
1
Third stage
Surgery
Lec-1
.د
م
دثر
1/1/2014
Introduction to trauma
OBJECTIVES
At the end of this lecture you should be able to:
• Define Trauma and injury .
• Recognize the importance of time in trauma management .
• know how to assess a trauma problem.
• Recognize the principles of response to a trauma problem.
• Understand The value of planning.
Trauma
• Trauma is an external physical or chemical force that affect the body and exceeds it`s
resilience leading to injury .
• The injury is the adverse effect of a physical (or chemical) force upon a person.
• Traumatology is the study of medical problems associated with physical and chemical
injury.
THE SCALE OF THE PROBLEM
• Trauma is recognised as a serious public health problem.
• In fact, it is the leading cause of death and disability in the first four decades of life
and is the third most common cause of death overall
• Fragility fractures are an increasing burden e.g. proximal femoral fractures.
• Look beyond the obvious in trauma management (non-accidental injuries)
THE IMPORTANCE OF TIME
• An identifying feature in the study of trauma is time.
• At time zero the person/patient is at their normal baseline. There is then some
interaction with an external force leading to injury.

2
The order ABCD, that is airway, breathing, circulation and disability (neurology), of the ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life
Support) system is founded upon this time dependence.
• Time pressure shapes our management of trauma
• There is a finite time to assess
• There is a finite time to respond
• For success these must fit into the available time before irretrievable damage or
death
Types of Injuries
• Penetrating: 1-Incisional.
2- stab
3-Firearm.
• Blunt : 1- Direct.
2- Indirect.
Incisional and stab injuries
• Require knowledge of anatomy
3
• The abdominal contents extend high into the chest
• Even cardiac injuries are treatable if recognised early and treated quickly
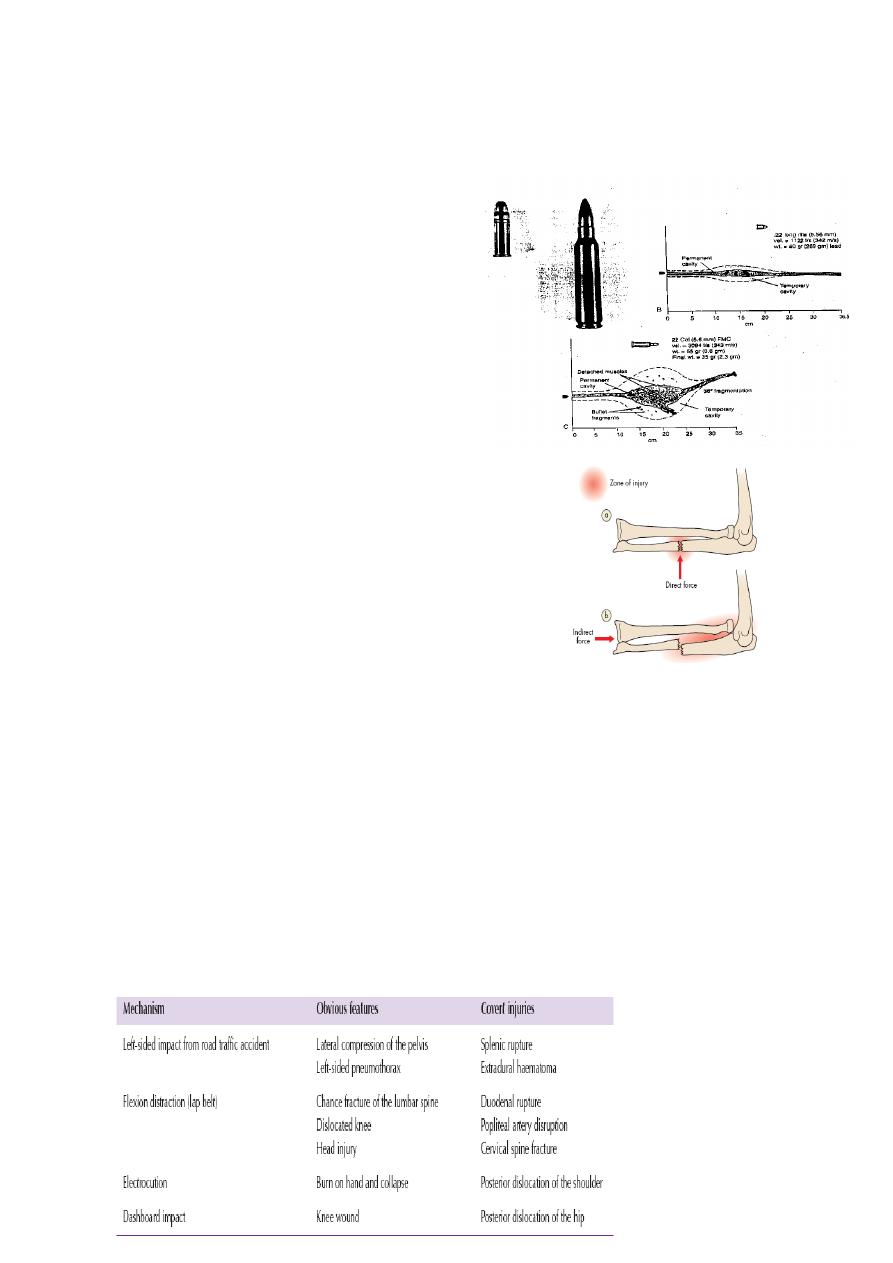
Firearm injuries
• Low-velocity bullets behave like knife
injuries
• High-velocity bullets cause cavitation
• The temporary cavity is large and draws
in foreign materials
• The permanent cavity is smaller and gives
no clue to the extent of damage
BLUNT INJURIES
• DIRECT
• INDIRECT
Overt versus Covert injuries
• OVERT INJURIES : Obvious injuries and can be expected from the patient type,
presentation and mechanism of injury
• Example?
Covert mechanisms & injuirs
• Patients usually tell the truth but may not if criminal activity is involved
• Fear of abuse may prevent vulnerable patients telling the truth
• Patients likely to have covert problems need careful checking even if their injury
appears to have a simple mechanical cause

4
Trauma can be divided into two basic types:
• Serious and life-threatening injury;
• Significant trauma requiring treatment but not immediately life threatening.
The approach to the traumatised patient is very different from that of a patient with an
undiagnosed medical condition as, in the latter, an extensive history, past medical history,
physical examination, differential diagnosis and investigations ordered to confirm or refute
this diagnosis are undertaken.
In the trauma setting, it is often not possible to obtain such information immediately;
hence, a standardised protocol of management is required.
The Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) system was therefore created initially in the USA
and rapidly taken up globally.
The steps in the ATLS philosophy
Primary survey with simultaneous resuscitation – identify and treat what can kill the
patient
Secondary survey – proceed to identify all other injuries
Definitive care – develop a definitive management plan
