Nesif Al-Hemiary
Stress & Coping

What is stress ?
Not easy to define
The term is borrowed from physics
Is the response of individuals to the
circumstances and events, called
stressors, that threaten them and tax
their coping abilities.

Factors involved in stress
Biological factors
Personality factors
Cognitive factors
Environmental factors
Socio-cultural factors

Biological factors
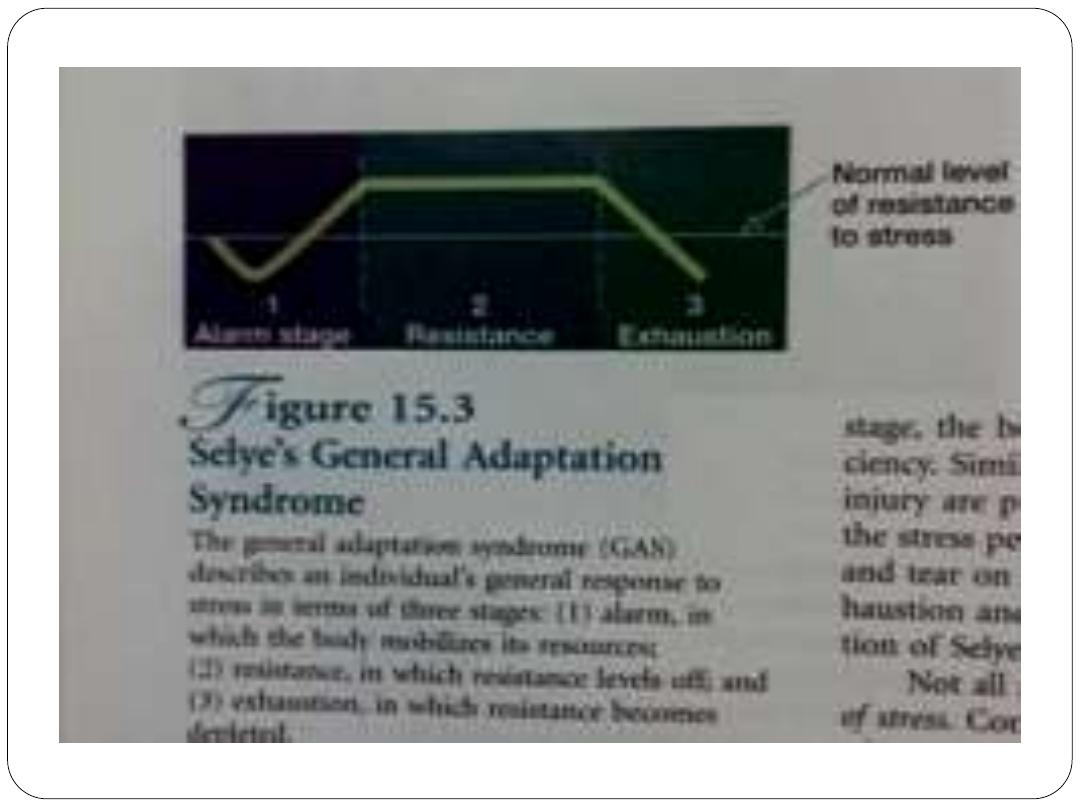
The general adaptation syndrome(GAS): Hans Selye
(1974,1983) , stress simply is the wear and tear on the body
due to the demands placed on it.
GAS is
Selye’s term for the common effects on the body
when demands are placed on it. It consists of three stages :
alarm , resistance, and exhaustion.
Alarm stage : temporary state of shock, a time when
resistance to illness and stress fall below normal limits. Body
quickly releases hormones which decreases immunity.
Resistance stage : a number of glands throughout the body
begin to manufacture different hormones that protect the
individual in many ways. So, the body can fight infections
and decrease inflammation.
Exhaustion stage : the all-out effort to combat stress fails
and the stress persists. The wear and tear on the body takes
its toll. Vulnerability to disease increases.

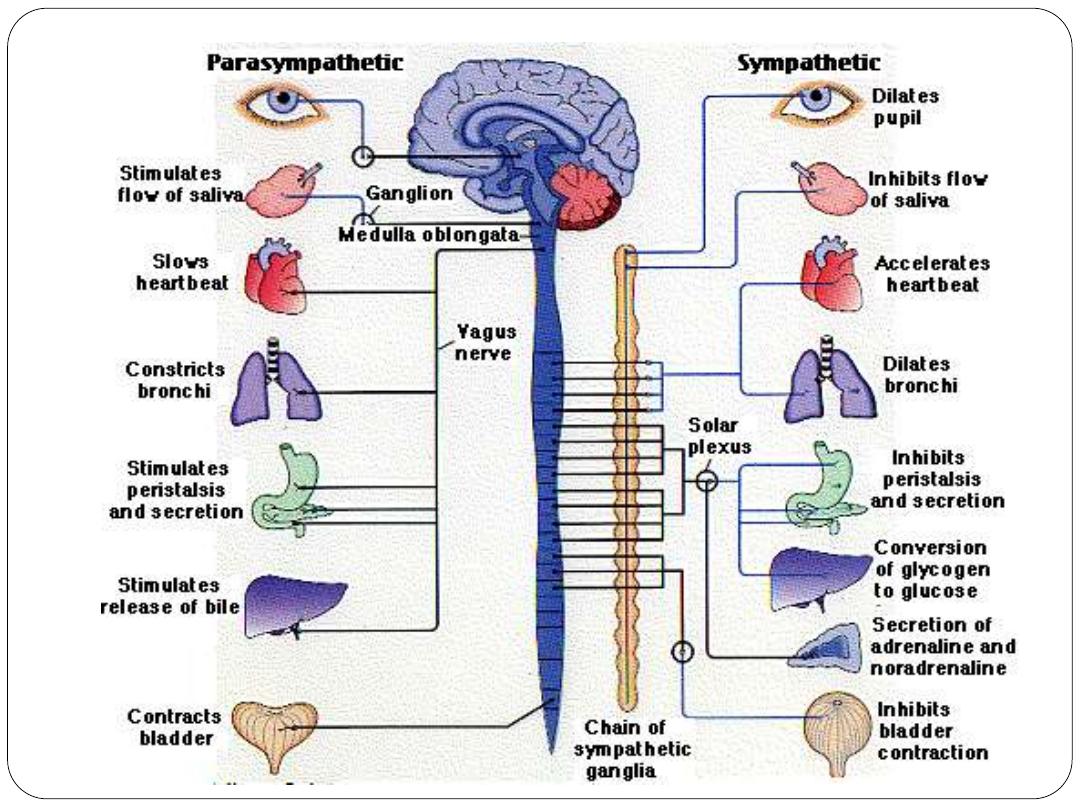
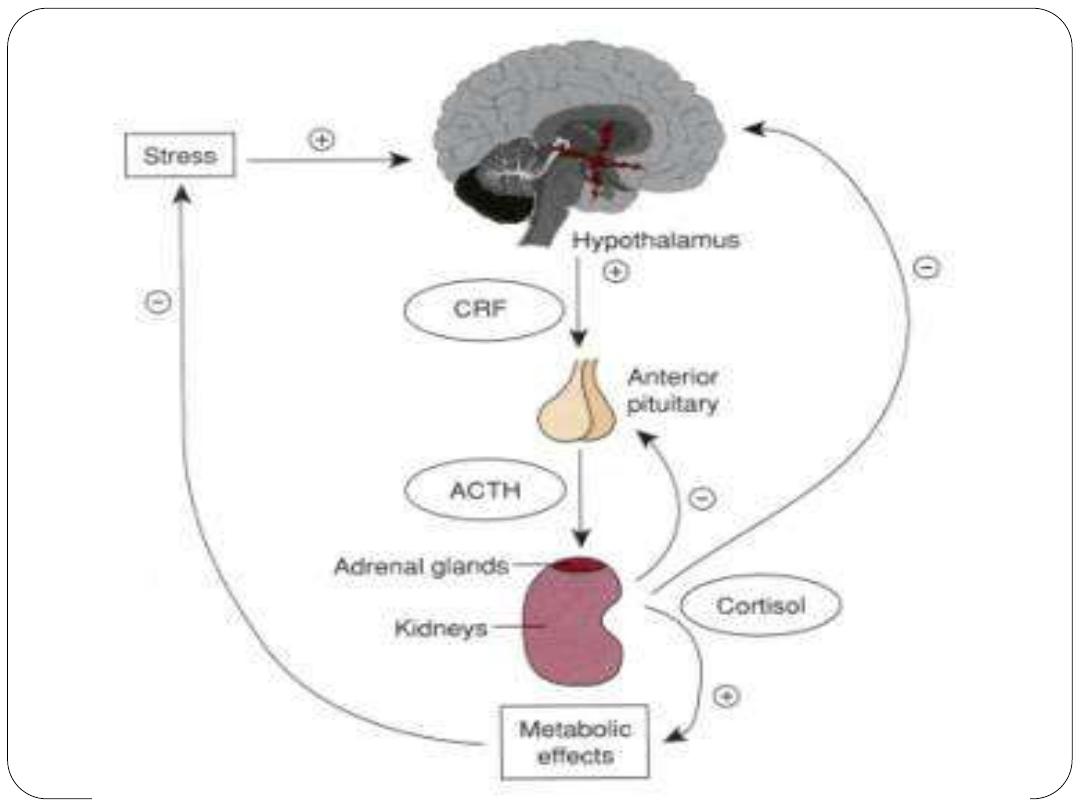
Two biological pathways to stress
The neuro-endocrine immune pathway:
hypothalamus --- pituitary ---adrenals---cortisol
The sympathetic system pathway: hypothalamus
--- autonomic nervous system(sympathetic) ---
adrenals ---epinephrine and norepinephrine

Think about these questions
Is all stress bad?
Are there positive features of
stress?
Eustress (normal stress) ?

Psychoneuroimmunology
The field that explores connections among
psychological factors( attitudes and emotions), the
nervous system, and the immune system.
CRH :corticotrophin releasing hormone, which is
produced by the hypothalamus, is a key hormone
shared by the nervous system and the immune system.
Connections between stress and immunity : by three
lines ;
1. acute stressors can produce immunological
changes to healthy individuals,
2. chronic stressors are associated with an increasing
downturn in immune system responsiveness ,rather
than adaptation,
3. bad quality of life decrease NK-cell ( natural killer),
these cells attack tumor cells.

Personality factors
Type A/Type B Behavioral patterns : Friedman &
Rosenman 1974.
Type A: excessively competitive, hard-driven,
impatient, and hostile.
Increased risk of heart disease
–
later research found that only hostility and anger are
linked to CHD (hot reactors)
Type B: relaxed and easygoing.
Hardiness : personality style characterized by a sense
of commitment, control, and a perception of problems
as challenges(the 3 Cs
–commitment , control, and
challenge). People with this personality are less prone
to stress and hence illness
Social support and exercise can buffer stress and
decrease its effects

Cognitive factors
To some degree, what is stressful depends on
how people cognitively appraise and interpret
events.
Cognitive appraisal (Lazarus 1993
): individual’s
interpretation of events in their lives as harmful,
threatening, or challenging , and their
determination of whether they have the resources
to effectively cope with the events.
Primary appraisal: whether an event involves
harm or loss that has already occurred , a threat
of some future danger, or a challenge to be
overcome.
Secondary appraisal: evaluate their resources
and determine how effectively they can be used
to cope with the event.

Environmental Factors
Overload ,conflicts , and
frustration
Life events and daily
hassles

Sociocultural factors
Acculturative stress: refers to the
negative consequences that results
from contact between two
distinctive cultural groups.
Poverty : many consequences like
poor housing, dangerous
neighborhood, burdensome
responsibilities, and economic
uncertainties.

COPING
Coping involves managing taxing
circumstances , expending
efforts to solve life’s problems,
and seeking to master or reduce
stress.
A stressful circumstance is
rendered considerably less
stressful when a person
successfully copes with it.

Ways of coping
Problem-focused coping and
emotion-focused coping
Optimism and positive thinking
Self-efficacy
Social support
Assertive behavior
Stress management
Multiple coping strategies

Problem-focused and emotional-focused
coping
Problem-focused coping involves
squarely facing one’s troubles and
trying to solve them
Emotional-focused coping consists
of responding to stress in an
emotional manner , especially using
defensive appraisal
Problem-focused coping is usually
the better coping strategy

Promoting health
Regular exercise
Proper nutrition
Not smoking
Sound sexual decision making :
sexual knowledge,
contraception, avoidance of
sexually transmitted diseases.
