vaccination
Dr.Hussein K.H. AlatabiMBChB,DCH,FICMS,CABP
the Vaccination is inoculation of any antigenic material for the purpose of producing active artificial immunity.so uses of
suspensions or extracts of dead or attenuated bacterial or viral cells,usedchiefly in the prophylactic treatment of certain infections means vaccinations
What is Vaccination?
A vaccine is any preparation intended to produce immunity to a disease by stimulating the production of antibodies.
The term vaccine derived from Edward Jenner's 1796 use of the cow pox to induce immunity in humans against smallpox.
(in Latin vacca means cow)
What is Vaccine?
Edward Jenner's an English Physician
World Health OrganizationReports
"Nearly nine million children under 14 years of age die every year from infectious disease. And at least a third of them could be saved if existing vaccines were more widely used, but the rest only if suitable new vaccines were developed..."
Active immunization
induces immunity by vaccination with a vaccine or toxoid (inactivated toxin). bystimulating immune system to produce antibodies and cellular immune responces that protect against infectious diseases.
Passive immunization
temporary protection through adminstration of exogenously prodused antibodies e.g. Immunoglobulin and monoclonal antibodeis ,It includes also transplasental passage of antibodies.
Types of Immunization
• 1-Live attenuated organisms (MMR, BCG, OPV),• Inactivated or killed organisms (DPT)
• Recombinant products (hepatitis B)
• Reassortants (rotavirus)
• Immunogenic components of organism (pertussis, Hib) including toxoids (diphtheria, tetanus
Preparation of Vaccines
1-Vaccine : apreperation of proteins,poly- saccharides or nucleic acids of pathogens deliverd to immune system to induce specific responces that inactivate,destroy or suppress pathogens.
2-Toxoid : amodified bacterial toxin made non-txic but retains its capacity to stimulate formation of antitoxin.
3-Immune gloubin (Ig) :antibodies containing solution derived from human blood by fractionation of large pools of plasma used to maintain immunity in immunization.
4-Antitoxin: antibodies derived from human or animal sera after stimulation with specific antigen,used to induse passive immunization
Immunizing agents
A-Live attenuated agents;produce immunologic response simulating response to anatural infection.Its more likely confer lifelong
protection.e.g, MMR
B-Inactivated,killed or detoxified agents or their B-Inactivated,killed or detoxified agents or their extracts;tend to have lesser antigenic response and requires repeated vaccine to provide protection,e.g. DPT vaccine,influenza vaccine,..
C-Others as
• Reassortants (rotavirus)• Immunogenic components of organism (pertussis, Hib) including toxoids (diphtheria, tetanus
• Recombinant products (hepatitis B)
Preparation of Vaccines
Vaccination schedule in Iraq
DateVaccine
At birth
• BCG, OPV0, HBV1 (at 1st 24 h.)
At 2nd month
OPV1, ROV1, DPT1, Hib1, HBV2
• At 4th month
OPV2, ROV2, DPT2, Hib2
• At 6th month
• OPV3, ROV3, DPT3, Hib3, HBV3
• At 9th month
Measles vaccine, vit. A 100,000 IU
• At 15th month
MMR 1
• At 18th month
• 1st booster of OPV, DPT, Hib with vit. A 100,000 IU
• At 4-6 years
2st booster of OPV, DPT, MMR 2 with vit. A 100,000 IU
• At 11-13 years
Rubella vaccine for girls
1-Chemical and physical characterestic of a vaccine.
2-Catobolic state of vaccine.
3-Route of adminstration of vaccine(parent- eral vaccine are more immunogenic).
4-Host factors:(a- Age of patients as immunity develops rapidly in adults after vaccination. b-nutritional status. C-HLA system of person.
4-Previous booster dose
Factors that control the efficiency of a vaccine :
1-Previous anaphylactic reaction to avaccine or to costituent of vaccine(e.g.:egg,gelatin ,antiboitic.
2-Moderate-severe illness with or without fever.
3-Immunocompromized persons with exception of measles and BCG vaccines for AIDS patients.
General contraindication for immunization;
1- Mild acute illness with or without low grade fever.
2-Low-moderate fever post vaccination3-Mild-moderate local reaction to avaccine e.g. redness, swelling ,soreness.
4-Current antibiotic therapy.
5-History of penicilline or other non specific allergies or fact that relatives have such
allergies
6-Premature babies.
7-Malnutrition
8-Breast fed babies
9-Pregnancy(theoritical risk for attenuated vaccines)
The following NOT contraindication ;
Specific types of vaccines
Dr.Hussein K. Alatabi
MBChB,DCH,FICMS,CABP
BCG(Bacillus Calmette Guerin)
-Live attenuated Mycobacterium tuberculosis vaccine.-50-70% protection for 7-10 years old children.
-Indused cell-mediated immunity (delayed type) in 4-8 weeks (SCAR)
-The dose :0.05 ml I.D.(less than 1 yr.), 0.1 ml( more than 1 yr.).Site ;usually upper
third of forearm e.g.deltoid
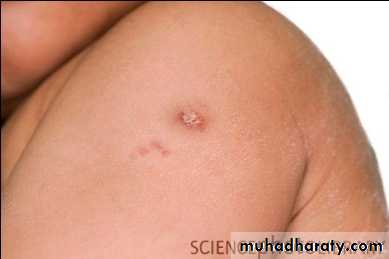
Scar of BCG vaccine
Appear at 4-8 weeksAdverse reaction of BCG:
-Generally safe-fever,pain.axillary lymphadenopathy,ulcer, lupus vulgaris,kelloid reaction.
*Indications ;
-Tuberculine negative infant in a household with active disease.-High TB incidence area.¬ given after 1st year age.
Poliovirus vaccines
-Tow types of vaccines are available and are equally protective; 1- IPV,an inactivated or killed v.(Salk),which not used in in secadule in Iraq but used in immuncompromised pat.( USA). 2- OPV,alive attenuated v.(Sabin)(in Iraq).
*OPV;80% protection,3 doses and boosters, 2-3 oral drops.
-OPV should not given to:-individuals known to be or suspected of being immunocompromised., household contacts of immunocompromised personsand subsequent siblings of achild with cogenital immunodeficiency,until the younger children have been shown to be normal.
OPV vaccine
2-3 oral dropsDPT vaccine
-DPT(Diphtheria,pertusis,Tetanus), killed vaccine.-0.5 ml IM or S.C in 3 doses & 3 boosters.*- 3 major contraindications are;-an acute fibrile illness,-an evolving or suspected neurologic disease and –severe reaction to prior dose of DPT.
*-Adverse reactions after DPT: local swelling and tenderness at injection site,slight fever,irritability, protracted inconsolable crying,unusual shock like syndrom(uncommon)and convulsions or manifestations of encephlopathy(rare, 1:500000)
-Since the risk of encephalopathy development, the DPT replaced by:
-DT orDaPT wich called(acellular pertusis), its less antigenic.*-Percautions(benefits versus risks);
A-Temp.<40 c withen 48 hours.
B-Collapse withen 3 days of 1st dose
C-Collapse withen 48 hours.
D-Persistent inconsolable cry>3 hours withen 48 hours..-E- Development of GBS withen 6 weeks.
H. inf.type B(HiB) vaccine
-The vaccine used with( the 4th vaccine) or ( with the 5th vaccine).
-As about 90% of infections caused by H.inf. Due to type B so vaccine used is type B.
-It is polysaccharid vaccine.
-Route: IM
MMR(measles,mumps,rubella)v.
-Compined,live attenuated vaccine, given as single dose 0.5 ml IM or S.C with 80% protection.*-Contraindication;
-pregnency,-immunodeficiency,-theraputic immunosuppresion,-acute fibrile illness, -anaphylaxis to egg ingestion.
*-Adverse reactions;
-transient rashes and fever 6-11 days after immunization to measles componant.-transient artharlgias,rare arthritis and paresthetic pains to the rubella component.
Measles Vaccine:
-Live attenuated virus.,single dose at age of 9 months (Iraq).and 15 months(USA). –booster dose may be given during preadolescent school years.,given as 0.5 ml SC-Adverse reaction: -mild measles- like rash 10-14 days after adminstration and cutaneous anergy,which may lasts up to 3 mo.
-Although vaccine is not recommended for use in patients with T cell dysfunction,it is recommended for use in patients with AIDS becouse measles disease in these patients may be life threatening.
Rubella vaccine
-Live attenuated vaccine.,usully given with MMR at 15 mo.and for girls at 11-13 yr.(Iq) ,antibody develops in 98% of those vaccinated and is believed to be lifelong.-0.5 ml S.C or IM.
-Adverse reactions;arthalgia,rare arathritis and paresthesia
-Although vaccine has never been shown to cause the congenital rubella syndrome, it is not recommended to be given during pregnancy.
Hepatitis B vaccine(HBV)
-Inactivated purified protein Ag of virus (recombinant type). -0.5 ml IM. -80% protection.
*In pretem baby the 1st dose of vaccine delayed till 1month age.
Rota V.vaccine(ROV)
-Rota virus responsible of about 45% of cases of diarrhea in childreen.-The vaccine is given as oral drops at age of . 2,4 and 6 months
-The age of child should not more than 3 months at 1st dose of vaccine
-No dose of vaccine should given after 8 months age.
NOTE
Unimmunized infants between 2 and 14 mo. Should be started on the same sequence of immunizations and intervals as younger infants.*Children 14 mo. -7 yr.require mdified schedule of vaccinations
Vaccines which are given selectively;
-1-Pneumococcal vaccine.(>2 yr. with functional or anatomic aseplenia).-2-Meningococcal v.,-3-Cholera v.
-4-Typhoid fever v.., -5-Hepatitis A v..
-6-Influenza v..,-7-Rabies v.
-8-N.meningi. v.,-9-Yellow fever v..
-10-Varicella v...
Post exposure prophylaxis
-1-Immunoglobulin (Ig):
-Measles. –Chicken pox. –Tetanus. –Rabies -Hepatitis A&B. –Influenza.
-2-Chemoprophylaxis:(By antibiotics):
-Pertusis(Erythromycin).-Meningitis (rifampicin).-Diphtheria(Pencillin,Erythr.) -Rheumatic fever(Pencillin). –TB(INH). -SBE(Pencillin).-Neonatal conjunctivitis (Silver nitrate).