1
Third stage
Medicine
Lec-2
د
.
فاخر
1/1/2014
Major manifestations of rheumatologic diseases
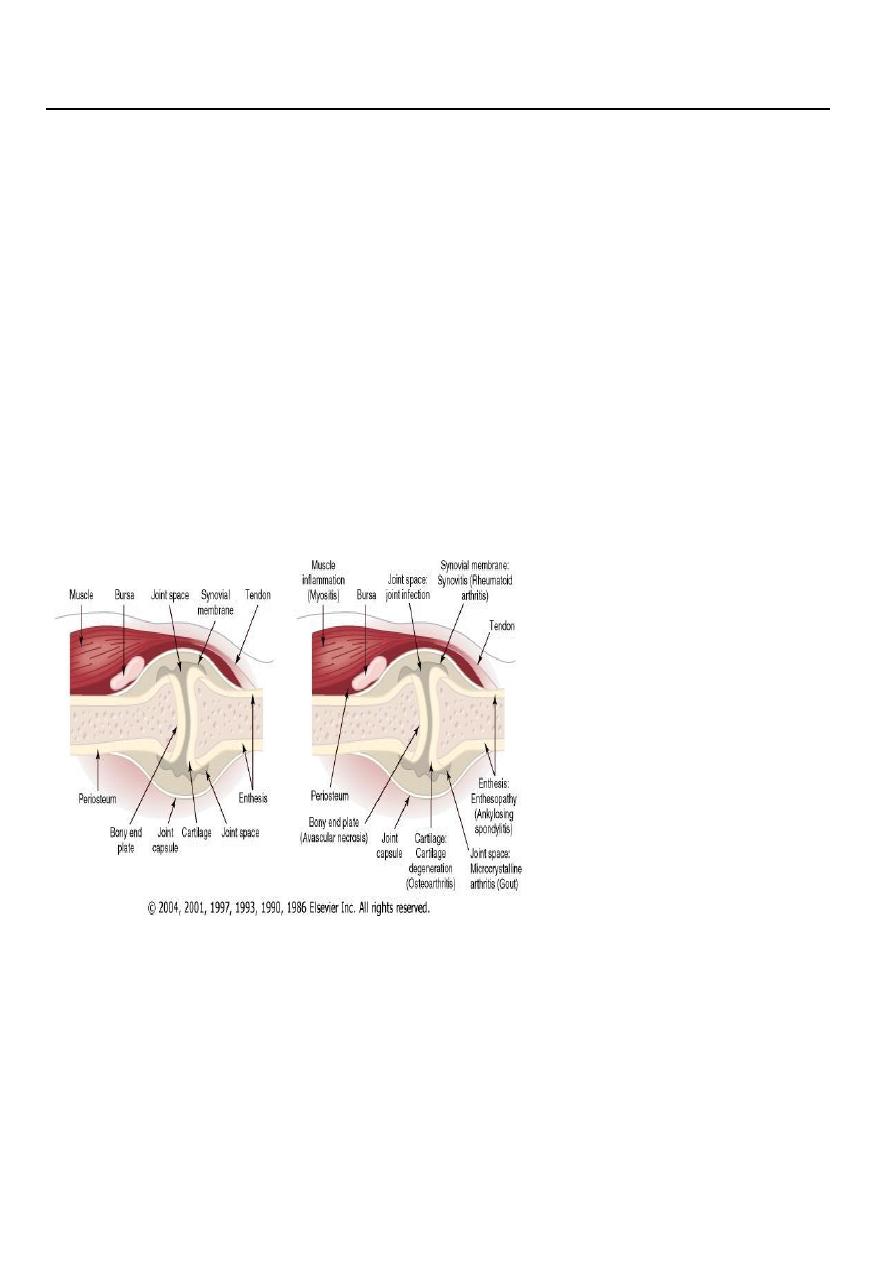
JOINTS
Bones are linked by joints. There are three main subtypes.
1- Fibrous joints characterized by limited .movement like skull sutures
2- Fibrocartilage joints These joints comprise a simple bridge of fibrous or fibrocartilage
tissue joining two bones together where there is little requirement for movement. The
intervertebral disc is a special type of fibrocartilage joint in which an amorphous area
termed the nucleus pulpous lies in the centre of bridge.
3-Synovial joints
Synovial joints are more complex structures containing several cell types and are found
where a wide range of movement is required. Articular cartilage In synovial joints the bone
ends are covered by articular cartilage. This is an avascular tissue consisting of
chondrocytes embedded in a meshwork of type II collagen fibrils that extend through a
hydrated 'gel' of proteoglycan molecules example the knee joint
Major Symptoms In Joint Disorders
Pain
Stiffness
Joint swelling and deformity
Functional impairments
Systemic manifestations
Extraarticular features

2
Pain
Usage pain-worse on use, relieved by rest (mechanical strain, damage) example disc
prolapse.
Rest pain-worse after rest, improved by movement (inflammation).example
rheumatoid arthritis.
Night or 'bone' pain-mostly at movement (bone origin)
Stiffness
Subjective feeling of inability to move freely after rest.
Duration and severity or early morning and inactivity stiffness that can be 'worn off'
suggest degree of inflammation .
Example rheumatoid arthritis stiffness more than hour .
Weakness
Consider primary or secondary muscle abnormality
Swelling (Fluid, soft tissue, bone)
Deformity (Joint, bone)
Non-specific symptoms of systemic illness (Reflecting acute phase reaction)
Weight loss,
± reduction in appetite
Fatigability,
poor concentration
Sweats and chills, particularly at night
Feeling ill,
Arthralgia
Is pain in one or more of your joints. The pain may be described as sharp, dull,
stabbing, burning or throbbing, and may range in intensity from mild to severe.
Arthritis Symptoms
Arthritis causes joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. Symptoms can
include:
Joint pain
Joint swelling
Reduced ability to move the joint
Redness of the skin around a joint
Stiffness, especially in the morning
Warmth around a joint
3
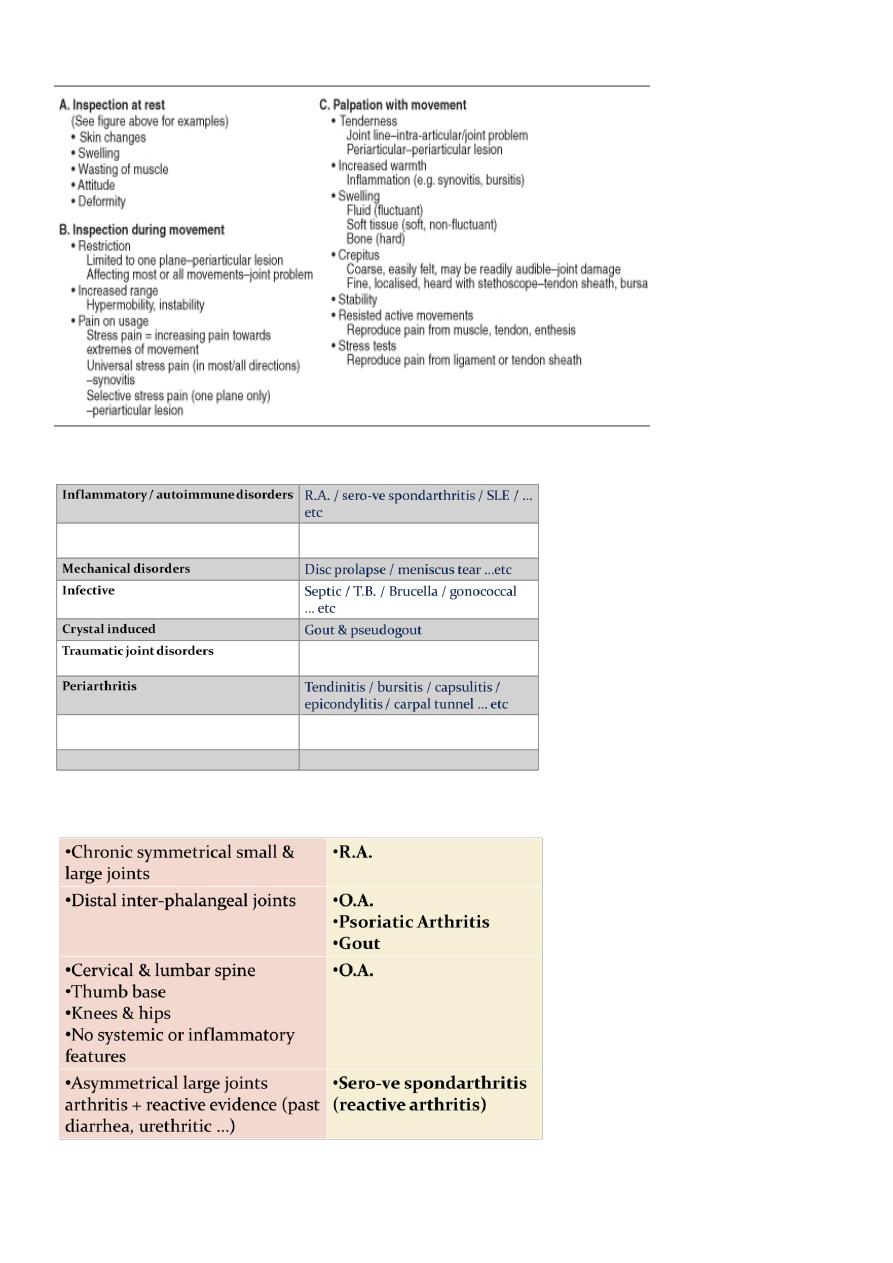
Examination
Classification of Joint Disorders
Joint Profile in Various Disorders

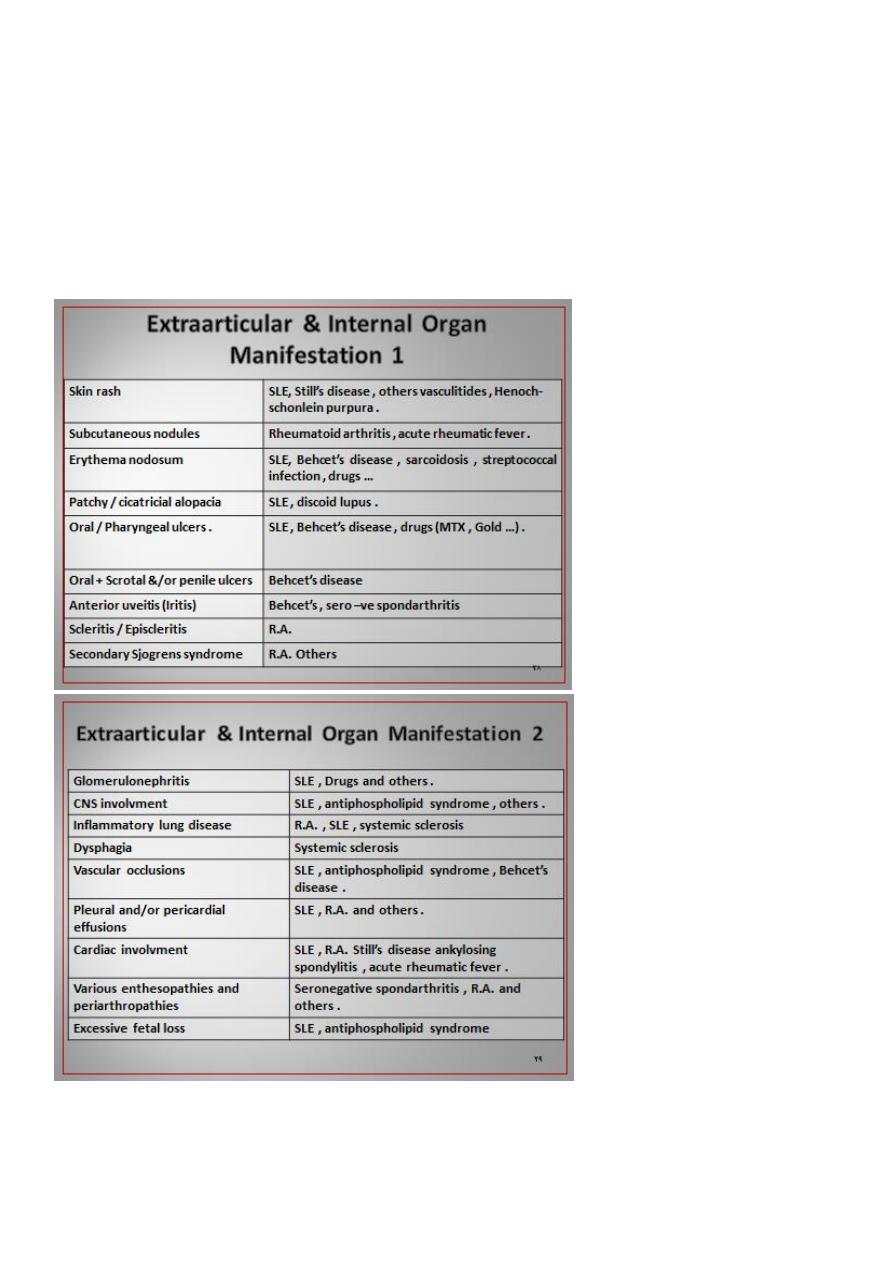
4
Joint Profile in Various Disorders
Clinical pointers to isolated periarthritis
Typical clinical pattern e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome, plantar fasciitis & tennis elbow
Good general health
Tenderness outside joint margin
Swelling is absent or outside the joint
Examples:, plantar fasciitis, subdeltoid bursitis, elbow epicondylitis.
Joint redness
Acute gout
Acute septic arthritis
Acute psoriatic arthritis
Inflamed overlying skin
Migratory Arthritis
Acute Mono-arthritis History
5
Polyarthritis: selected causes
Rheumatoid arthritis juvenile rheumatoid arthritis ,
spondylarthropathies ,
systemic lupus and .
Generlized osteoartAhritis .
Gout .
Pseudogout .
Sarcoidosis .
