1
Fifth stage
Gynecology
Lec-4
د.براء
17/4/2014
Sterilization
permanent contraception
Female sterilization
This involves the mechanical blockage of both fallopian tubes to prevent sperm reaching &
fertilizing the oocyte.
Bilateral salpingectomy or hysterectomy may be used if there is coexistent gynaecological
pathology.
It is most commonly performed by laparascopy under general anesthesia as a day case.
Alternative technique is mini-laparatomy with small suprapubic incision or through the
posterior vaginal fornix [colpotomy].
Avariety of methods used for tubal occlusion
Include:
Ligation
Electrocautery
Laser
Falope ring
clips
Methods of female sterilization

2
Informed concent
Discussion with patient must take place and cover the following details:
It must be a voluntary decision
Discussion of other options
Discussion of method of sterilization
Sterilization is permanent
Probability of failure
Discussion about methods of contraception for prevention of STDs
Special consideration for women with mental disabilities
Monopolar coagulation
It is laparascopic procedure
Complications
Bowel Burn
Bleeding
Longer portion of tube is damaged
Failures and ectopic pregnancy
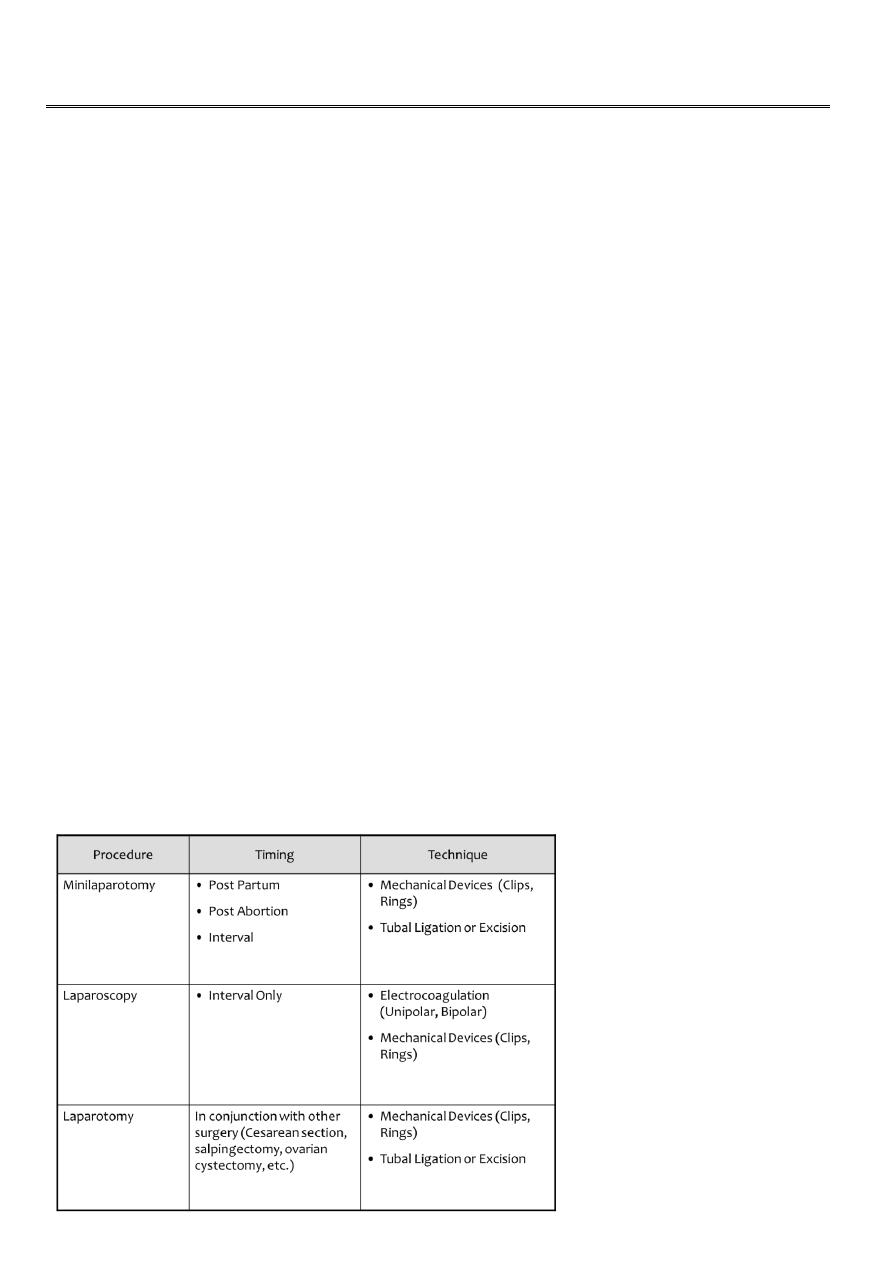
Bipolar coagulation
Laparoscopic
Benefits
Most common method of laparoscopic sterilization
Burn several locations along the tube
Complications
High rate of ectopic pregnancy
Potential for bowel burns
Reversals are potentially more difficult due to the extent of tube damage
3
Falope ring
Mechanical occlusion invented in 1974
Tubal occlusion accomplished by placing a silicone band around the
tube
Thicker tubes may be problematic
May not be suited for postpartum
Complications
Increased patient discomfort during recovery – large area of necrosis
Filshie Tubal Ligation System
Can be used in minilaparatomy & laparascopy
Used as interval or postpartum srerilization
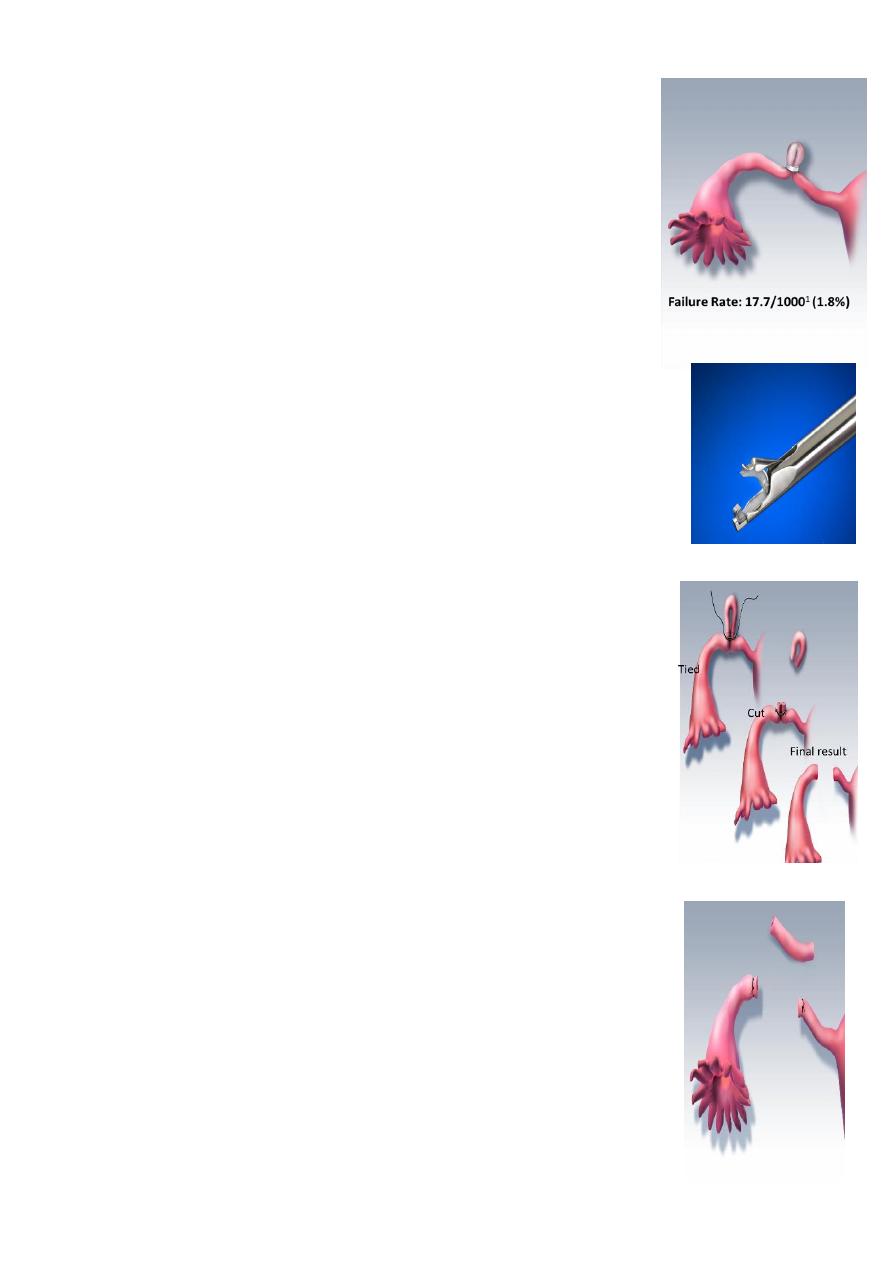
Pomeroy technique
– Incision – suprapubic and subumbilical
– Isthmic portion is ligated twice
– Segment is then excised
• Benefits
– Easy technique
– Highly effective
– Relatively inexpensive)
Parkland technique
Isthmic portion of tube is segmented and ligated at two points
An avascular area in the mesosalpinx is opened
Proximal and distal ligated and segment exiced
Benefits
Good success rates
Few complications
Inexpensive to perform
4
Irving technique
Bury the proximal tubal stump within the myometrium
Benefits
Used in conjunction with cesarean delivery
Complications
Moderate level of difficulty to perform
Pomeroy and Parkland are quicker
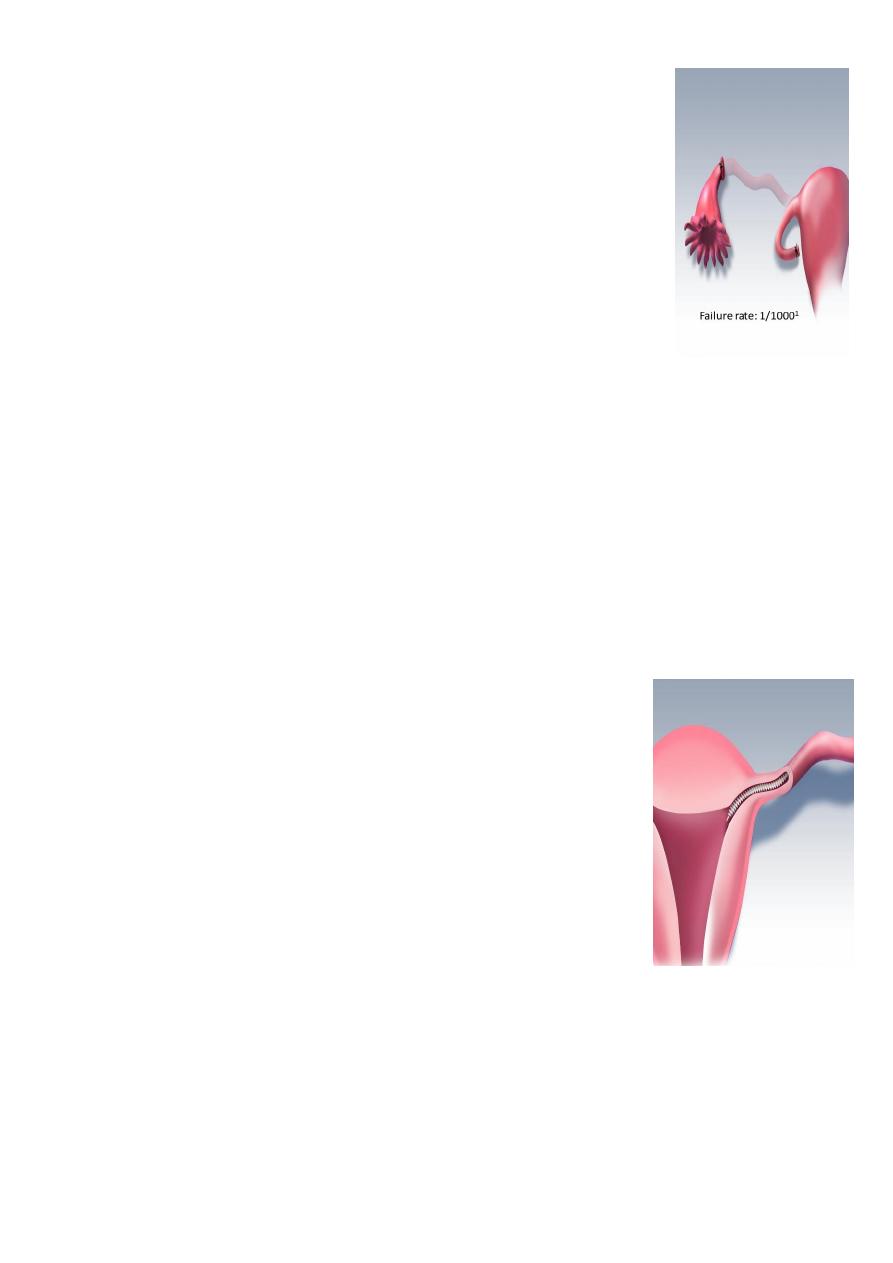
Essure
Essure microinsert sterilization device
Hysteroscopic procedure
– Approved in 2002
– The coil-like device is inserted under local anesthesia into the fallopian tubes where it is
incorporated by tissue
– Micro-insert placed into each tube, The device induces a local inflammatory response
and, eventually, fibrosis of the intramural tubal lumen. these fibers stimulate in-growth
over several weeks
– 86% Success Rate for 1st time
– placements of micro-inserts
– The woman is advised to use
– contraception for 3 months
– until hysterosalpingography
– HSG procedure confirms
– occlusion of both tubes
complications
-Short term
Anesthetic problems.
Intra-abdominal organ damage.
Gas embolism.

5
Thromboembolic disease.
Wound infection
-Long term
Women may experience regret post-procedure
Ectopic pregnancy
Failure rate 1-2/1000 operation.
Menstrual disorders
Psychological disorders
Reversibility
All surgical tubal occlusion procedures are considered to be
permanent female sterilization methods
success restoration of tubes does not mean always success of
pregnancy and carries a significant risk of ectopic pregnancy
Male sterilization (vasectomy)
-Safe and permanent birth control procedure
- Involve division or occlusion of the vas deference on each side to prevent the passage of
sperm & seminal fluid from epididymis
Its advatages are-safe, inexpensive,done under local anesthesia& with less complications
than female sterilization.i
Its disadvantages is not effective immediately,
Need 12- 16 weeks to be effective.
The man should have semin analysis till two samples free from sperms.

6
Vasectomy procedure
Office visit – approximately 1 hour
Local anesthetic to the overlying skin
Clamp the vas through the skin
Incision made
Small segment removed (3 mm)
Cut segments
-Tied
-Cauterized
-Clipped
Complications
-Bleeding ,hematoma :
-Infection
-Sperm granuloma at the cut ends of the vas
-antisperm Antibodies development
-Chronic pain:
-Failure as 1 in 1000
-Concerns of testicular and prostate cancer but
-Data do not support a risk
Reversal
– 50-70% who had procedure reversed are fertile
– Better success the shorter the interval from procedure to reversal
• <3 yrs – 76% successful
• >15 yrs – 30% successful
