Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
1
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
OBESTITRICS
Aim of Prenatal Diagnosis
The aim of prenatal diagnosis relate to the identification of fetal
abnormality in order to:
*Reassure parents by reducing the likelihood of undiagnosed fetal
abnormality.
*Assist parents in decision making if by maximizing information
about the underlying diagnosed fetal abnormality.
*Allow parents of affected pregnancies to prepare to birth of an
affected child.
*Allow appropriate perinatal management and intrauterine
treatment.
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests:
* Screening tests :- are tests performed on all women in order to
identify a subset of pt who are at high risk for a disorder.
* Diagnostic tests:- are tests carried out on pregnancies that
have been identified as
high risk by prior screening test they are usually invasive &
carry a risk for miscarriage.
Invasive diagnostic tests are
# Amniocentesis.
# Chorionic Villous Sampling CVS.
# Cordocentesis.
Non invasive test as USS
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
2
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Screening tests
Diagnostic tests
1) population
tested.
All women
Women at high
risk
2) purpose of
the test.
To select a high-
risk group
To diagnose
abnormality
3) usual method
of testing
-Maternal history
-USS
-Maternal biochem.
-Maternal virology
-USS
-Amniocentesis.
-CVS.
-Cordocentesis
4) pre requisite
to test
Diagnostic test
available
Patient aware of
potential risks
5) risk of test.
Anxiety of a
screen positive
result
Small risk of
miscarriage from
invasive test
Diagnosis of Structural Abnormalities
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
NTDs are among the most common major abnormalities.
they occur due to defects in the formation of the neural tube
during embryogenesis.
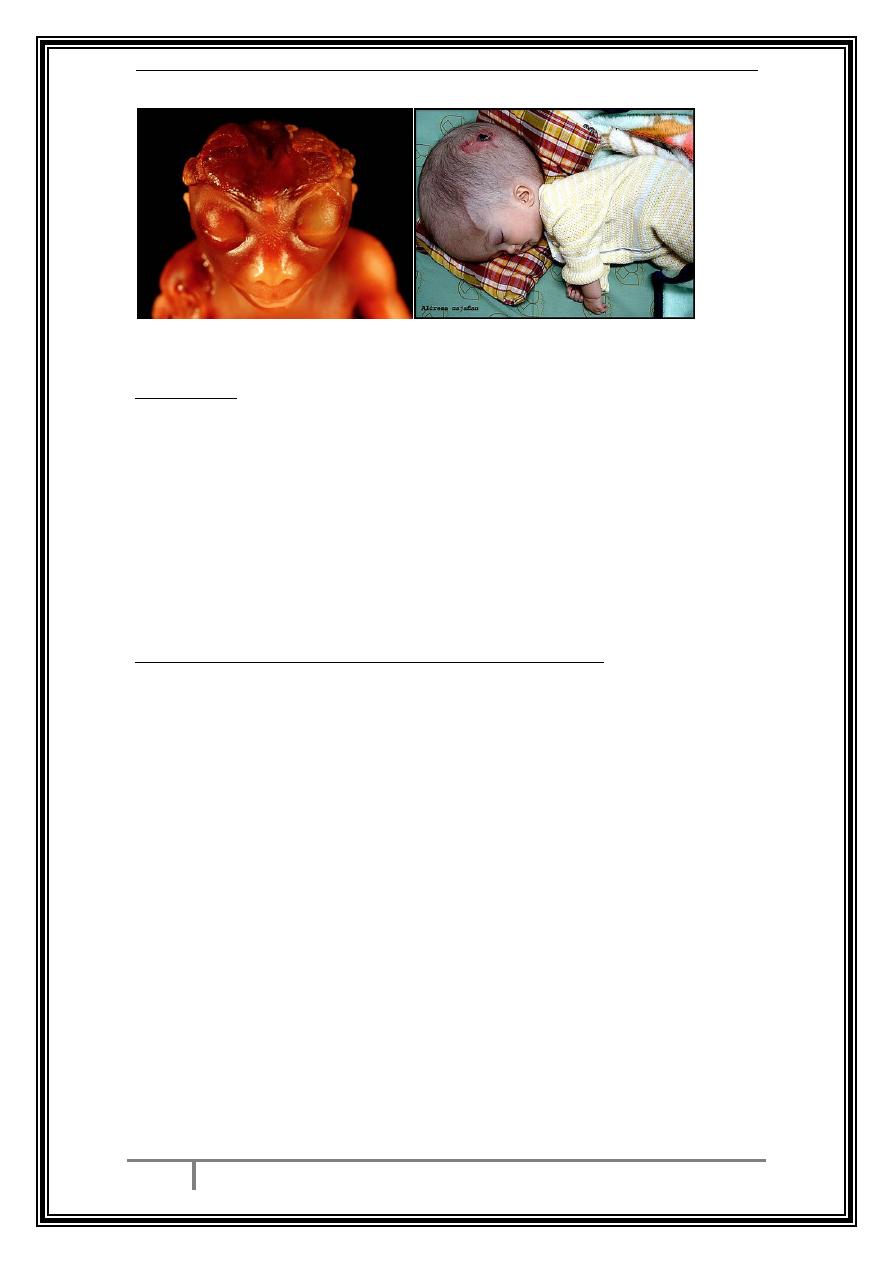
These either affect the cranial vault present in ultrasound as
anencephaly (which is universally lethal) or encephalocele (its
prognosis is related to the size of defect) or hydrocephaly.
or affecting the spinal cord the caudal end which is termed as
spina bifida (the local effects of spina bifida like paralysis of the
legs, urinary and fecal incontinence depends on the spinal level
and the number of spinal segments affected).
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
3
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Etiology :
multi-factorial, with well-defined
environmental
Genetic
pharmacological
geographic factors.
Prenatal screening and diagnosis of NTDs :
when a parent or a previous sibling has had NTD, the risk of
recurrence is 5-10%.
* Mid trimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels
are increased in pregnancies affected by open NTDs. These
were once used as the established screening tests for NTDs,
with screen-positive women being referred for amniocentesis.
The presence of acetylcholinesterase (a CNS neurotransmitter)
in amniotic fluid was taken as diagnostic for open NTD.
*The need for a two-step screening/diagnosis process was
quickly superseded by the development of high resolution u/s.
Anencephaly and encephaloceles are detectable on first
trimester u/s. spina bifida can be detected at a routine 20-week
anomaly scan. The diagnosis may be suspected from the
visualization of the 'lemon"(shape of skull) and
"banana"(absent cerebellum) signs in the fetal brain at this
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
4
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
examination. The sensitivity of u/s for both open and closed
NTDs is greater than 95%.
*Other CNS abnormalities such as hydrocephalus can also be
detected at the 20-week scan.
Prevention :
Folate deficiency and drugs that interfere with folate
metabolism (like anti-epileptics) are implicated in about 10%
of NTDs.
Periconceptual folate supplementation of the maternal diet
reduces the risk of developing these defects by about half.
Folic acid should be given for at least 3 months prior to
conception and for the first trimester of pregnancy.
The dose of folic acid is 400mcg for primary prevention and 4-
5 mg for prevention of recurrence of a NTD or for those of high
risk like type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
These are also common congenital abnormalities.
Etiology:
genetic factors, environmental factors and viral infections could
be implicated. Gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities
account for less than 5% of cases.
Prenatal diagnosis of CHDs: A 4 chamber view at 20-week
anomaly scan is indicated in high risk patients (like those with
previous CHD, diabetes mellitus); provides information about
the position and size of the fetal heart, the cardiac chambers,
and the atrio-ventricular connection.
CHDs associated with abnormal 4-chamber view include
hypoplastic left heart, hypoplastic right heart, atrio-ventricular
canal defects, large atrial and ventricular septal defects, and
others. Although 90% of such anomalies can be detected in a
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
5
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
specialist centers, unfortunately only 30% can be detected at
routine 20-week anomaly scan
Gastrointestinal Abnormalities :
Bowel obstruction above ileum like duodenal and esophageal
atresia, usually results in polyhydramnios and easily visualized
with u/s.
Doudenal atresia is characteristically associated with a
"double bubble' appearance on u/s. One third of cases will be
associated with Down's syndrome, and karyotyping should be
considered.
Abdominal wall defects: 50% of omphaloceles (due to midline
abdominal wall defect through which peritoneal sac herniates)
have associated cardiac or chromosomal abnormalities.
Renal Tract Abnormalities :
Major abnormalities of the renal tract such as renal agenesis will
normally be detected by 20-weeks because of the associated
oligohydramnios.
Diagnosis of Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities
**** aneuploidies
**** sex chromosomal abnormality
** Down syndrome:- the commonest chromosomal abn at birth
characterized by IU lethalityof 40%at 12-40 wk , with MR,
defness,short sightedness, flat facies , macroglossia, cardiac septal
defect, intestinal atresia ,premature ageing reduced immunity,
leukemia, reduced life span

Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
6
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Screening tests for down syndrome:-
1
) maternal Hx:the prevalence of Down syndrome increase with
advancing maternal age, therefore women above 35y are routinely
screened, & women with previous Hx of Down baby.
2) maternal serum biochemistry : by estimating the maternal serum
level of alpha-feto protien (decreased) ,hCG (increased) & estriol at
15-22 week (triple test).when we add S.inhibin to them then called
quadriple test.
3) nuchal translucency :By sonographic measurement of the
translucent space on the neck of the fetus at 10-13 week gestation
this NT is increased in majority of aneuoploidy, sensitivity of this test
is 75-80% .
4) second trimester USS : identify the soft tissue marker as Echogenic
intracardiac focus ,Echogenic bowel,Mild renal pelvis dilatation
,Widened gap between first and second toes ,Clinodactyly,
hypoplastic mid-phalanx of fifth digit ,Single transverse palmer
crease, Short femur ,Short humerus
Diagnostic tests by amniocentesis & CVS.
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
7
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Invasive Diagnostic Tests :
A number of different tests exist to sample material of fetal origin.
The sample obtained can be used for
cytogenetic
biochemical
enzymatic
DNA analysis
to give a prenatal diagnosis.
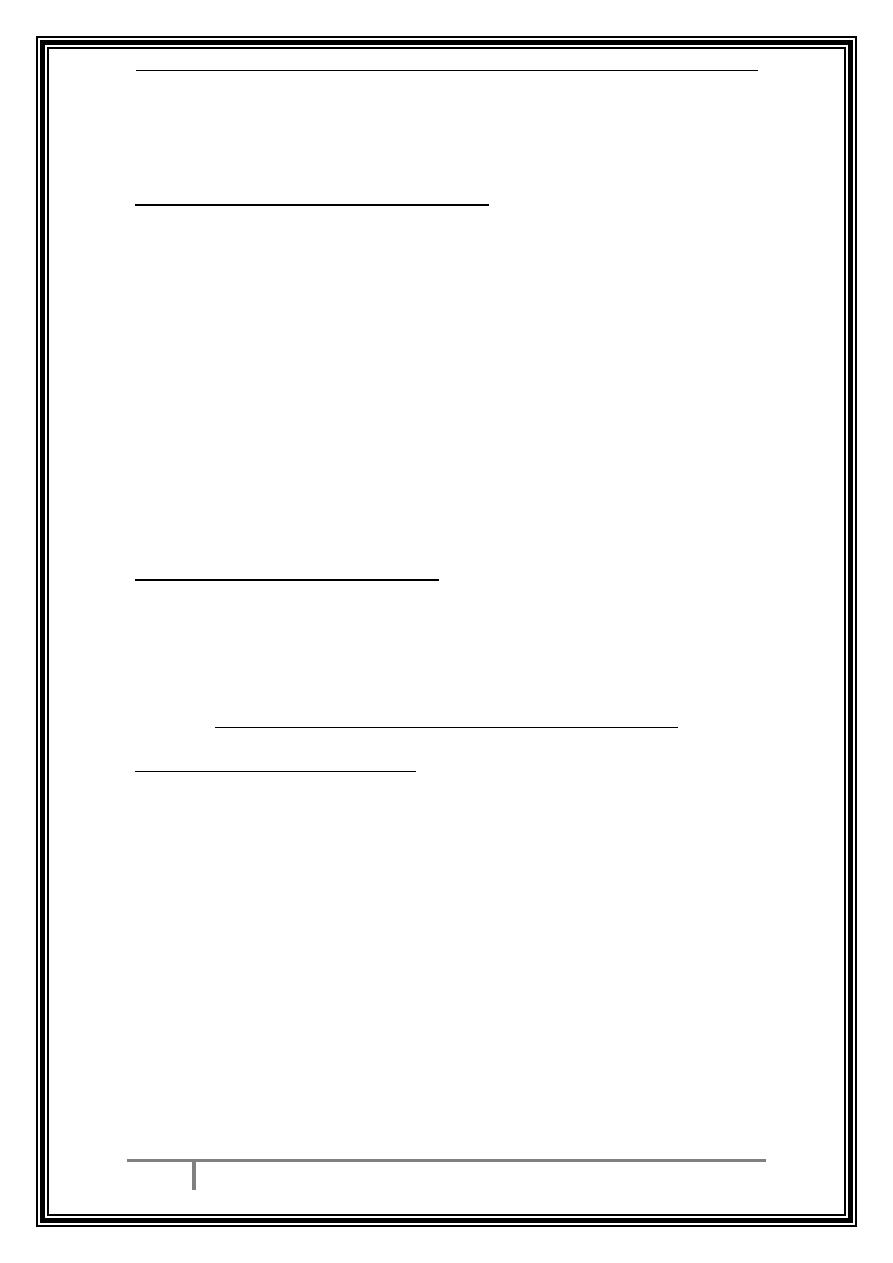
Amniocentesis :
A thin needle is passed transabdominally under ultrasound
guidance into the amniotic cavity. A small amount of amniotic fluid is
removed which contains fetal fibroblasts. This test is usually
performed at or after 15 weeks' gestation.
Amniocentesis Indication :
1. Women with positive screening for Down's syndrome.
2. Women with advanced maternal age (traditionally >35 years).
3. U/S detection of abnormality or soft markers.
4. Parental balanced translocation.
5. Previous history of chromosomal abnormality.
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
8
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Complication:
1. Miscarriage rate of 1%.
2. Cell culture may fail in 0.5% necessitating further invasive tests.
3. Early amniocentesis (<10 weeks) has higher risk of fetal loss rate,
fetal talipes, reduced amniocyte culture rate.
4. Cell culture for karyotyping takes 2-3 weeks
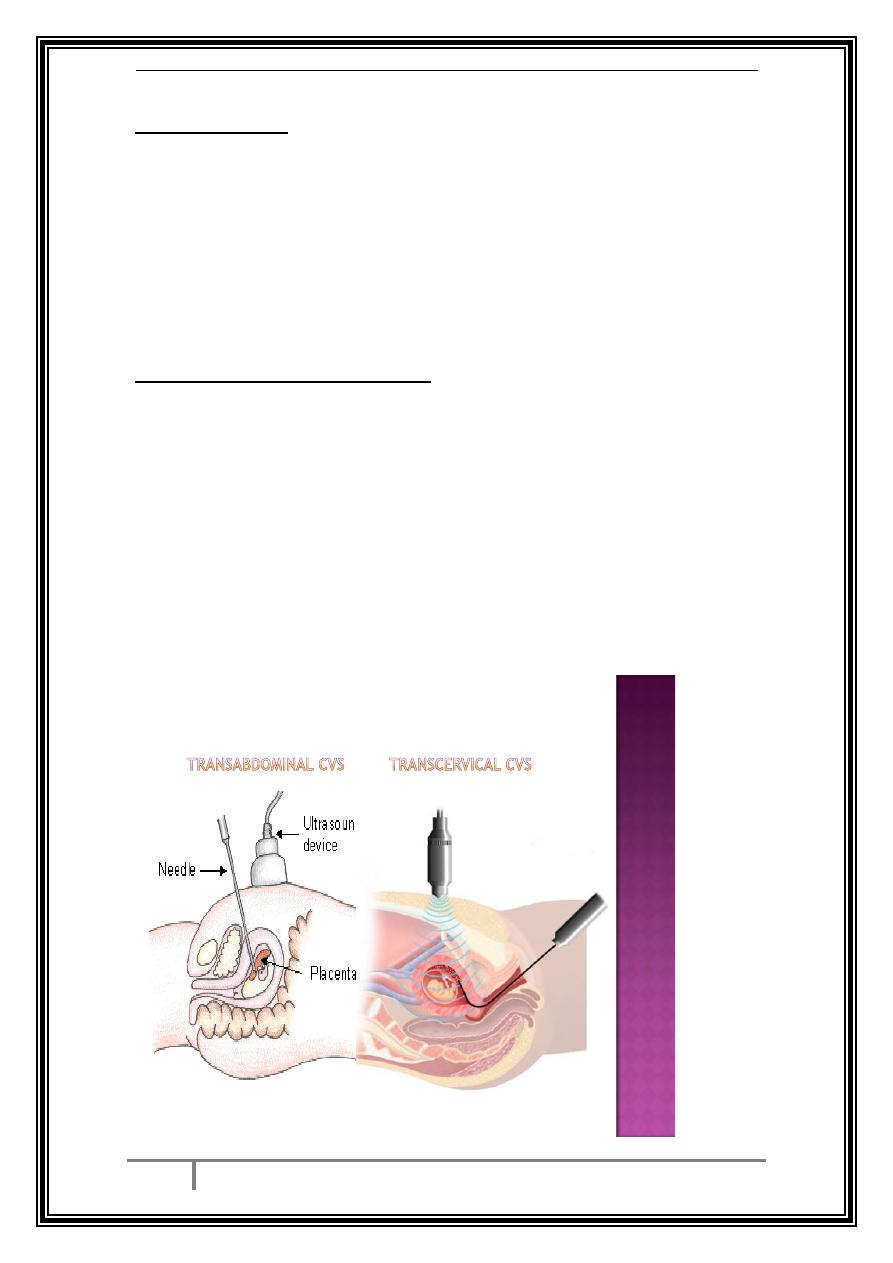
Chorionic Villus Sampling :
A thin needle is passed transabdominally or trascervically
under u/s guidance into the placenta.
Chorionic villi are feto-placental in origin. This test is usually
performed at or after 10 weeks.
Although, it is technically possible to do CVS at earlier
gestation, this is generally avoided as it is associated with a
higher rate of cleft lip/palate and digital amputation
abnormalities.
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
9
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Chorionic Villus Sampling :
Indication:
CVS has the advantage of yielding a large amount of tissue and is
therefore is the method of choice in when large amount of DNA
are required as in:
Diagnosis in monogenetic disorders.
Early diagnosis of Down syndrome.
Rapid karyotyping within 24-48 hrs.
Complication:
Miscarriage and fetal loss in 1%.
Placental mosaicism in about 2%.
There is association between CVS and limb defect when the
procedure is performed at earlier gestational ages.
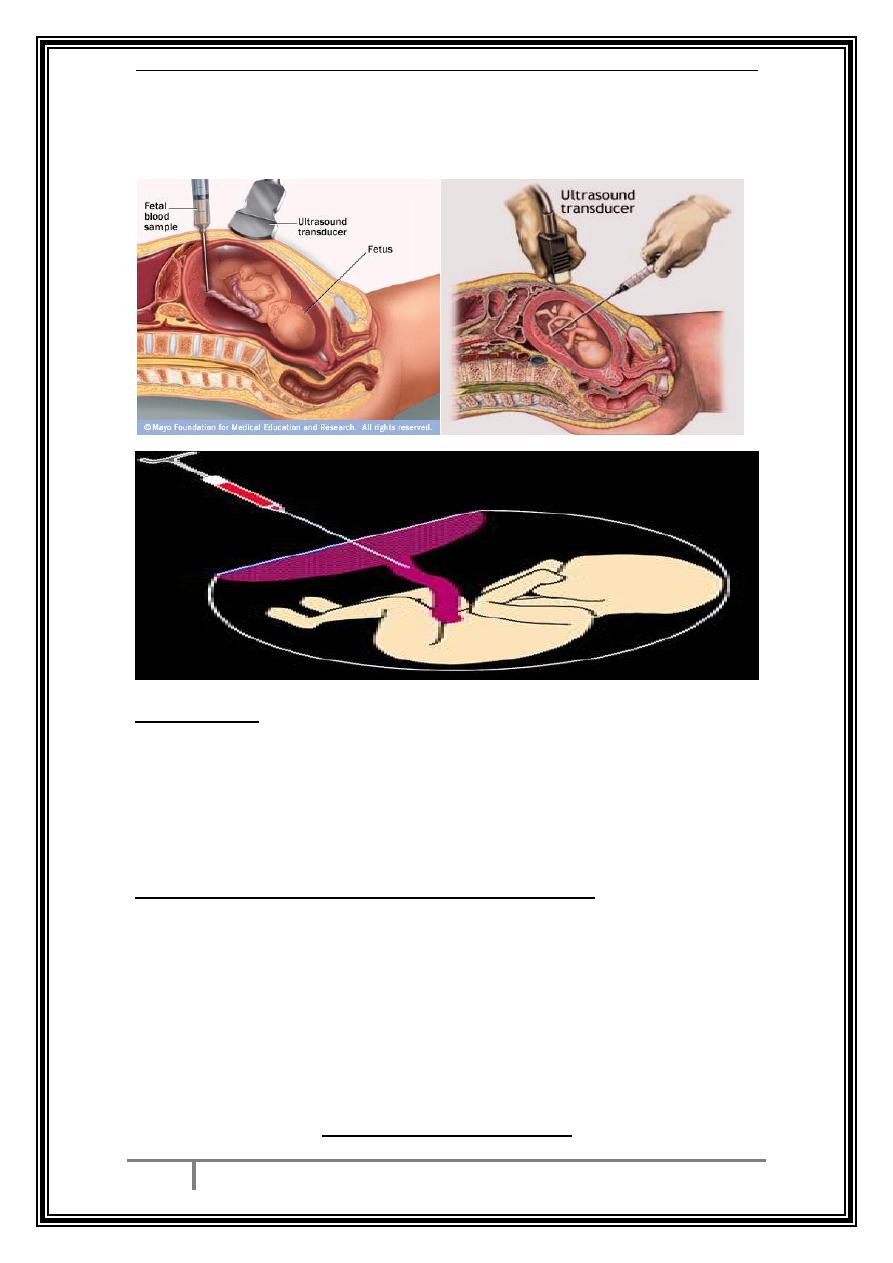
Cordocentesis
a thin needle is inserted transabdominally under u/s guidance into the umbilical
cord to sample fetal blood. This test usually performed at or after 20 weeks'
gestation.
Indication:
Rapid high-quality karyotyping within 48-72 hrs.
Diagnosis of haematological problems such as anemia,
thrombocytopenia.
Assessment of acid- base status of fetus with growth restriction.
Complication
:
Bleeding at the site of needle.
Fetal bradycardia.
Fetal loss is 1-2%.
Dr. Najmah Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital and Genetic Diseases 21/4/2016
10
BY:TAHER ALI TAHER
Introduction of infection, more importantly if mother is carrying
(HIV )virus transmission to the fetus may occur.
Fetoscopy :
with improvement of fiberoptic technology, direct in-utero
visualization of the fetus can now be achieved. It is useful in
identifying small structural abnormalities and facilitating direct
organ biopsy such as skin and muscle biopsy.
New Developments in Prenatal Diagnosis:
1. Analysis of fetal cells in the maternal circulation.
2. Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis.
3. Three-dimensional ultrasound.
4. Fetal magnetic resonance imaging.
…THE END…
