
Principles of Health
Administration

Health Administration
Sound administration is essential for the success of any public health
program whether on the national, intermediate or the local level.

Definition of Sound Administration
“ The process of achieving defined goals at a defined time through the
guidance, leadership, and control of the efforts of a group of
individuals and the efficient utilization of non-human resources
bearing in mind adequacy, speed, and economy to the utmost
possible level.”

Another definition
“Administration is the art and science of guidance, leadership, and
control of the efforts of a group of individuals towards some common
goal.”

Management
• Management is the operational part of administration.
• It is defined as:
“ It is a set of interactive processes through which the utilization of
resources results in the accomplishment of organization objectives.”
• It is a “conversion mechanism”.
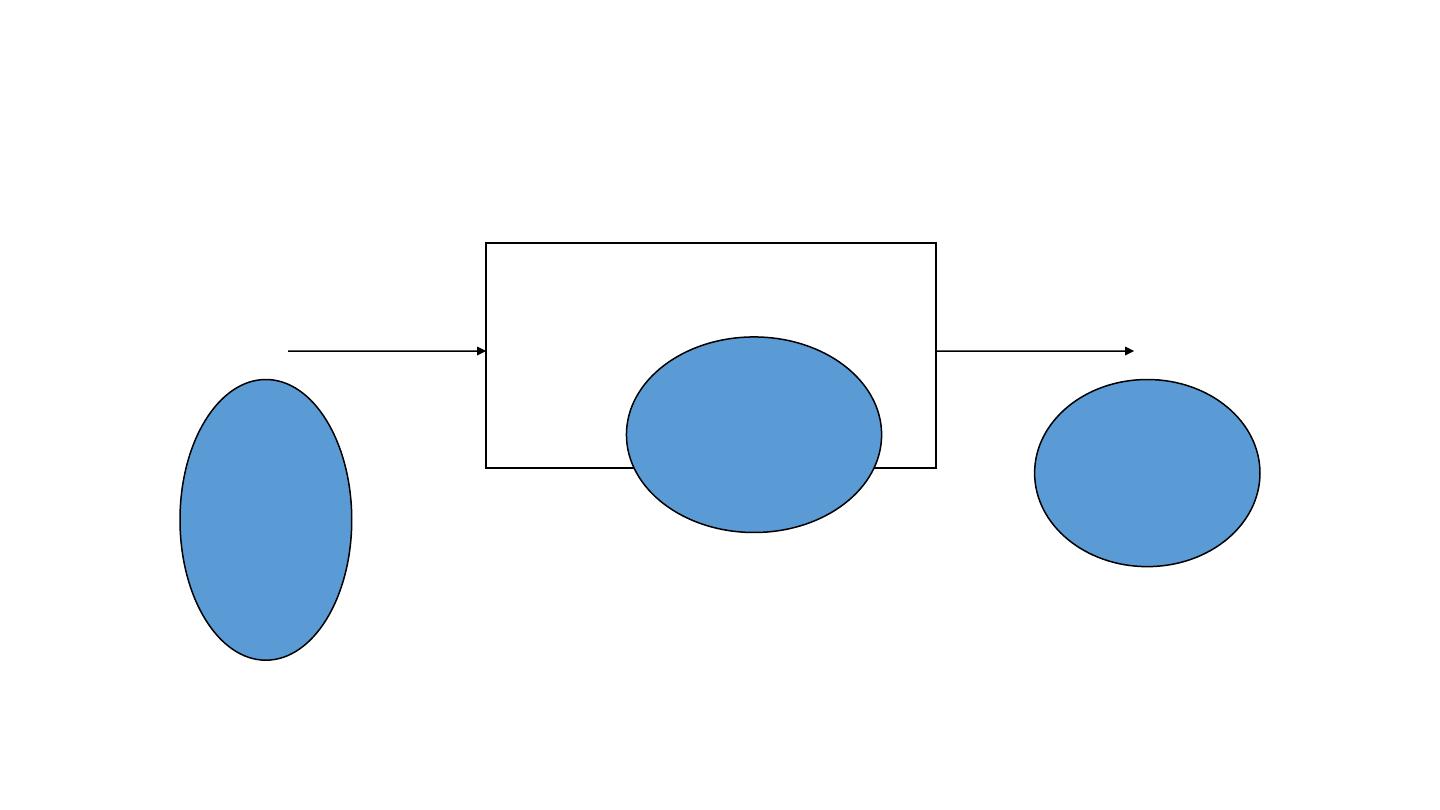
Process
Inputs
Outputs
A systems view of management:
Human
resources
Non-
human
resources
Conversion
mechanism
Objectives
achievement

• It is through “management” that the objectives of the health care
organization are achieved by gathering and positioning of resources.
• There are several elements for administration. In practice all these
elements are interrelated to one another.
• There are also 3 levels of administration.

Elements of Administration:
• Planning
• Organization
• Staffing
• Directing
• Coordinating
• Reporting
• Budgeting
• Supervising
• Evaluation
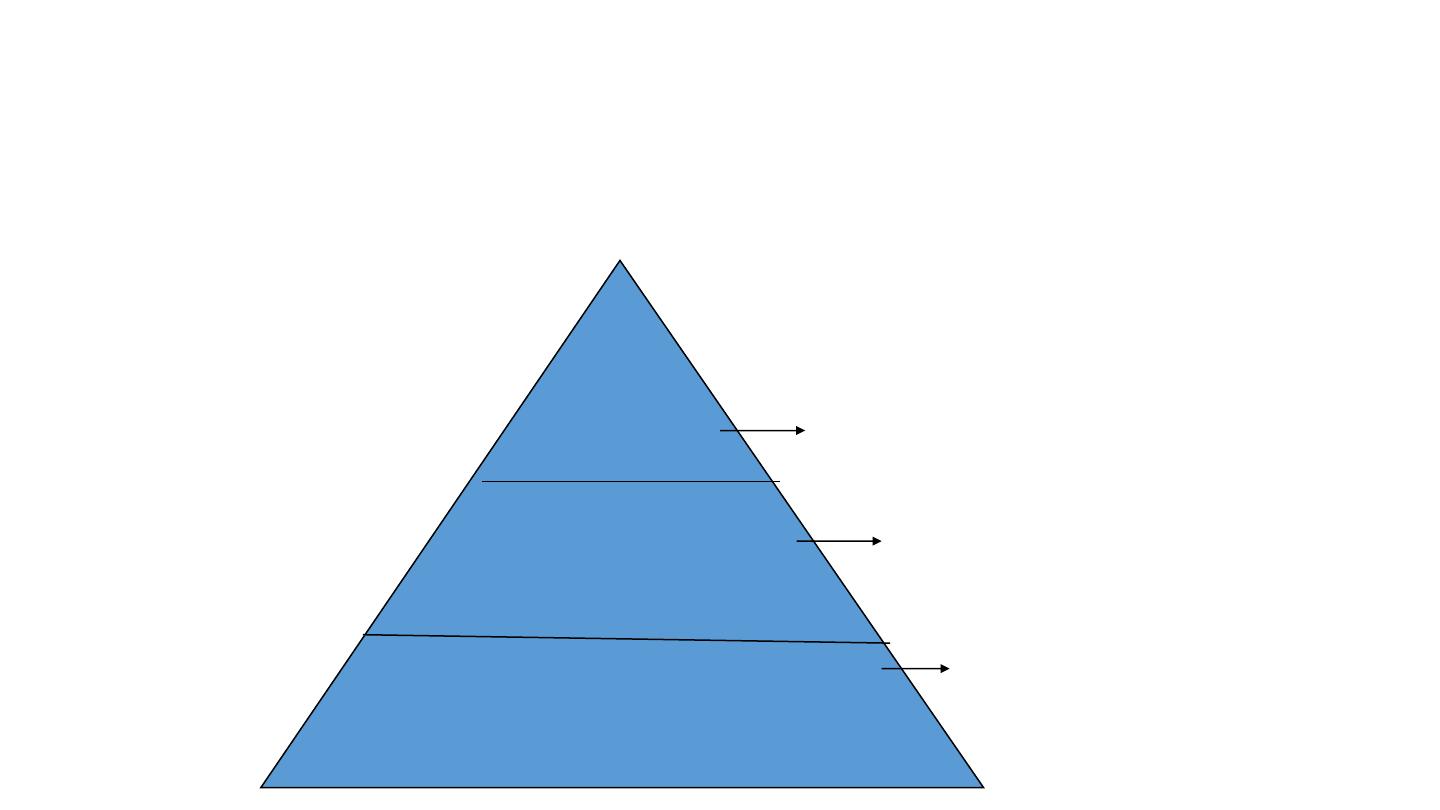
Levels of Administration
Central
level
Intermediate
level
Local Level
Ministry of health
directorates of health
e.g. health office,
Hospital, health
care unit

Every program must have an overall (general) goal which confirms
with that of the nation’s policy, and various objectives to be achieved
according to a definite plan.

Goals versus Objectives
• A GOAL: is a long range specified state of
accomplishment towards the activity it is directed.
Goals are not constrained by time or existing
resources.
• AN OBJECTIVE: is a measurable state of
accomplishment aimed towards the goal. The
objective should include a description of “what”
outcome is desired, “when” it is expected, and
“where” it will take place.

Planning
• Planning is considered the most important element of the
administrative process. The higher the level of administration, the
more the involvement and time devoting to planning. A good plan is
the basis of any successful program. Sufficient time should be given to
the process of planning. More than one plan should be available to
choose from to meet the existing plan.

Definition of Planning
• “Planning is a projected or predetermined course of action designed
to achieve a specific goal or objective.”
• Planning determines What? When? Where? How? Why? And by
whom? Things will be done.
• It involves “decision making for future events”.
Process of systemic planning
1. Establishing goals and objectives
2. Designing alternative courses of action
3. Analysing and predicting the consequences
4. Selecting the best course of action
5. Implementing the selected plan and performing periodic evaluation to assure
success of plan

Principles of planning
• Being an intellectual activity it needs knowledge, experience,
foresight, reasoning and the mastering of special skills and
techniques. Examples of different techniques of planning are:
• PPBS: Planning/Programming/Budgeting system
• PERT: Performance/Evaluation/Review technique
• CPM: Critical Path Method
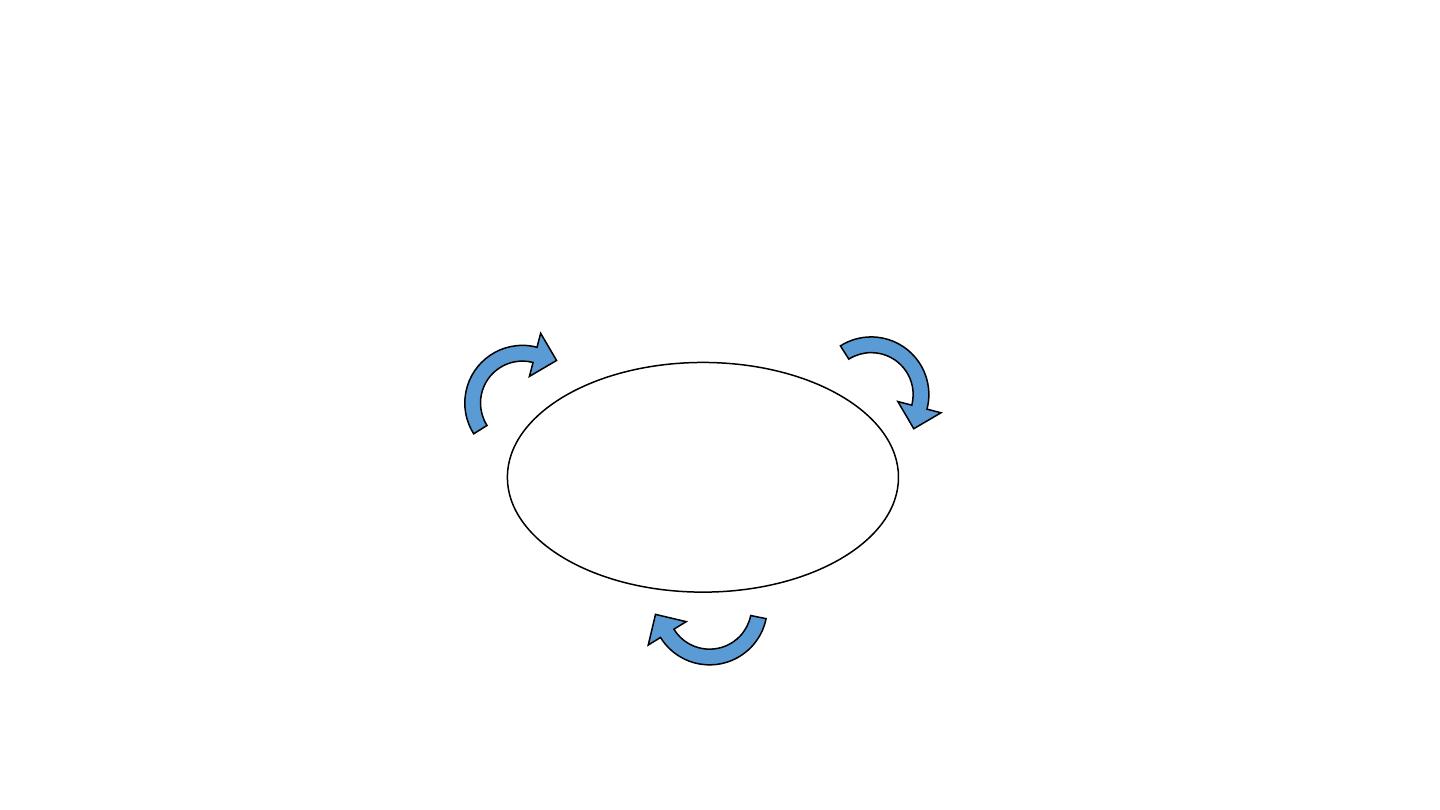
• Planning is a dynamic (non-static) process
• It is a continuous circular process
Planning
Execution
(implementation)
Evaluation
• Futuristic
• Decision making process
• Dynamic
• Flexible

• Participative planning is sharing the program planning with other
people, staff and agencies concerned with the program.
• Participative planning have advantages and disadvantages.

• Planning of a program is based on:
• Needs and demands of the public
• Available resources
• Attitude of the public

• Constraints (intervening factors) to a plan may be social, economical
or political, and they may be related to either:
• External environment (community)
• Internal environment (the organization)
• Establishing priorities are essential in planning
(What are these priorities???)

Organization
• Definitions:
“ Organization is any collection of persons, materials,
procedures, ideas or facts arranged and ordered that
the combination of parts makes a meaningful whole
that works towards achieving organizational
objectives.”
“The process of organization implies to the
arrangement of human and non-human resources in
an orderly fashion to make a meaningful whole that
accomplishes organizational objectives.”
