Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 1 of 7
Gynecologic Tumors with Pregnancy
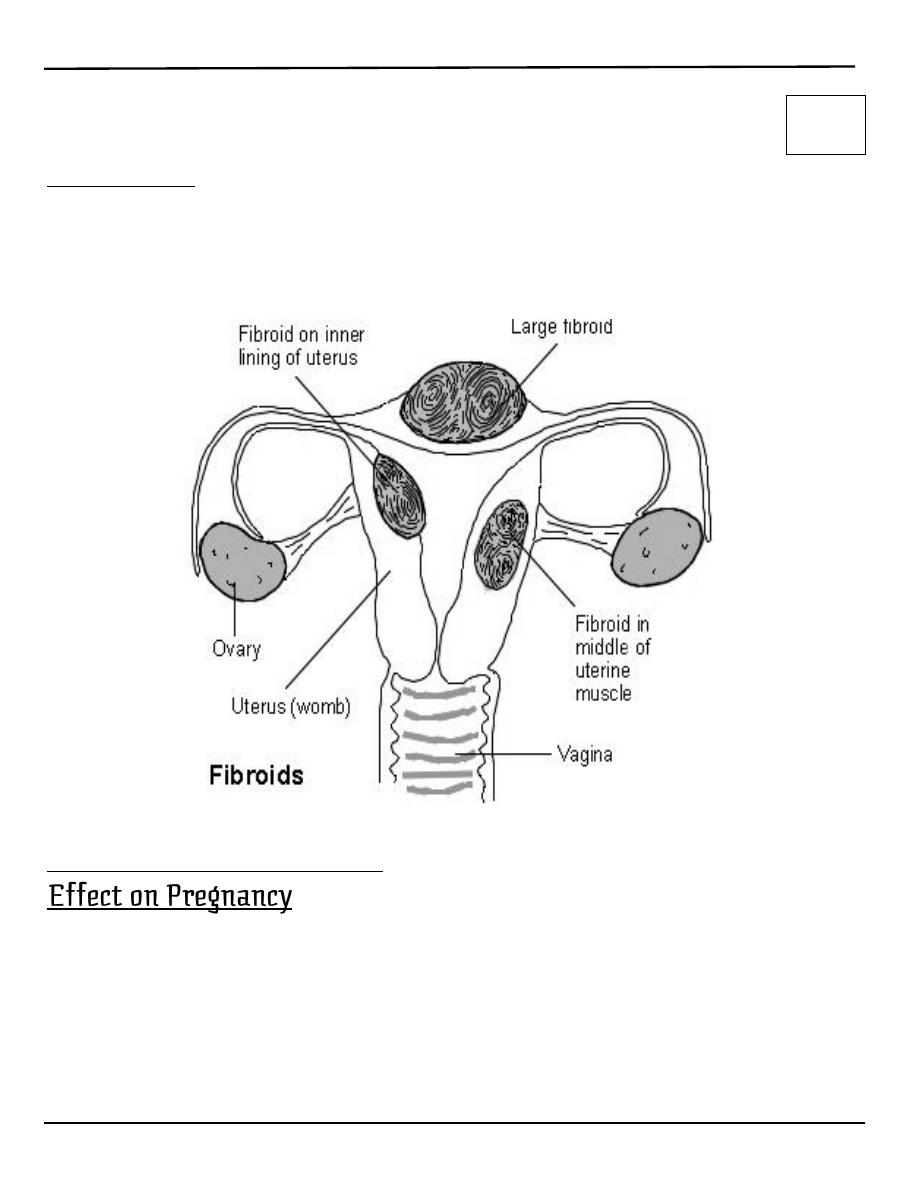
Leiomyoma
o About 1% in pregnant women
o It is formed of fibers and muscle of uterus and can be
submucous, interstitial, or subserous
Fibroid with Pregnancy
1. Abortion… increase with submucous
2. Incarceration of RVF gravid uterus (posterior wall)
3. Ectopic pregnancy if pressing on the tube
4. Preterm labor
5. Pressure symptoms …increase size of uterus above expected
date
:العدد
4
9/3/2014

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 2 of 7
o Large abdominal tumor may cause abdominal discomfort,
dyspnea, palpitation
o Pelvic tumor may increase pressure on bladder, rectum and pelvic
veins
6. Malpresentation
7. non-engagement of presenting part
8. Placenta Praevia due to interference with implantation of
fertilized ovum in the upper segment
9. Acute abdomen ...
a) Red degeneration
b) torsion of pedunculated subserous fibroid
c) hemorrhage from ruptured surface vein
1. Uterine Atony… due to mechanical interference with uterine
contractions:
a. Prolonged labor
b. retained placenta
c. Postpartum Hemorrhage
2. Submucous fibroid increase incidence of placenta accreta and
retained placenta
3. Obstructed labor:
a. cervical fibroid
b. subserous fibroid impacted in the pelvis below the
presenting part
1. Subinvolution
2. Secondary Post partum hemorrhage (submucous or fibroid
polyp)
3. Inversion of the uterus may be caused by fundal submucous
fibroid
4. Increased incidence of puerperal sepsis due to infection of

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 3 of 7
traumatized tumor and interference with drainage of uterus
1. Increase size of fibroid due to hypertrophy and increased
vascularity
2. Softness of the tumor due to interstitial edema….flattening of
fibroid and may become indistinct
3. Subserous tumor may be readily palpated as the uterus enlarges
and on occasion may be mistaken for fetal parts
4. Submucous and fibroid polyp are more prone to infection
specially in puerperium and after abortion
5. Red degeneration is common leading to subacute or acute
abdomen
6. Torsion of pedunculated subserous fibroid is common in
puerperium when there is rapid involution of uterus and laxity
of abdominal wall leading to increased mobility of intra-
abdominal organs
Management
A. Red degeneration with abdominal pain:
1) bed rest
2) reassurance
3) analgesics
B. Torsion of subserous fibroid: surgery and removal of the
stalk with fibroid …no other interferences
C. Caeserean section if fibroid causing obstruction to labor ..no
interference with fibroid to avoid excessive bleeding and re-
evaluate after 6 weeks
D. Caeserean hysterectomy may be indicated wit multiple
fibroids in patient competed her family

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 4 of 7
Cancer cervix and Pregnancy
o The incidence of CIN varies but it is generally between 1% to
8% of abnormal cytology.
o Invasive cancer is the most common solid tumor during
pregnancy
o Fortunately its incidence is 0.2% to0.9% of all
pregnancies..1.4% of all cases of cancer cervix
Symptoms:
1. Usually asymptomatic, detected during routine Pap smear
2. Vaginal bleeding and discharge may be mistaken for pregnancy
.complications
3. Pelvic pain..less frequent
o Cervical cancer peaks between age 30 to 49 years
o The mean age of pregnant women with invasive cervical cancer
31.8y.
o Significant numbers diagnosed in 2nd or 3rd trimester
o Efficacy and safety of screening is well-documented
1. Colposcopy is safe and well tolerated and should be used to
evaluate abnormal Pap smear
2. Any suspicious lesion should be biopsed
3. The overall risk of biopsy-related complications is
approximately 0.6% usually mild bleeding.
4. Cervical conization during pregnancy..crucial in diagnosis and
staging of MIC.

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 5 of 7
Complications:
1. Hemorrhage 2-13%
2. Fetal loss 17%-50%, <10% in 2nd, 3rd
3. PMRM (Premature Rupture of Membrane)
4. Preterm labor
5. Infection,
6. Laceration and stenosis
7. Fetal Salvage 89-95%
1. Physical examination
2. cervical biopsy
3. conization
4. chest x-ray with abdominal shield
5. since about 83% of cases are stage I cystoscopy and
proctoscopy are eliminated.also I.V.U and Enema.
o No indications for immediate treatment of cases with CIN
during pregnancy
o Pap smear and colposcopy every trimester
o Vaginal Delivery with higher rate of regression at 6-week
examination compared to Caesarean delivery
o Definitive treatment…6 weeks postpartum
o Invasive cancer during pregnancy is curable
o Treatment is clear in the 1st and 3rd trimester but less clear in
the 2nd trimester
o The two modalities used are surgery or Radiotherapy as in non-
pregnant

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 6 of 7
First trimester (1-12weeks)
1. Fetal salvage is not feasible in women receiving treatment for
invasive cancer
2. The maternal risk from delaying therapy until fetal maturity is
excessive
3. Surgery with the fetus in situ
Second trimester (13-25weeks)
o The period of greater uncertainty
o Fetal salvage is exceedingly rare with high neonatal mortality
rate
o Delaying therapy for several weeks may subject the mother to
the theoretical risk of disease progression
o If patient elects to interrupt pregnancy.. The same as in 1st
trimester
o If not ..define a target gestational age for fetal delivery
o Monitor by U/S..and MRI for tumor extension
o Documented lung maturity
3rd trimester Treatment
o Wait for few weeks till fetal maturity then apply definitive
therapy
o Surgery in 89% may be coordinated with fetal delivery and
completed as a 1-stage operation.
o If R.T..external beam immediately after delivery followed by
intracavitary radiation
Ovarian tumors with pregnancy
o Incidence 1:1000 pregnancy
o Benign tumors are common e.g. luteal cyst and Dermoid cyst
o Malignant tumors 5%
o Ovarian malignancy has no effect on pregnancy and pregnancy
has no effect on prognosis of ovarian cancer

Lecture 6 continue
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Gynecologic Tumors With Pregnancy
Page 7 of 7
o Benign cyst may undergo torsion causing acute abdomen
commonly in puerperium
o First trimester….observe and follow-up with ultrasound till
second trimester (to reduce risk of abortion) and then removal
through laparotomy
o Second trimester….laparotomy
o Third trimester.. Caesarean section and removal of tumor
o Malignant tumors …treated as non-pregnant i.e. surgical
staging and cytoreductive surgery
By: Mu’taz Fathi
