
Abnormal labour
Dr: Hayder Al-Shamma’
a

types
•I :- Malposition and Mal-presentation of the
head ( occipito-posterior, face presentation
,brow presentation)
•II:- Breech presentation
•III:- Shoulder presentation(Transverse lie)

Risks of abnormal labour
•Abnormal labour carries increased risks to the
mother and the fetus more than normal labour
, specially if the labour is attended by an
inexperienced personel

Maternal risks of abnormal labour
1. prolonged labour
2. Infection
3. Obstructed labour
4. Anesthesia
5. Traumatic delivery
6. Hemorrhage
7. DVT
8. Pressure necrosis and fistula
9. death

Fetal risks
1. Cord prolaps
2. Hypoxia
3. Infection (chorio-amnionitis , pneumonia)
4. Traumatic injuries
5. Meconium aspiration (pneumonitis)
6. death

Malposition & mal-presentation of the
fetal head
1) Occipito-posterior position
2) Face presentation
3) Brow presentation

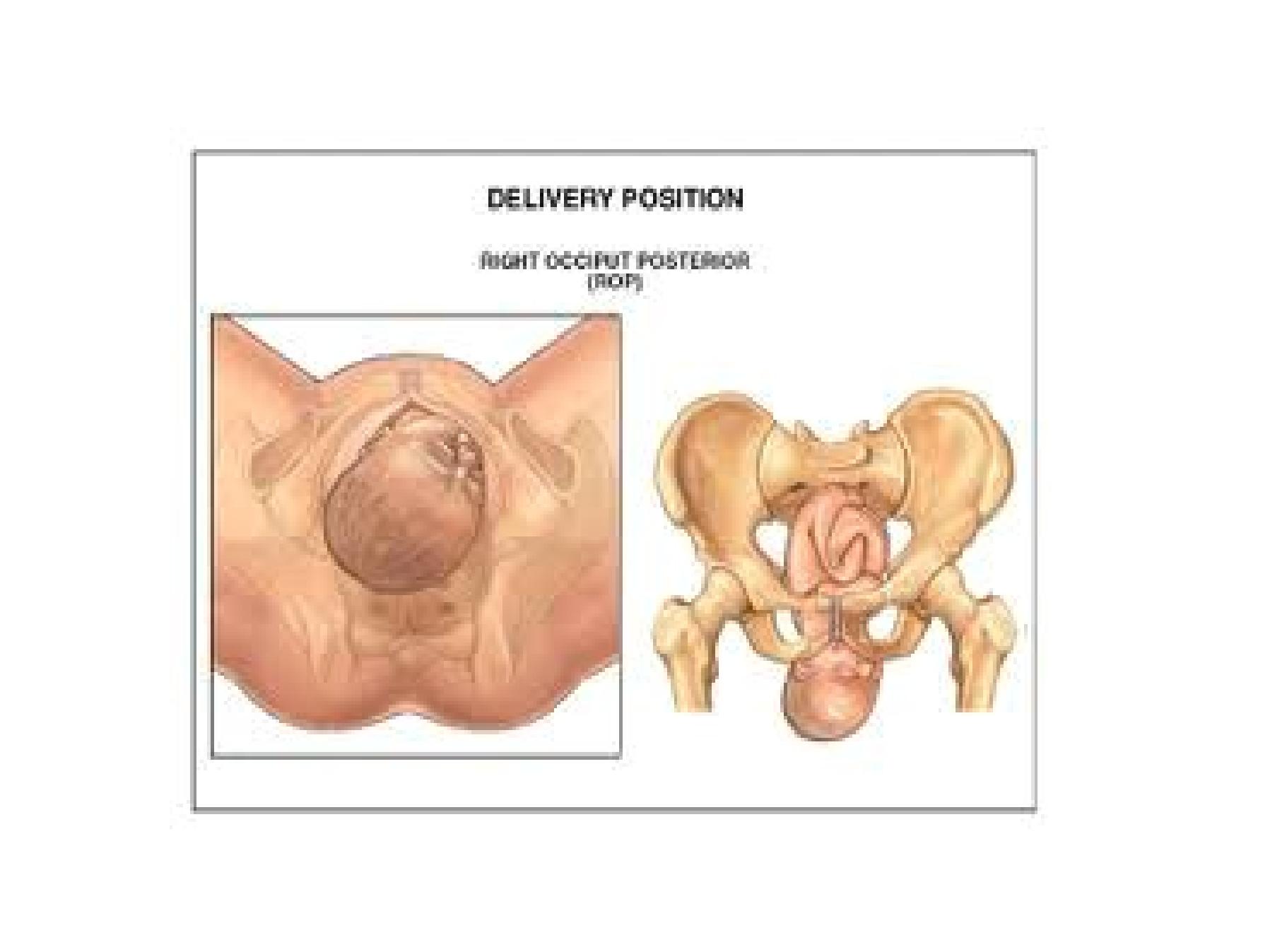
Labour in occipito-posterior position
•The denominator is the occiput
•The occiput occupy the posterior part of the
female pelvis ie. occiput near the sacrum
Occipito-posterior

Causes of O. P.
• Anthropoid pelvis favor direct o.p position
• Android pelvis favor oblique o.p. position
• Anteriorly situated placenta
• gross pendulous abdomen
• Congenital malformations
• Abnormal extensor tone
• Polyhydramnious
• Prematurity
• Multiple pregnancy

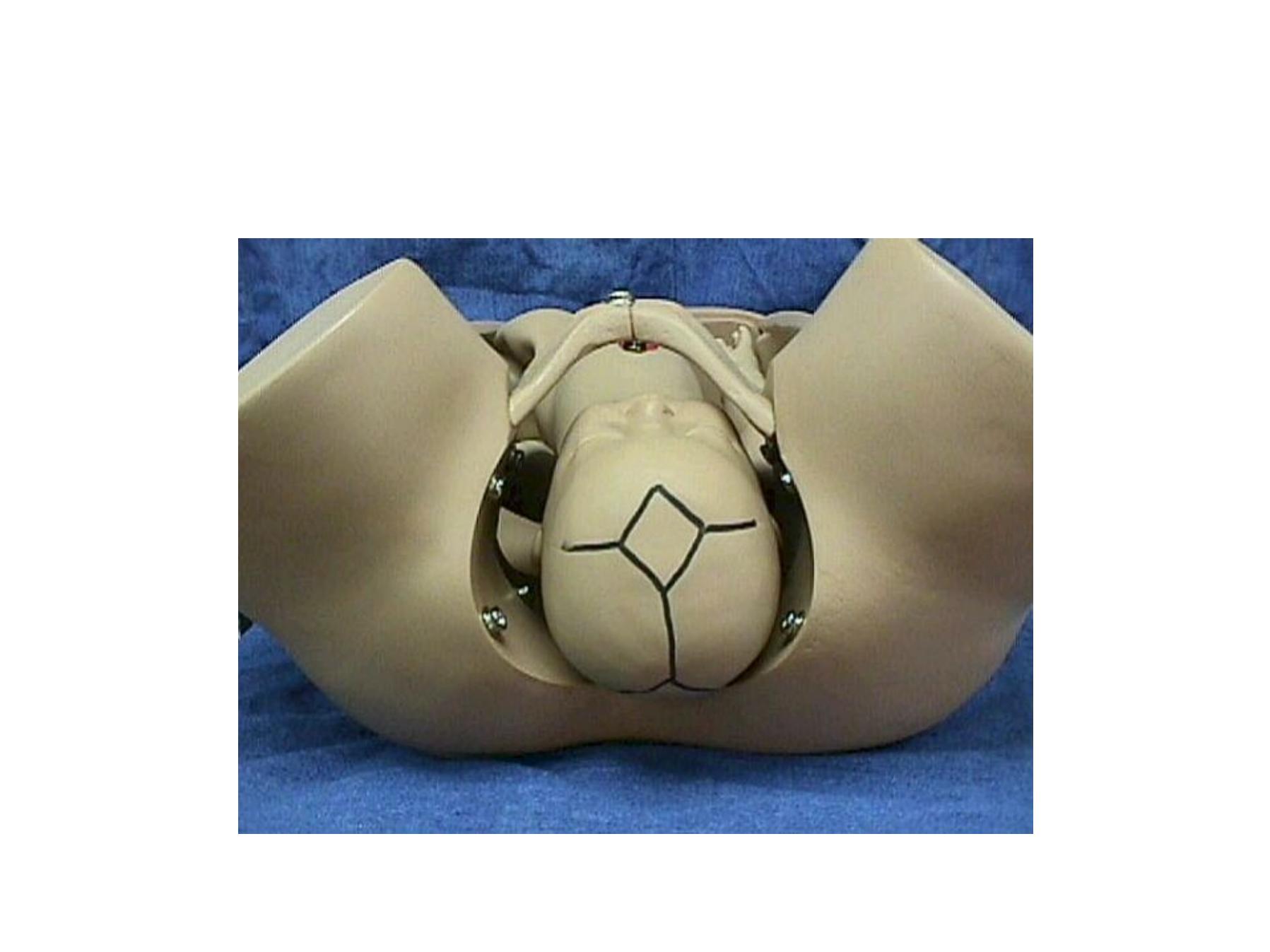
Diagnosis of occipito posterior
•By abdominal exam.
1. Flat lower abdomen below the umbilicus
2. easy to feel Fetal limbs anteriorly
3. difficult to feel the Fetal back
4. Head not engaged
5. Fetal heart at the flanks

Diagnosis of occipito posterior
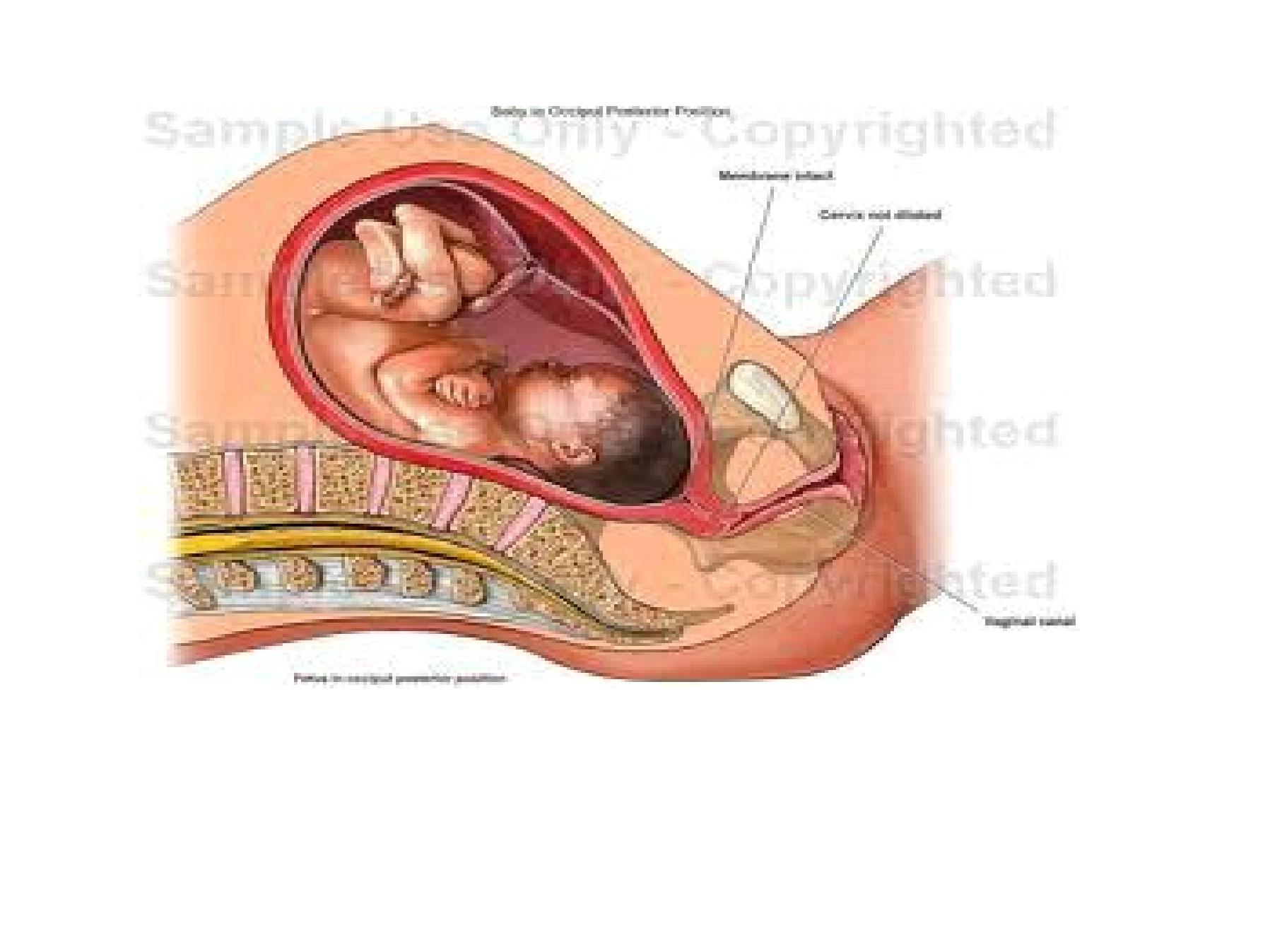
• By pelvic exam.
1. High presenting part
2. Bulging sausage shaped membranes
3. Or early rupture of membranes (cx.less than 3cm)
4. Easy to feel the anterior fontanel behind the pubic
symphysis
5. Difficult to feel the posterior fontanel near the sacrum
6. ear directed posteriorly (in excessive caput & edema)

Mechanism of labour in O.P.
•Engagement in ROP (ROP 3times than LOP)
•Engaging diameter is suboccipito-frontal 10.5
cm if the head well flexed .
• Or occipito-frontal 11.5 cm if the head deflexed
(both larger than normal OA suboccipito-
bregmatic 9.5 cm)
•This gives an oval shaped presenting part not
fit well on the cx. Of larger dimentions

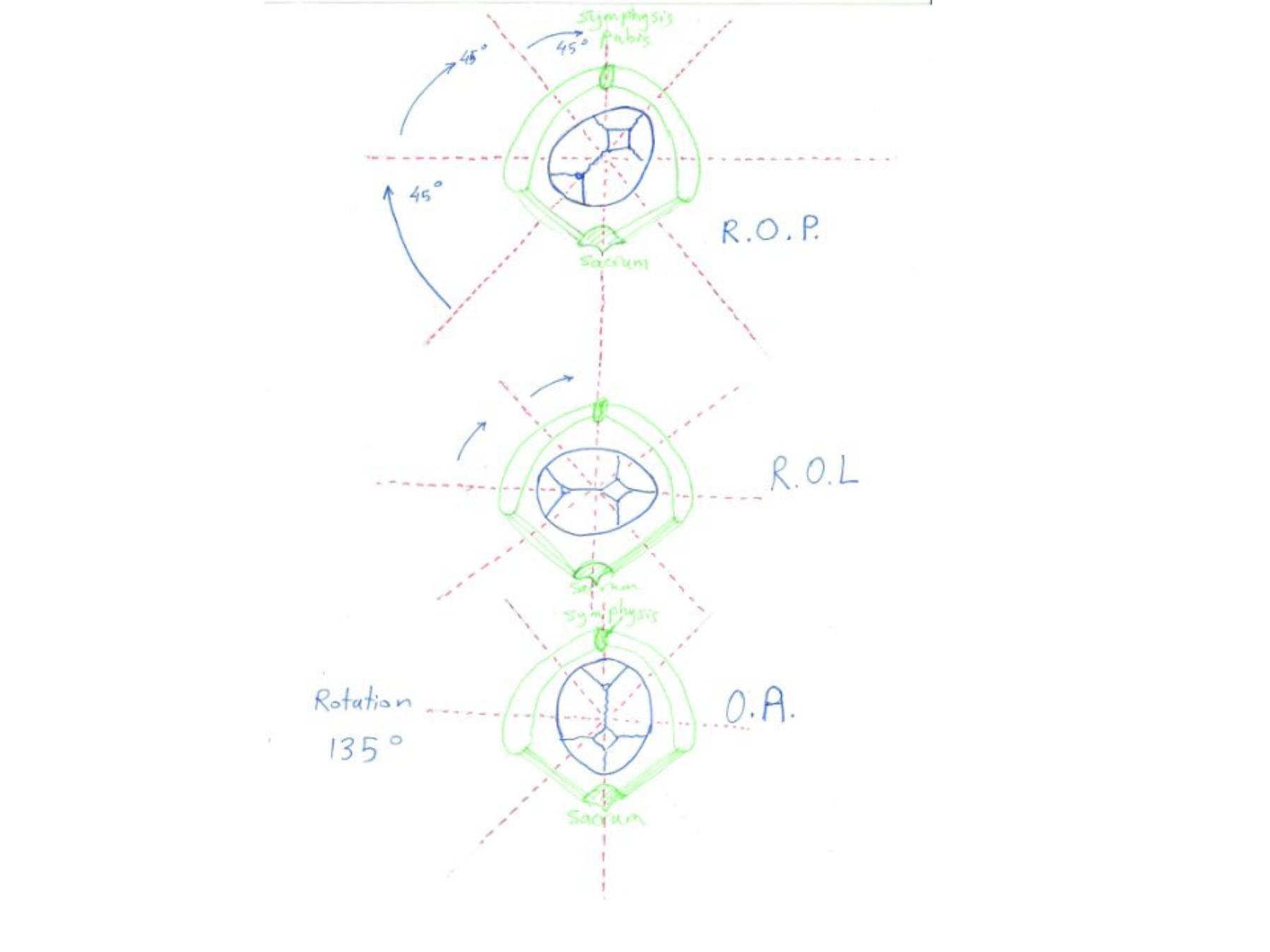
Mechanism of labour in O.P.
•Internal rotation:- if the head well flexed the
occiput will touch the pelvic floor first and
rotated anteriorly 3/8
th
of a circle 135 and
become occipito-anterior and the mechanism
then continue as in OA. But it takes longer time
to rotate
•This occurs in 70% of cases

Mechanism of labour in O.P.
• If the head is deflexed :- the sinciput touches the pelvic
floor first so rotates anteriorly and the occiput rotates
posteriorly through 1/8
th
of a circle (45 ) short rptation
giving direct occipitoposterior
• The mechanism differs , descent continues and the head
delivers by a combination of flexion first, followed by
extention
• The emerging diameter is occipito-frontal of 11.5 cm
causing great distension at the vulva and perineum and
perineal tears may occur unless episiotomy performed
• Occurs in 10% of cases

Mechanism of labour in O.P.
•Arrest of rotation at lateral position (right
occipito-lateral or left occipito-lateral)
•No mechanism of labour
•Deep transverse arrest
•Need assisted delivery
•Occurs in 20% of cases

Features of labour in O.P.
1. Slow progress (slow cx. dilatation, descent,
rotation)
2. Backache is more
3. Incoordinate uterine contraction
4. Early rupture of membranes
5. Higher chance for cord prolaps
6. Higher chance for infection
7. Higher chance for perineal laceration
8. Excessive moulding of the head may cause
tentorrial tear

Treatment of O.P.
Before the onset of labour , no attempt for correction
During first stage of labour
1.
Correction of malposition cannot be done
2. Observation of uterine contraction, cx dilatation, descent,and
use partogram
3. Continuous fetal heart monitoring
4. Due to increased risk for operative delivery and anesthesia ,
give nothing by mouth, only occasional sips of water
5. Maintain maternal hydration by iv fluid
6. Oxytocin infusion is often indicated to correct incoordinate
uterine contractions

Treatment of O.P.
•Cesarean section is indicated in first stage in
the following conditions
1. Failure to progress in spite of good uterine
contractions for 3 hours
2. Fetal distress
3. Maternal distress

Treatment of O.P.
•Treatment in second stage
•Mistaken diagnosis of 2
nd
stage is not
uncommon, the patient have urge to
pushdown before full dilatation (pressure
effect of the large occiput on the pelvic plexus
•p/v exam is essential to confirm the diagnosis

Rx of 2
nd
stage continue
•p/v to assess degree of deflexion
•Determine excessive molding
•Determine caput succidanium
•If detect that , spontaneous labour is unlikeley
to occur
•Pain relieve is essential in O.P.
•Epidural analgesia , pethidine

Need assisted delivery
Fetal distress
Maternal distress
Failure to progress
Deep transverse arrest

Assisted delivery
•Oxytocin
•Manual rotation with or without forceps
extraction
•Forceps rotation (Kielland forceps)
•Vacuum extractor
•Cesarean section

Manual rotation
•Correction of malposition by manipulation with
the hand under epidural anesthesia
•Disadvantage need anesthesia, hand take
additional space , may cause trauma, pulling is
not feasible
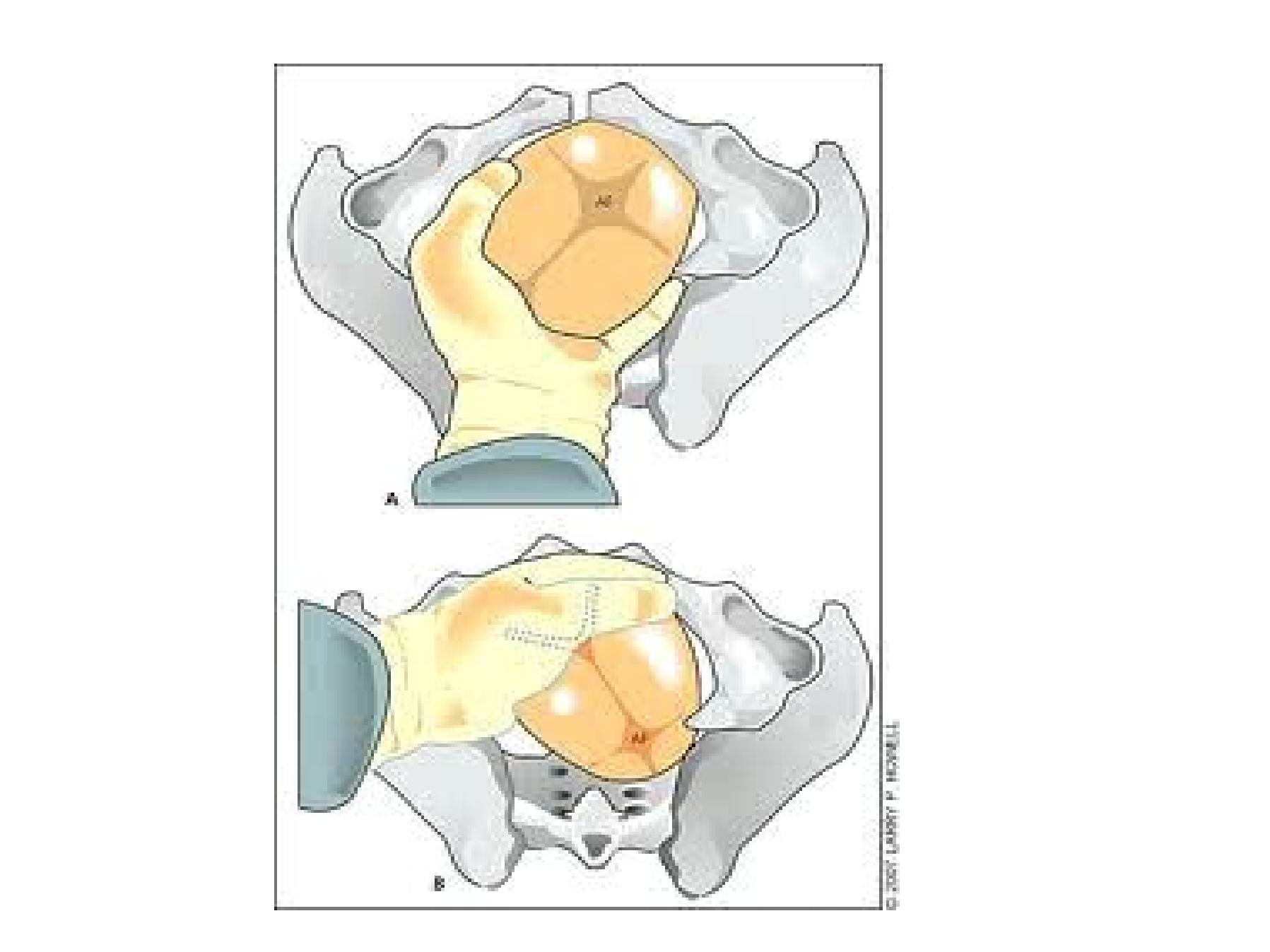

•Kielland forceps rotation
•Same disadvantages but ,can pull the head
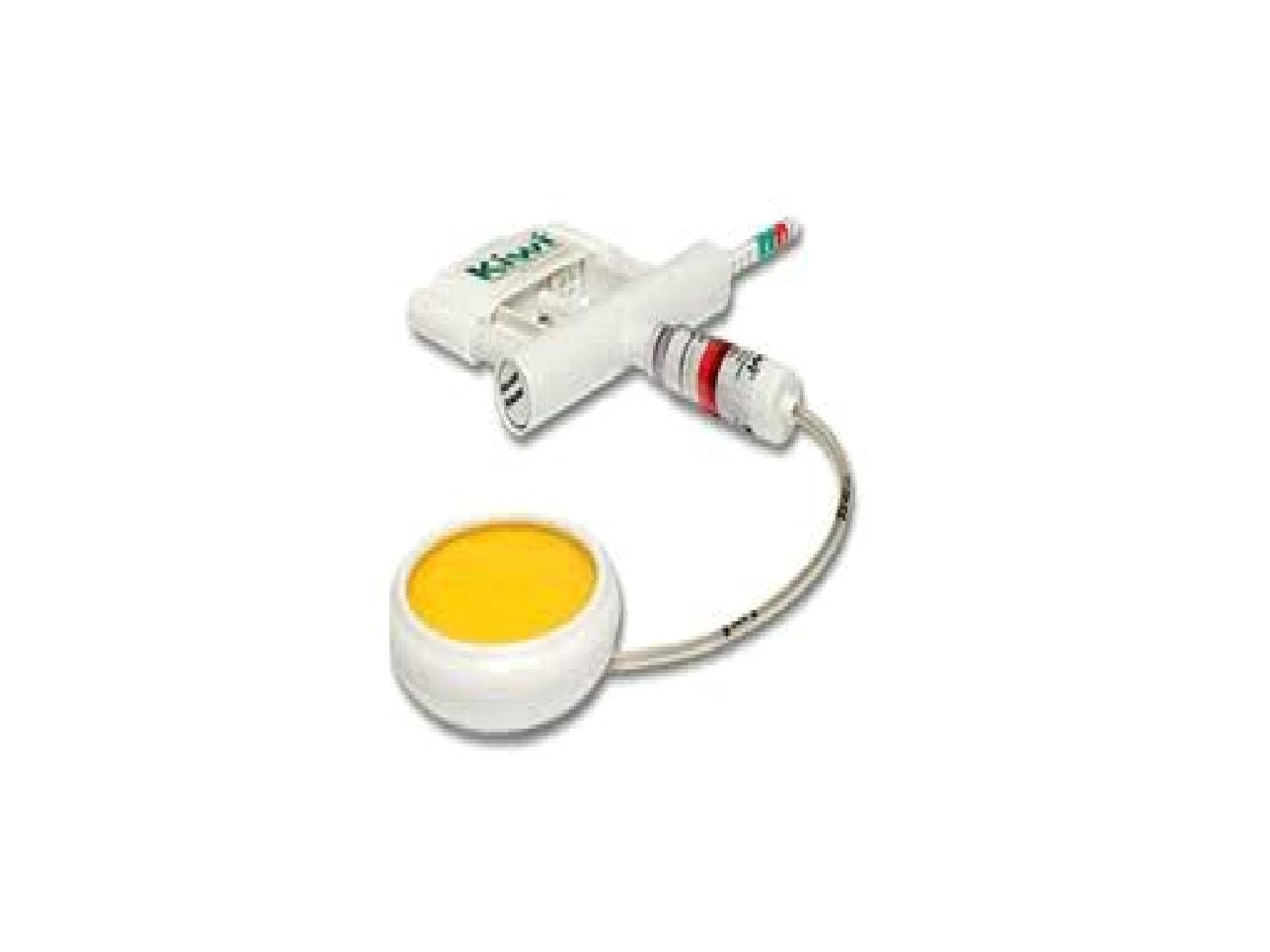
Vacuum extraction ( Vantouse , Kiwi)
Advantages
Applied without anesthesia, not take extra space,
easy to use minimal skills



No comment !!!!!

No comment !!!!!!

No comment !!!!!

Face presentation
•The head is fully extended
•1/300 deliveries
•Causes : same as O.P.
•The denominator is the mentum (chin)
•Mento-posterior no mechanism of labour the
chest try to enter the pelvis at the same time
with the head (sternobregmatic 16-18cm)
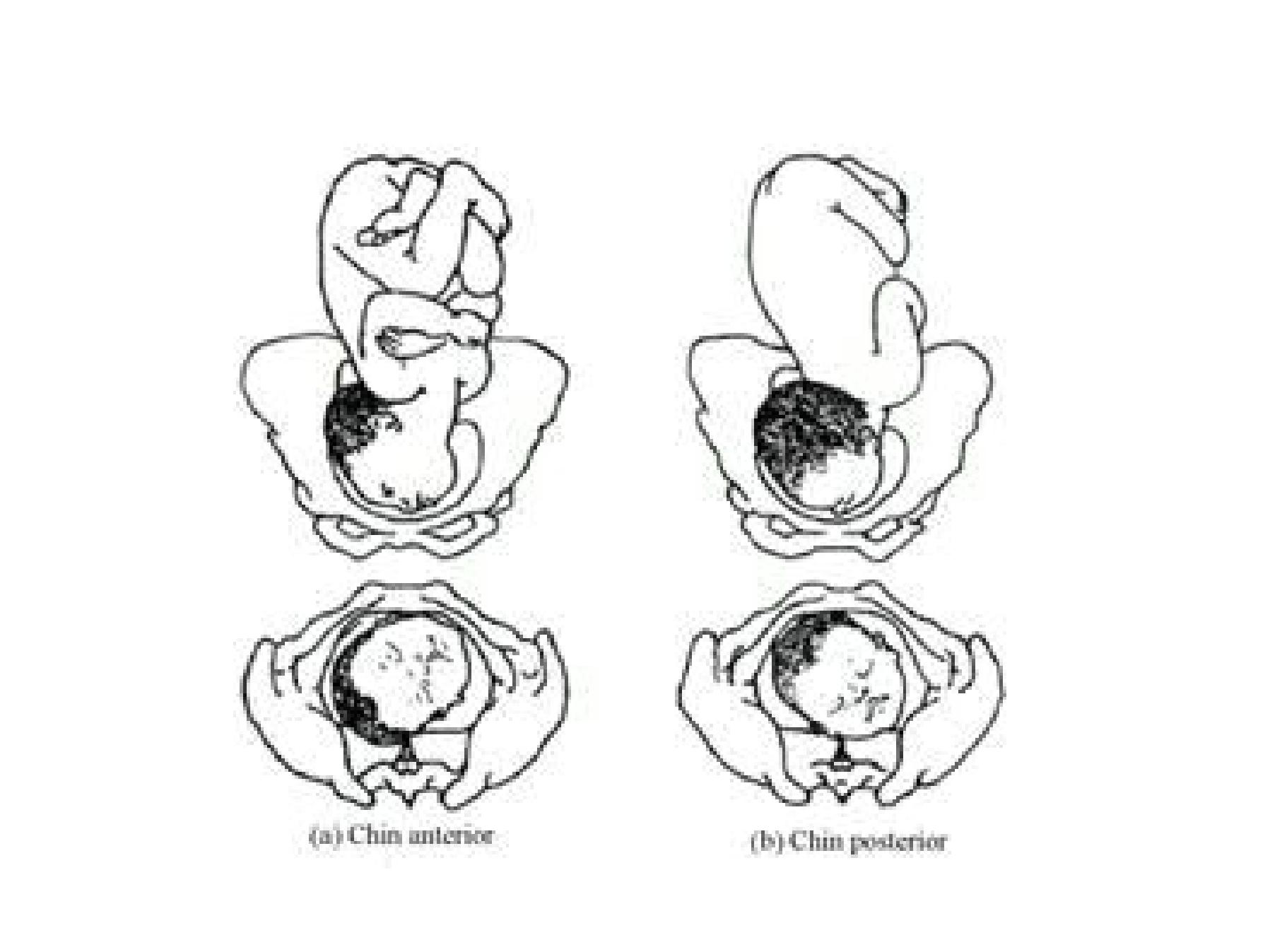

Mechanism of labour in mento anterior
• Engagement in mentolateral ML or RMA
• Engaging diameter is the submento bregmatic 9.5
cm
• Descent occurs slowly
• Rotation occur late in 2
nd
stage
• Engagement occur at + 2 or + 3 station
• Delay in 2
nd
stage due to oblique line of thrust from
the back to the head
• The face deliver by flexion
• Emerging diameter is the submentovertical 11cm

Diagnosis of face presentation
•Abdominal findings:- Longitudinal lie, cephalic ,
a groove can be felt between the head and
back , the head is high
•p/v feel the chin, mouth, jaws, nose, orbital
ridge

management
•Exclude CPD, hypertension , placenta previa,
other risk factors , estimated fetal wt 3.5kg
•If any of the above cesarean section safer
•Manage as in case of O.P.

Brow presentation
• 1/1000
• Incomplete extension
• It is usually a transient presentation , either change
to vertex or to face
• Causes as face
• Diagnosis
• On abdominal exam as in face but the groove is less
prominent
• p/v :- feel ant. Fontanel, orbital ridge, roote of the
nose, eyes, but not the chin
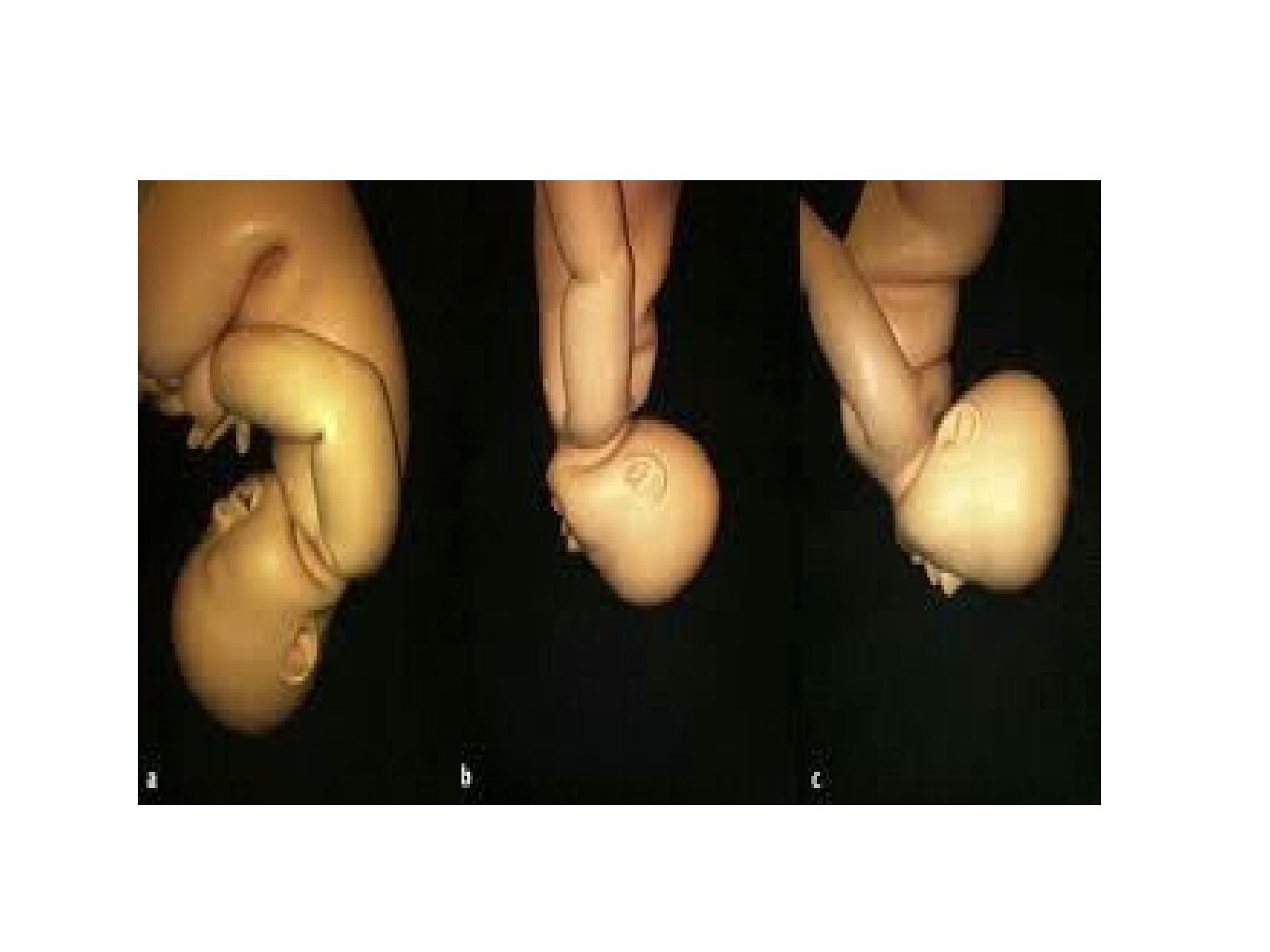

Mechanism of labour in brow
•No mechanism of labour . The engaging
diameter is the mentovertical 14 cm so
cesarean section is indicated in persistent brow

Thank you
