
Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
Lec. 4
SAS
Tues. 22 / 12 / 2015
Done By: Ibraheem Kais
2015 – 2016
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺁ
ﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ
SAS Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
22-12-2015
1
Sleep – Disordered Breathing
Sleep Apnea Syndrome (SAS)/ Obstructive Sleep
Apnea (OSA)
Sleep – disordered breathing
It is a variety of respiratory disorders manifest themselves during Sleep, for
example: nocturnal cough & wheezes (clinical features of Asthma) & hypoventilation
(that occurs in normal sleep can exacerbate Respiratory Failure in patients with
Restrictive Lung Diseases like: kyphoscoilosis, diaphragmatic palsy, & muscle
weakness, or in patients with Intrinsic Lung Diseases like: COPD & pulmonary
fibrosis).
In contrast, a small but important group of disorders can cause problems only
during sleep.
Sleep Apnea Syndrome (SAS)
There is a recurrent upper airways obstruction during sleep, & the mild form of
this syndrome is the “Snoring”.
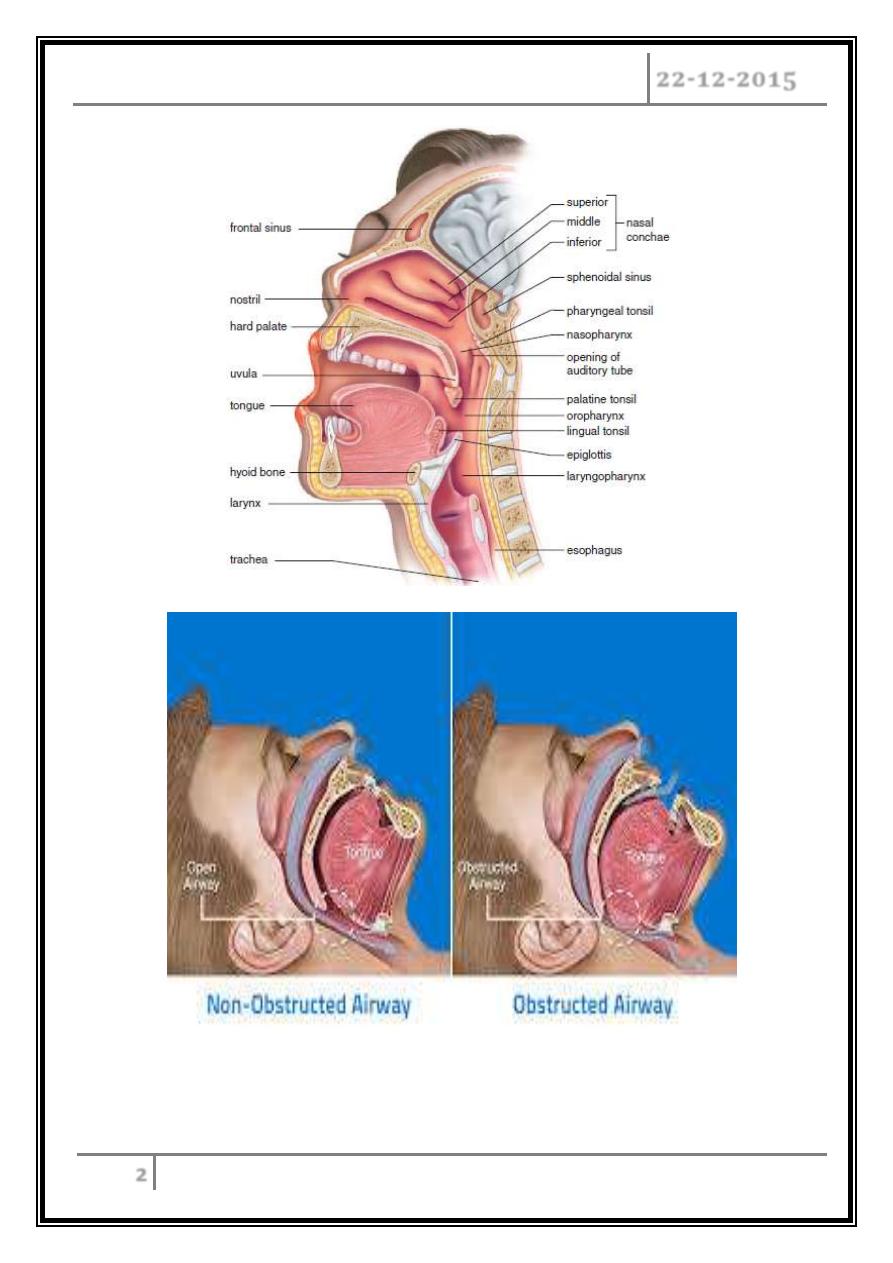
As we know, the “Throat” is the upper airway opening, if we take a deep breath, a
negative pressure will be created, & since there is soft tissues in the throat, it tends to
collapse because of this negative pressure; but because of the presence of the upper
airways dilating muscles (which are: Palatoglossus & Genioglossus), they tend to
tense themselves & so keeping the throat opened.
SAS Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
22-12-2015
2
SAS Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
22-12-2015
3
So, if there is a slight narrowing of this opening, snoring will develops (snoring is
present in 40% of males & 20% of females), & if the narrowing is so severe, occlusion
or near occlusion of the upper airways opening will occur, no air will get in, & this
will stimulate the respiratory center due to hypoxia & hypercapnia, & this will send a
signal to the respiratory muscles to perform more work, this will awake the patient,
then the patient sleeps, leading to “Apnea”, & again awake the patient. This condition
is repeated many times during sleep, so the patient will not get enough sleep, with the
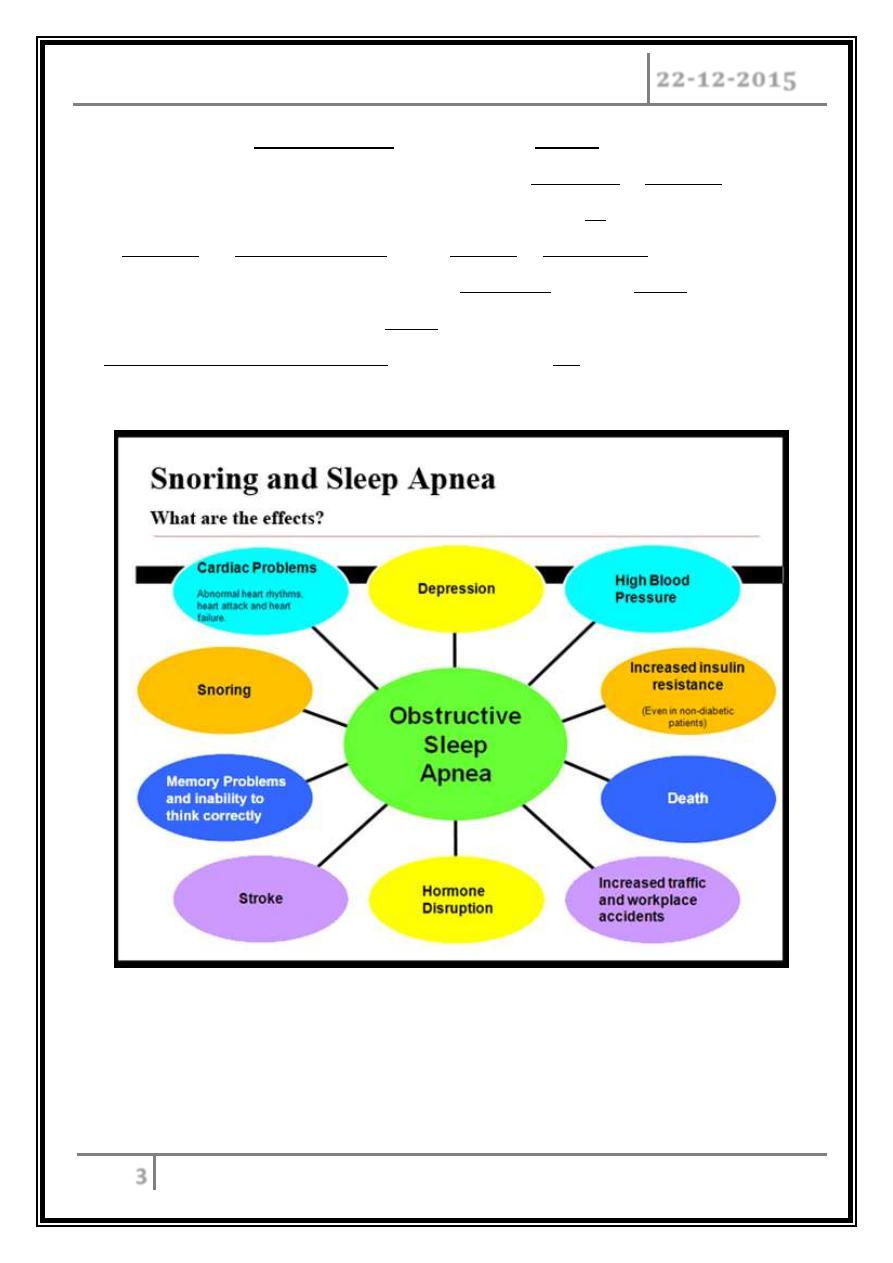
tendency to develop HTN, IHD, & stroke.

SAS Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
22-12-2015
4
Causes
Familial causes (especially in males).
Obesity*, because of more fatty tissue causing smaller opening of the
upper airways.
Patients with acromegaly.
Patients with hypothyroidism.
Alcoholic patients.
Patients taking sedative drugs.
Clinical Features
Excessive day-time sleepiness is the principle symptom.
Snoring is virtually universal.
The patient usually feels that he/she has been asleep at night but wakes un-
refreshed.
Lack of concentration*.
He will have impaired cognitive function &
work performance.
Also, he will have Depression, Irritability, & Nocturia.
*Obesity,
is one of the important predisposing factors for this syndrome,
& the tendency of obesity is increased nowadays in the community, & in a
report (from another country) that about
(2 – 4 %) of the population are having
SAS
.
* So, those patients are largely involved in
Road Traffic Accidents
.
SAS Dr. Adnan M. Al- Jubouri
22-12-2015
5
Differential Diagnosis
We should exclude some conditions by a careful history.
Narcolepsy is rare cause of sleepiness, & it is account for only 0.05%.
There is other associated illnesses like: Cataplexy*, Hypnagogic Hallucination
(occurs at sleep onset), & Sleep Paralysis.
Also, Idiopathic Hyper-somnolence which occurs in young individuals & it is
characterized by long nocturnal sleep.
Treatment
It is usually directed to the cause:
Obesity, reduce the weight.
Treat acromegaly & hypothyroidism.
Stop alcohol & sedative drugs intake.
But, the proper treatment is by using a Specific Nasal Mask that keeps a
continuous positive pressure in the throat, so no negative pressure will cause no more
collapse & sleep becomes normal.
... End …
*Cataplexy
: happens when the muscle tone is lost in a very
conscious person in response to emotional triggers
& they may flap over.
