
L.N. – Reactive hyperplasia
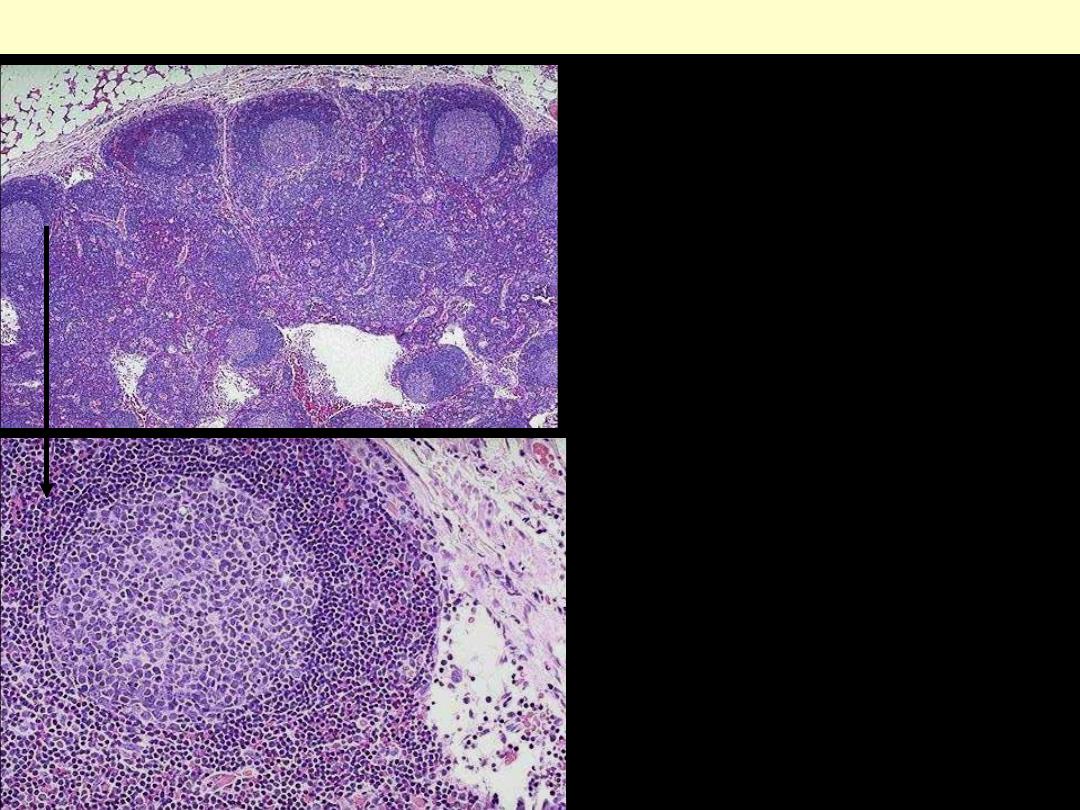
A benign reactive lymph node.
At the top is the capsule.
Beneath the capsule is the
paracortical zone interrupted
by lymphoid follicles; these
consists of a pale germinal
centre surrounded by a dark
blue mantle (cuff) of small,
mature lymphocytes.
Reactive follicular hyperplasia lymph node
At higher power one of the
reactive follicles is seen. The
pale color of the germinal
center is due to its content of
larger lymphoid cells &
macrophages. At the lower
right is the subcapsular sinus.
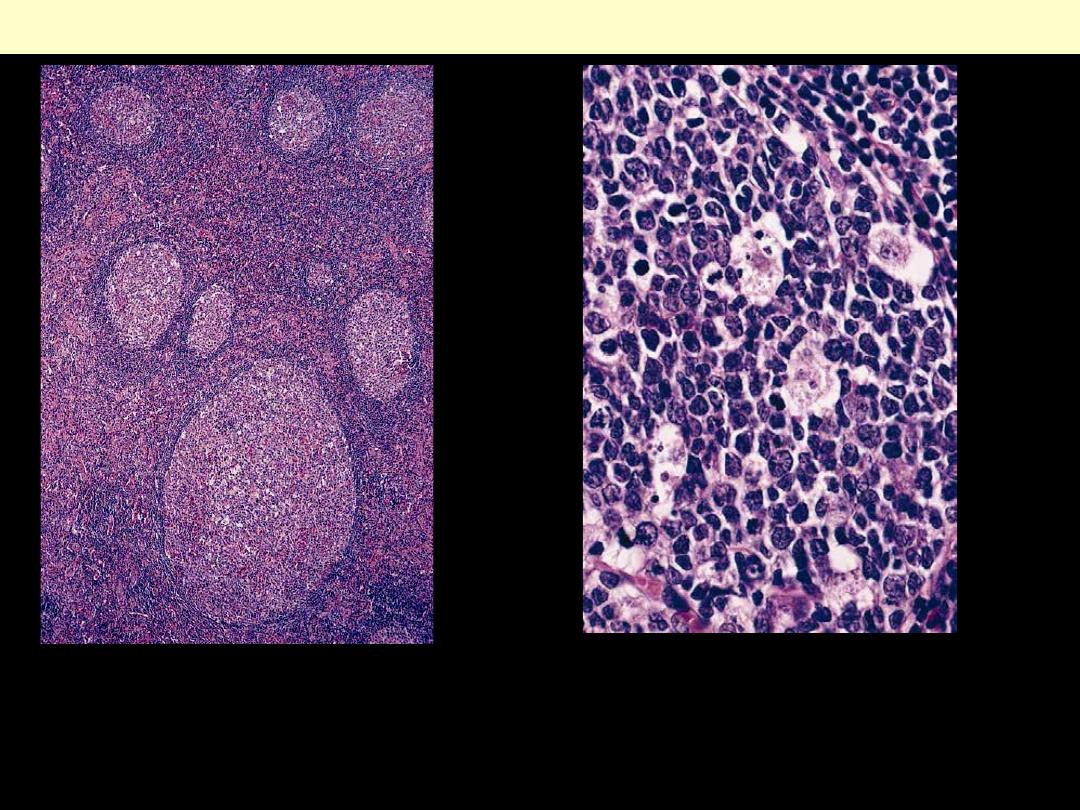
A, Low-power view showing marked differences in size of germinal centers, their
well-circumscribed character, and the fact that they are surrounded by a well-
defined mantle. B, High-power view of the germinal center showing numerous
"tingible-body" macrophages admixed with follicular center cells.
Reactive follicular hyperplasia lymph node
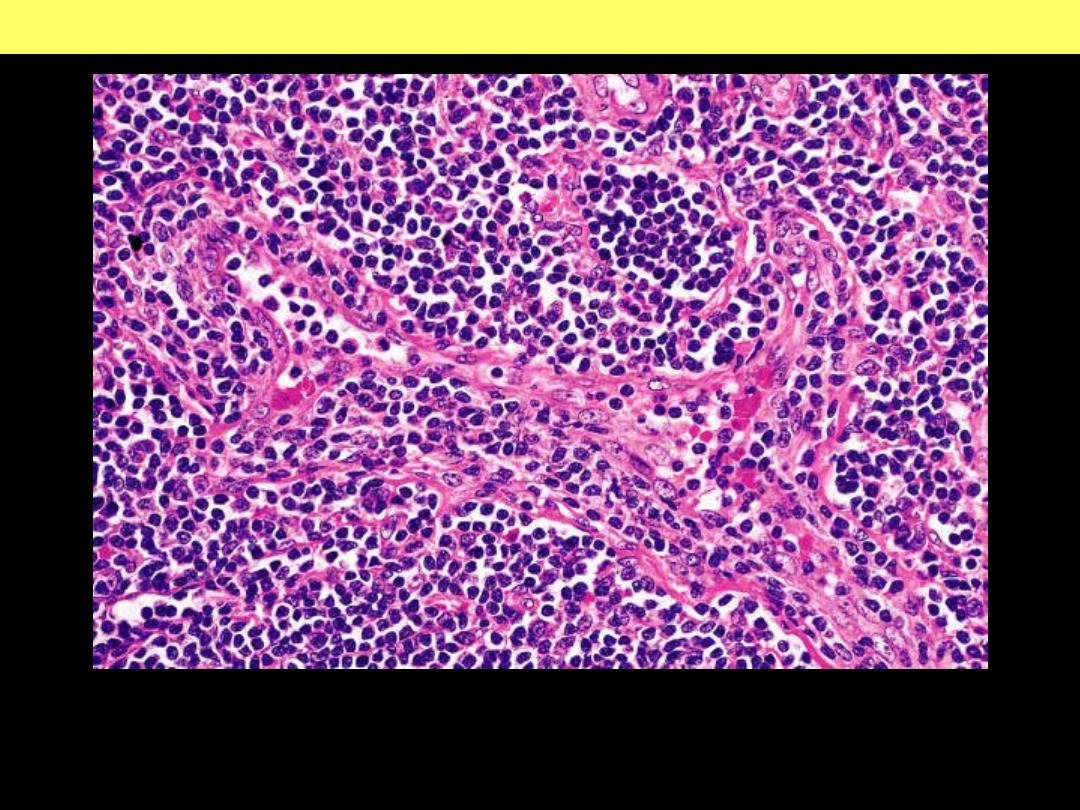
Paracortical hyperplasia, identified by the prominence of
postcapillary venules.
Lymph node: Paracortical hyperplasia
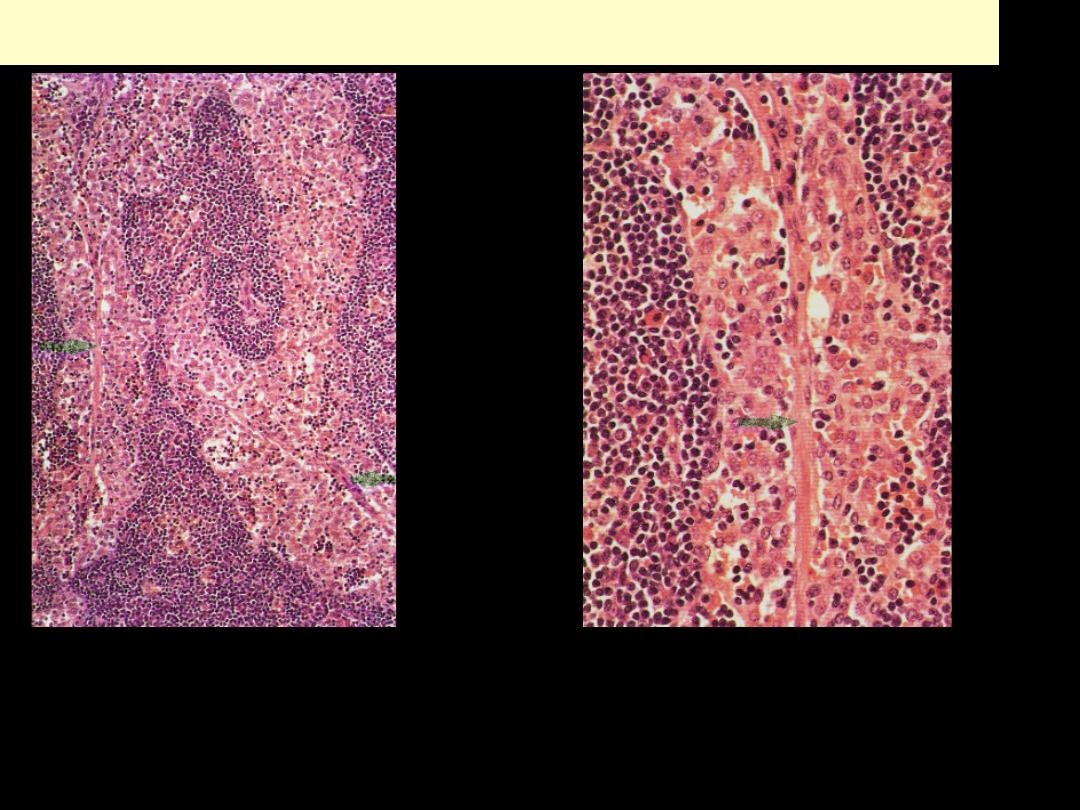
Sinus histiocytosis (Reactive sinus hyperplasia)
There is a marked increase in the number of macrophages in the lymph node sinuses. Two
medullary lymphatic sinuses are shown. They are greatly distended, and their lumens
filled with large numbers of large histiocytes with pinkish cytoplasm. The small dark-
staining cells accompanying the macrophages are lymphocytes. The medullary lymphoid
tissue outside the sinuses consists of small lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes.
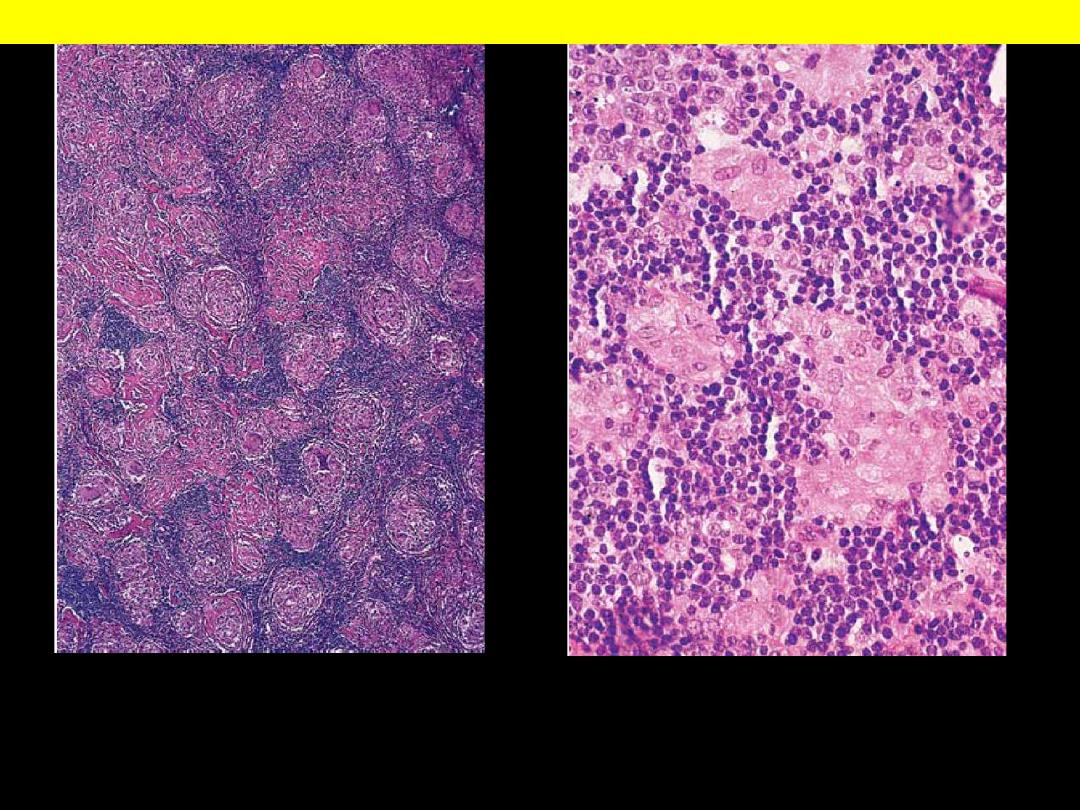
Multiple adjacent, well-defined, rounded granulomas. A granuloma is a focus of
chronic inflammation consisting of a microscopic aggregation of macrophages that
are transformed into epithelioid cells surrounded by a collar of mononuclear
leukocytes, principally lymphocytes and occasionally plasma cells.
Granulomatous Lymphadenitis

Lymphoma
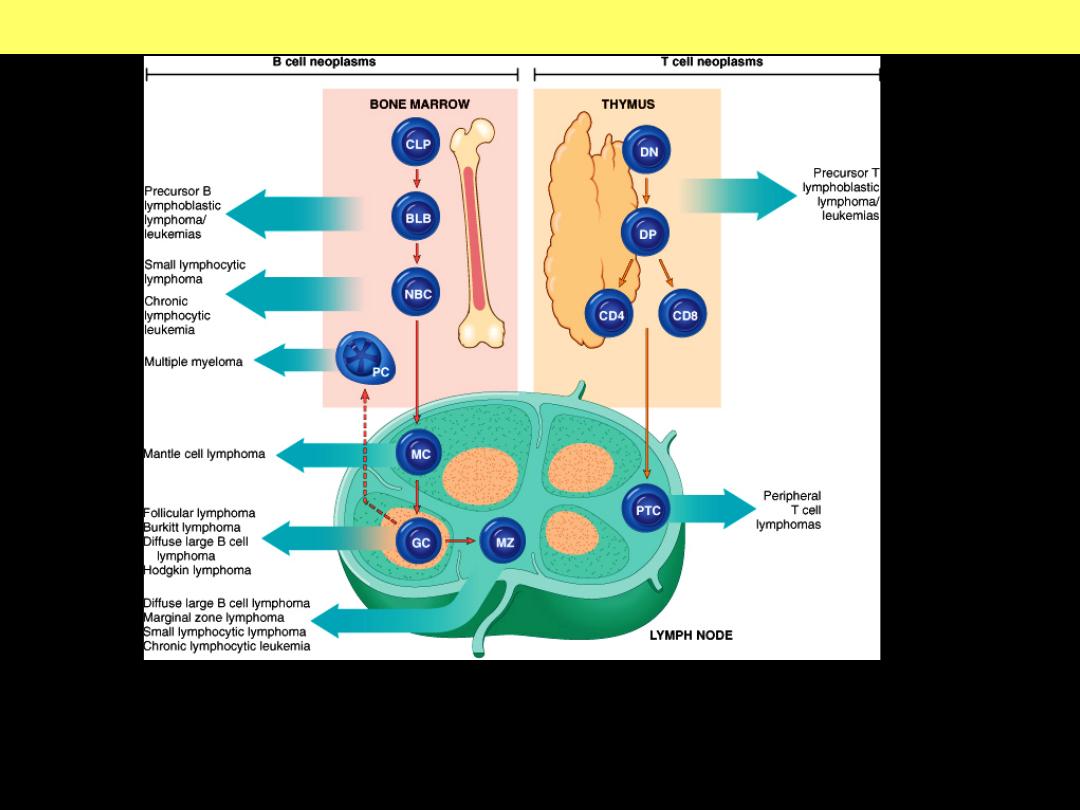
All lymphomas are derived from a single transformed cell and thus are:
monoclonal. B- and T-cell tumors are composed of cells derived from specific
stages of their normal differentiation pathways.
Cellular origin of lymphoma
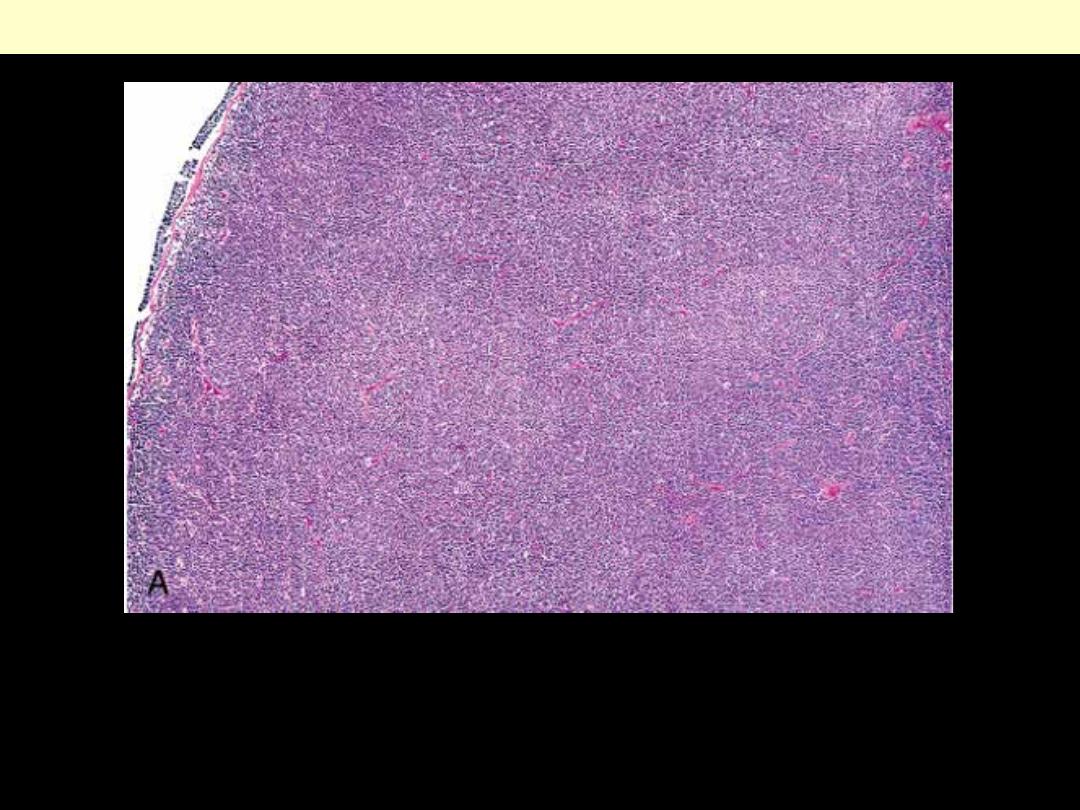

Small lymphocytic lymphoma lymph node
Low power view showing diffuse monotonous proliferation of small
lymphocytes that effaces the architecture of the node.
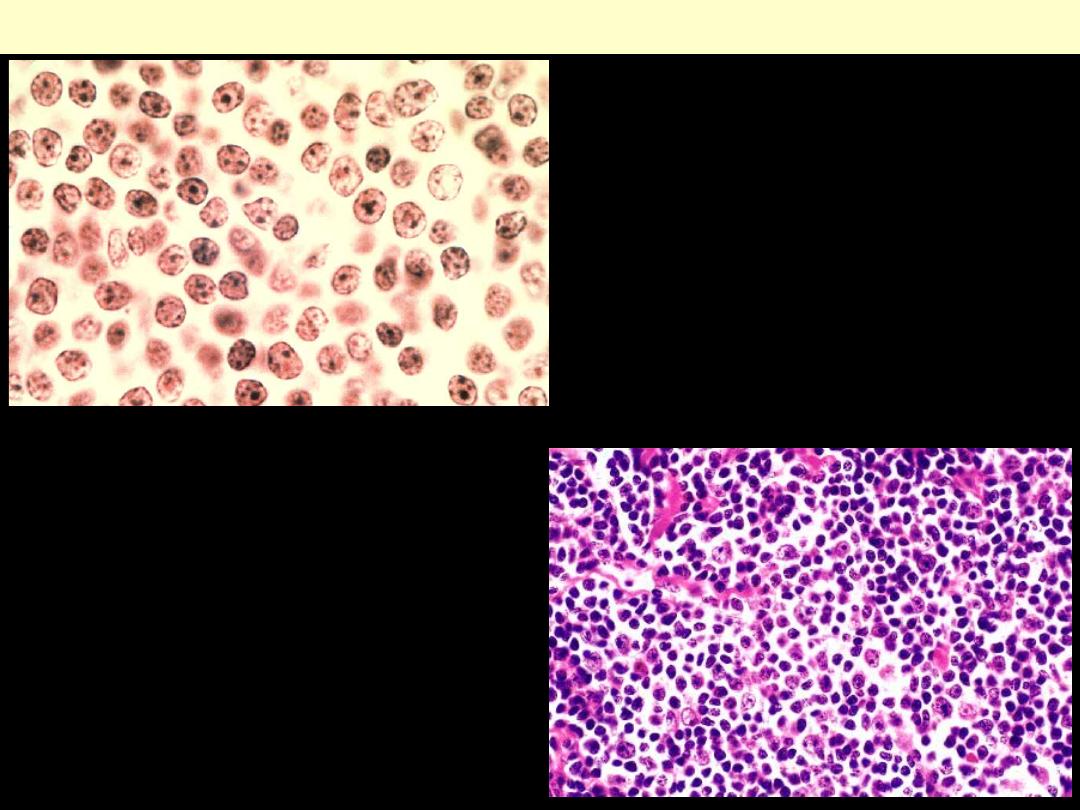
Small lymphocytic lymphoma lymph node
HP view of small lymphocytic
lymphoma. The nuclear
contours are regular, the
chromatin is clumped, and
nucleoli are inconspicuous.
Proliferative center in a lymph
node involved by small
lymphocytic lymphoma.
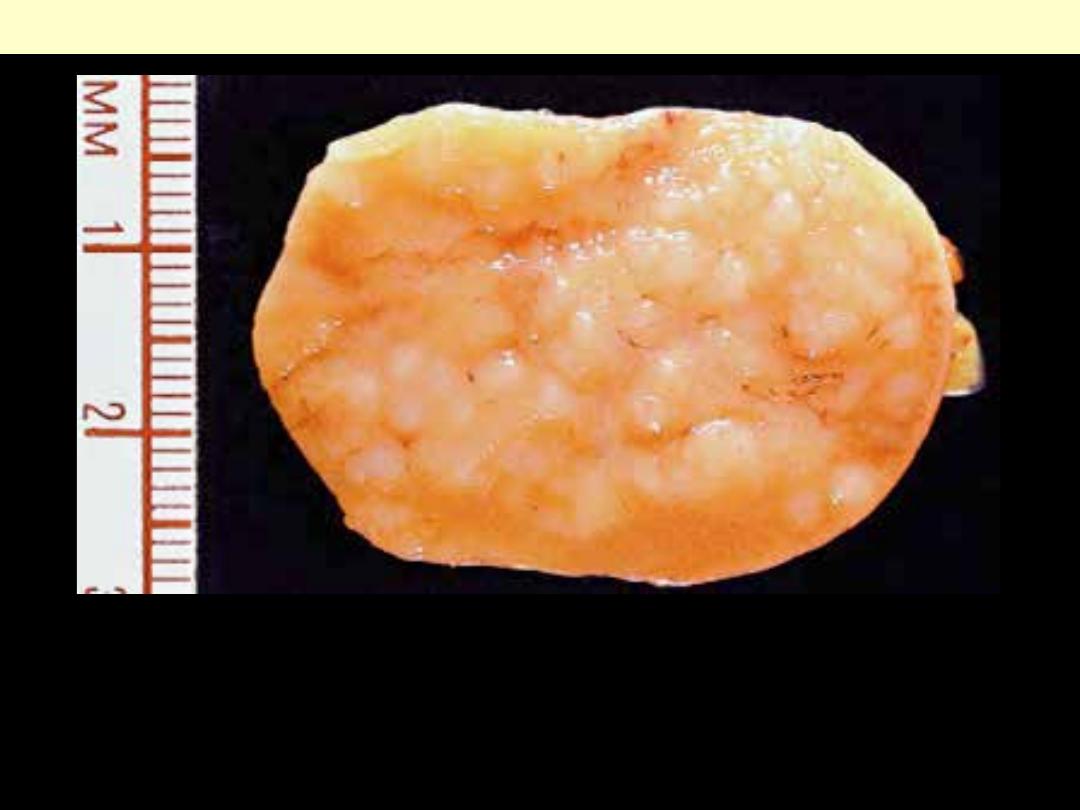
Lymph node involvement by follicular NHL
The neoplastic nodules bulge onto the cut surface of the involved
lymph node
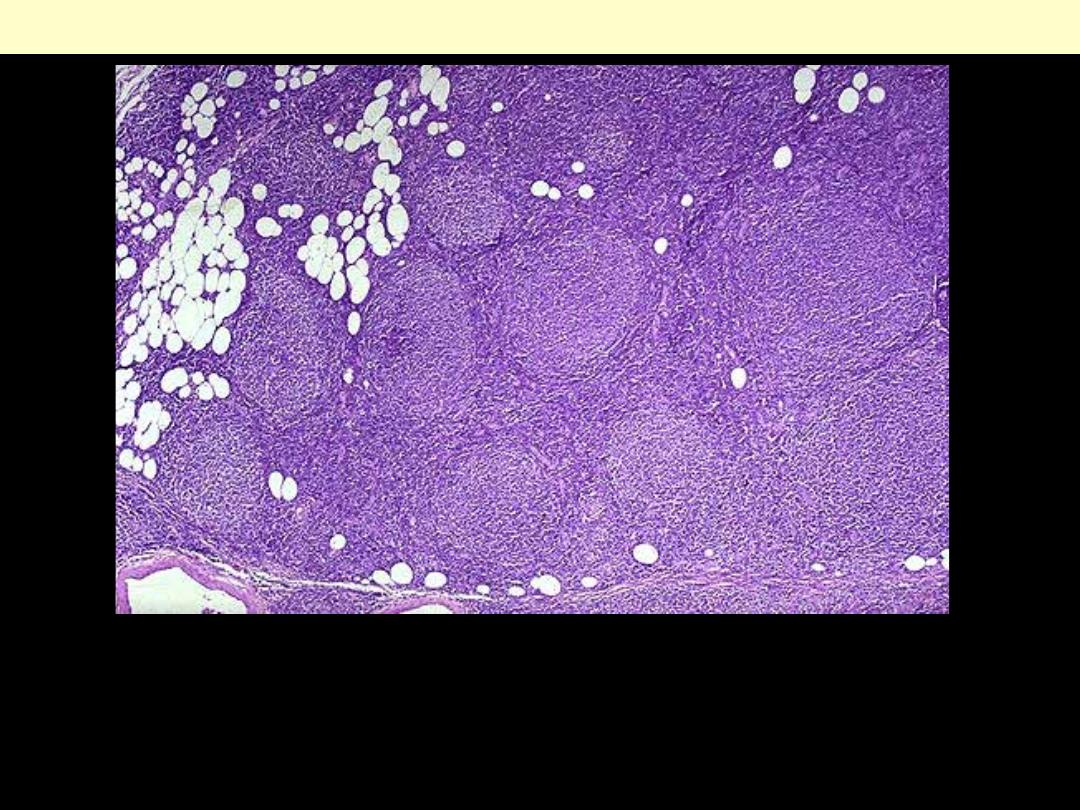
The lymph node architecture is replaced by numerous follicles (nodules) of
lymphoid cells. The latter are of relatively similar size. The capsule of the
node has been invaded and the lymphoma cells extend into the
surrounding adipose tissue. Note that the follicles are numerous.
Follicular lymphoma
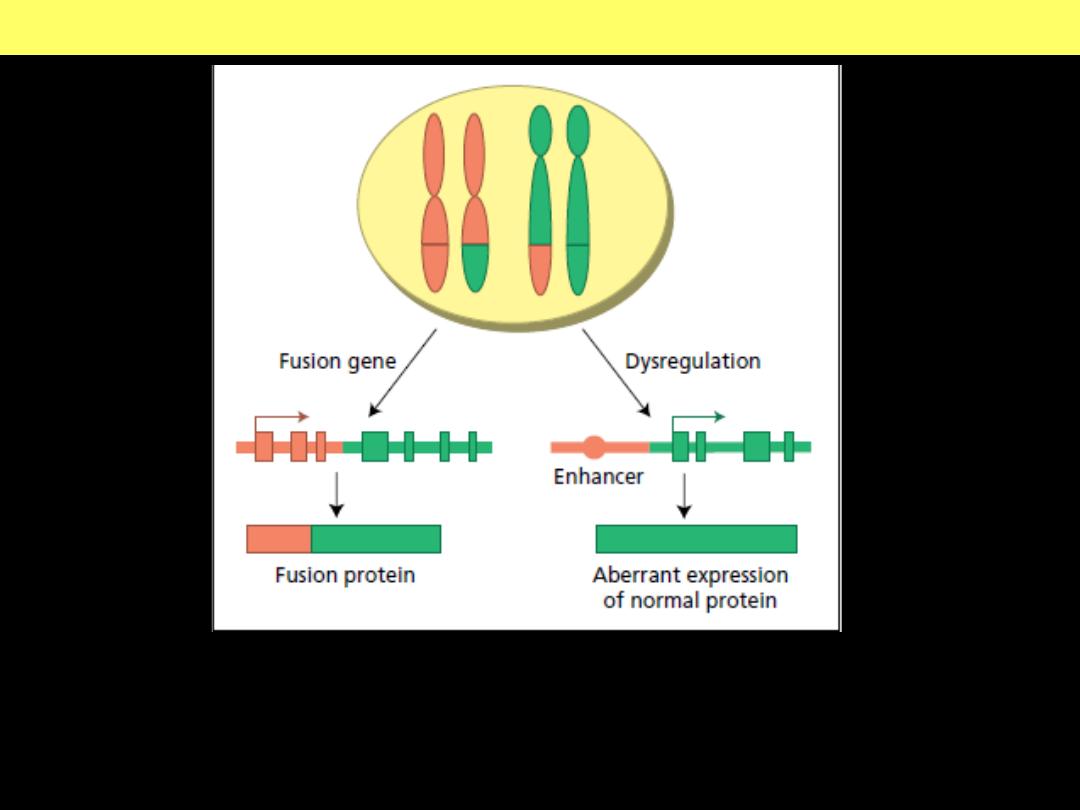
Recurrent translocations may result in fusion gene formation or
transcriptional dysregulation of an intact target gene.
t(14;18) translocation
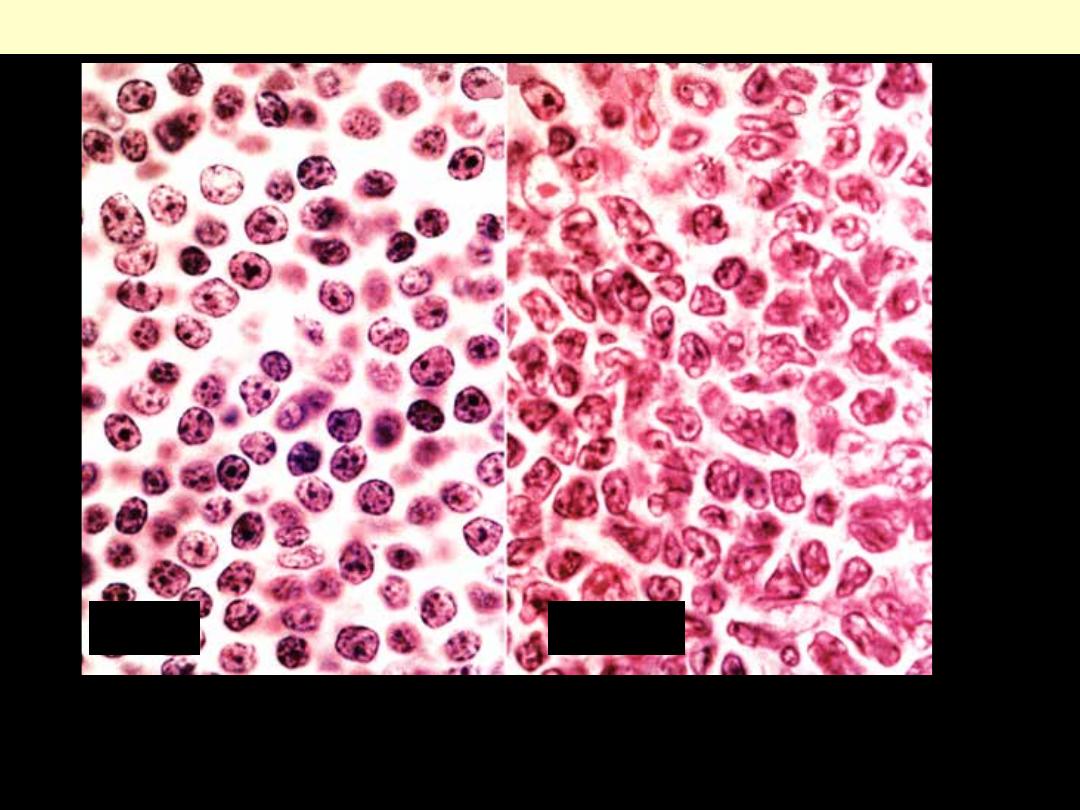
Marked contrast between the cleaved cells of follicular lymphoma (B) and
the regular mature lymphocytes of small lymphocytic lymphoma (A).
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Vs Follicular Lymphoma
A
B
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (centroblastic)
Prakash, S. et al. J Clin Pathol 2007;60:1076-1085
The constituent cells are large with large nuclei, many of which have
more than one prominent nucleoli.
Copyright ©2007 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Prakash, S. et al. J Clin Pathol 2007;60:1076-1085
There are numerous large lymphoid cells each with a prominent single
nucleolus and a moderate amount of often eccentrically placed cytoplasm.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (immunoblastic)
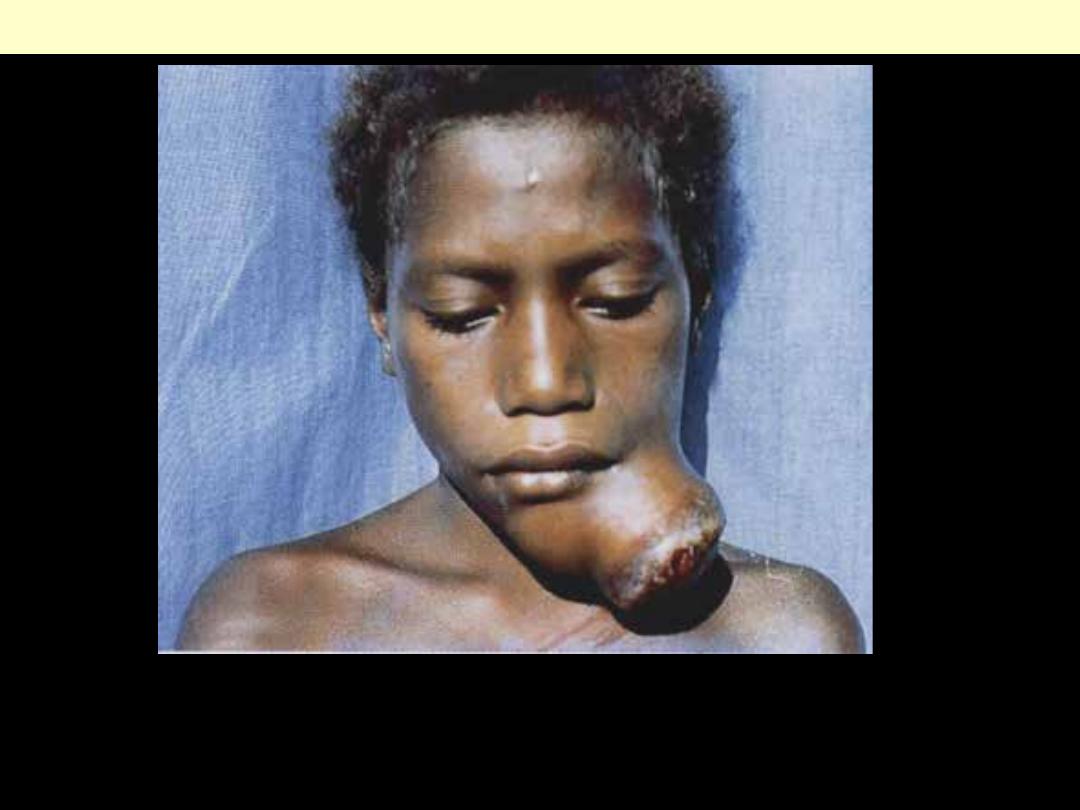
Burkitt's lymphoma
A fungating mandibular tumor that ulcerates through the skin.
Facial involvement is a feature of the endemic form of the disease.
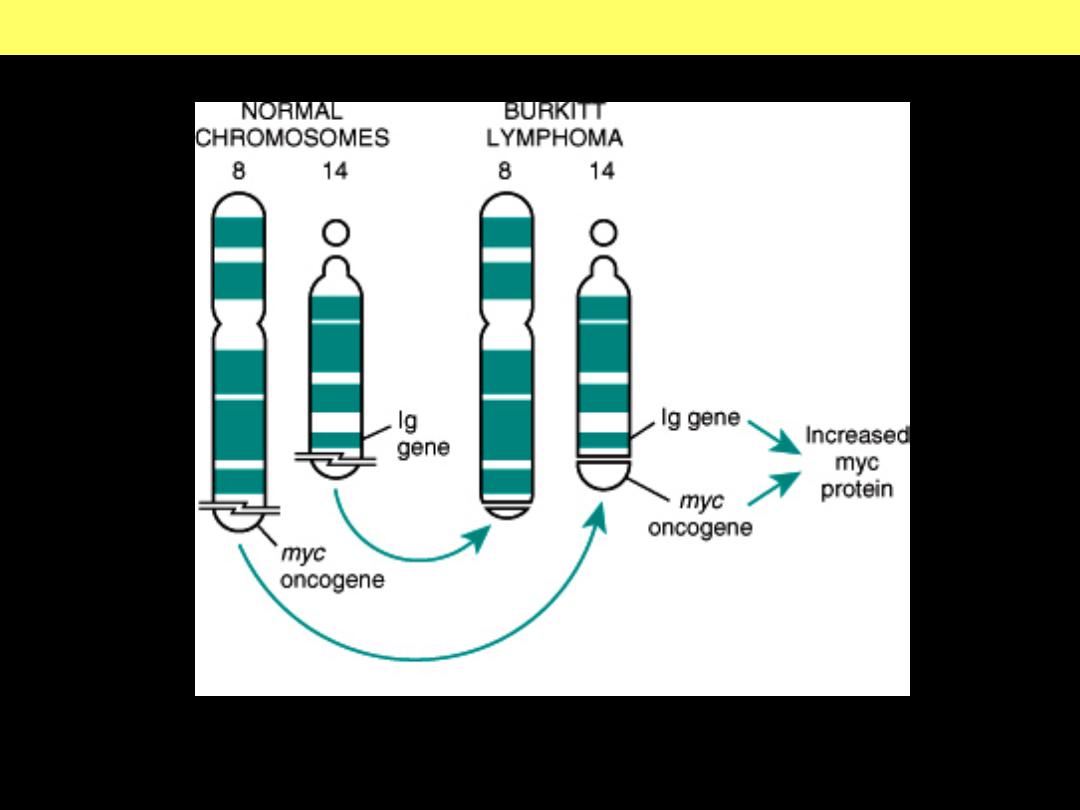
Burkitt Lymphoma : t(8;14) translocation
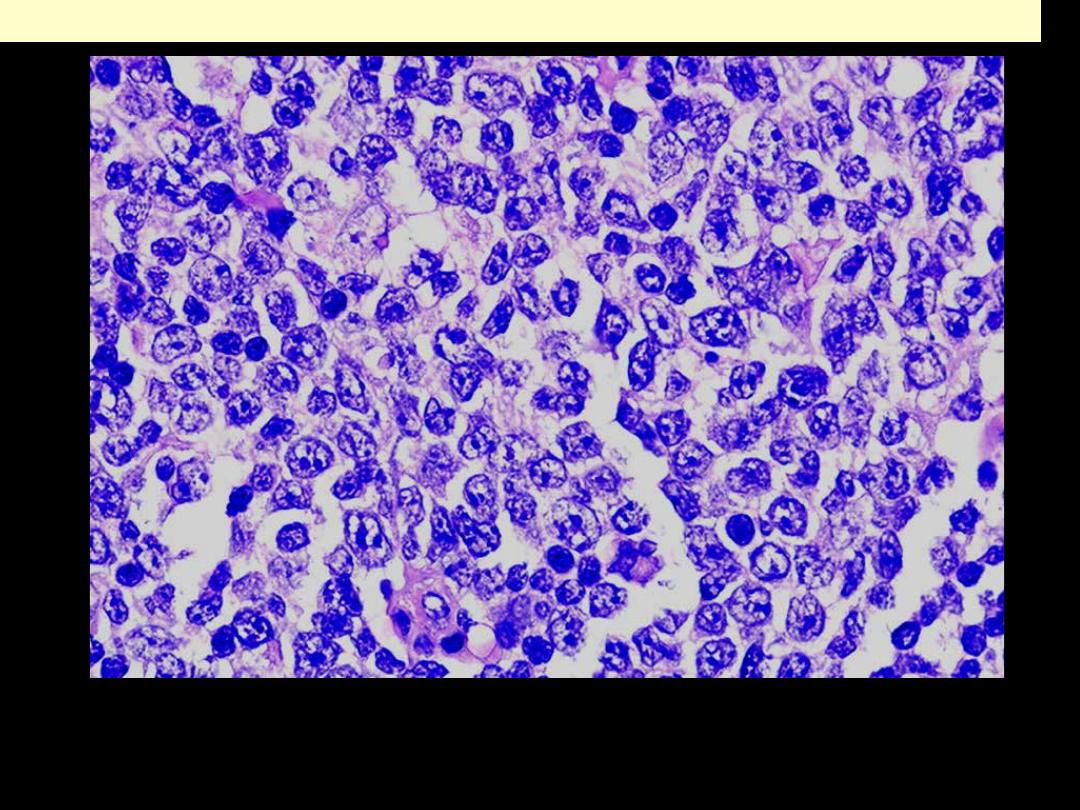
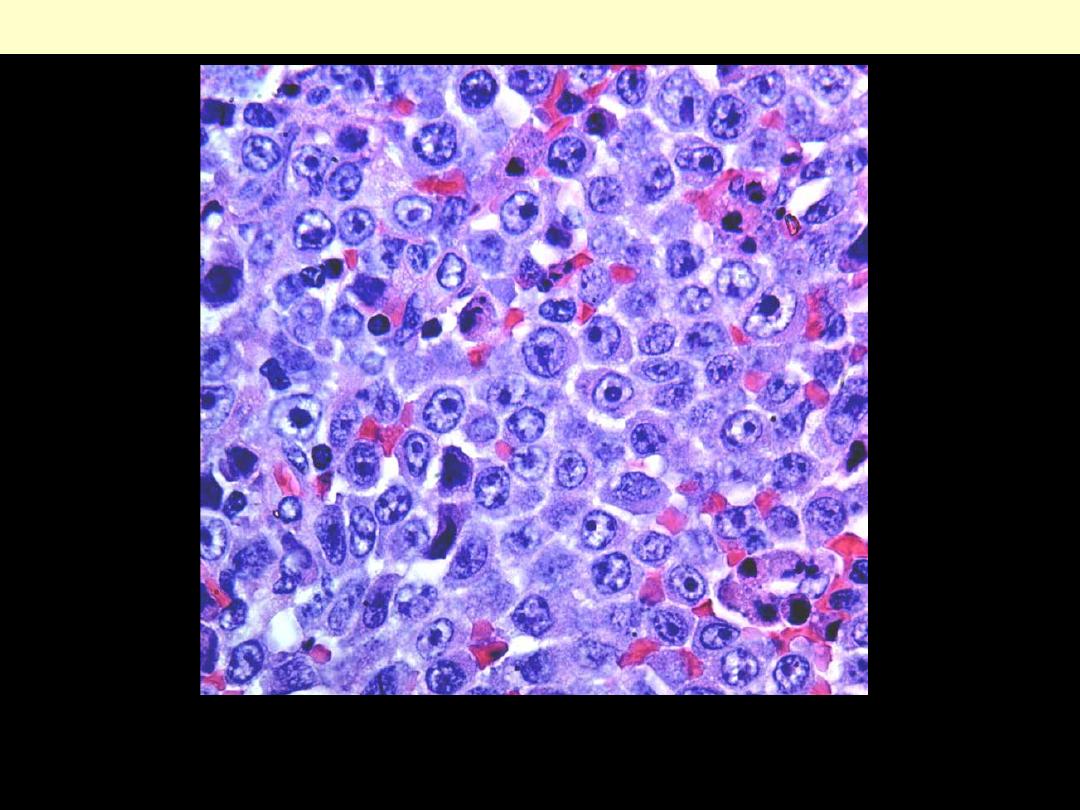
High-grade neoplasm with features of Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia
involving bone marrow. The neoplastic cells are medium size with
cytoplasmic (lipid) vacuoles. A mitotic figure is present.
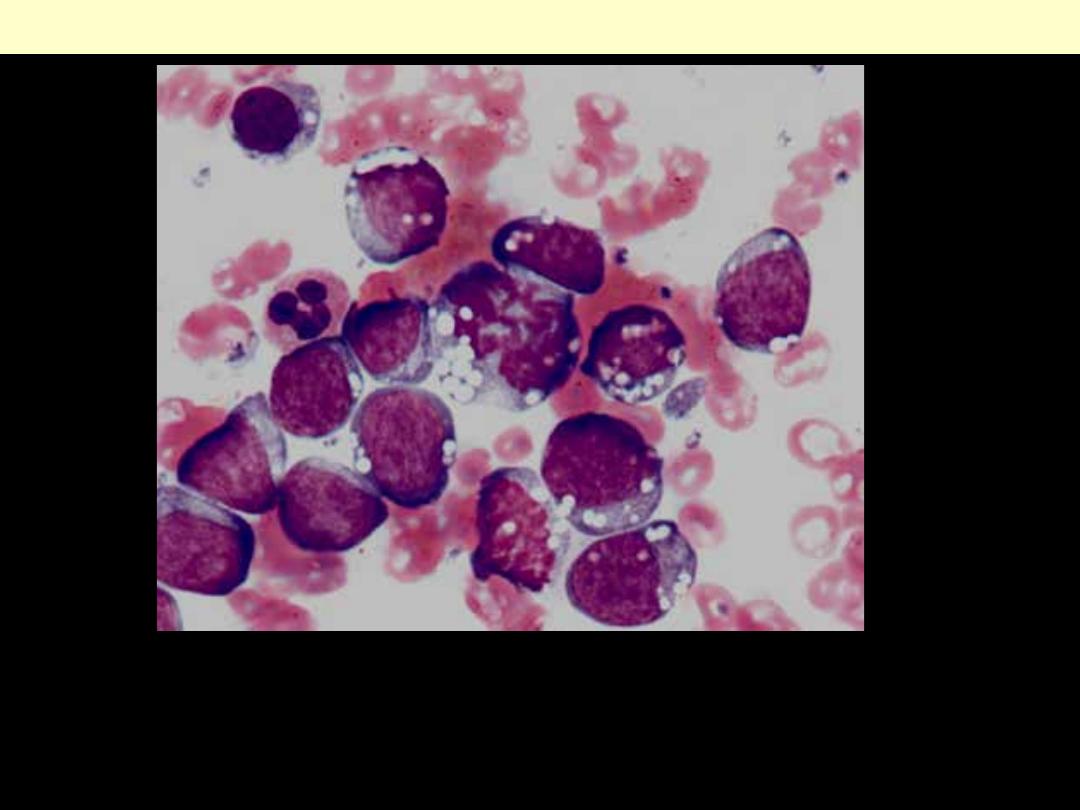
Burkitt lymphoma Bone marrow cytological smear
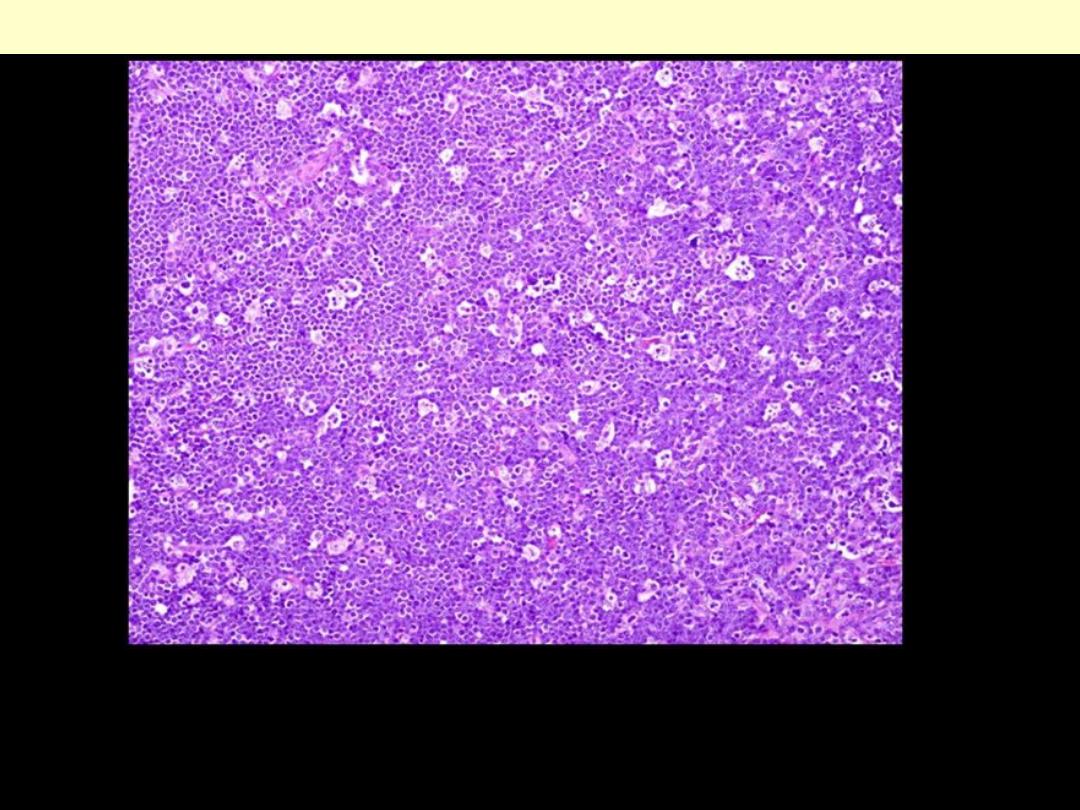
The presence of numerous pale staining reactive macrophages
containing ingested nuclear debris within a blue background (of
lymphoma cells) gives a "starry sky" pattern.
Burkitt lymphoma histological section of the tumor
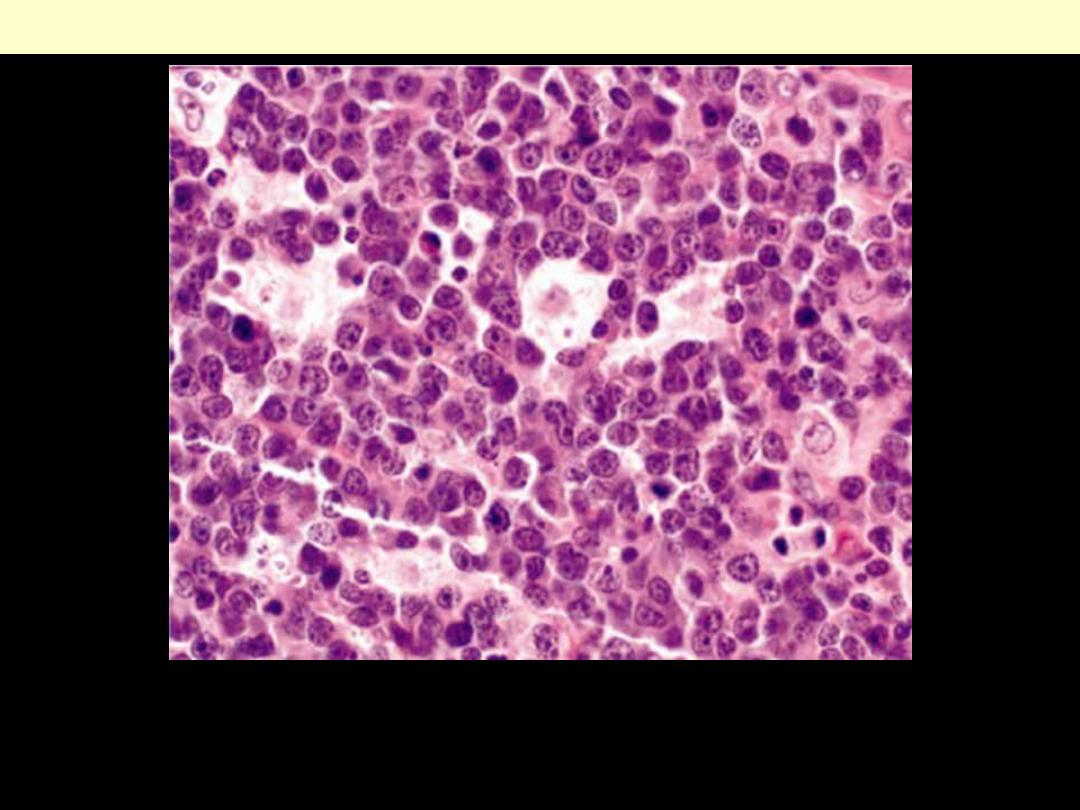
High-grade neoplasm with features of Burkitt lymphoma involving mesenteric
lymph nodes. The tumor infiltrate displays a prominent starry-sky pattern and the
neoplastic cells are of medium size with round nuclei containing several nucleoli.
Burkitt lymphoma histologic section of the tumor (high power)
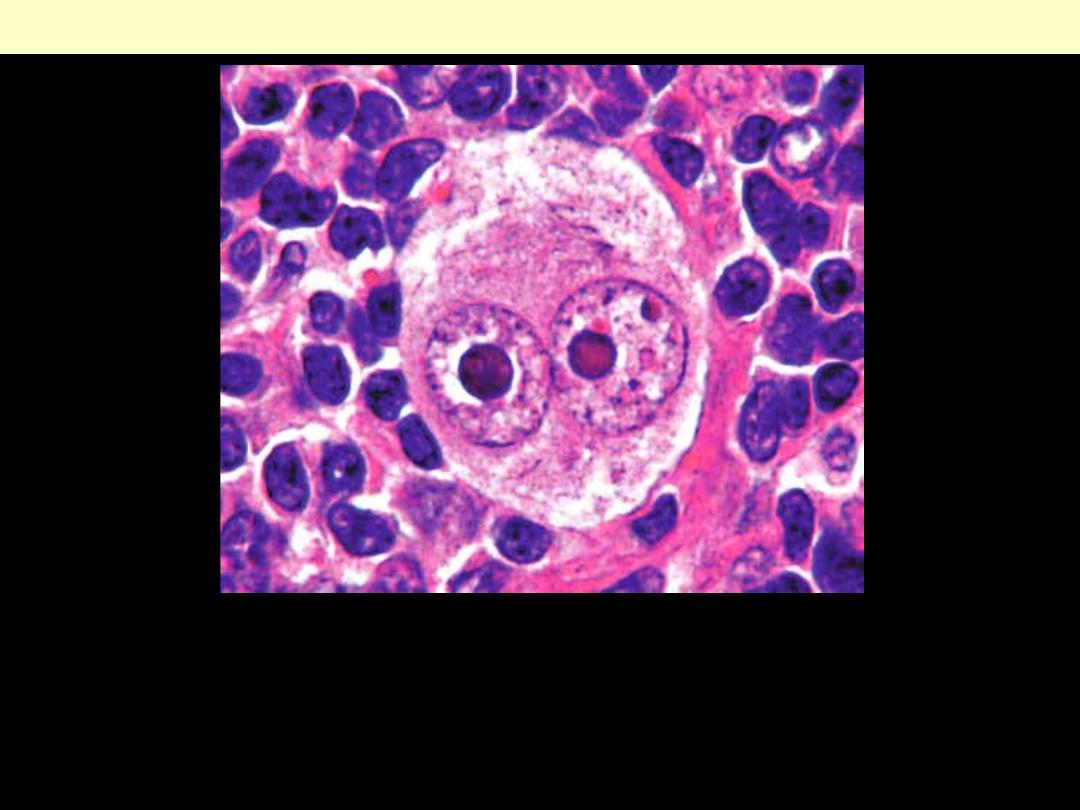
Classical Hodgkin’s Reed-Sternberg (RS) cell
A large cell with two enlarged nuclei having prominent nucleoli,
and abundant, slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm, each with a large
acidophilic nucleolus surrounded by a distinctive clear zone. The
nuclear membrane is thick.
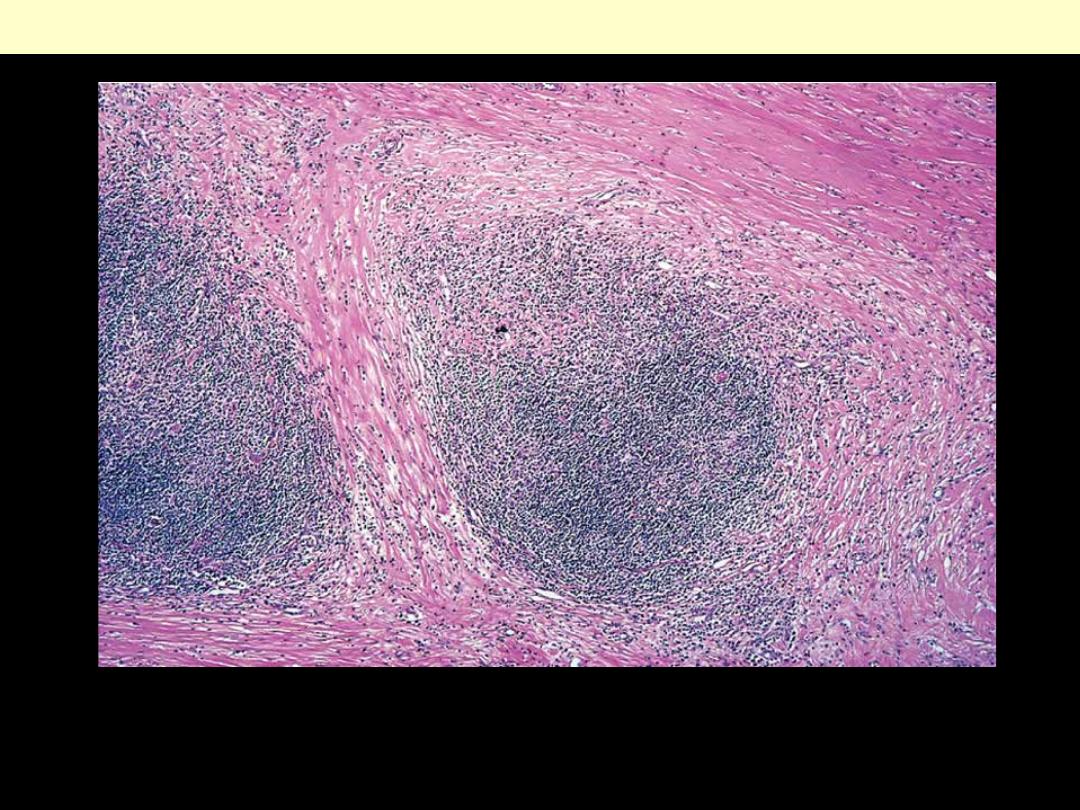
Note the bands of pink collagenous tissue dividing the field.
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma, nodular sclerosis lymph node
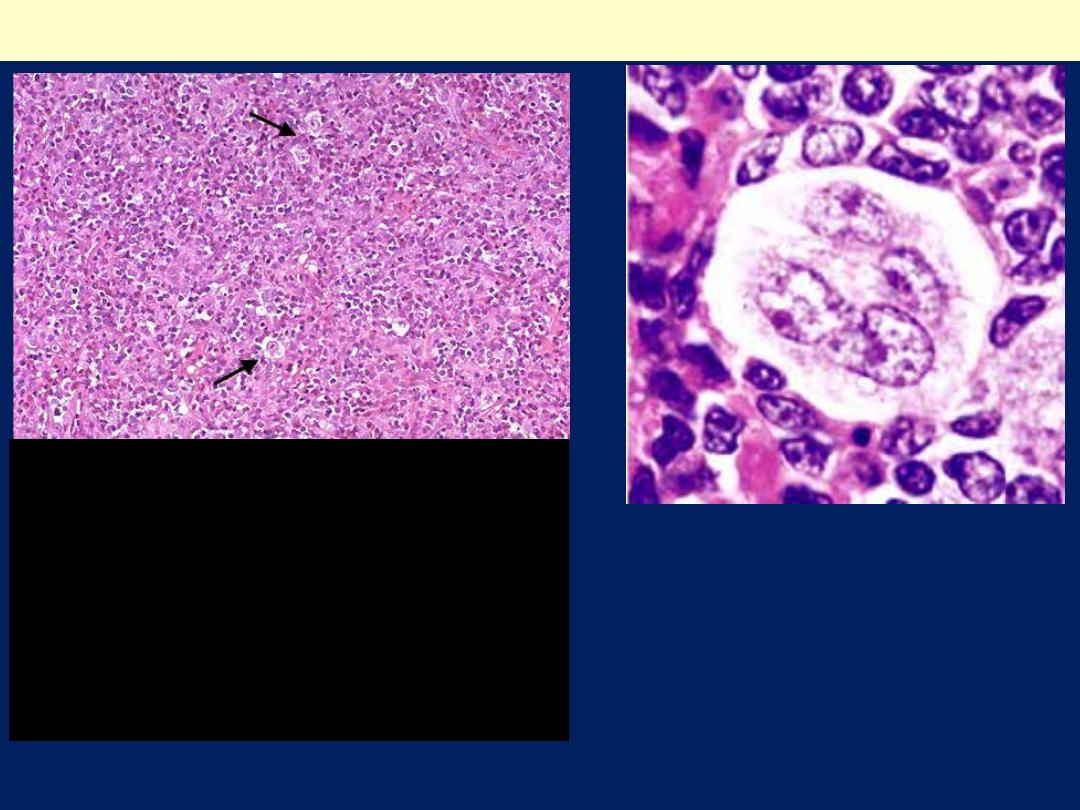
Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: Nodular Sclerosis Subtype
There are scattered large
cells with a surrounding
prominent clear space.
These are the lacunar
cells.
A lacunar cell in nodular
sclerosis HL
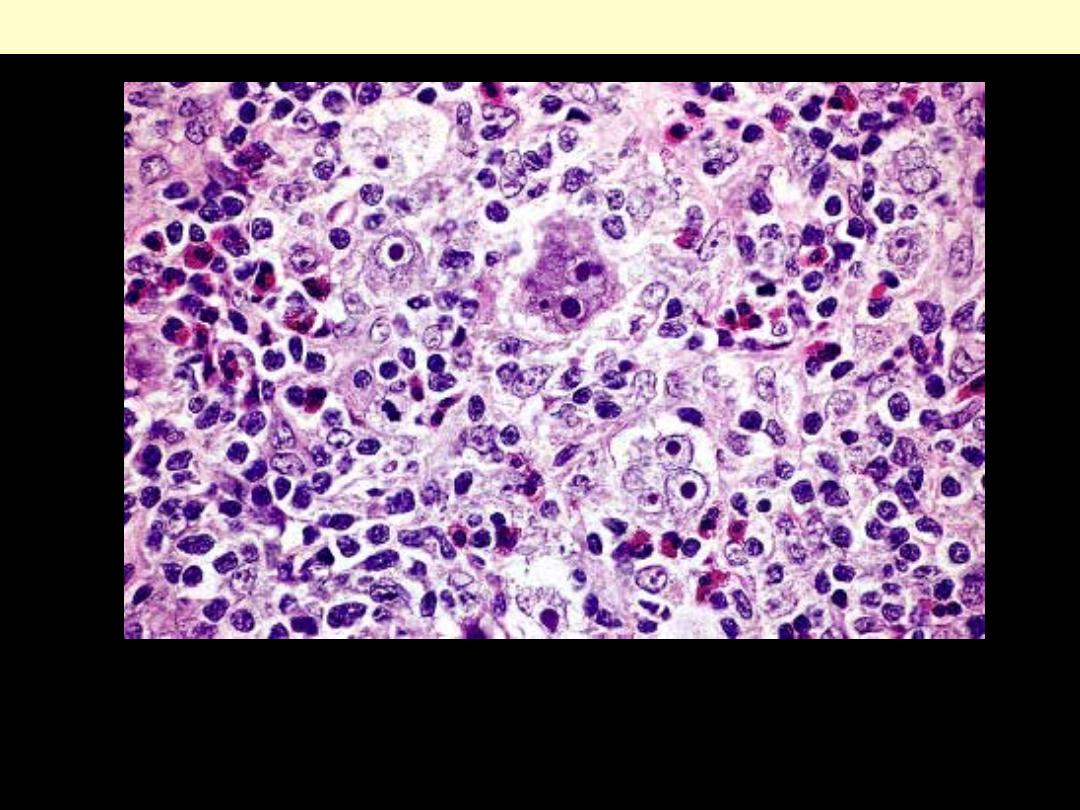
Several diagnostic Reed-Sternberg cells are seen admixed with a
mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate rich in eosinophils.
Mixed cellularity subtype of Classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma
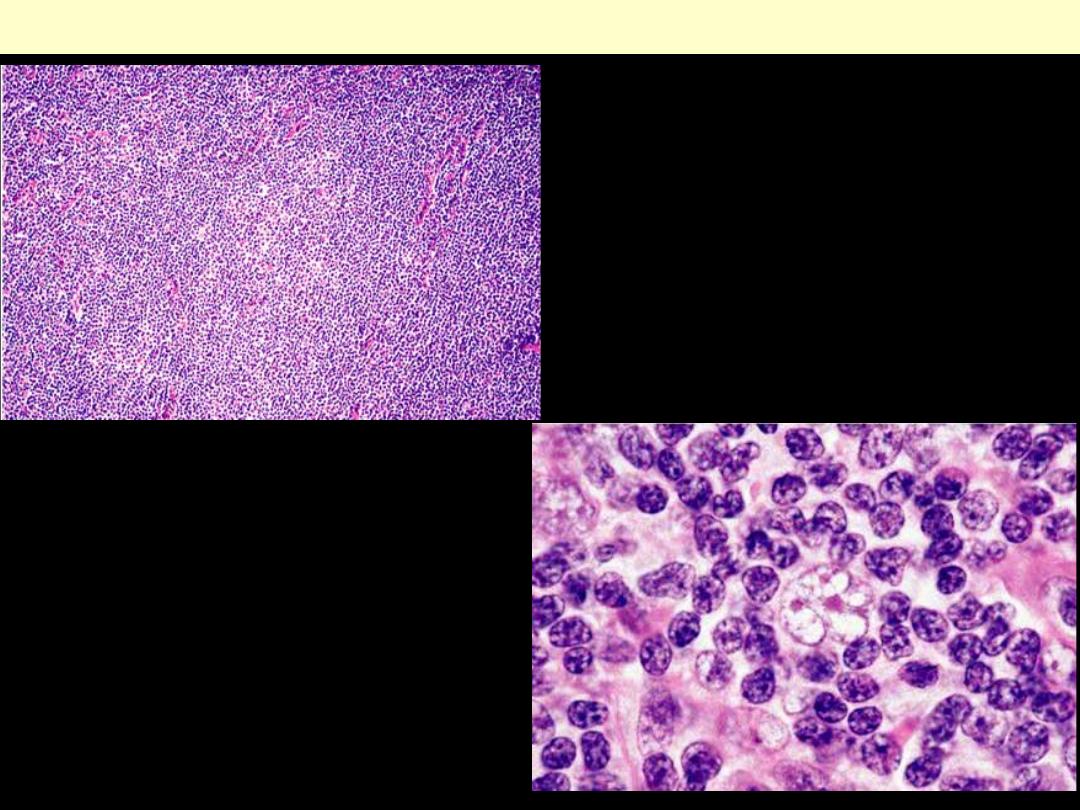
Nodular Lymphocyte
Predominance Hodgkin’s
lymphoma: showing a mottled
appearance of the node.
Hodgkin Disease: Nodular Lymphocyte Predominance-Lymph Node
Nodular Lymphocyte
Predominance Hodgkin’s
lymphoma: showing the
lymphocytic and/or histiocytic
(L&H) type of cell (“popcorn”
cell) that is characteristic of this
condition.
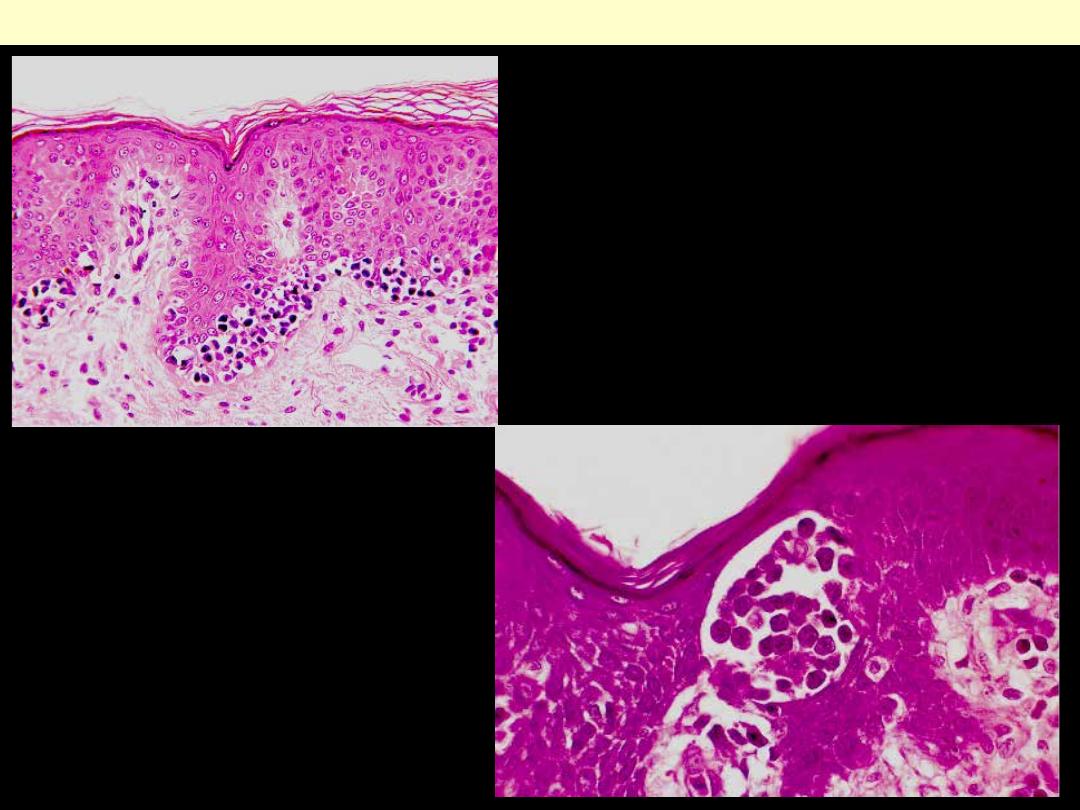
neoplastic lymphoid cells in
mycosis fungoides involving the
epidermis.
So-called Pautrier
microabscess in mycosis
fungoides.
Mycosis fungoides
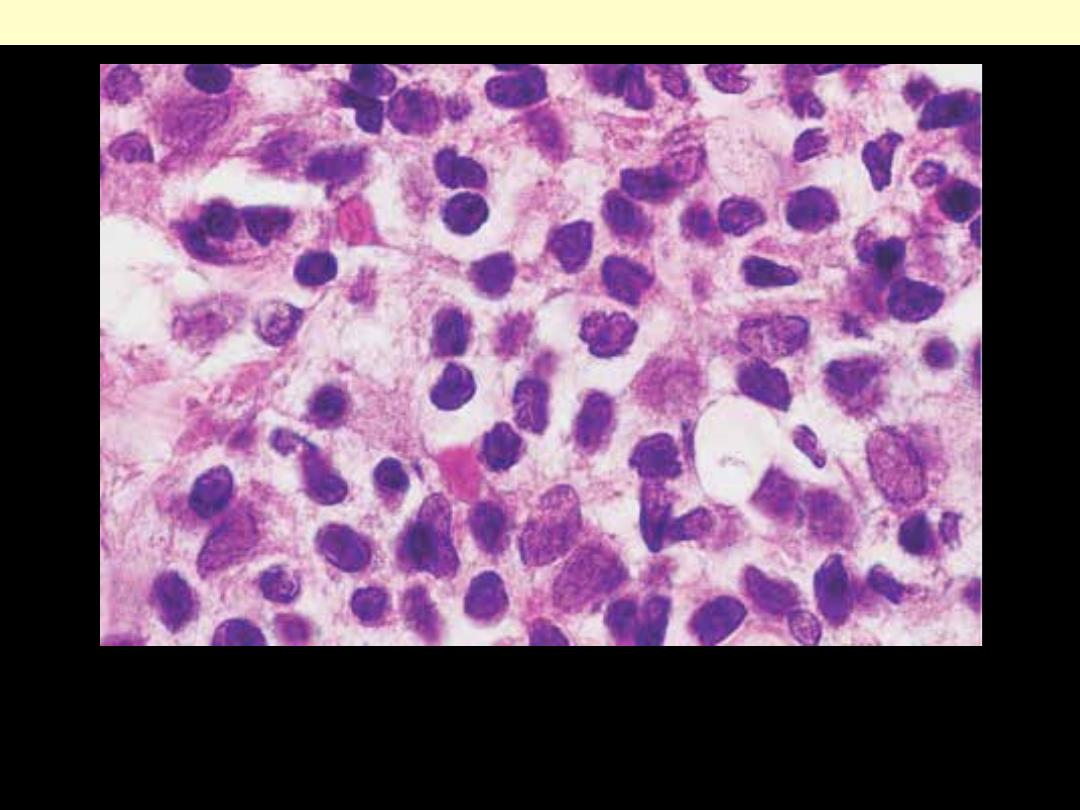
High-power view of mycosis fungoides cell, showing marked
nuclear irregularities.
Mycosis fungoides

Thymoma
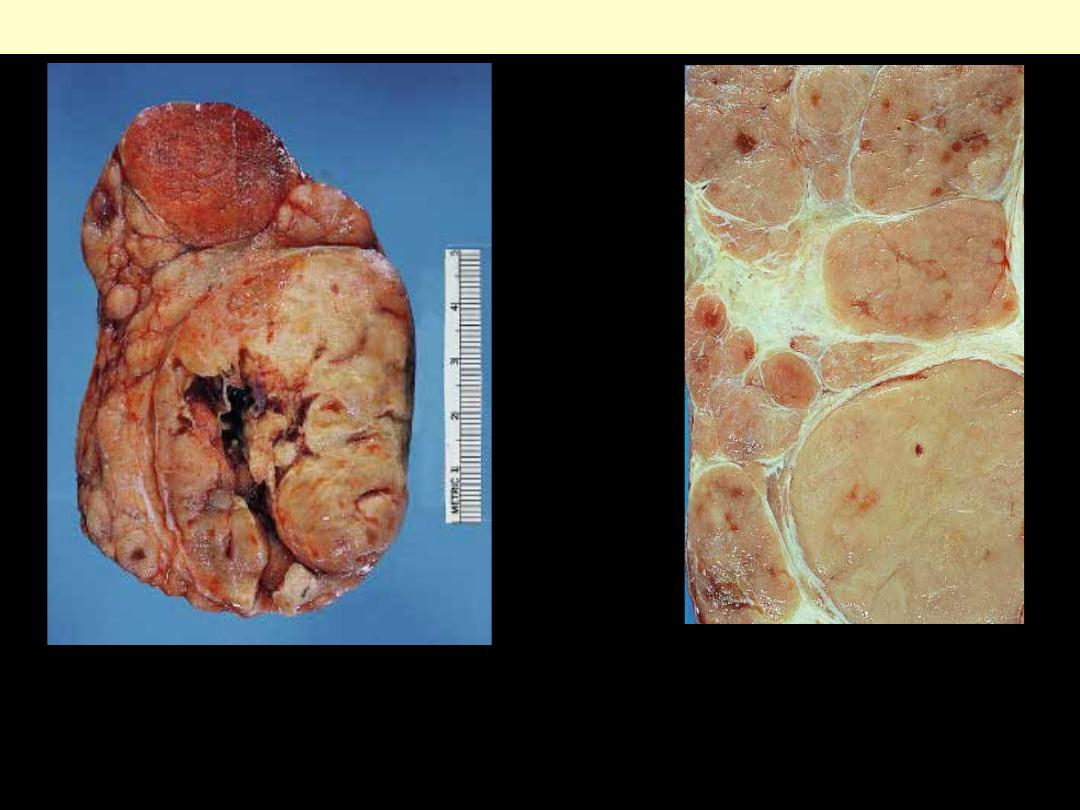
Gross appearance of a thymoma
showing distinct lobulation. There is
focal cystic change in the larger
nodule.
Thymoma
Close-up of the cut surface of thymoma.
Note the sharp lobulation induced by the
fibrous bands. The pointed ends of some of
the nodules are particularly typical of this
entity.
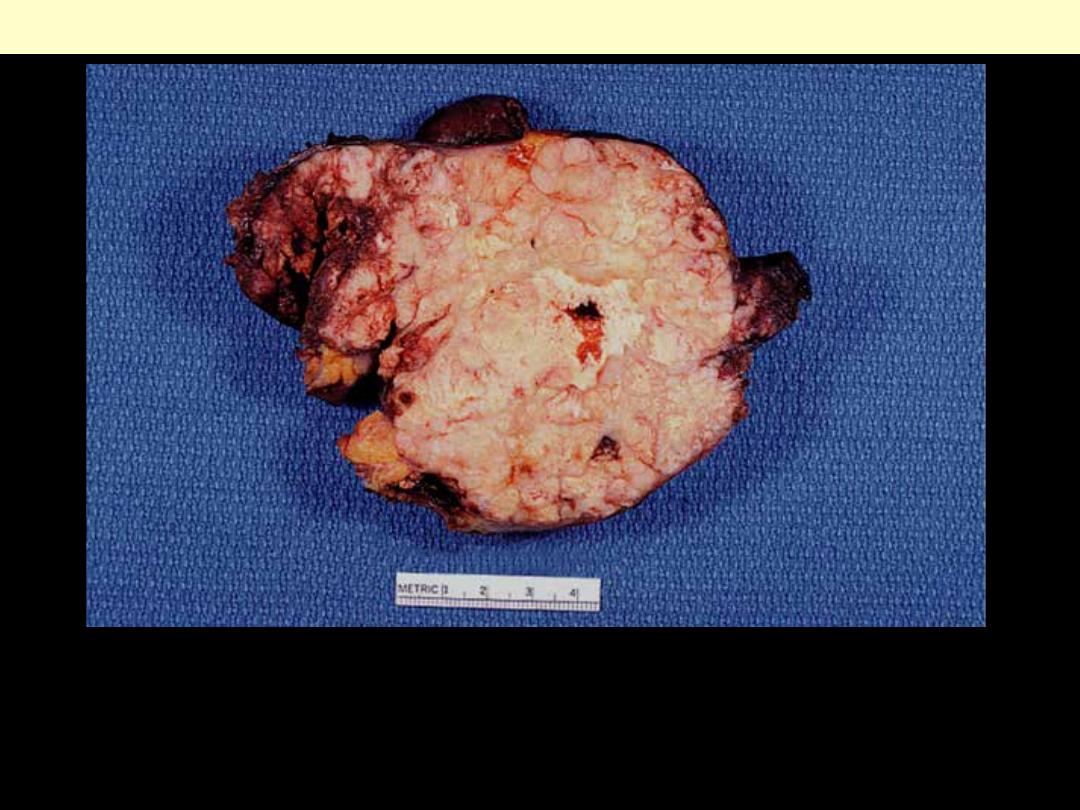
The tumor is invasive and shows foci of yellow necrosis.
Thymic carcinoma invading surrounding tissues
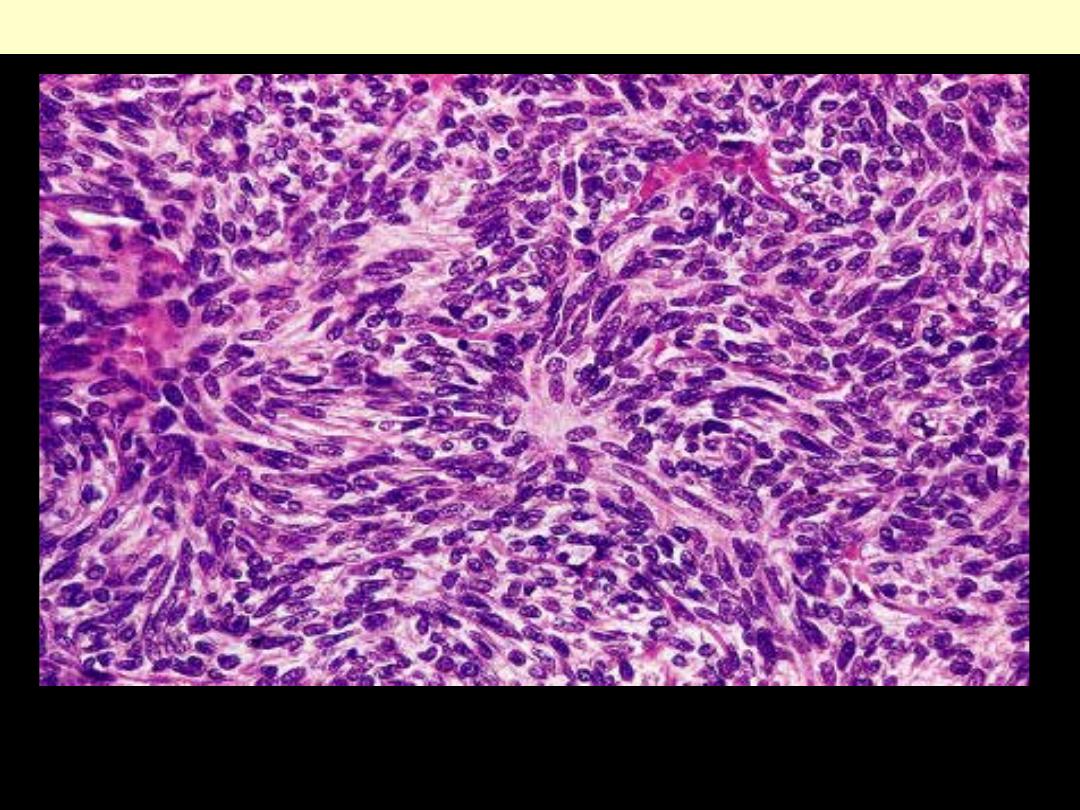
Benign spindle cell (Medullary) thymoma
The tumor shows spindled or elongated epithelial cells that resemble
those normally populate the medulla
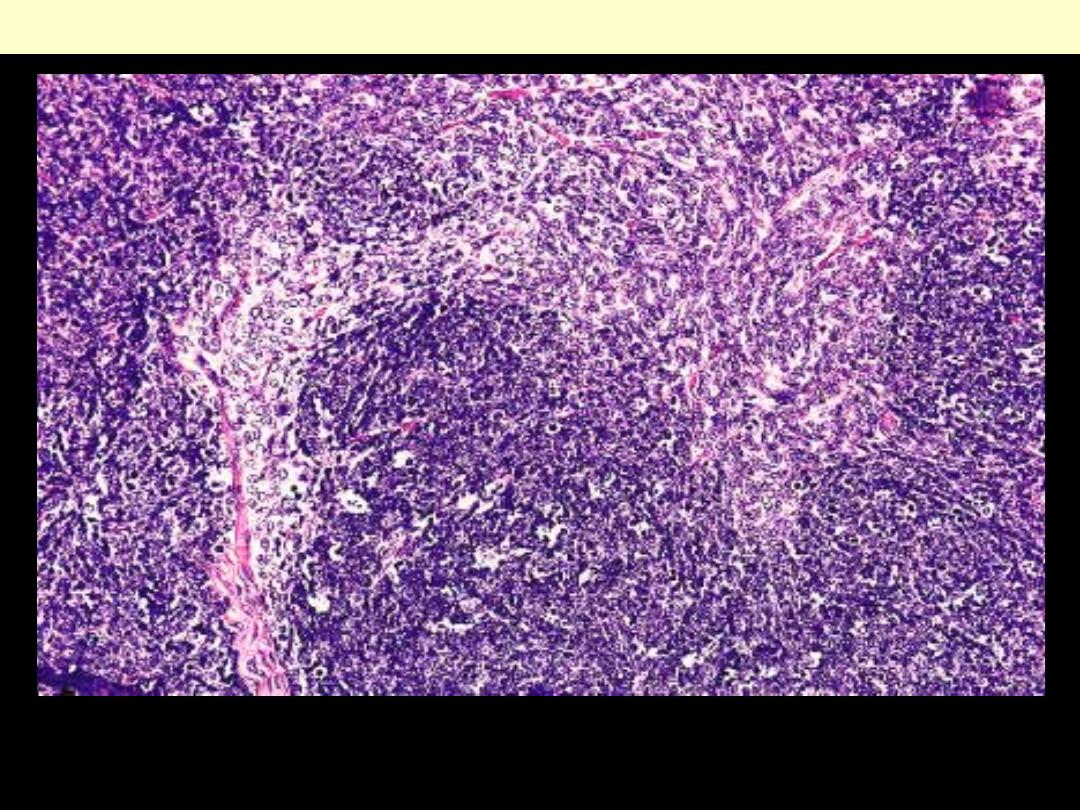
This is one of the most common thymoma subtypes.
Mixed Thymoma (epithelial & spindle cells)
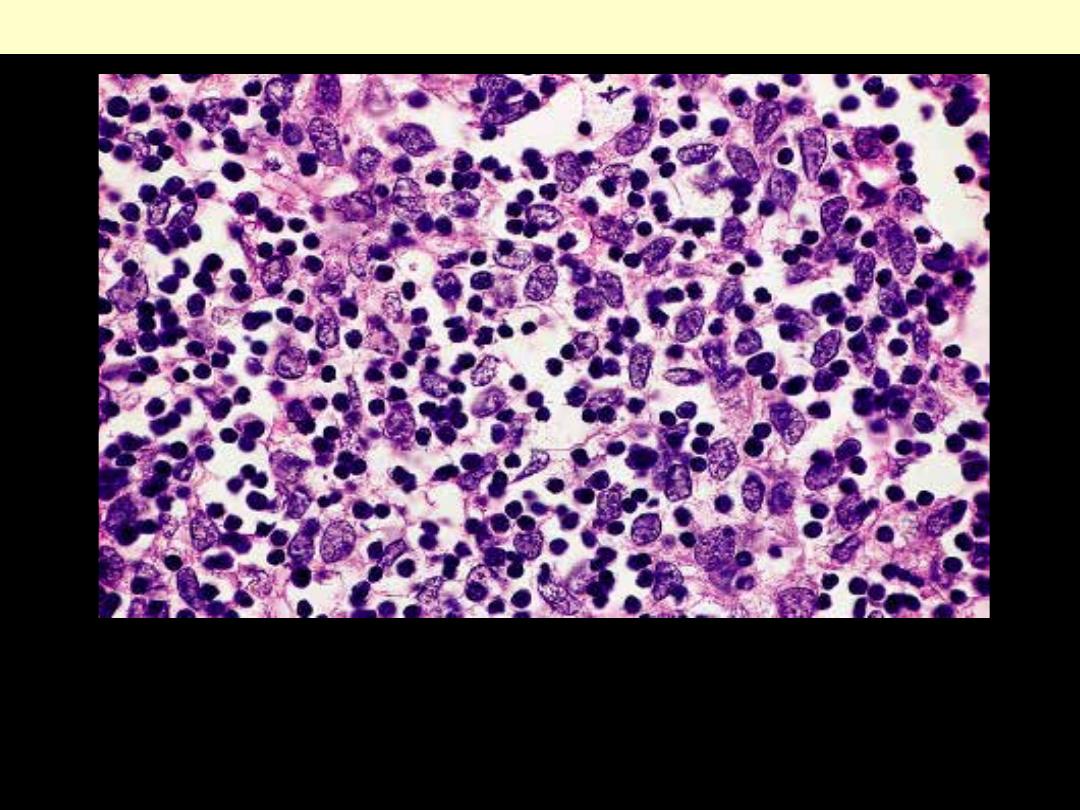
Epithelial thymoma
There is an even proportion of neoplastic epithelial cells and non-
neoplastic lymphocytes.
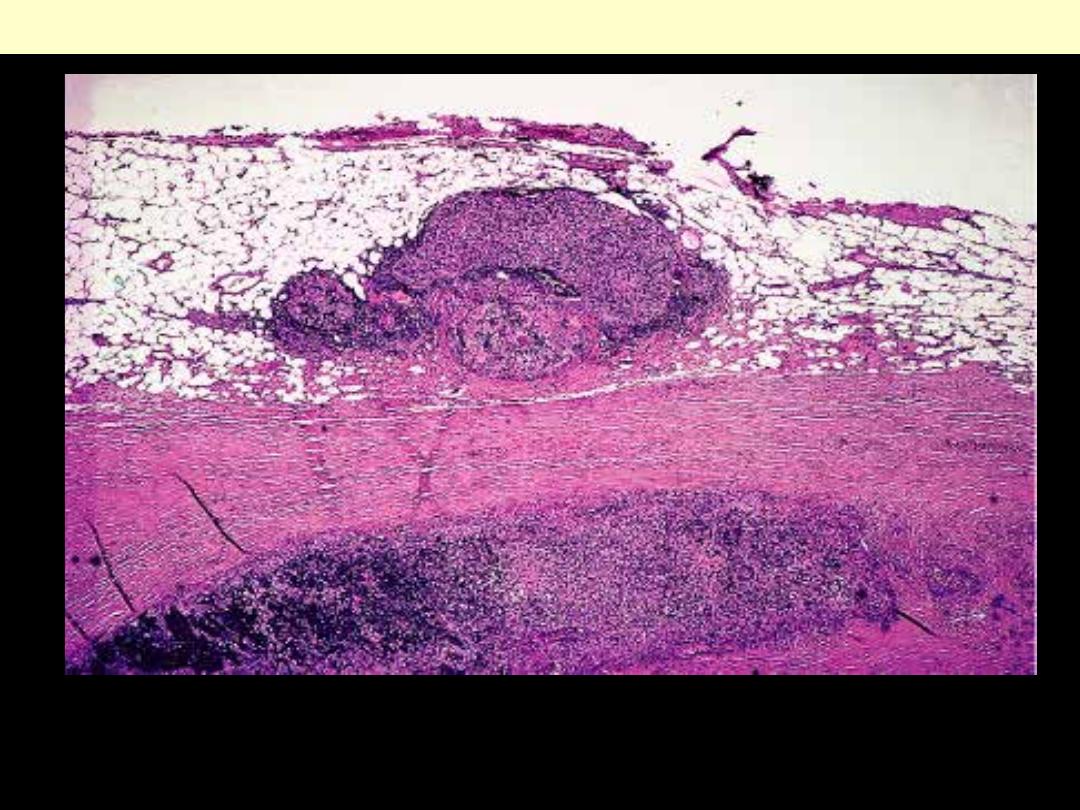
Invasive thymoma
Minimal invasion of the mediastinal fat beyond the thick fibrous
capsule of a thymoma.
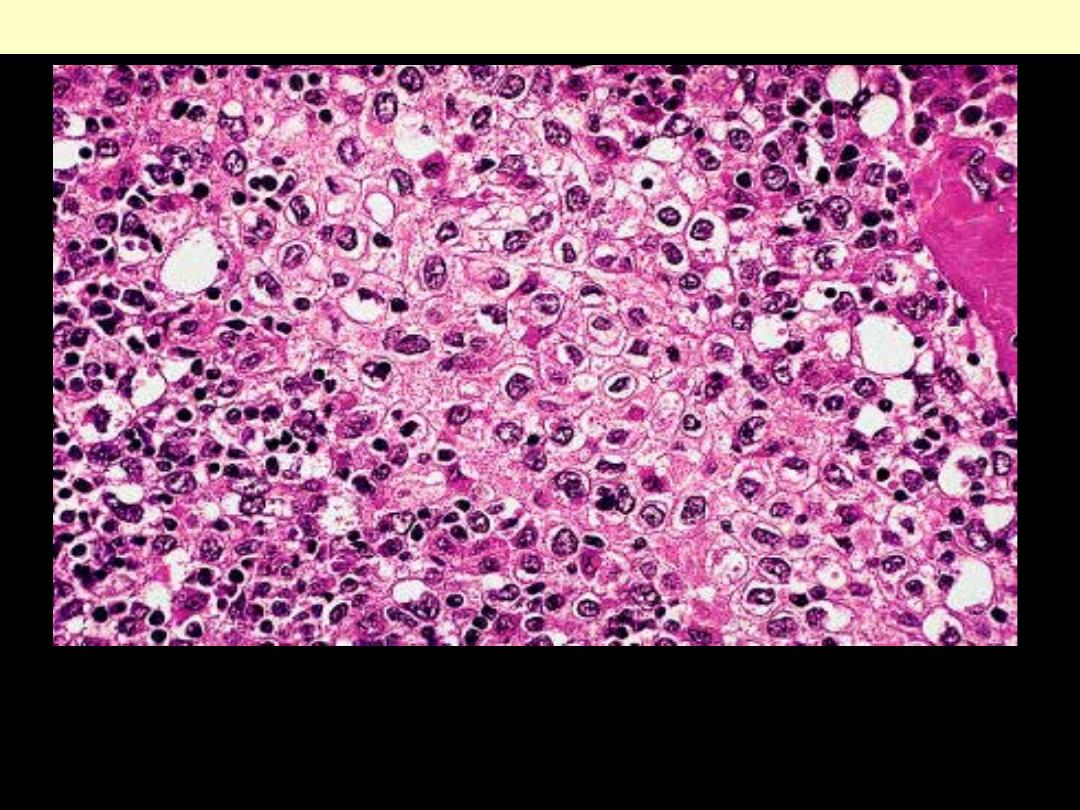
Thymic carcinoma (Squamoid)
This tumor, which is predominantly composed of atypical neoplastic
thymic epithelial cells, is known as well-differentiated thymic
carcinoma. Note the presence lymphocytes.
