lesion.
weakness+hypertoniaUMN lesion.
in CP ,child will be spastic(opsthitonous) with persisting fisting posture after 3months
of age .
جسمه رح يكون مقوس
some cases of CP are NOT eliciated at birth,they will develop as the child/infant grows
,because infection such as meningitis during the first years of life (as brain continues its
development ) CP.
child with wasting & weight < 60% of the predicted weigh for that age marasmus
(S.albumin )
if edema & weight of infant/child < 80% of the predicted weight for that age
kwashiorkor.
sometimes pt presented with edema BUT weight <60% of the predicted
weightmarasmic kwashiorkor.
In both conditions there is low protein level BUT the degree of reduction is
important,,in pt with kwashiorkor;;there will be edema ,low protein level but fat is still
present,,while in marasmus, low protein ,severe wasting without edema.
Lumbar puncture procedure:
Fine needle inserted at level of two iliac crest (between L4&L5)
after completing the
drawing of CSF
pack the area to close it
because as CSF leaks
child will have severe
headache.
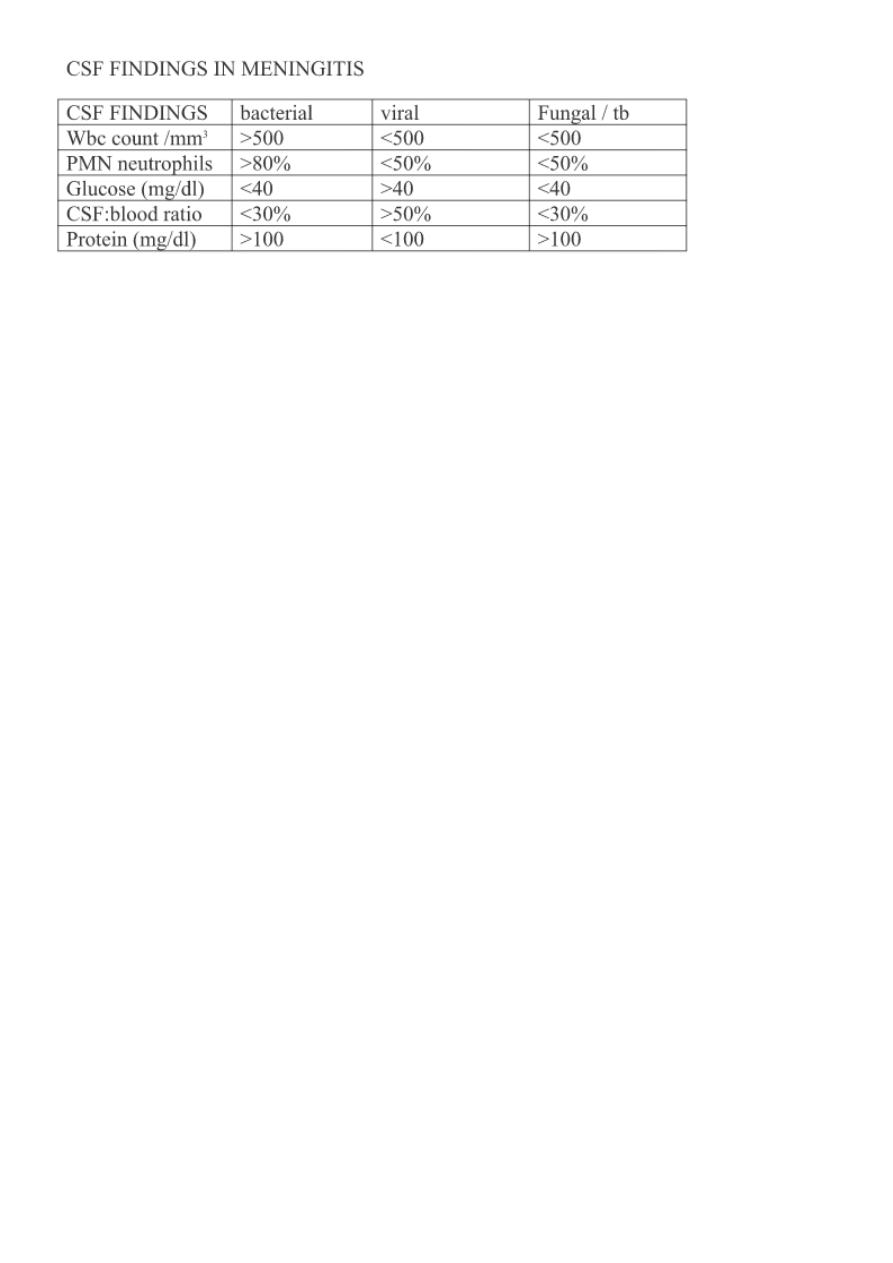
Features of CSF exam:
1.Appearanceturbid in infection.
2.Chemistries
a-proteins: high in bacterial
b-glucose: low in bacterial.
3.Cellsthe count less than 5 normally.
a-neutrohils: high in septic meningitis.
b-lymphocytes: high in perimeningeal infection.
3
pt with suspicion of degenerative diseases investigate the case with:-
CT
MRI
Lumbar puncture (unless contraindicated);;such as in increased ICPthis leads to
herniation.
*in white matter degenerative diseases vision is NOT affected BUT
HYPERACUSIS.
*نسال االم هل لما يكون صوت بالبيت يقوم الطفل يصرخ ويبكي*
In degenerative diseasestreatement is only supportive , some recommend
immunotherapy (it is equivocal).*
*in grey matter degenerative diseasevision will be affected.
*in speech delayask about the family (this may be normal *familial*)
*Bulbar palsyproblems in deglutition & swallowing.
Hip dislocation tests:
(developmental dislocation of Hip*DDH*)
these tests only performed for those below the
3 months age
put your finger on greater trochanter,then move the thigh backward &
outward ,,,then inward &forward
if +ve
click sound will be heard(indicates dislocation of
head of femur from acetabulum);;for those over 3 months if u performed it
tear of
capsule occurs ; so don’t do it.
Notes about RTI:
always when you take a history of cough & u find that more than one member in the family
is affected whooping cough(mostly).

4
Especially if the mother said (I feel him choking during the attack) or (he vomited directly
right after the attack).
& when u examine the chest normal finding mostly.
*neblizer used for asthma,bronchiolitis&croup ,etc.
o In asthma put salbutamol.
o In bronchiolitis & croupput N.S.
Notes about the cases of GIT:
in the history ,try to use the term (loss of appetite) in child over 2 yrs& the term
(reluctant to feeding) in those below 2yrs.
if fat droplets in the stool
small bowel disease.
if blood with stool passing + tenesmus(feeling of incomplete emptying ,infant or
child will cry when he defecates)
large bowel disease.
if blood pass after defecation
fissure in ano.
If diarrhea is lasting for long period in the same patient or recurrent bouts
ask
about
1. water supply
2.type of food if u suspect allergy
3.If bottle feeding
ask about way of sterilization,way of preparation&type of the
formula.
in patient with diarrhea
investigate with:-
1.GSE(general stool exam)
2.stool culture.
3.CBC.
hyperbilirubinemia is very important in the first 5 days (because blood brain barrier
is very permeable in this period)
as the neonate low in weight
as the bilirubin control level is important(as in
premature).
Aim of phototherapy:
1-to prevent Hb from falling to a level that causes HIE.
2-to prevent bilirubin passing BBB as this leads to kernicterus.
*Contraindication of phototherapy:-
1-direct hyperbilirubinemia.
2-porphyria.
Bronze baby syndrome
5
*keep in mind that phototherapy never subsituate for blood transfusion when it is
indicated.
*in phototherapy:-cover the eyes,gentilia&
fluid intake to avoid dehydration.After u
control the pt's bilirubin level,let the pt remain in hospital for 24hrs(because rebound
phenomenon is common).
Types of phototherapy:
1.single light source.
2.double light source(which is in use nowadays).
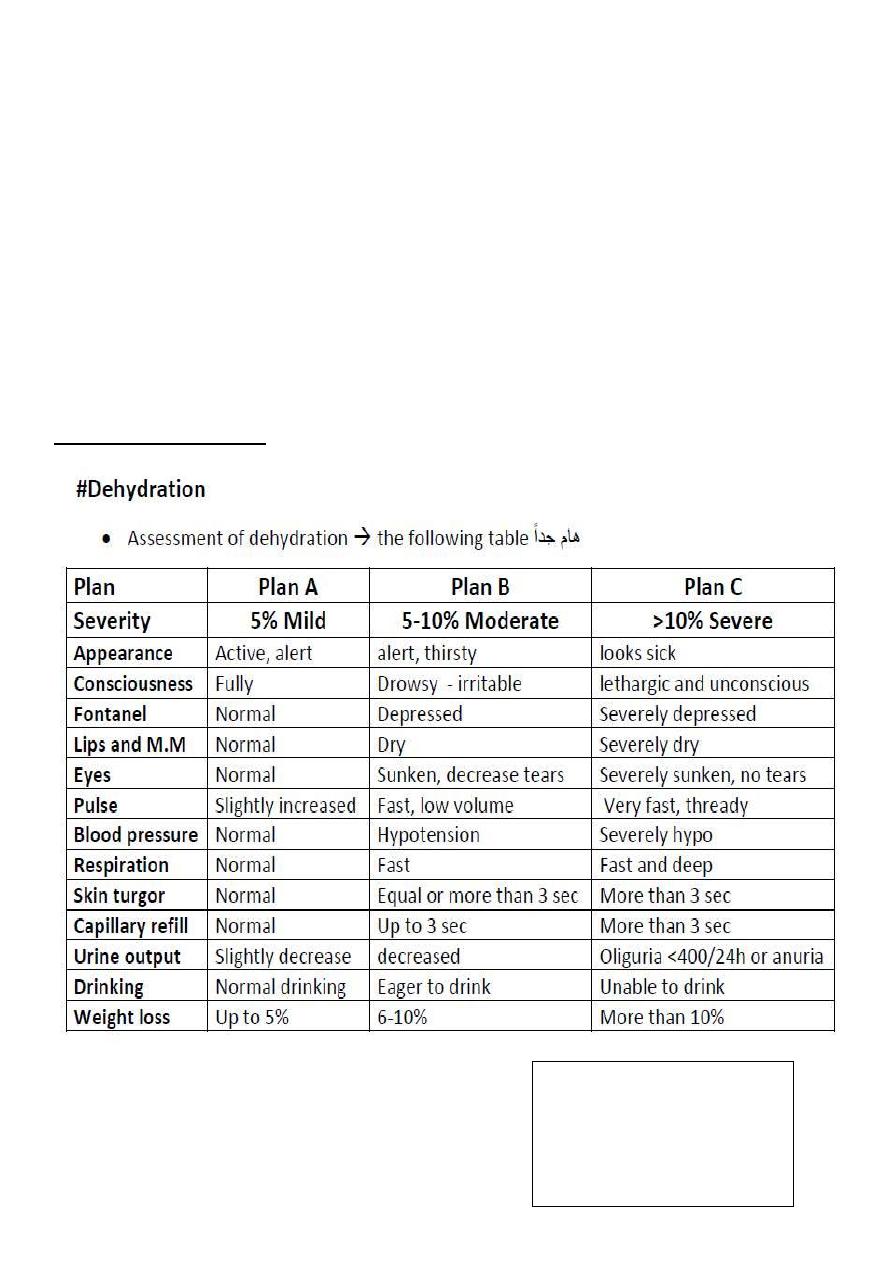
Signs of dehydration: (very important).
When you examine the fontanelles
1-baby should be in sitting position.
2-NOT crying.
When you examine the
fontannelle
1-baby should be in
sitting position.
2-NOT crying.
