ADRENAL GLANDS
• Objectives• At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to:
• Describe the physiology of adrenal hormones secretion.
• Determine the synthesis of adrenal hormones.
• Recognize the functions of the adrenal hormones.
• State the pharmacological actions and therapeutic principles of corticosteroids.
• Identify the side effects of steroid abuse.
• State the importance of steroid tapering after prolonged use.
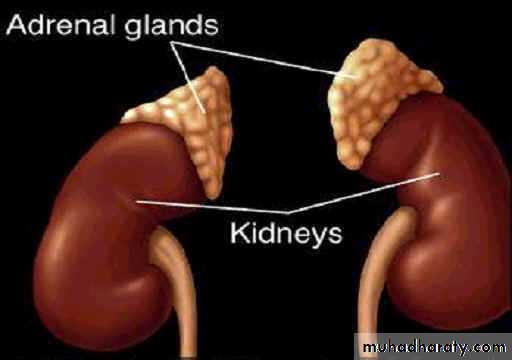
About 5x3 cm in size, combined weight in an adult human ranges from
7 to 10 grams.Anatomy and Function
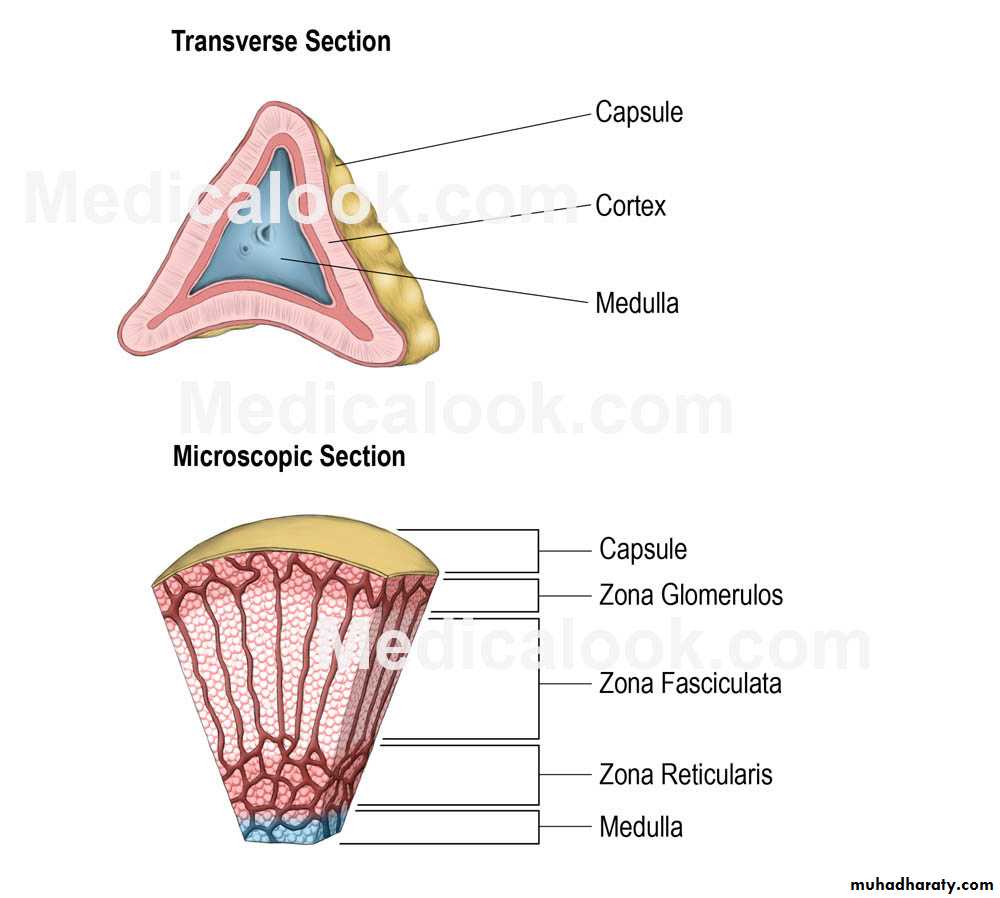
CapsuleCortex (outer) has 3 zones:
1- Zona glomerulosa : mineralocorticoids, mainly aldosterone, responsible for the regulation of BP. It affects the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the kidney
(increased reabsorption of Na + and excretion of
both K + and H + ions).
2- Zona fasciculata: glucocorticoids, such as
11-deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, and
cortisol.
3- Zona reticularis: produces androgens, mainly dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione (the precursor to testosterone) in humans.
Medulla (core of the gland)
It secretes norepinephrine and epinephrine. Catecholamines (aa tyrosine ), water-soluble, the major hormones underlying the fight-or-flight response.Receives input from the sympathetic nervous system through preganglionic fibers originating in the thoracic spinal cord from T5–T11.
Cortisol also promotes epinephrine synthesis.
History
1855 – Addison's disease
1856 – Adrenal glands essential for life
1930 – Cortex > medulla
1932 – Cushing’s syndrome
1949 – Steroids in rheumatoid arthritis
1952 – Aldosterone
• Basal secretions
• Group
• Hormone
• Daily secretions
• Glucocorticoids
• Cortisol
• 5 – 30 mg
• Mineralocorticoids
• Aldosterone
• 5 – 150 mcg
• Sex Hormones
• Androgen
• Progestogen
• Oestrogen
• DHEA
• Progesterone
• Oestradiol
• 15 – 30 mg
• 0.4 – 0.8 mg
• Trace
From Essential of Pharmacotherapeutics, ed. FSK Barar. P.351
Cholesterol
PregnenoloneProgesterone
Corticosterone
11-Desoxy-corticosterone18-Hydroxy- corticosterone
ALDOSTERONE
17-α- Hydroxy pregnenolone
11- Desoxy- cortisol17- Hydroxy progesterone
21,β hydroxylase
CORTISOL
11,β hydroxylaseDehydro-epi androsterone
Andro-stenedione
Oestrone
OestriolTESTOSTERONE
OESTRADIOLACTH
Pharmacological Actions• Carbohydrate
• Protein
• Lipid
• Electrolyte & water
• CVS
• Sk. Muscle
• CNS
• Stomach
• Blood
• Anti-inflammatory
• Immunosuppressant
• Respiratory system
• Growth & Cell Division
• Calcium metabolism
Actions: Carbohydrate and protein metabolism
Gluconeogenesis
- In the liver (synthesis of glucose from aa and glycerol ).
- Mobilization of amino acids from extrahepatic tissues as substrates for gluconeogenesis.
- Stimulation of fat breakdown in adipose tissue: The fatty acids released by lipolysis are used for production of energy and the released glycerol provide another substrate for gluconeogenesis.
Peripheral utilization of glucose
- Inhibition of glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue
Glycogen deposition in liver
(activation of hepatic glycogen synthase)Negative nitrogen balance & hyperglycemia
Redistribution of FatBuffalo hump
Supraclavicular fat
Moon face
Promote adipokinetic agents activity
(glucagon, growth hormone, adrenaline, andthyroxin)
Actions: Lipid metabolism
Aldosterone is more important, acts on D.T. & C.D. of kidney
Na+ reabsorption
Urinary excretion of K+ and H+
Glucocorticoids assist in the normalization of extracellular fluid volume by regulating body’s action to atrial natriureteric peptide.
Cortisol reduces the capacity of osteoblasts to produce new bone tissue and decreases the absorption of calcium in the GIT.
Actions: Electrolyte and water balance
Restrict capillary permeability
Maintain tone of arteriolesMyocardial contractility
Actions: Cardiovascular system
Mineralocorticoids induced hypertension
Na+ sensitize blood vessels to the action of
catecholamines & angiotensin
Addison's disease: weakness & fatigue is due to
Prolonged use:Actions: Skeletal Muscles
Needed for maintaining the normal function of Sk. muscleinadequacy of circulatory system
Steroid myopathy, weakness, reduced muscle mass and
repair
Direct:
Mood (euphoria)
Behavior, psychosis
Brain excitability
Significant impact on vigilance (attention deficit disorder) and cognition (memory).
Actions: CNS
ICP (pseudotumor cerebri)Aggravate peptic ulcer. May be due to
Acid & pepsin secretionimmune response to H.Pylori
Actions: StomachRBC: Hb & RBC content
(erythrophagocytosis )WBC: Lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes,
basophilsActions: Blood
Recruitment of WBC & monocyte- macrophageinto affected area & elaboration of chemotactic
substances
Lipocortin
TNF from phagocytic cells
IL1 from monocyte-macrophage
Formation of Plasminogen Activator
Fibroblastic activity
Expression of cyclooxygenase II
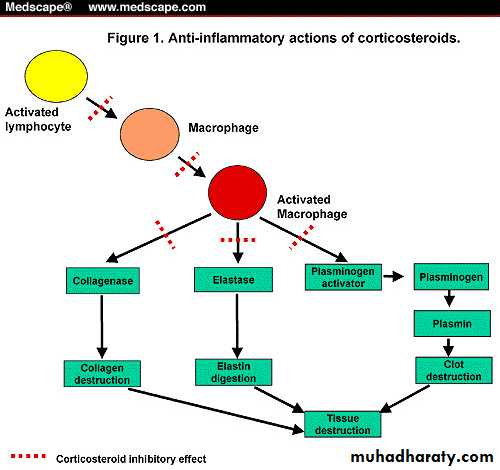
Actions: Anti-inflammatory
PhospholipidsArachidonic acids
lipoxygenase
Cycylooxygenase
Leukotriene
Prostaglandins,
Thromboxane
Prostacyclins
Suppress Phospholipase A2
Lipocortin- 1
Corticosteroids
PAF by lipocortin
Anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids
Corticosteroid inhibitory effectImmunosuppressive & anti-allergic actions
Suppresses all types of hypersensitivity & allergic phenomenon.At High dose: Interfere with all steps of immunological response.
Causes greater suppression of CMI (graft rejection & delayed hypersensitivity).
Transplant rejection: antigen expression from grafted tissues, delay revascularization, sensitization of T lymphocytes.
Main pathogens of concern in glucocorticoid-induced immunodeficiency:
Legionella micdadei, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Nocardiaasteroides, Salmonella species, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococci
Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Candida albicans and nonalbicans species, Coccidioides
immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans , Histoplasma capsulatum. Penicillium marneffei,
Pseudallescheria boydii, Zygomycosis
Adenovirus, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus, Human papillomavirus,
Influenza/parainfluenza, Respiratory syncytial virus, Varicella zosterOther
Cryptosporidiosis/lsospora belliPneumocystis carinii
Strongyloides stercoralis
Toxoplasma gondii
Inhibit cell division or synthesis of DNA.
Delay the process of healing.Retard the growth of children.
Delay puberty
Actions: Growth & Cell division
Intestinal absorptionRenal excretion
Excessive loss of calcium from spongy bones (e.g., vertebrae, ribs )
Actions: Calcium metabolismNot bronchodilators
Most potent and most effective anti-inflammatory.Effects not seen immediately (delay 6 or more hrs).
Inhaled corticosteroids are used for long term control.