SPONDYLOLISTHESISLec-3
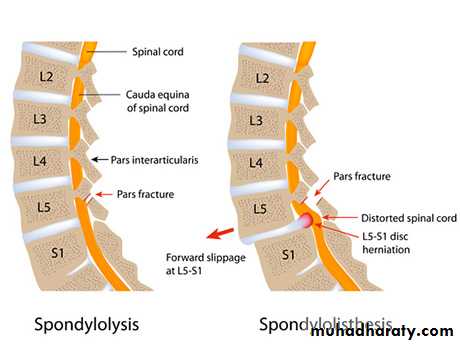
Dr.Sadeq Al-mukhtar - Consultant orthopaedic surgeonSpondylolisthesis Def: It is forward slippage of a cephalic vertebra on a caudal vertebra.
Spondylos (vertebra).
Olistharein (slip or fall)
Spondylolysis: Greek word lysis (Loosening).
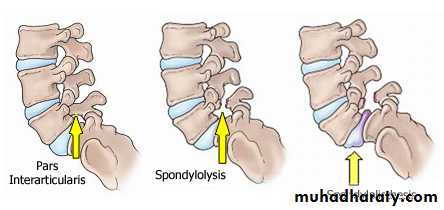
It is used to describe a bony defect in the Pars interarticularis ”the portion of neural arch just caudal to nconfluence of pedical and the superior articular process and at the most cephalic part of the lamina and the inferior articular process”.Spondyloptosis: Ptosis is falling. This refers to the most severe form of spondylolisthesis .When the body of L5 has slipped into the pelvis and is positioned directly anterior to the sacrum
Clinical Feature:
The symptom are caused by chronic muscle contraction (spasm) as the body attempt to limit motion around painful pseudoarthrosis of pars interarticularis by tears of annulus fibrosus of a degenerating disc or by compression of nerve roots.In children there is no pain.
In adolescents usually back pain of movement particularly with hyper-extension as well as hamstring fatigue and pain, sometimes there are symptoms of sciatica.
Over 50 years there is backache.
Examination:
Flat buttocks.Abnormal transverse loin lines (loin creases).
Step of spine.
Spine movement: normal in young but restricted in elderly.
CLASSIFICATION - Wiltse-Newman-Mcnab classification
Type-1: Congenital Dysplastic(20%):-Dysplastic disorder in the posterior elements of upper sacrum.
Type-2: Isthmic (50%):-
Three subtypes:Lytic-stress fracture of Pars
Elongated-healed lytic type
Acute fracture of Pars.
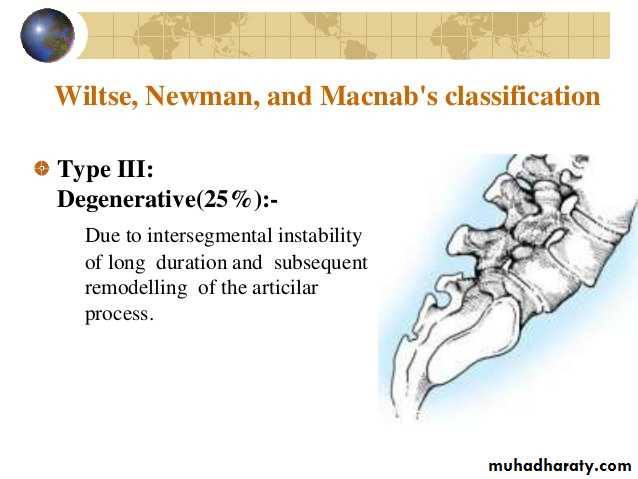
Type-3: Degenerative”Pseudospondylosis” 25%
Neural arch including pars is intact and olisthesis result from longstanding segmental instability.
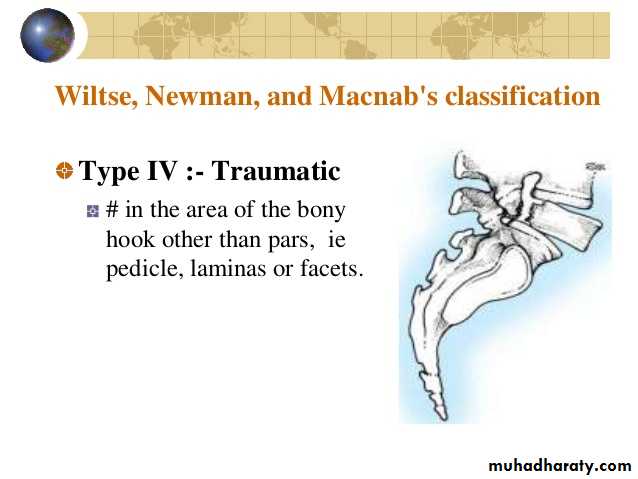
Type-4: Traumatic: Fracture of bony hook rather than the pars (articular process).
Type-5: Pathological; Generalized or localized bone disease that predisposes to olisthesis.
Type-6: Post-surgical; Loss of posterior elements secondary to surgery.
e.g: excessive removal of facet or arthrodesis above.Treatment
Conservative:
Rest, Analgesia, NSAIDS ,and physiotherapy.
Surgery:
Indications-
1-High-grade slip>50%.
2-Intractable pain or neurological signs.
3-Progressive postural deformity or gait abnormality.
Types of Surgery
Primary repair of pars interarticularis defect under screen” Image intensifire”Instrumental postero-lateral fusion in situ.
Arthrodesis.
Decompression.
Radiological Assessment
Plain x-Ray:Anterior and Lateral:
Shows the degree of subluxation and also reveal pars interarticularis deficit if present.
Oblique views used to see Scott Dog sign.
Meyerding classification: Radiological classification
Grade -1: 0-25%
Grade -2: 25-50%
Grade -3: 50-75%
Grade -4: 75-100%
Grade -5: >100%
Slippage is graded as a percentage relative to the sagittal diameter of the inferior body.
CT Scan
MRI.