4th stage
SurgeryLec-
Dr.Mohammed
20/12/2015
Carcinoma of the prostate CAPOne of the most common malignant tumor affecting males over the age of 65 in western countries.
Pathology :
95% of the tumor are adenocarcinoma and derived from acinar epithelium75% of CAP arise from peripheral zone.
grading:
Gleason’s grade based on the degree of glandular differentiation and growth pattern.
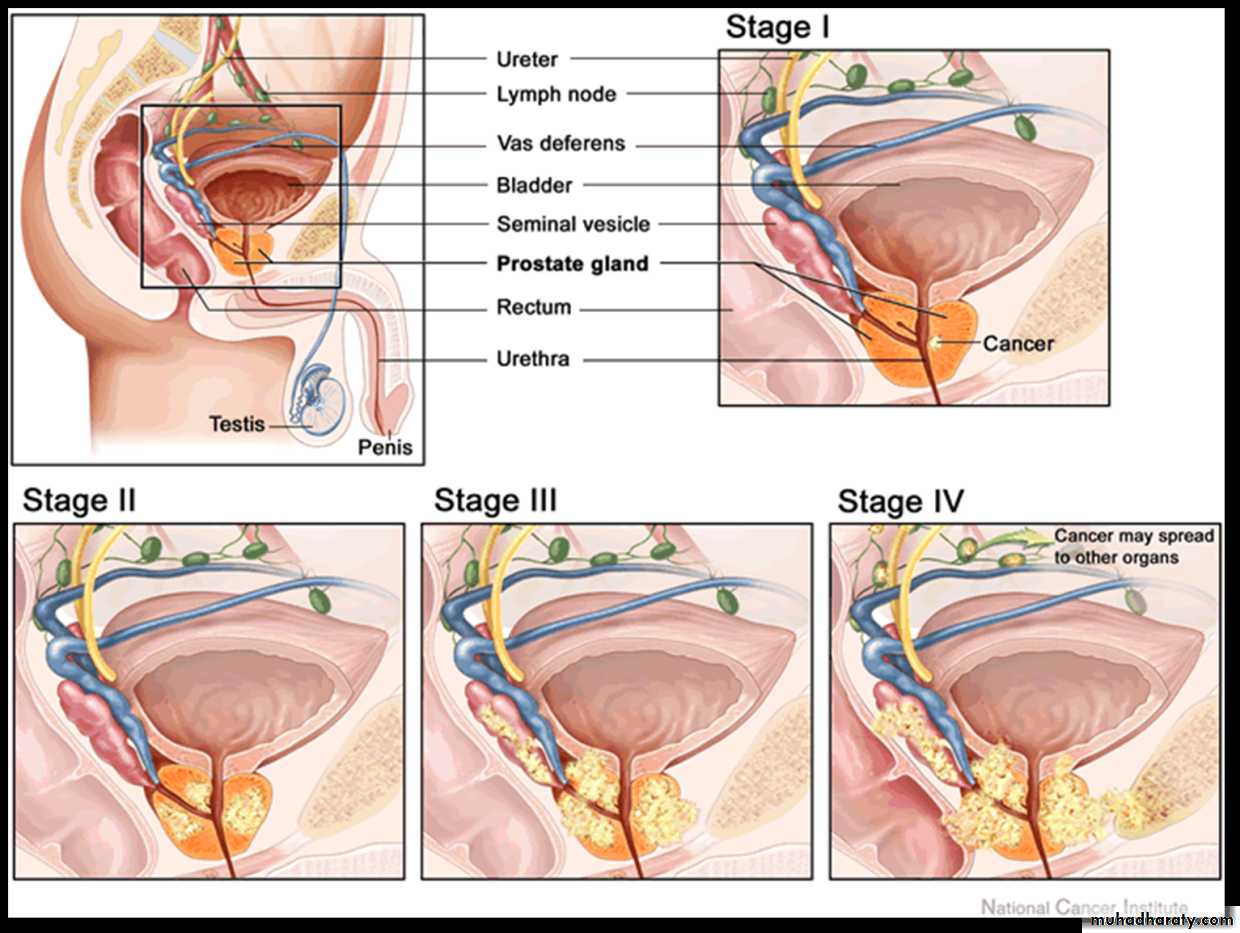
Spread :
Direct invasion: to nearby structures.Denonvvilliar’s fascia act as barrier.
Lymphatic: internal, external & common iliac
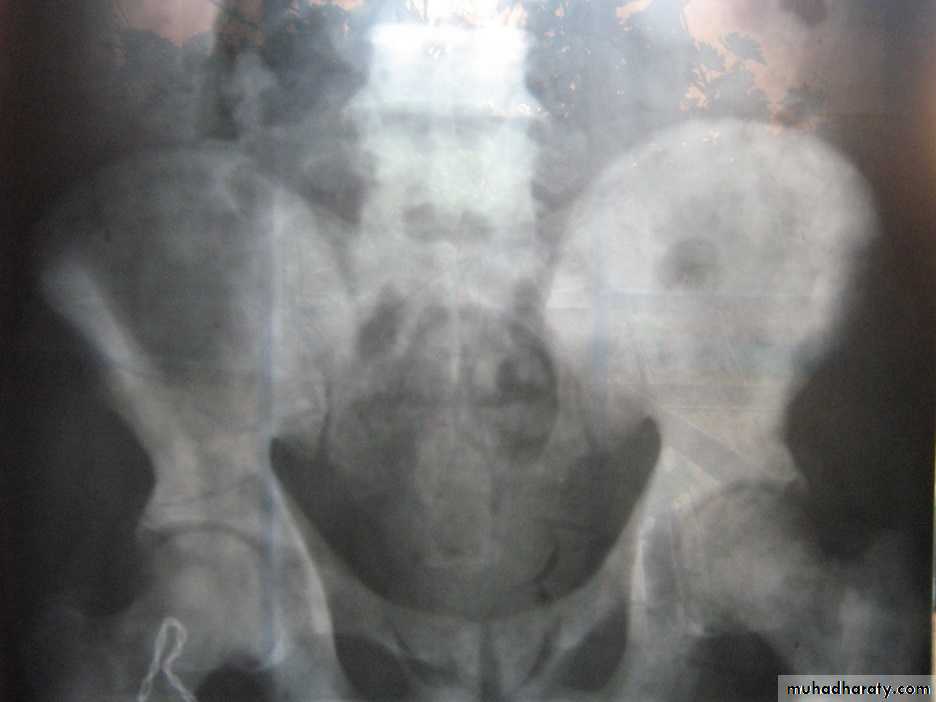
Blood: to the lower lumber vertebrae & pelvic bones due to reverse blood flow from vesicoprostatic plexus to the emissary veins of the bones during coughing & sneezing (OSTEOBLASTIC)
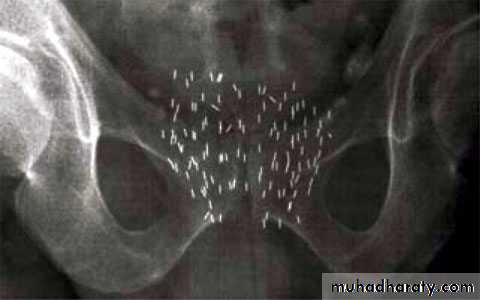
Osteoblastic lesion of secondary CAP
Presentation :
Accidental during histopathological ex after prostatectomy.During PR ex
High PSA
BOO.
Metastatic: back ache, sciatica, paraplegia or pathological fractures.
BPH CAP
Younger age older
Symptoms slowly progressive rapid progressionUsually no back or bone pain more back ache &neurological symptoms
Smooth rubbery prostate with sulcus hard irregular prostate with obliterated
Sulcus
Rectal examination:
Stony hard irregular prostatic nodule, obliterated median sulcus, difficulty in moving the rectal mucosa over it and fixity.Normal PR ex does not exclude CAP.
Investigations :
PSA: prostatic tumor marker for diagnosis and follow up, it may also increase in prostatitis and BPH.10 ng/ml normal, 10-15 suspicious.
>15 is diagnostic.
Acid phosphatase: prostatic fraction.
Alkaline phosphatase: in bone metastasis.
Radiological investigations :
Plain X ray: osteoblastic lesion.Bone scan: hot areas (active).
CT scan.
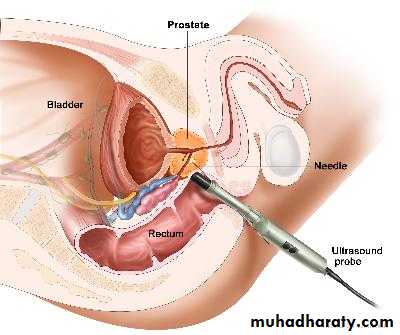
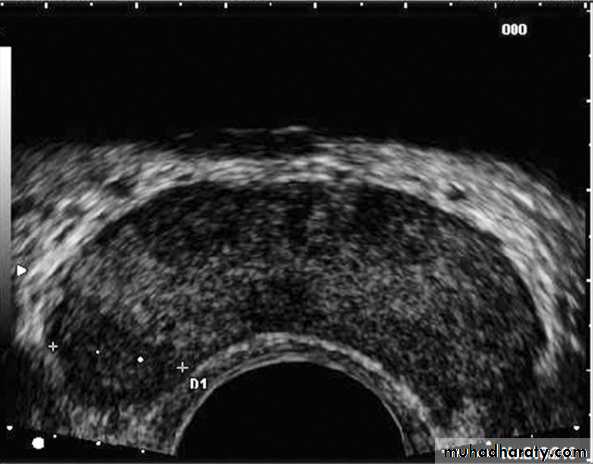
TRUS & biopsy (sixtant biopsy).
Differential Diagnosis :
Not all patients with an elevated PSA concentration have CaP.(BPH, urethral instrumentation, infection, prostatic infarction, or vigorous prostate massage)Not all patients with an Induration of the prostate have CaP.(chronic granulomatous prostatitis, previous TURP or needle biopsy, or prostatic calculi).
Not all patients with sclerotic bony lesion and elevated alk. phosphatase have CaP.(Paget disease)
Treatment :
Watchful waiting:
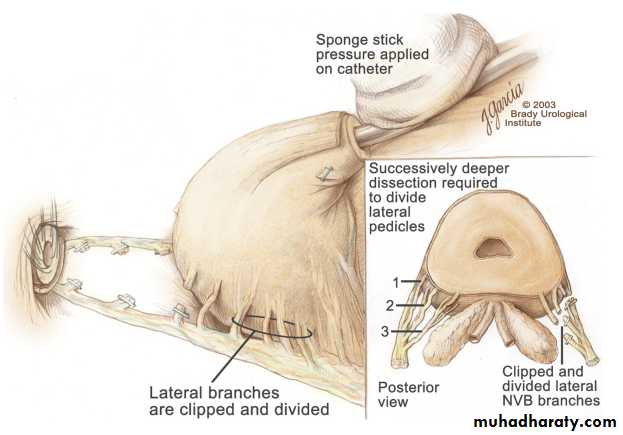
Radical prostatectomy:
Enblock surgical removal of the entire prostate, seminal vesicles and pelvic lymph nodes. The bladder anastomosed to the urethra.
Indicated for early disease and healthy fit pt.
Radical prostatectomy
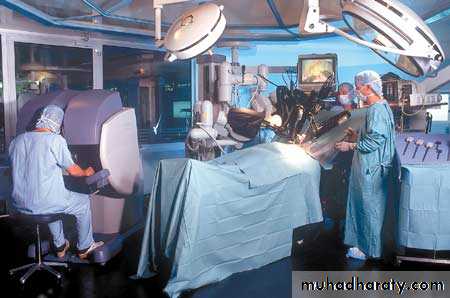
ROBOTIC RADICQL PROSTQTECTOMY
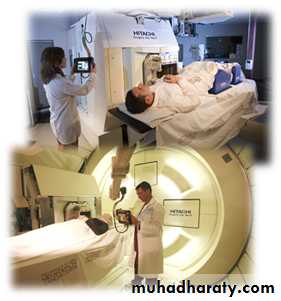
Radiotherapyexternal beam & brachytherapy
Indication:1- Locally advanced disease.
2- Unfit patient for surgery.
3-Symptomatic metastases to relieve pain.
Brachytherapy external beam therapy
Hormonal therapy
Its trearment of choice for metastatic tumorCap is hormonal dependant (androgen), and about one third of tumors are hormone-insensitive.
Androgen ablation may change the course of the disease
Methods of androgen ablation :
-Surgical:Bilateral orchiectomy: complete or subcapsular.
-Medical:
LHRH agonist: (Zoladex)/28 days SC.
Anti androgen: (Nilutemide) 250 mg/6h.