
Breech presentation
Dr Hayder Al Shamma’
a

objectives
• The student should be able to define breech presentation
• Able to differentiate the types
• Should be able to describe the mechanism of labour
• Should be able to list the causes
• Able to list and describe the complications
• Should be able to diagnose the condition and differentiate it
from face presentation
• Should be able to manage 1
st
, and 3
rd
stages of labour
• should be able to select patients for breech vaginal delivery
• Should have an idea about ECV and know the complications
and contraindications

•Occurs when the leading part of the fetus is
the buttock (breech)
•2-3% of term pregnancy
•The denominator is the sacrum

Causes of breech presentation
1. Prematurity ( at 30 wks. 25% breech )
2. Uterine abnormalities
3. Fetal factors prevent spontaneous version
4. Placenta previa
5. fibroids
6. Hydrocephaly
7. unknown

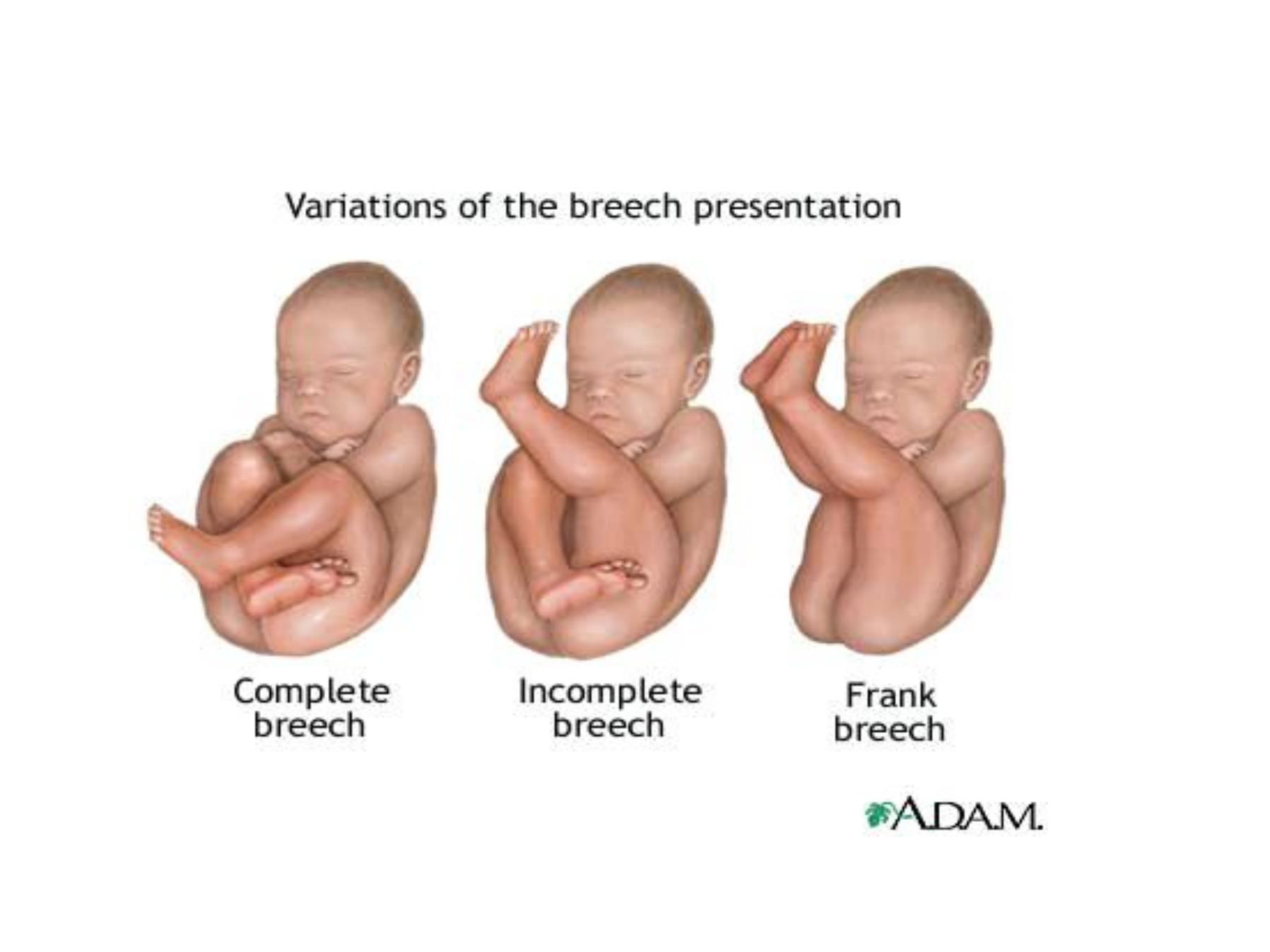
Types of breech
I. Flexed breech (complete breech) , hips flexed ,
knees flexed.
common
in multiparous women. The presenting part is
irregular and not fit well on the cx
II. Extended breech (frank breech) , Hips flexed ,
knees extended .
common in
primigravida. Fits well on the cx
III. Footling breech , partial extension of one or both
hips ( the feet below the buttock ).

Diagnosis of breech
•On abdominal examination:-
•Long. Lie
•Head felt at the fundus as hard rounded mass
smooth and ballotable
•Lower segment feels as firm irregular non
ballotable mass
•Fetal heart heard above the umbilicus .

•On vaginal examination:-
•Signs of mal-presentation
•Feel the soft buttocks
•Soft natal cleft
•Irregular hard sacrum
•Hard ischeal tuberosities
•The anus with tuberosities form a strait line
•The feet can be felt

Differentiation from face
•Soft cheecks
•Hard chin
•Hard maxillae
•Chin and maxillae form triangle
•Mouth in the center of the triangle
•(while anus at the base of the triangle between
the tuberosities )

Differentiation between hand and foot
•The foot has a prominent heal , no heal in the
hand
•The thumb can be abducted to 90 ,while the
big toe can not

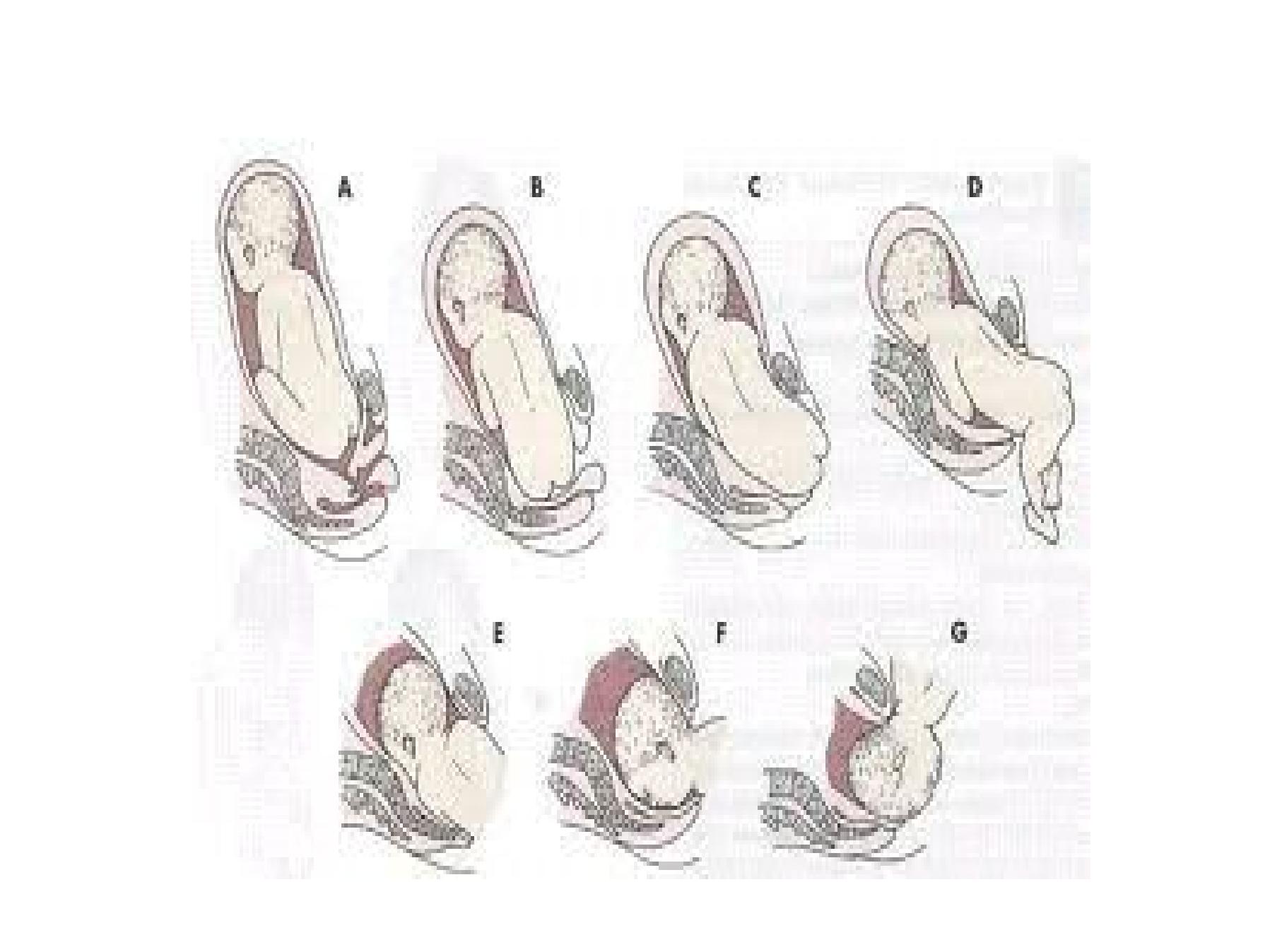
Mechanism of labor
• The largest diameter of the breech is the
bitrochanteric diameter of 10 cm
• Engagement of the bitrocanteric diameter in the
transverse or oblique diameter of the pelvis (Left
sacro-anterior or direct sacro-anterior)
• Descent in pelvic cavity followed by rotation one
buttock becomes anterior
• Further descend by lateral bend of the trunk
• Delivery of anterior buttock followed by the
posterior

Mech. Of breech ..continue
•Then engagement of the shoulders
(bisacromial diametr in transverse or oblique
diameter followed by descend of the shoulders
and rotation
•One shoulder become anterior and delivered
first

Mech. Of breech ..continue
•Engagement of the head now start to effect in
the oblique diameter of the pelvis (LOA) with
descend of the head it rotates to OA
•Rarely rotates to OP difficult labor !!!
•The head delivers by flexion

Prognosis of breech delivery
• Perinatal mortalities is X4
1.
Hypoxia
a) delayed delivery of the head
b) cord compression
c) reduced placental flow ( uterine retraction )
d)respiratory efforts aspiration of clots or meconium
2. Intracranial hemorrhage (rapid delivery of the head ,compression
decompression of the head ) as no time for molding
3.
Cervical spine injuries from excessive traction on the shoulder
4.
Soft tissue injuries ( rupture spleen, liver and bowel)
5.
Fractures of long bones

Prognosis of breech, continue….
•Maternal risks
1. Increased operative deliveries
2. Increased Genital tract injuries
3. Increased Cesarean section
4. Increased Risks of anesthesia
But the major disadvantage of vaginal breech
delivery is burdened by the fetus

Management of breech
•Wait to 36 wks
•Consider external cephalic version ECV if
1. No indication for C/S
2. Technically possible ( normal liquor, fetal size,
relaxed uterus ,etc…..)
3. No contraindication.( previous C/S, APH, PE,
twins, bad obstetric history, abnormal baby,
infertility , etc….)
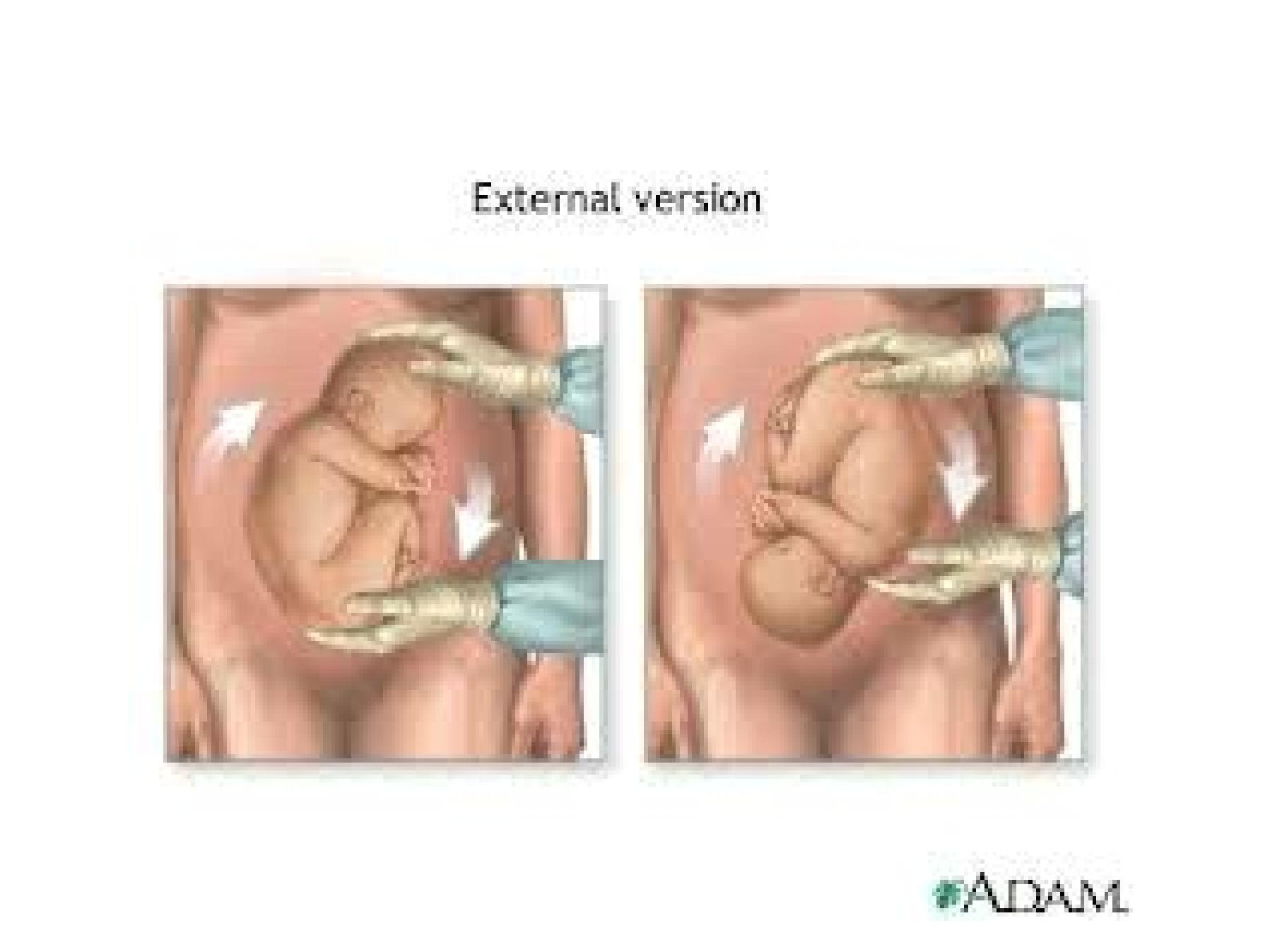

Risks of ECV
1. Premature labour
2. Premature preterm rupture of membranes
(PPROM)
3. Feto-maternal transfusion
4. Formation of knotes in the cord
5. Abruptioplacentae.

Management of persistant breech
• Selection of cases for vaginal delivery
Assessment for medical or obstetrical risks
1.
PE
2.
diabetes
3.
bad history
4.
Rh isoimmunization
5.
footling breech
6.
previous C/S
7.
suspected CPD
8.
fetal wt
3.7 kg
9.
gestational age
40 wks.
10. others like wish of the parents
All need elective C /S

Management of vaginal breech delivery
•First stage managed as high risk labor
•2
nd
stage should be conducted by the most
senior resident available
•Patient should be in lithotomy position
•Iv fluid ,epidural anesthesia available

Management of vaginal breech delivery
continue
The second stage managed as follows
1. Spontaneous delivery till the umbilicus
2. Rapid delivery of the trunk and shoulders
3. Controlled delivery of the head in 4-6 minuets

Delivery of the head
•3 methods
1. Burns Marshal method
2. Jaw flexion shoulder traction
3. Forceps for the after-coming head
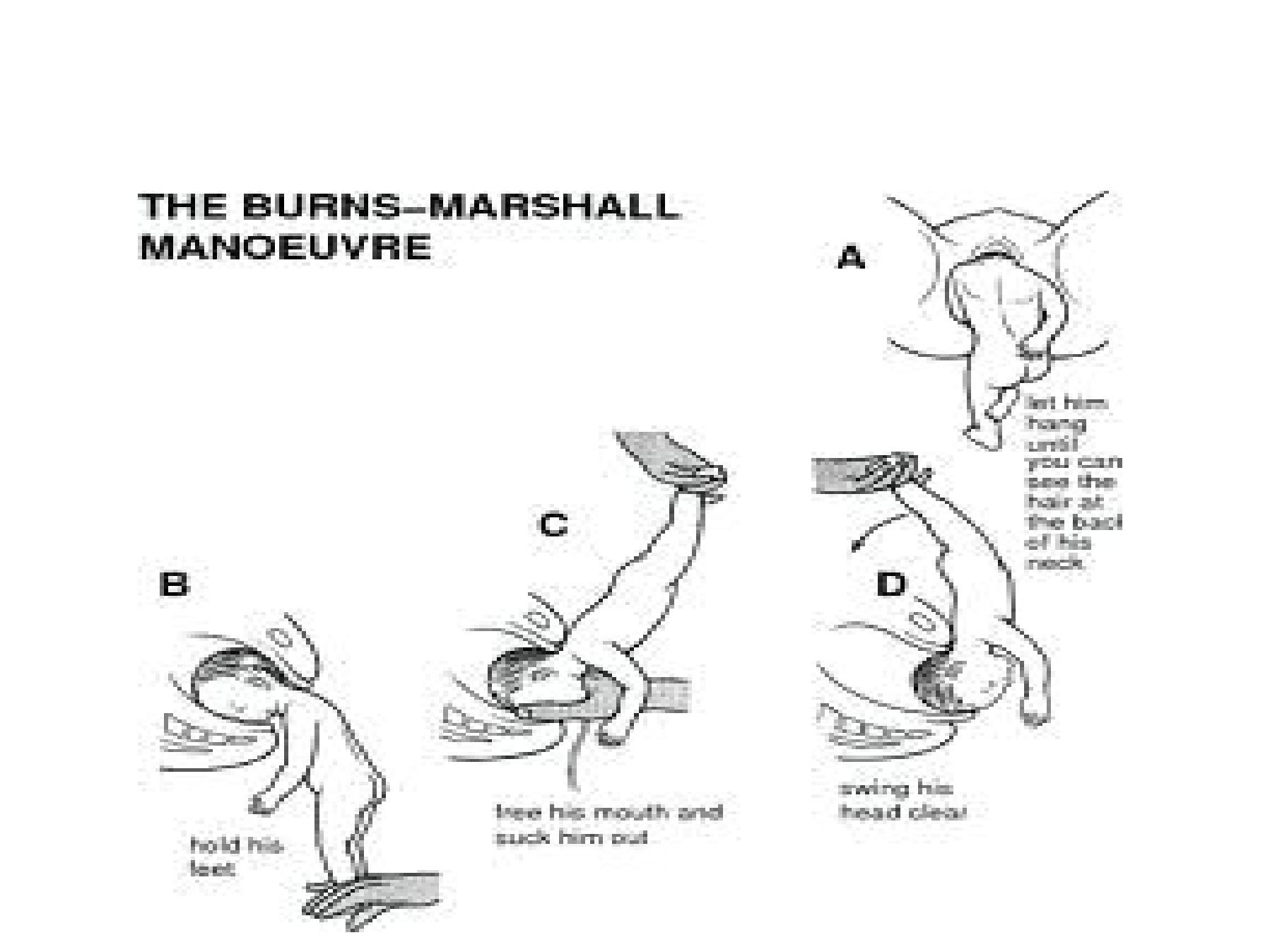
Burns Marshal /Prague Seizure method
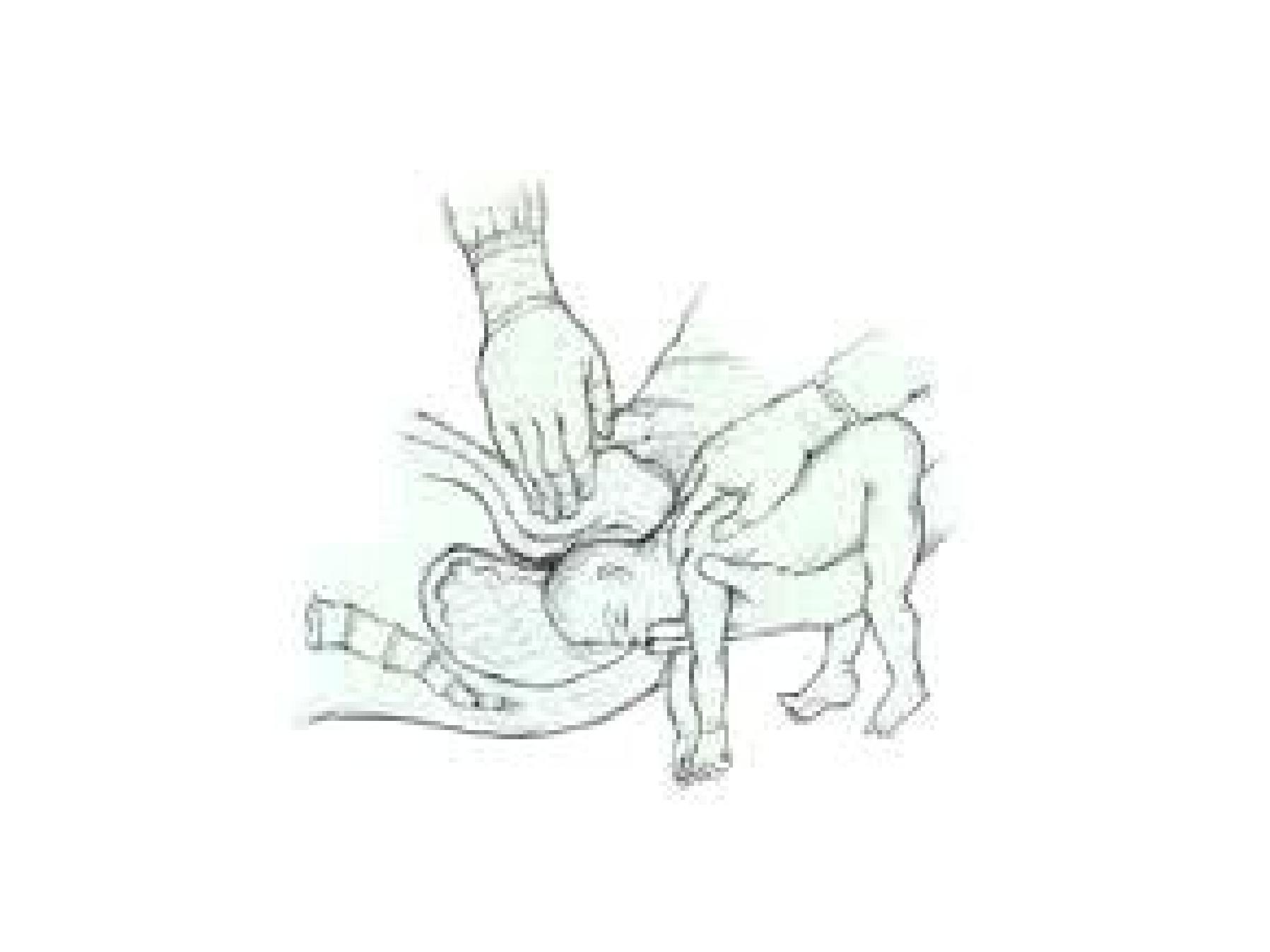
Jaw flexion/ shoulder traction
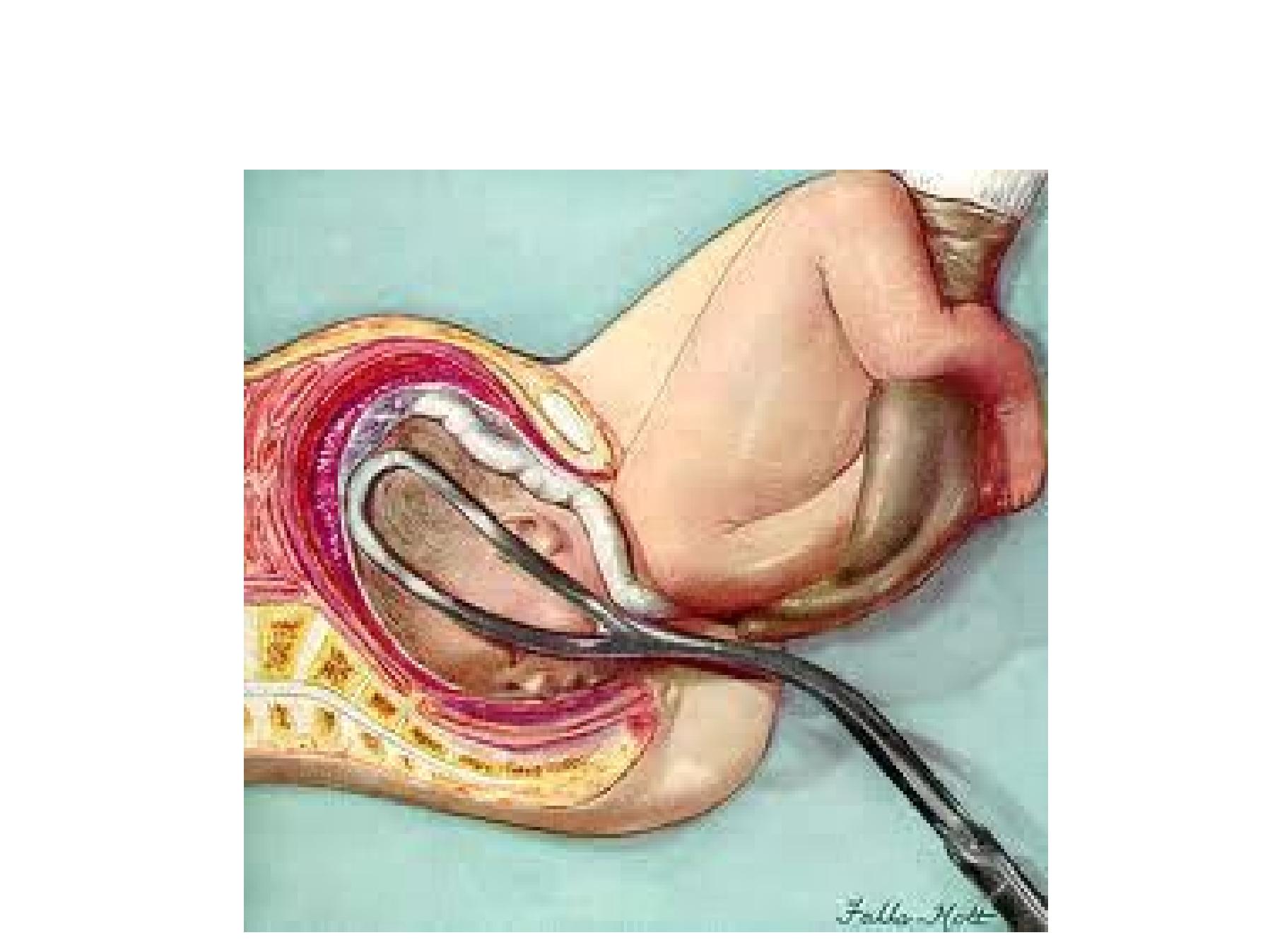
Forceps for the after-coming head
