
Descriptive Epidemiology
and Epidemiological Triads
Dr Faris Al L ami

E
E
p
p
i
i
d
d
e
e
m
m
i
i
o
o
l
l
o
o
g
g
y
y
The study of the
distribution
and
determinants
of health-related states
and events in specified population and
the application of this study to the
control
of health problems.
Last, 2001

The Five W’
s of Journalism / Epidemiology
• What
• Who
• Where
• When
• Why / How
= Diagnosis
(the disease or condition
being investigated)
= Person
(who is getting the disease, who
is at risk)
= Place
(residence, work, school, etc.)
= Time
(date and/or time of onset of
disease, time of exposure)
= Cause, mode of transmission,
risk factors
The Five W’
s of Journalism / Epidemiolog y
•What
•Who
•Where
•When
•Why / How
=
Clinical
=
Person
=
Place
=
Time
=
Cause,
=
mode of
transmission,
risk factors
Descriptive
Epidemiology
( Distribution)
Analytic
Epidemiology
( Determinants)
Basic Epidemiologic Approach
• Observe
• Count cases (events)
• Describe
- Time, place, person
- Calculate rates,
• Compare rates
• Develop hypothesis
• Test hypothesis
• Implement actions (control, prevention)
Descriptive
Epidemiology
Analytical
Epidemiology

Descriptive Epidemiology
•Activities related to characterizing the
distribution of diseases within a population
Analytical Epidemiology
•Activities related to identifying possible
causes for the occurrence of diseases
The Epidemiological Triad
Descriptive epidemiology: Distribution
§
Person (who gets the disease?)
§
Place (where?)
§
Time (when?)
Place
Person
Time

P
P
e
e
r
r
s
s
o
o
n
n
Age
Hobbies
Sex
Pets
Occupation
Travel
Immunization status
Personal Habits
Underlying disease
Stress
Medication
Family unit
Nutritional status
School
Socioeconomic factors
Genetics
Crowding
R eligion
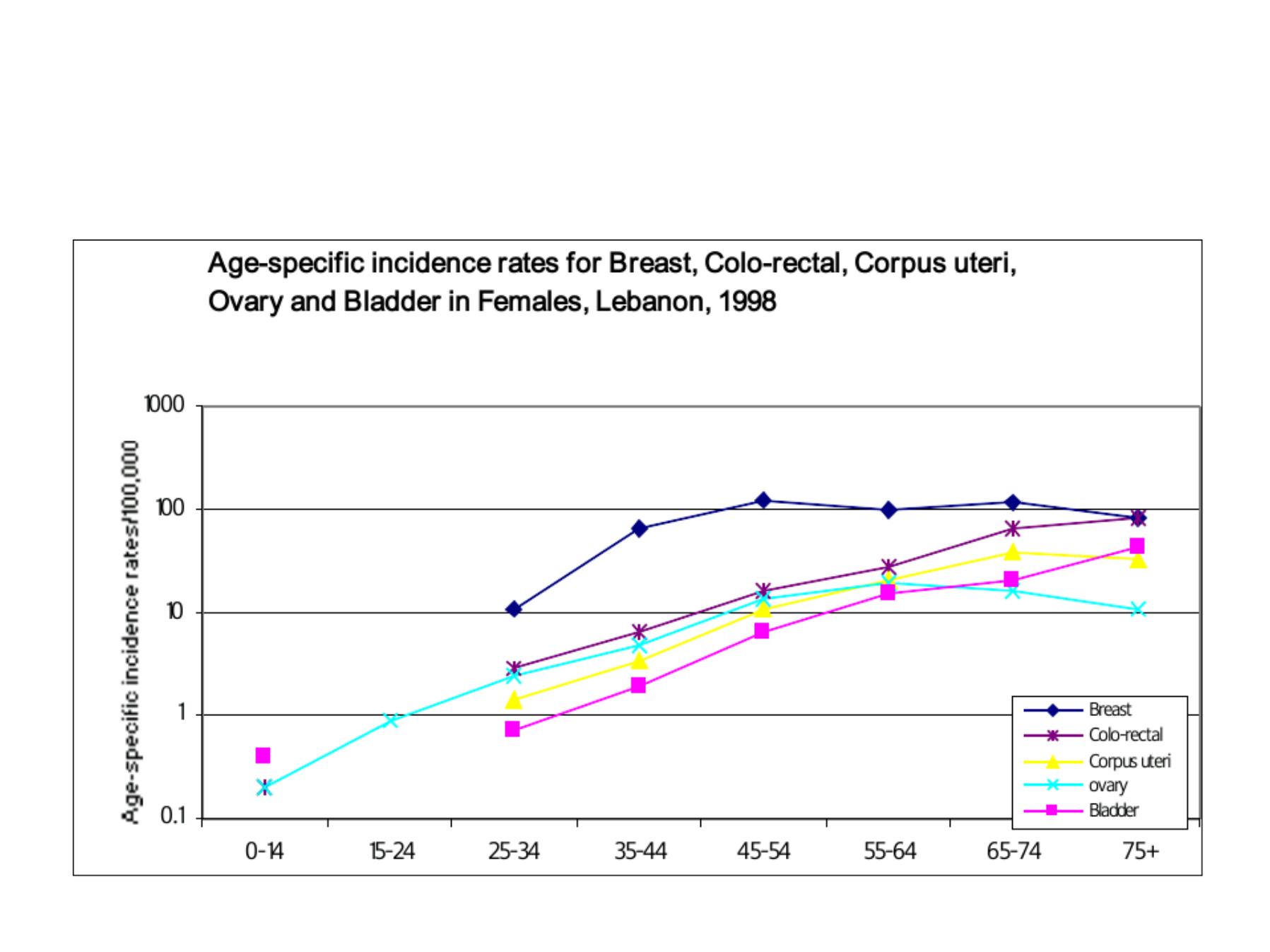
Descriptive epidemiology by
persons
:
an example of health status description
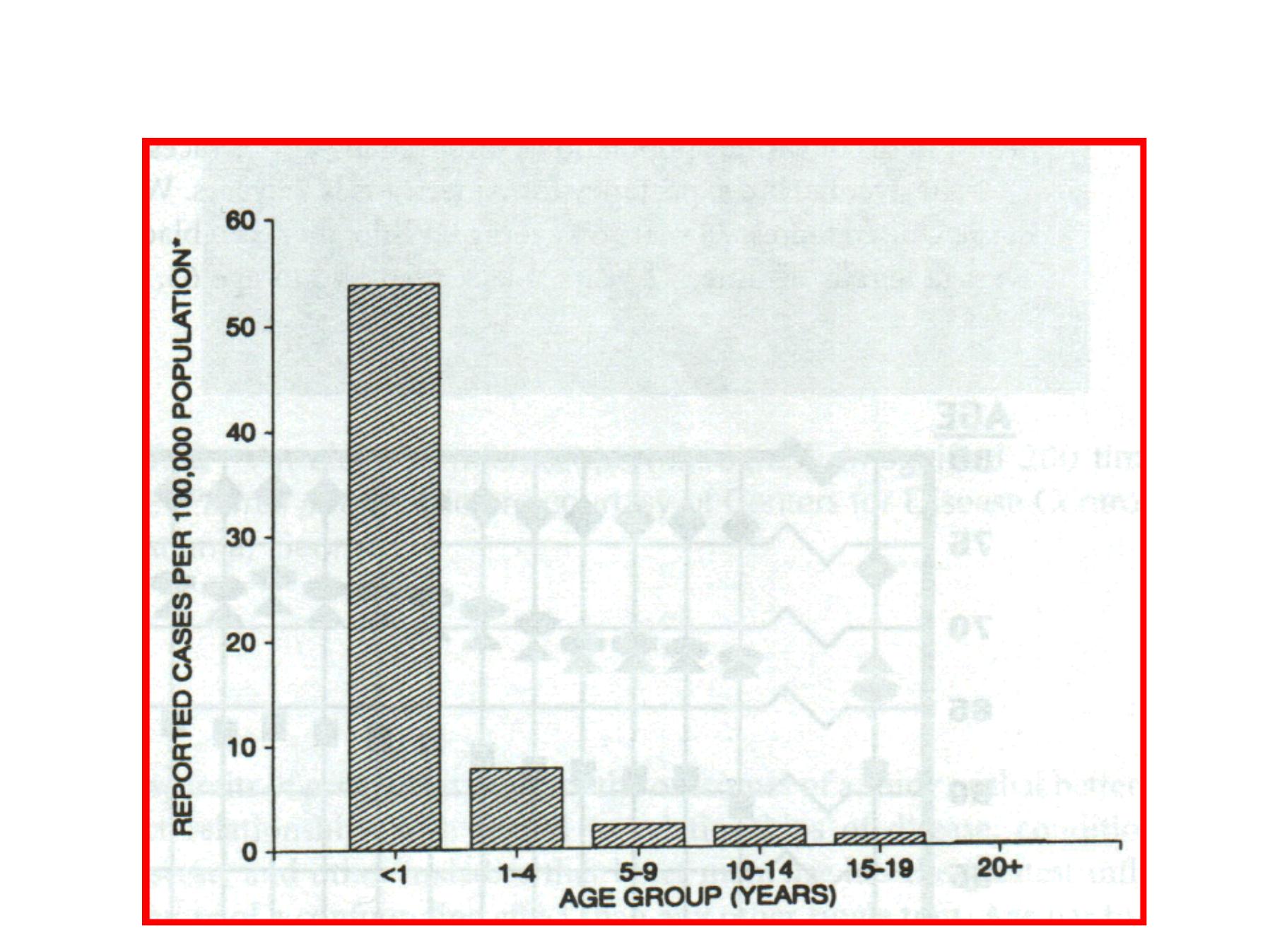
Age
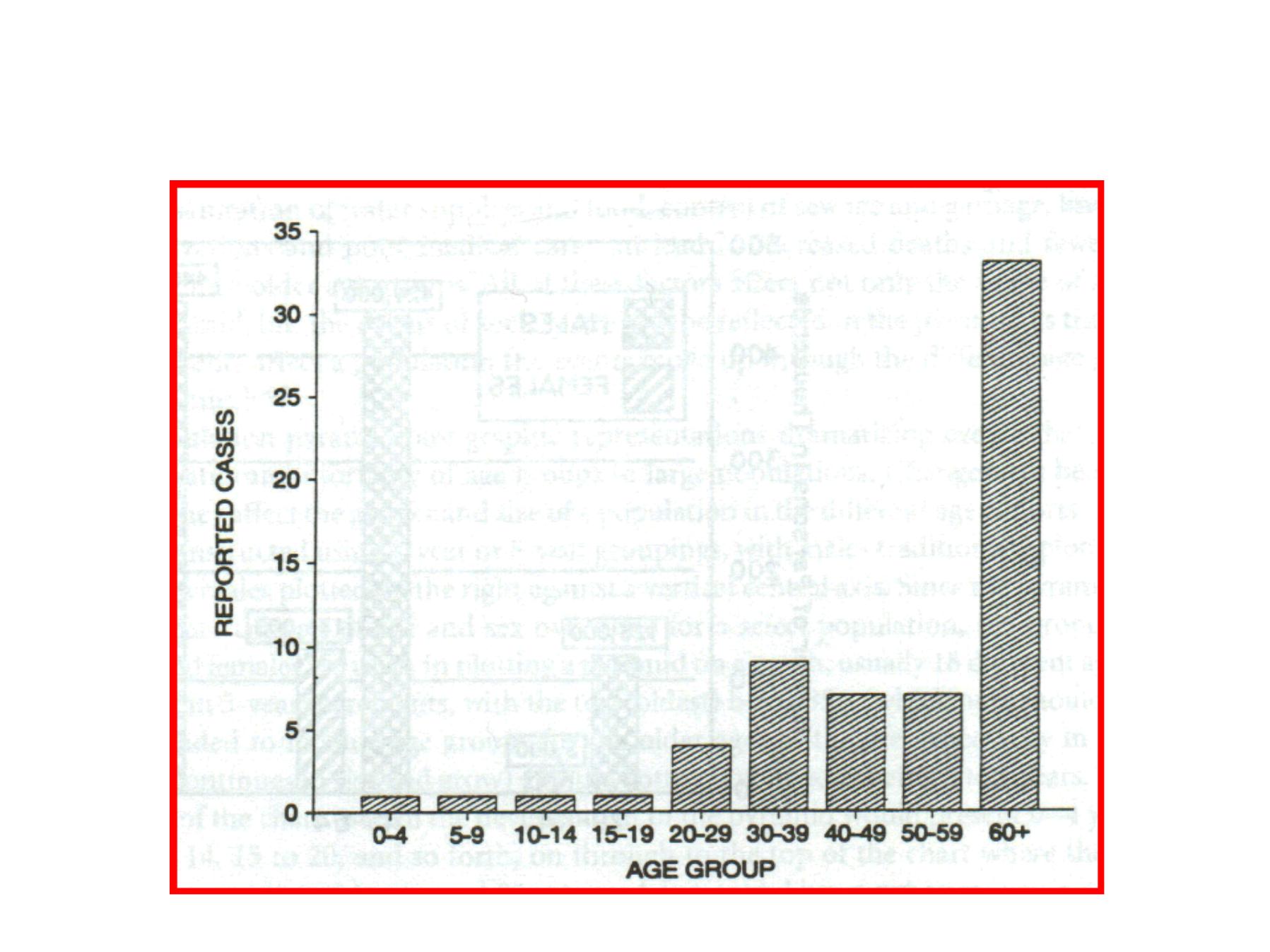
Age
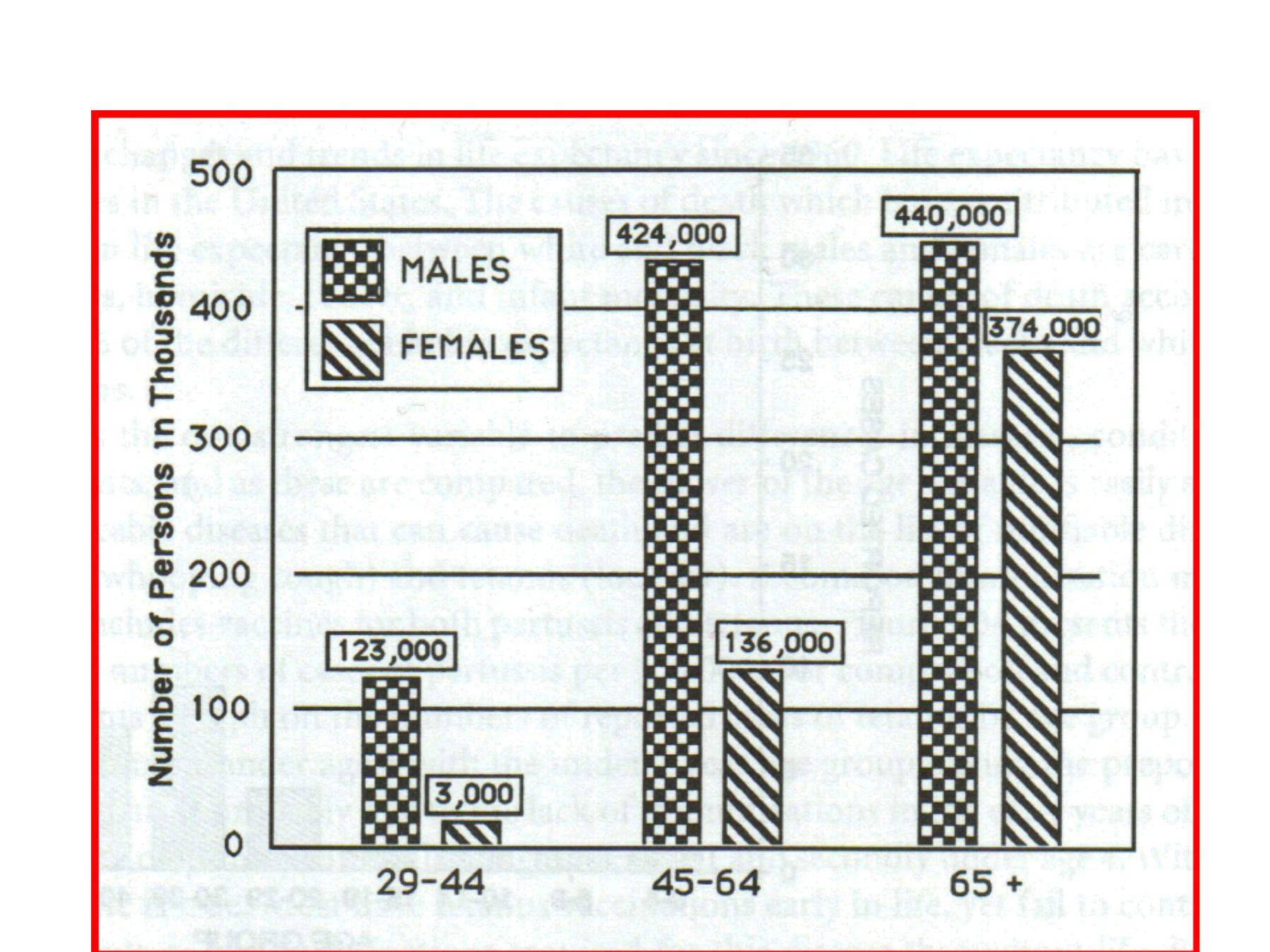
Sex

P
P
l
l
a
a
c
c
e
e
(
(
w
w
h
h
e
e
r
r
e
e
?
?
)
)
•International
•Variation within countries
- Urban-rural
- Local
•Building Maps
•Climate effects (temperature, humidity,
combined effects..)
•Relation to environmental exposure (water,
food supply, etc)
•Multiple clusters or one?

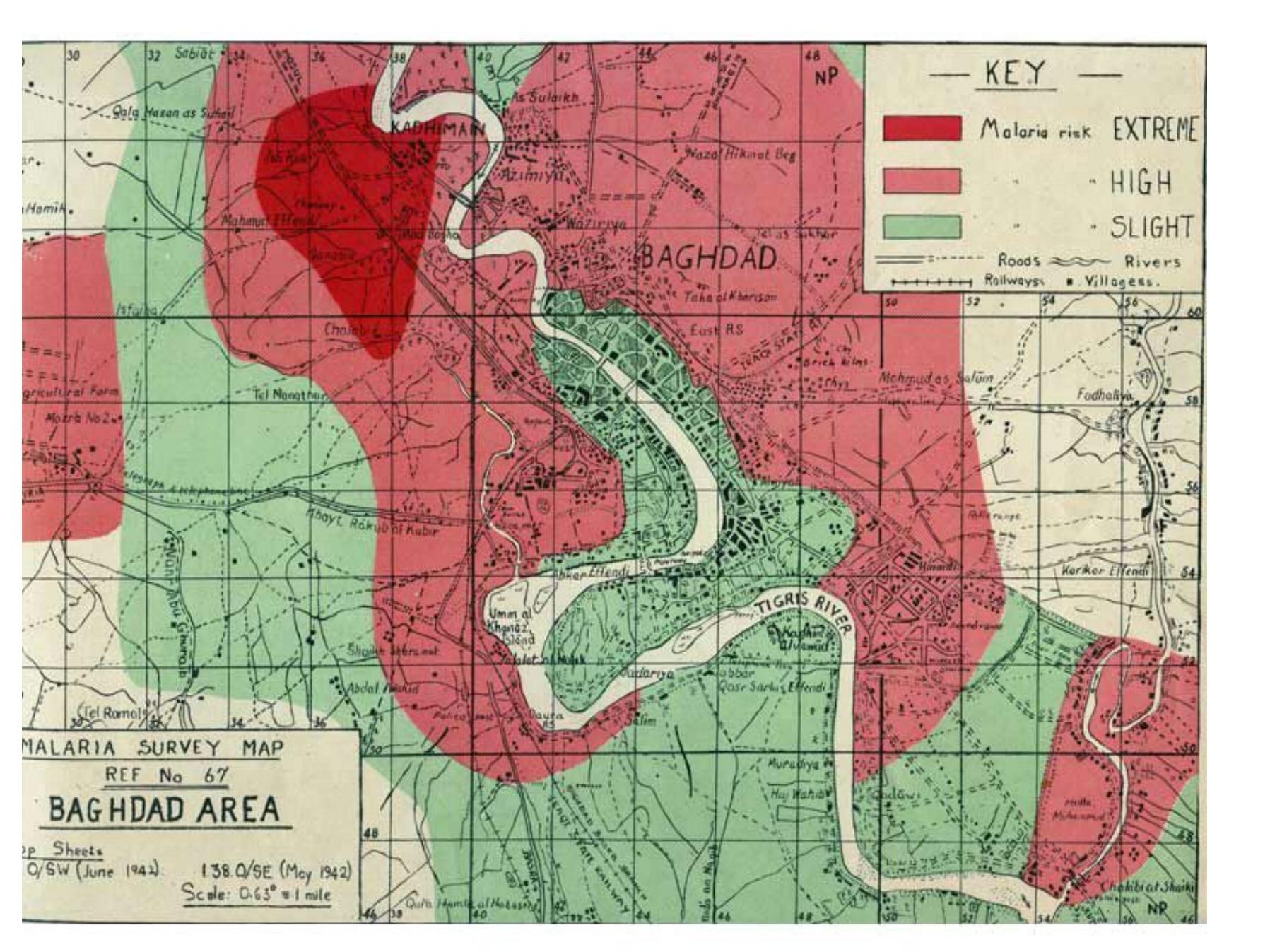
Building Maps

T
T
i
i
m
m
e
e
(
(
w
w
h
h
e
e
n
n
?
?
)
)
• Changing or stable?
• Clustered (epidemic) or evenly distributed (endemic)?
Time-trends:
• Secular change (long-term)
• Point epidemics (short-term), propagated
• Cyclic trends
• Seasonal variation
• combinations
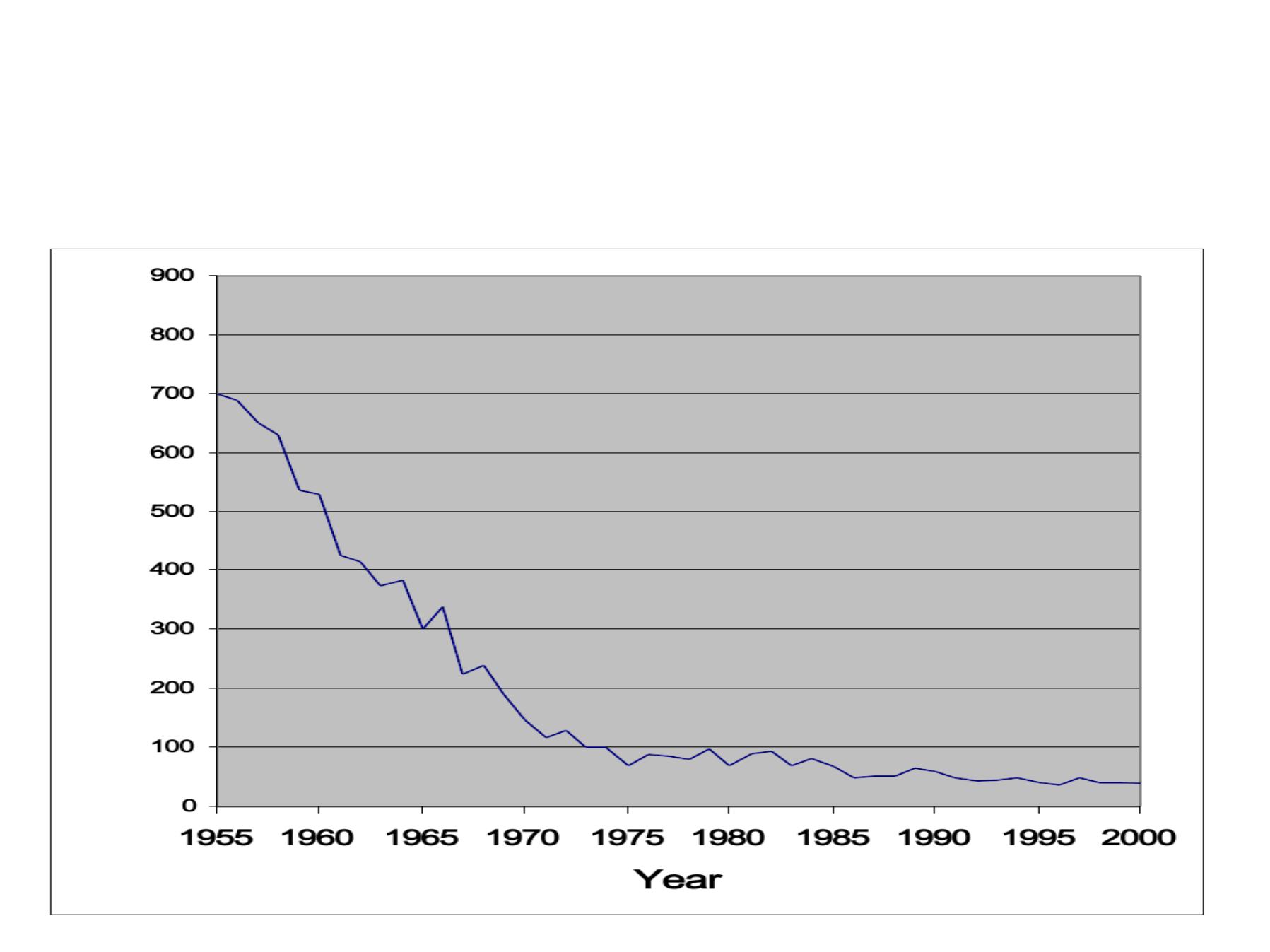
Secular Trend,
The long-time trend of disease occurrence
Tetanus –by year, USA, 1955-2000
During 2000, a total of 35 cases of tetanus were reported.
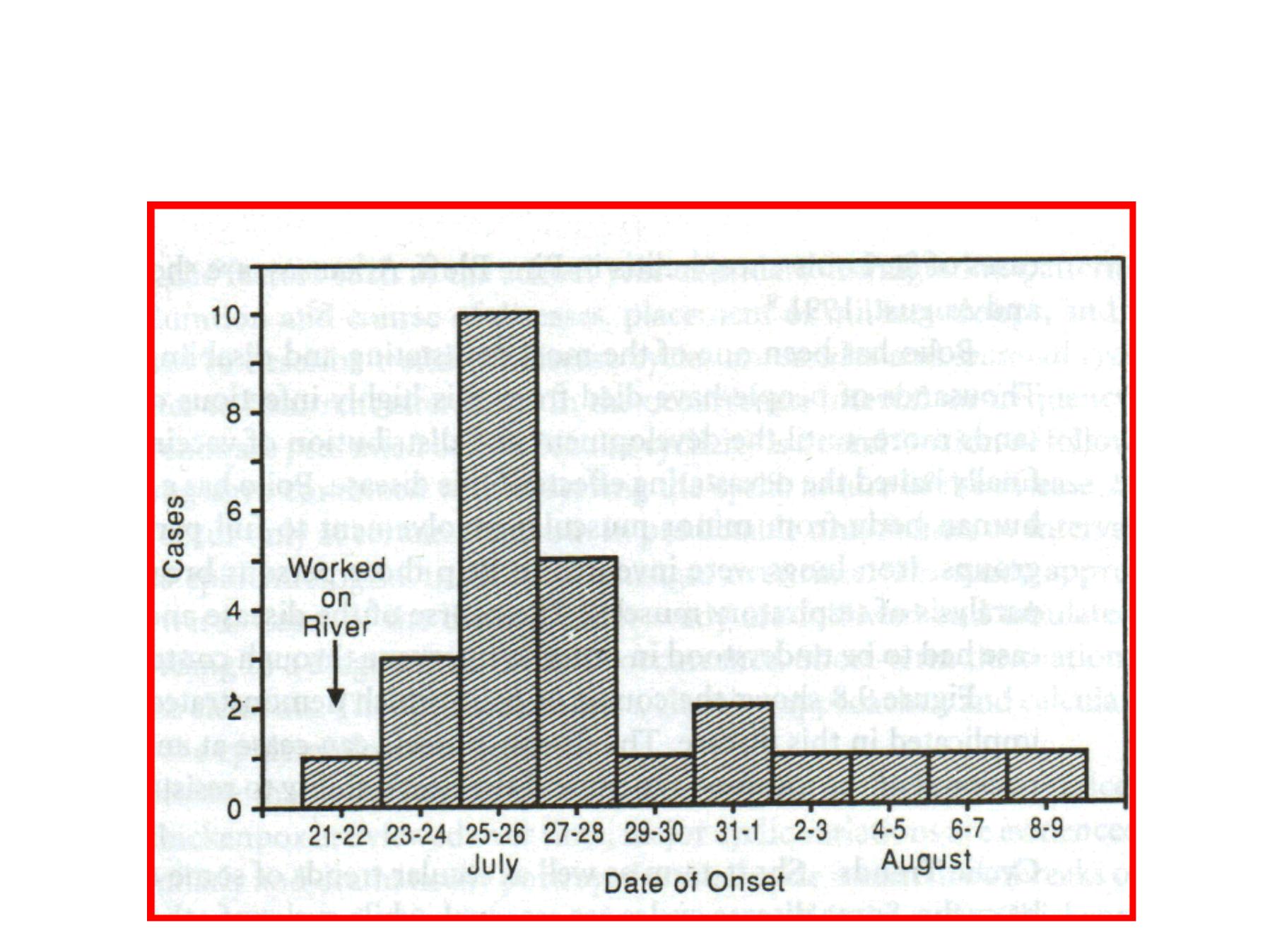
Point Epidemics
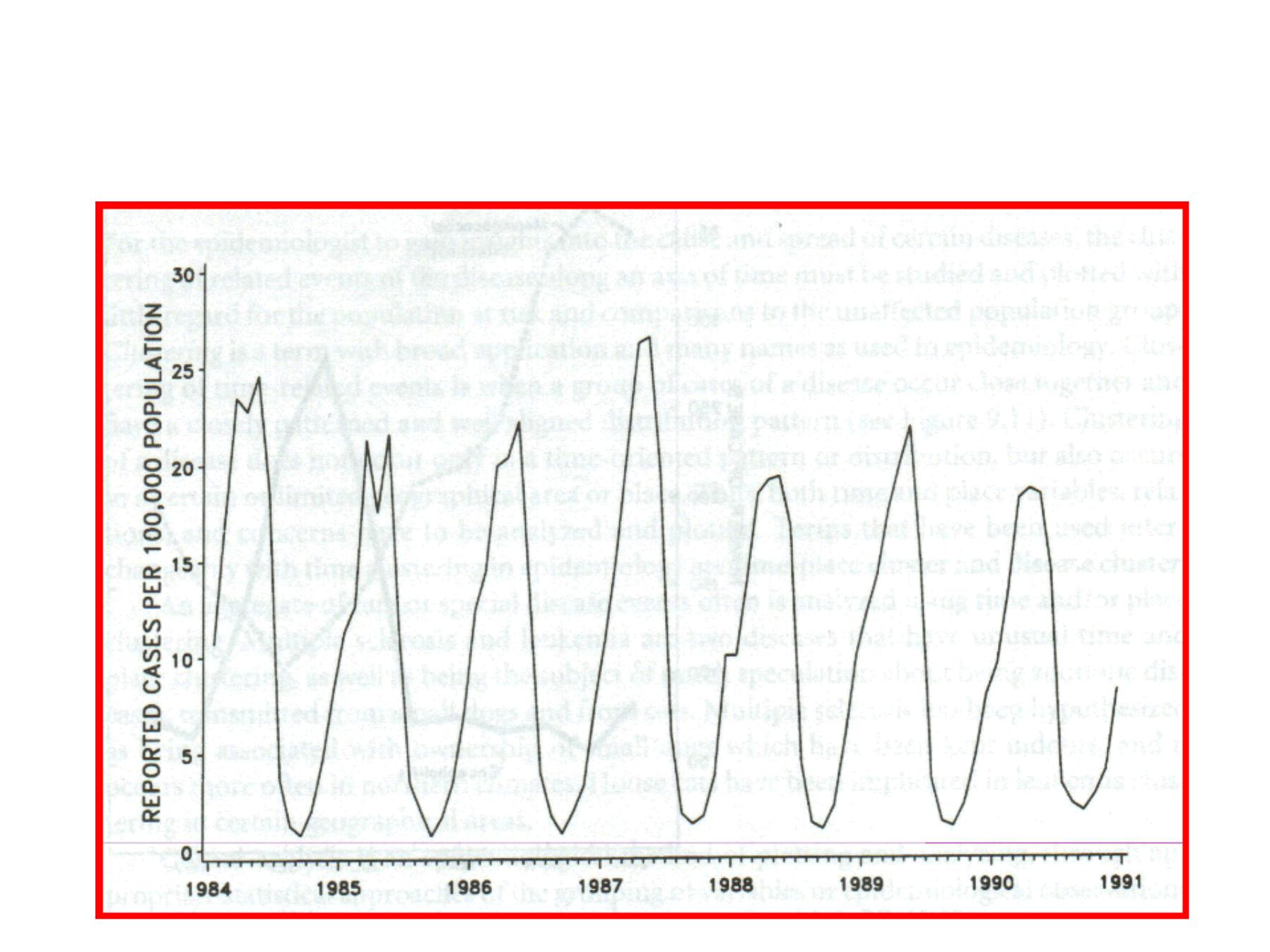
Cyclic Trends

Seasonal Variation

Seasonal
•A cyclic variation in disease frequency
by time of year & season.
Ø
Seasonal fluctuations in,
v
Environmental factors
v
Occupational activities
v
Recreational activities
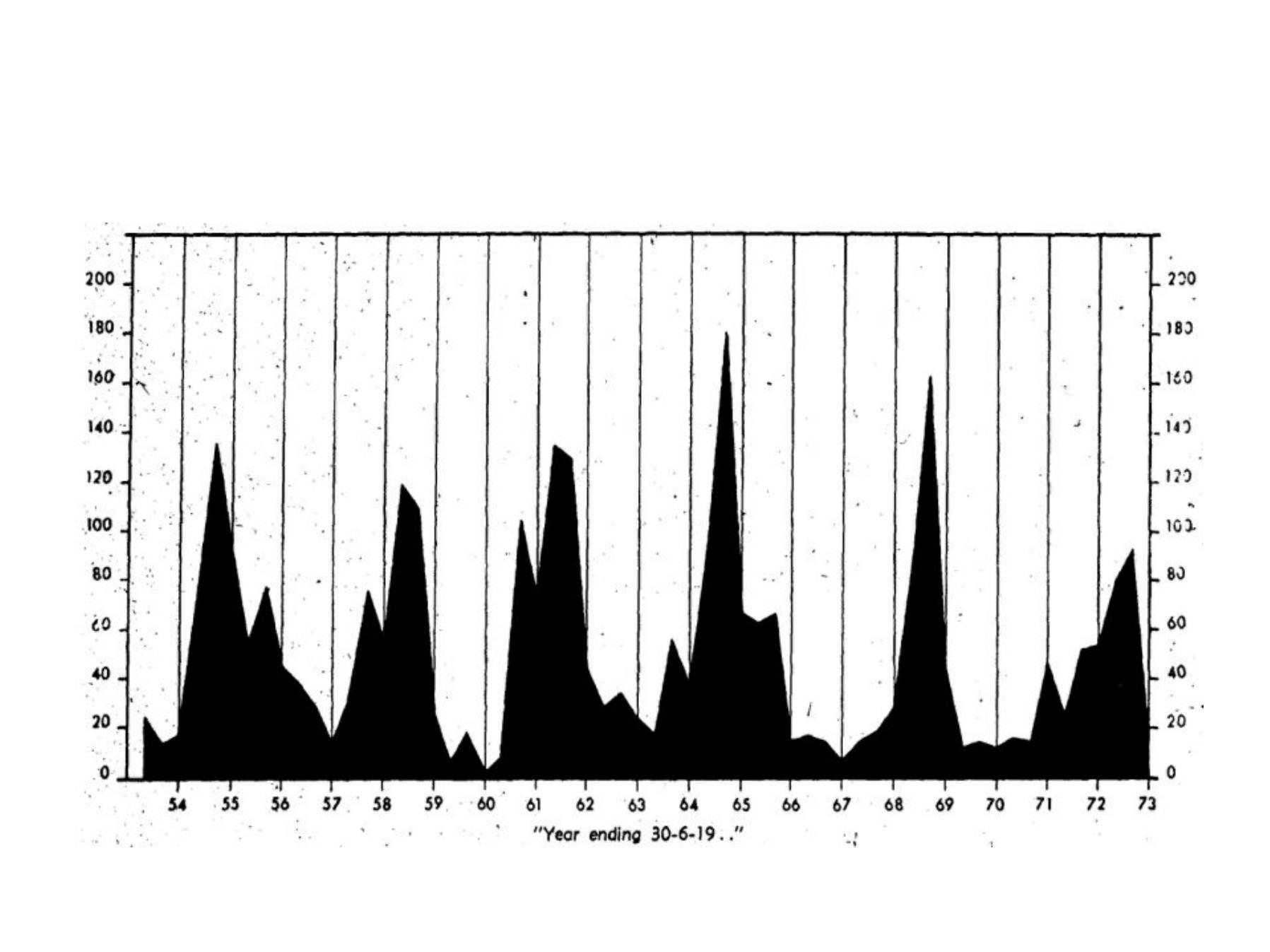
Whooping Cough - Four-monthly
admissions, 1954-1973
Descriptive epidemiology by
time
:
An example of health status description
Per 100,000
Leading causes of death in the US
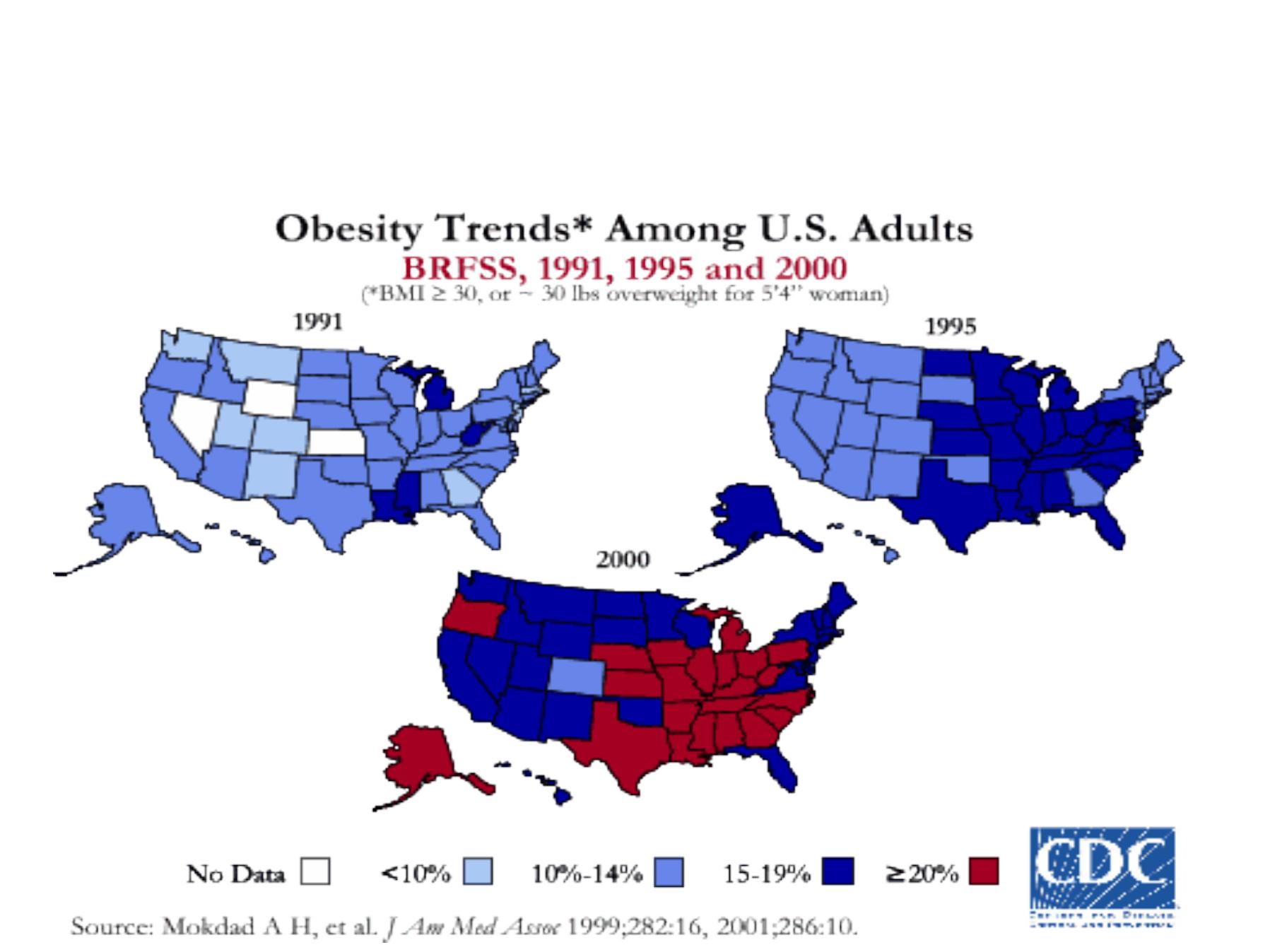
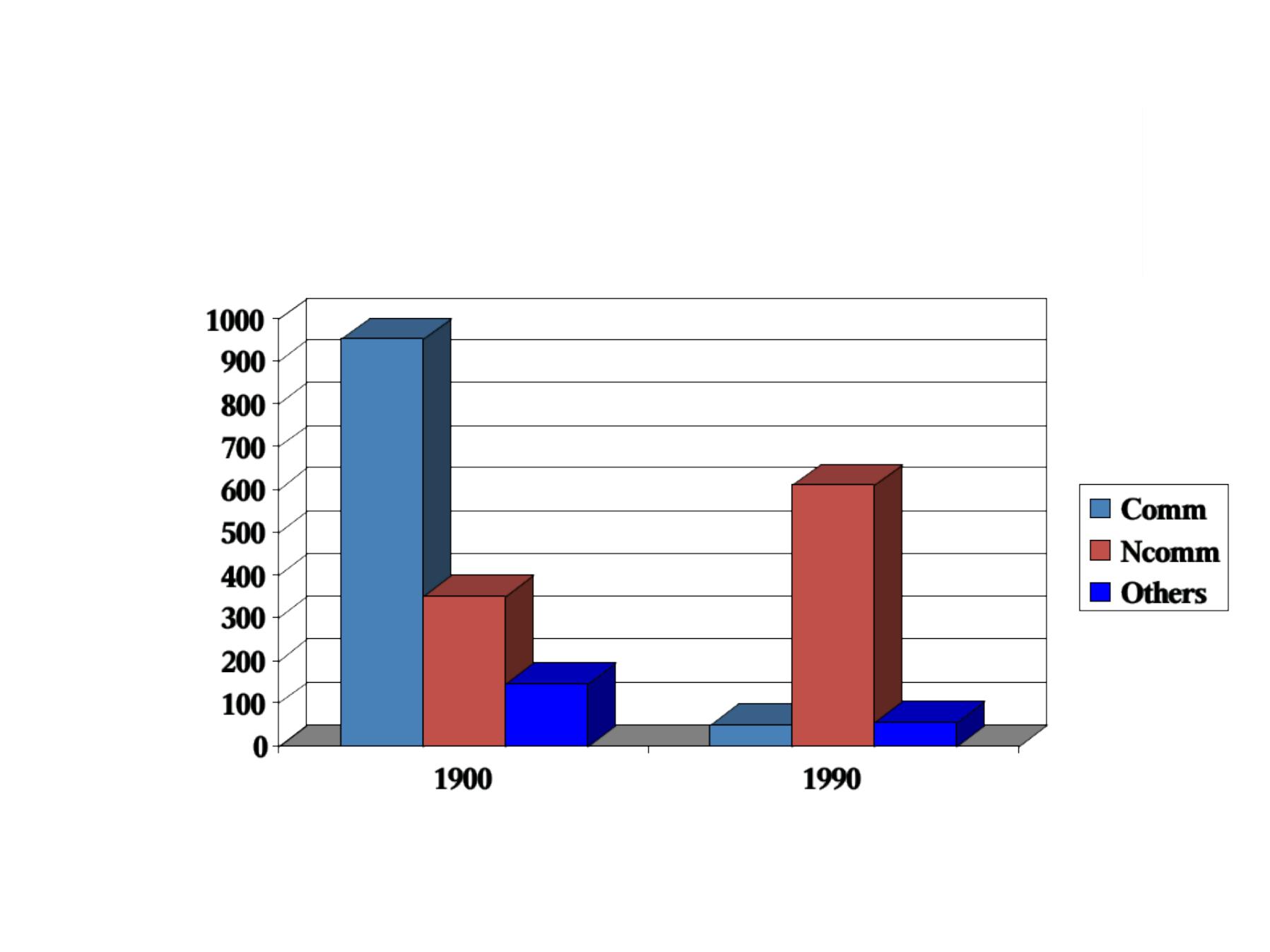
Descriptive epidemiology by
time and place
:
An example of health status description
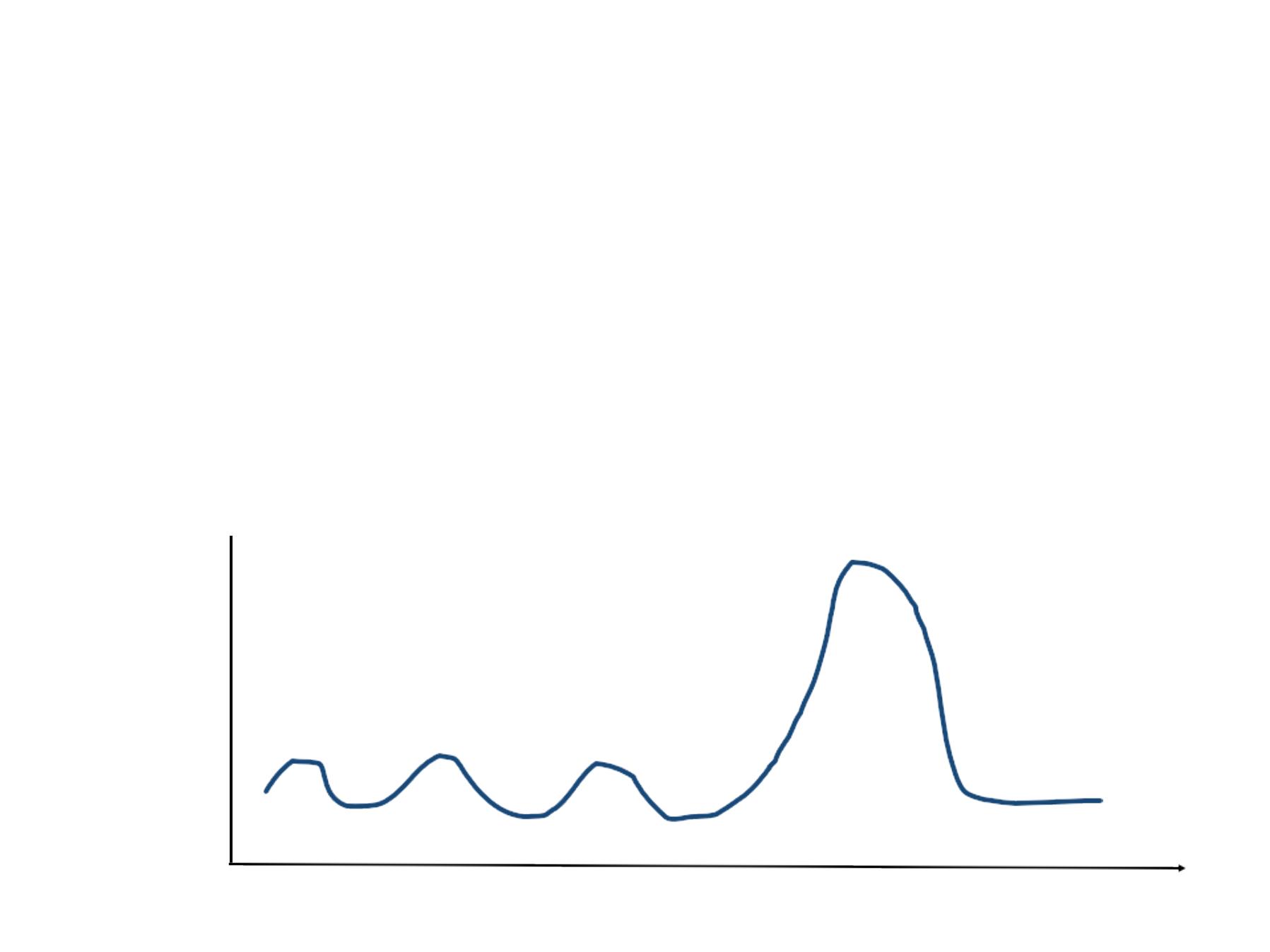
Endemic, Epidemic and Pandemic
• Endemic
- The habitual presence (or usual occurrence) of a
disease within a given geographic area
• Epidemic
- The occurrence of a disease clearly in
excess of normal expectancy, and generated
from a common or propagated source
• Pandemic
- A worldwide epidemic affecting an exceptionally
high proportion of the global population
Number
of Cases
of
Disease
Time
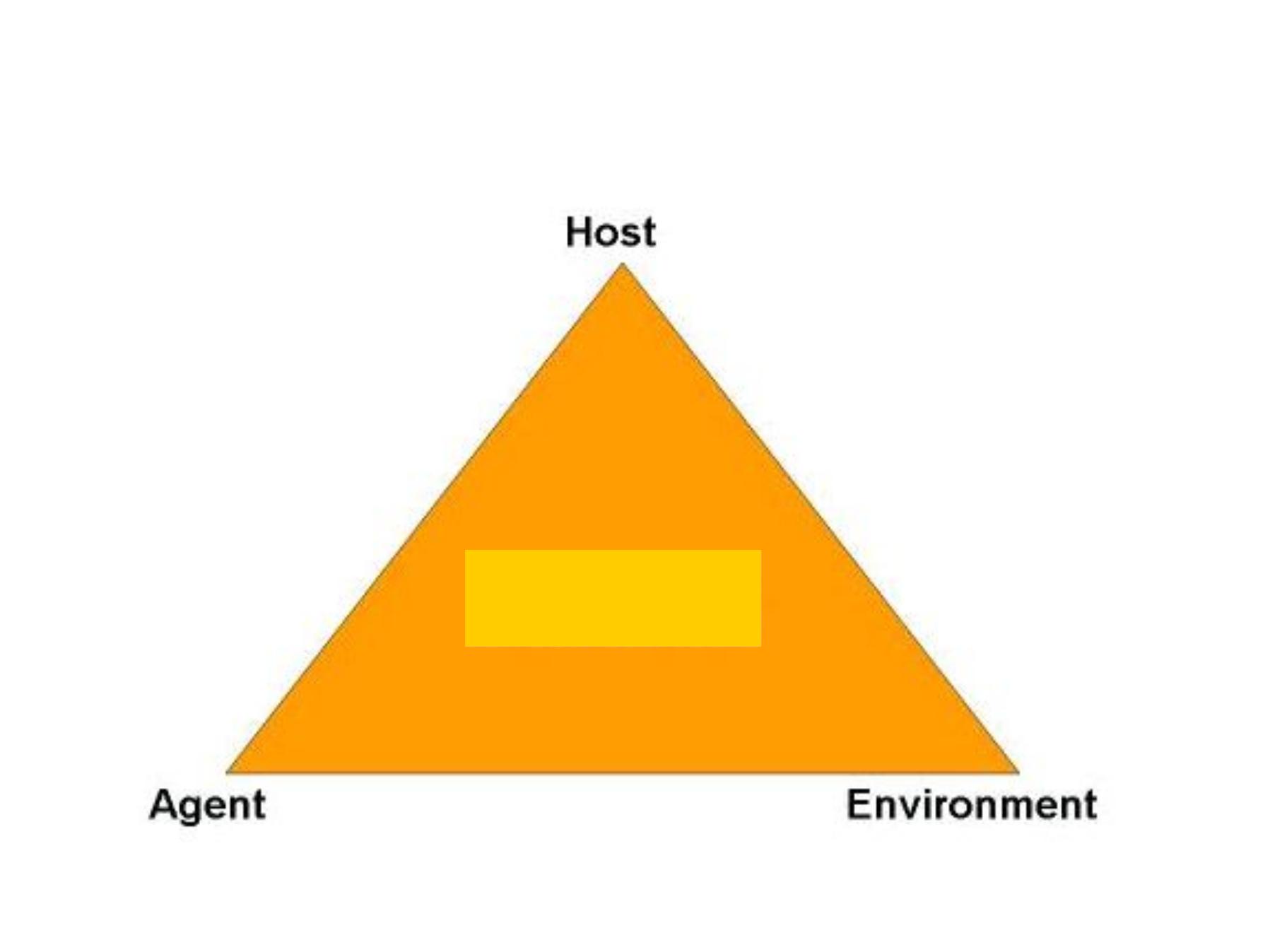
The Epidemiology Triangle
Time

Agents
•
Biological
(micro-organisms)
•
Physical
(temperature, radiation,
trauma, others)
•
Chemical
(acids, alkalis, poisons,
tobacco, others)
•
Environmental
(nutrients in diet,
allergens, others)
•
Psychological
experiences

H
H
o
o
s
s
t
t
F
F
a
a
c
c
t
t
o
o
r
r
s
s
•
Genetic endowment
•
Immunologic status
•
Personal characteristics
•
Personal behavior
•
Definitive versus intermediate
(in vector-borne diseases)

E
E
n
n
v
v
i
i
r
r
o
o
n
n
m
m
e
e
n
n
t
t
• Living conditions (housing, crowding, water supply,
sewage, etc)
• Physical: geography; atmosphere / climate
• Modes of communication: phenomena in the
environment that bring host and agent together, such
as: vector, vehicle, reservoir, etc)
• Biological: vectors, reservoirs of infection
• social: crowding, support
Environmental:
Crowding
Immunity
:
host factors
Tuberculosis
Microorganism:
the agent
An example of multiple causes of an infectious disease
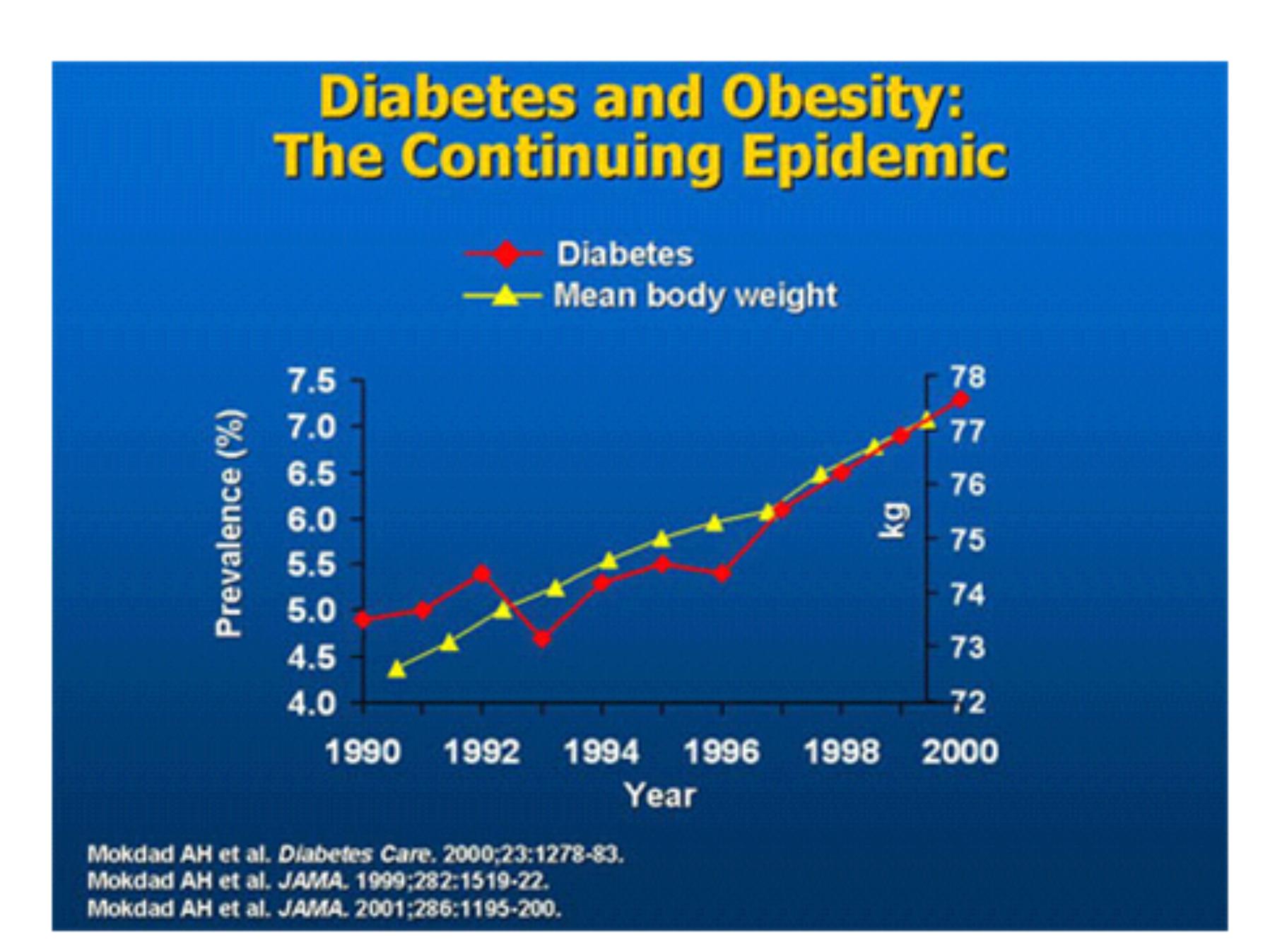
Genetics and obesity:
host factors
Diabetes mellitus
Nutrition:
the agent
An example of multiple causes of a chronic disease
E
n
v
ir
o
n
m
e
n
ta
l:
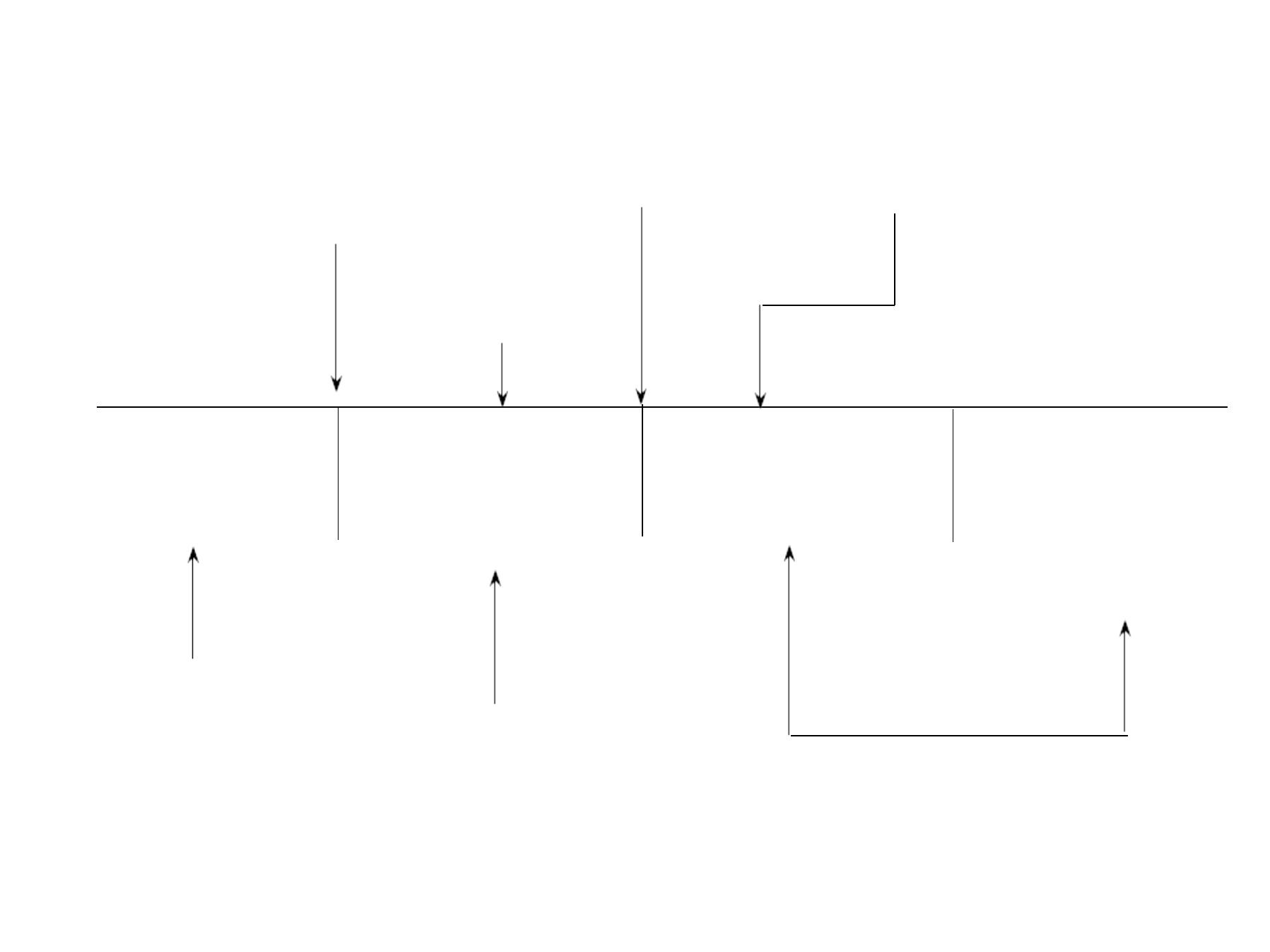
N
N
a
a
t
t
u
u
r
r
a
a
l
l
H
H
i
i
s
s
t
t
o
o
r
r
y
y
o
o
f
f
D
D
i
i
s
s
e
e
a
a
s
s
e
e
Stage of
susceptibility
Stage of
subclinical
disease
Stage of
clinical
disease
Stage of
recovery,
disability or
death
P
P
R
R
I
I
M
M
A
A
R
R
Y
Y
P
P
R
R
E
E
V
V
E
E
N
N
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
S
S
E
E
C
C
O
O
N
N
D
D
A
A
R
R
Y
Y
P
P
R
R
E
E
V
V
E
E
N
N
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
T
T
E
E
R
R
T
T
I
I
A
A
R
R
Y
Y
P
P
R
R
E
E
V
V
E
E
N
N
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
Exposure
Pathologic
changes
Onset of
symptoms
Usual time of
diagnosis
Natural History of Disease
STAGE 1:
Susceptibility
DESCRIPTION:
Risk factors which assist
the development of
disease exist, but disease
has not developed
EXAMPLE:
Smoking

Natural History of Disease (cont’
d)
STAGE 2:
Presymptomatic disease
DESCRIPTION:
Changes have occurred
to lead toward illness but
disease is not yet
clinically detectable
EXAMPLE:
Alveoli deteriorate

Natural History of Disease (cont’
d)
STAGE 3:
Clinical Disease
DESCRIPTION:
Detectable signs and/or
symptoms of disease exist
EXAMPLE:
Emphysema detected by
pulmonary function test

Natural History of Disease
(
(
c
c
o
o
n
n
t
t
’
’
d
d
)
)
STAGE 4:
Disability
DESCRIPTION:
Disease has progressed to
the point of causing a
residual effect
EXAMPLE:
Person has difficulty
breathing

Q?
