
Adrenal Gland

Adrenal cortex - Tumors
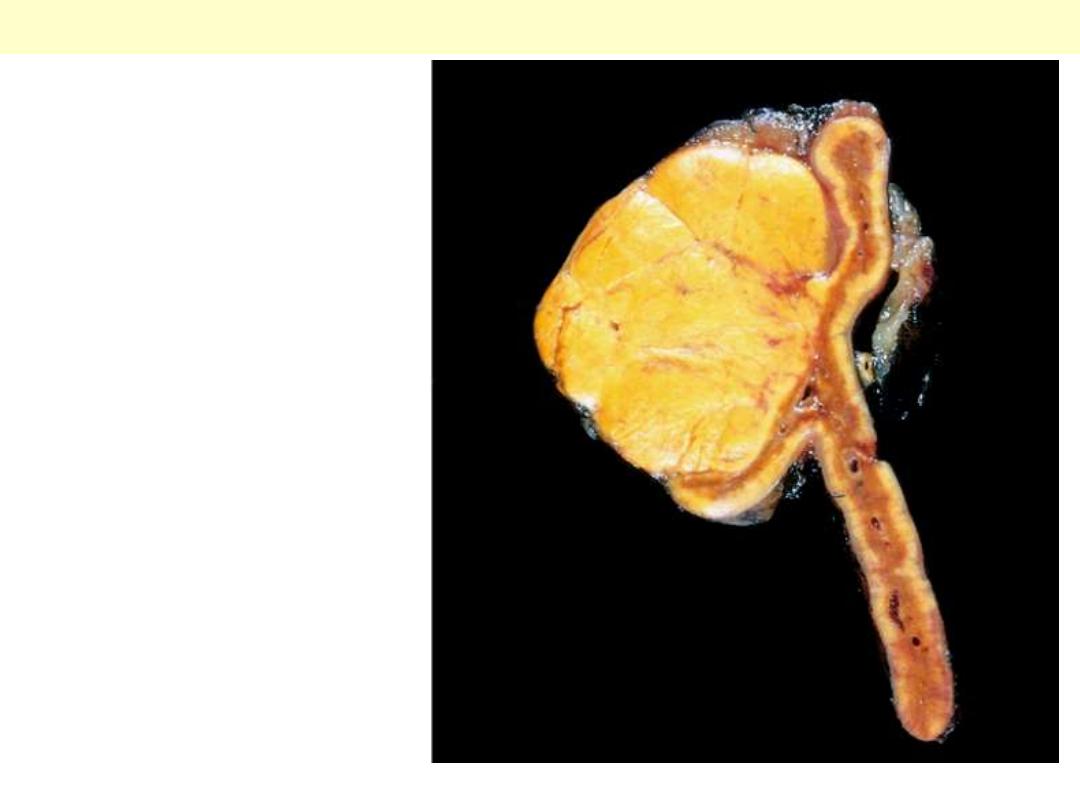
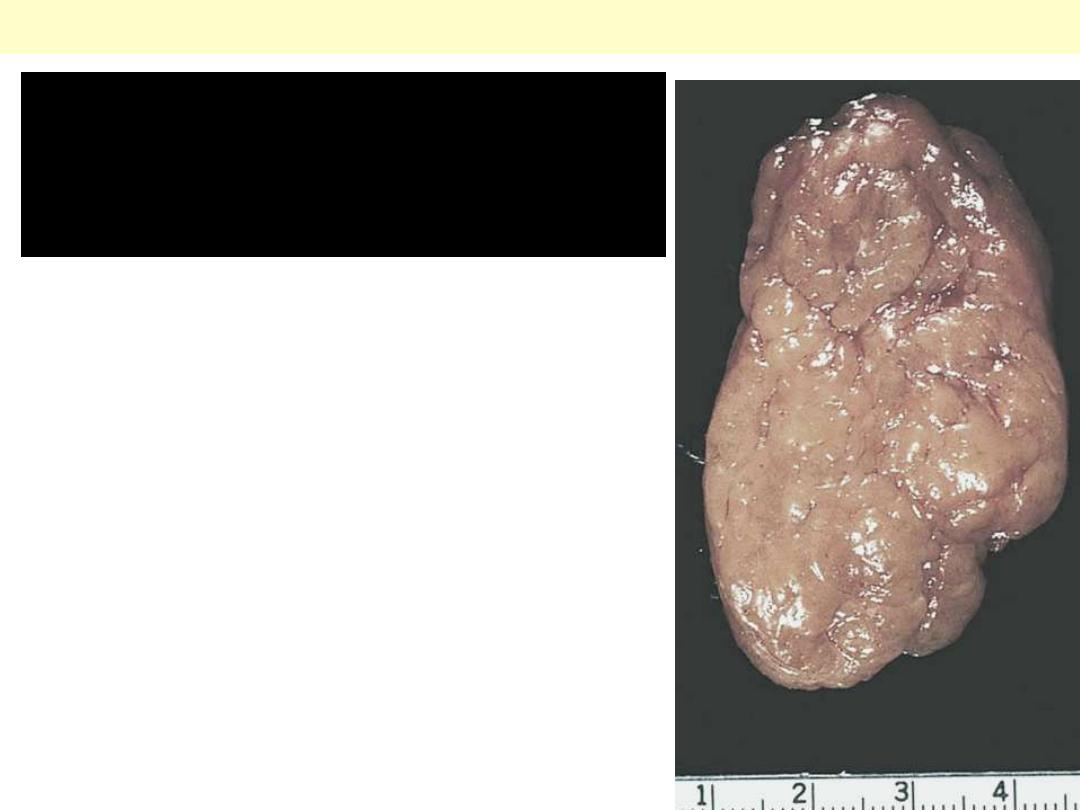
The adenoma is
distinguished from
nodular hyperplasia by
its solitary,
circumscribed nature.
The functional status of
an adrenocortical
adenoma cannot be
predicted from its gross
or microscopic
appearance.
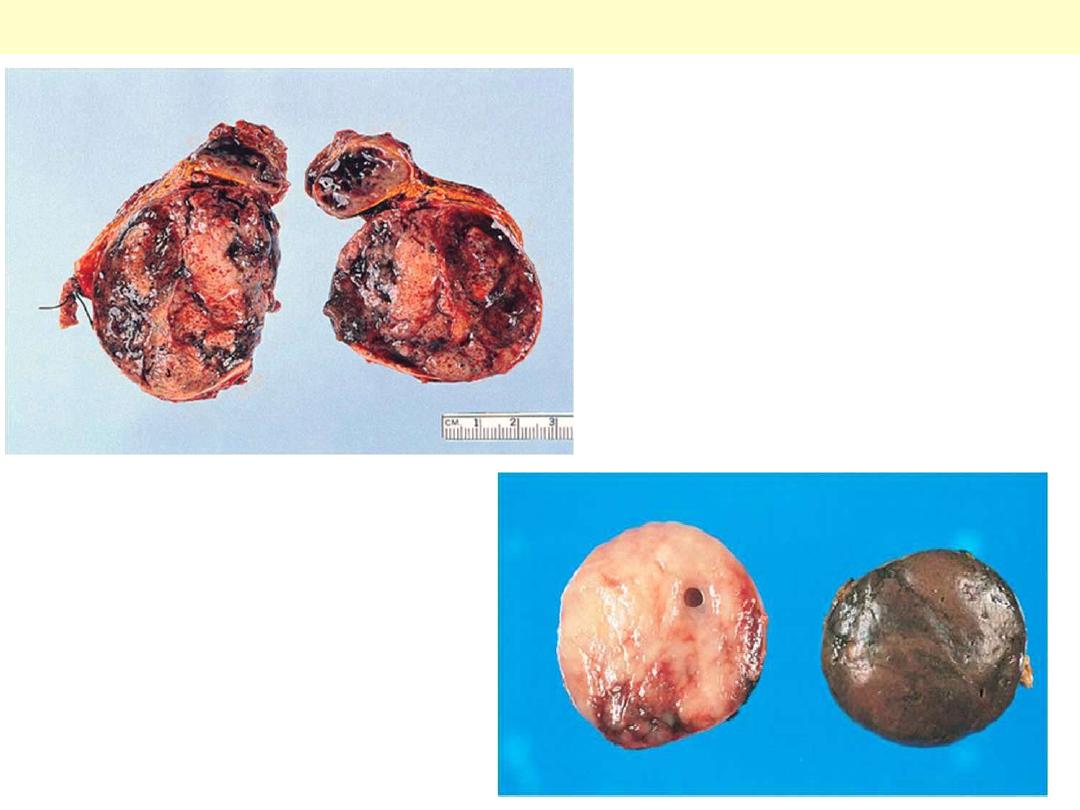
Adrenocortical adenoma
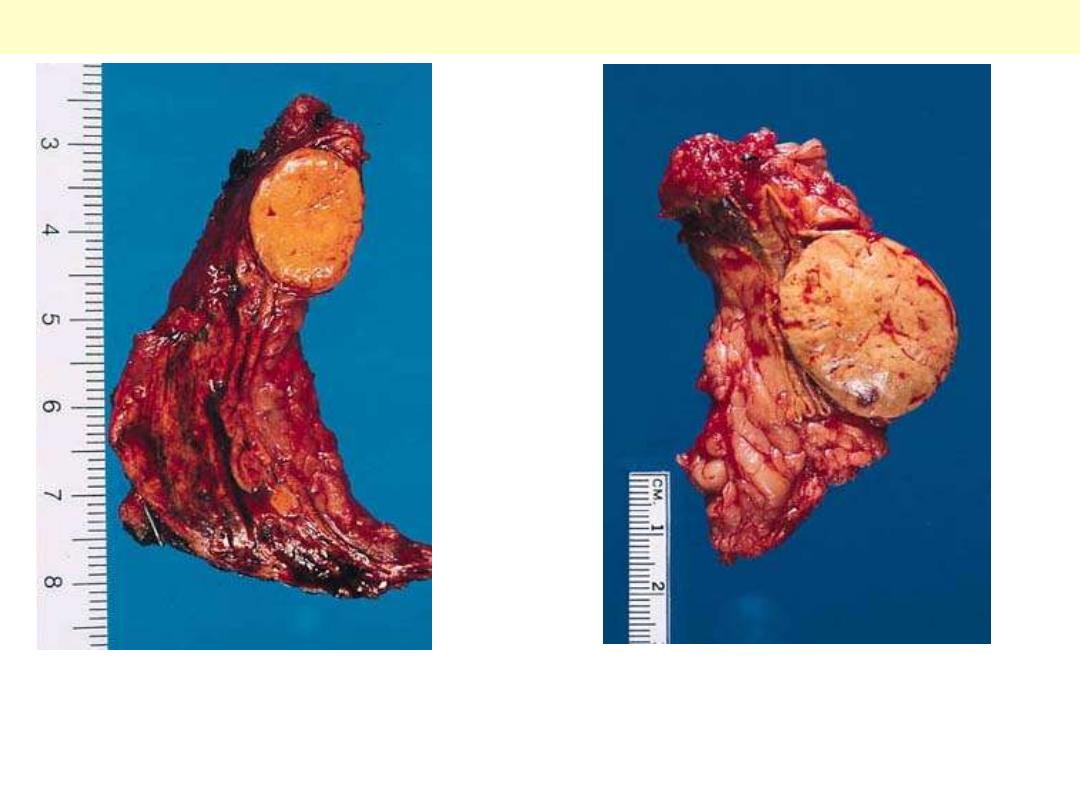
A and B: Adrenal cortical adenoma. Both tumors are well
circumscribed, of homogeneous appearance, without hemorrhage or
necrosis. They are typically golden yellow in color
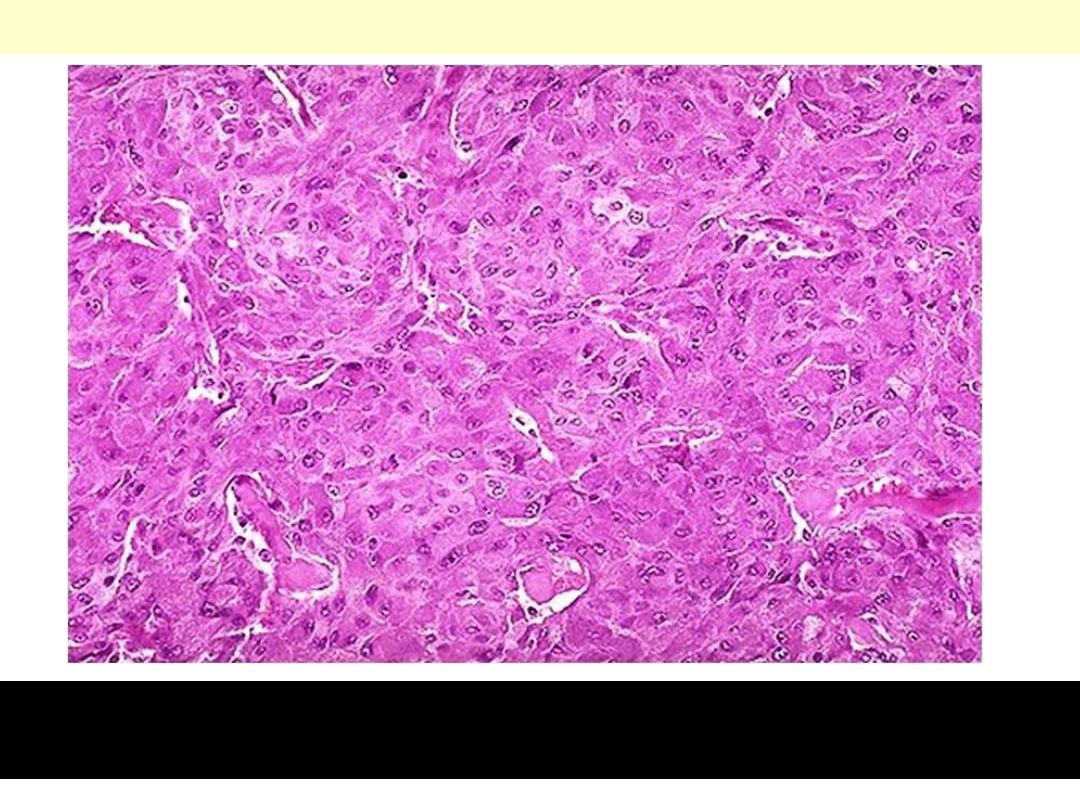
Adrenocortical adenoma
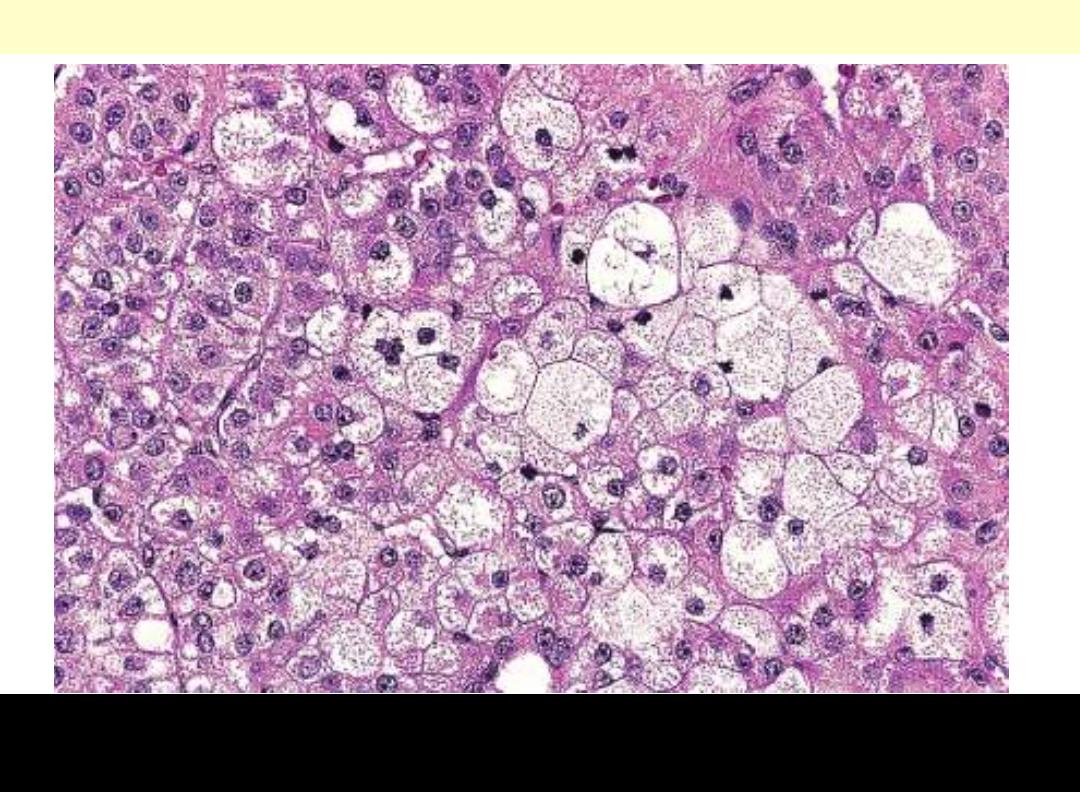
The tumor shows numerous lipid-laden clear cells similar to those of
the normal fasciculata layer.
Adrenal cortical adenoma
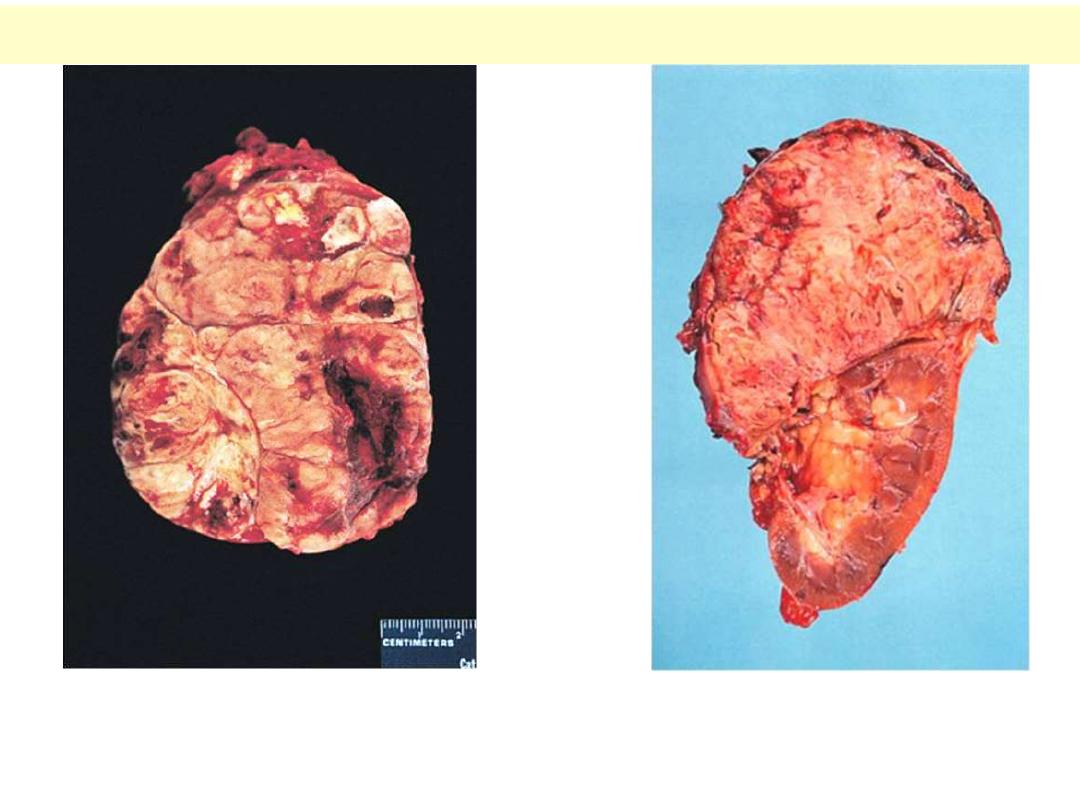
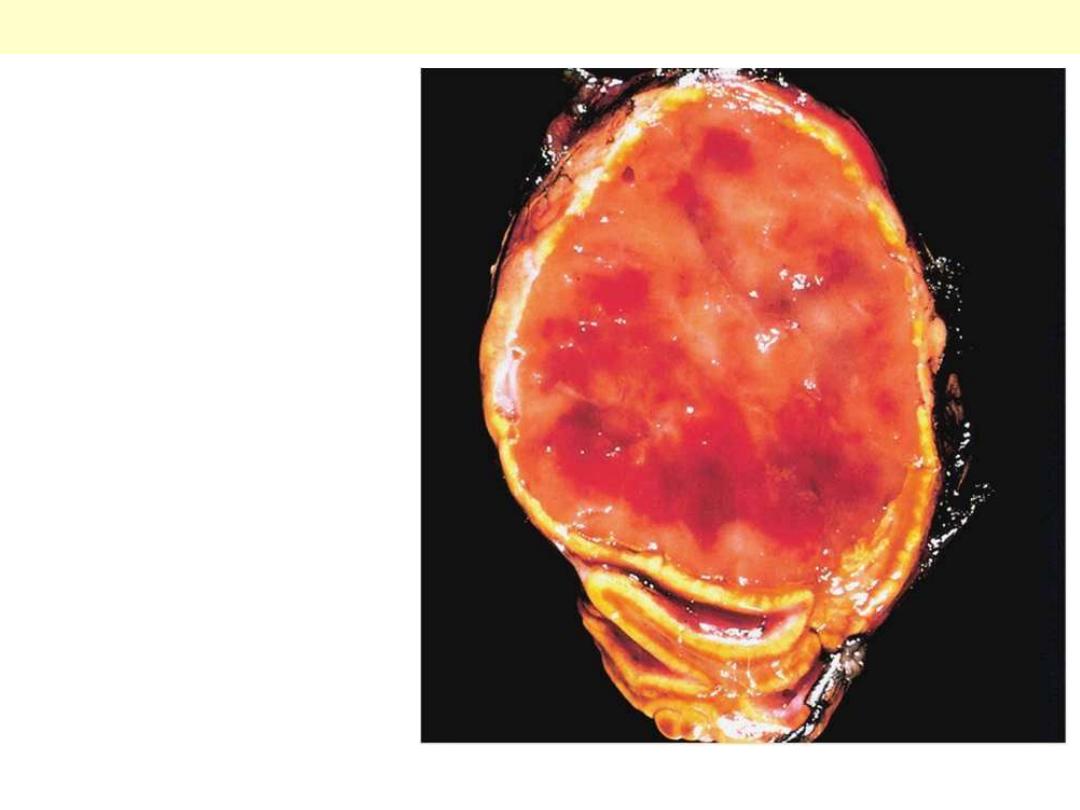
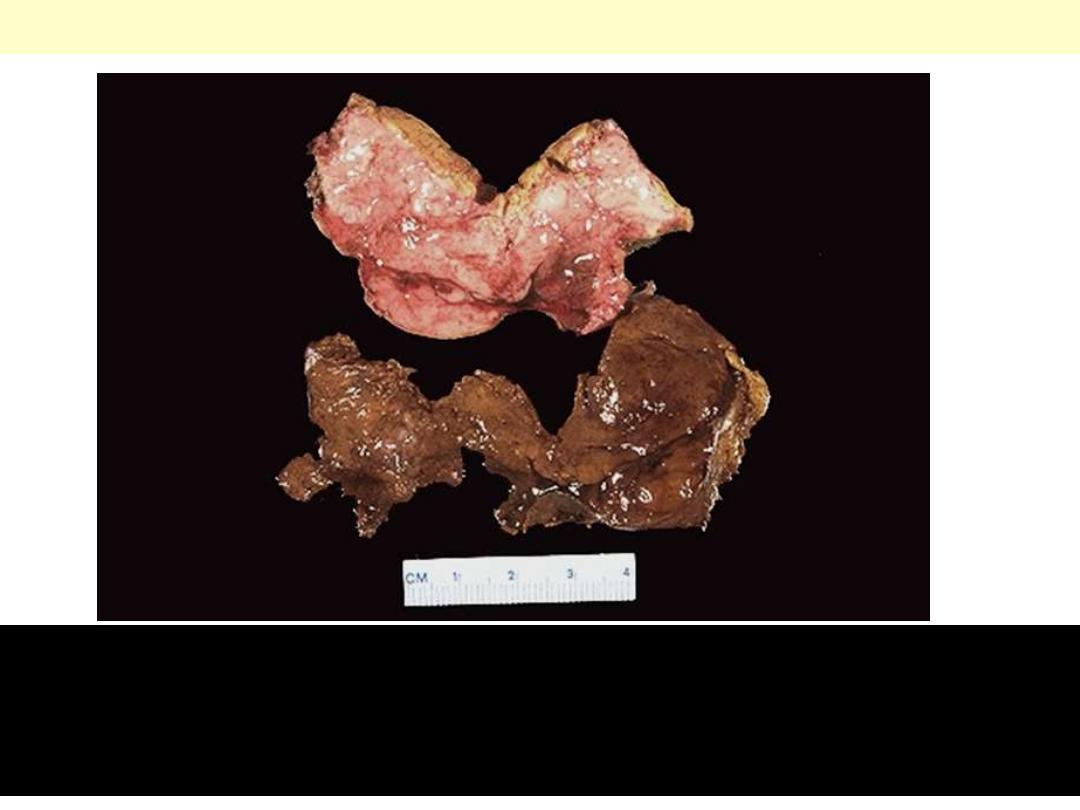
Adrenal cortical carcinoma
A large tumor that exhibits areas
of hemorrhage and necrosis.
A large tumor that exhibits areas of
hemorrhage and necrosis. The tumor shown
here has destroyed the upper pole of the kidney.
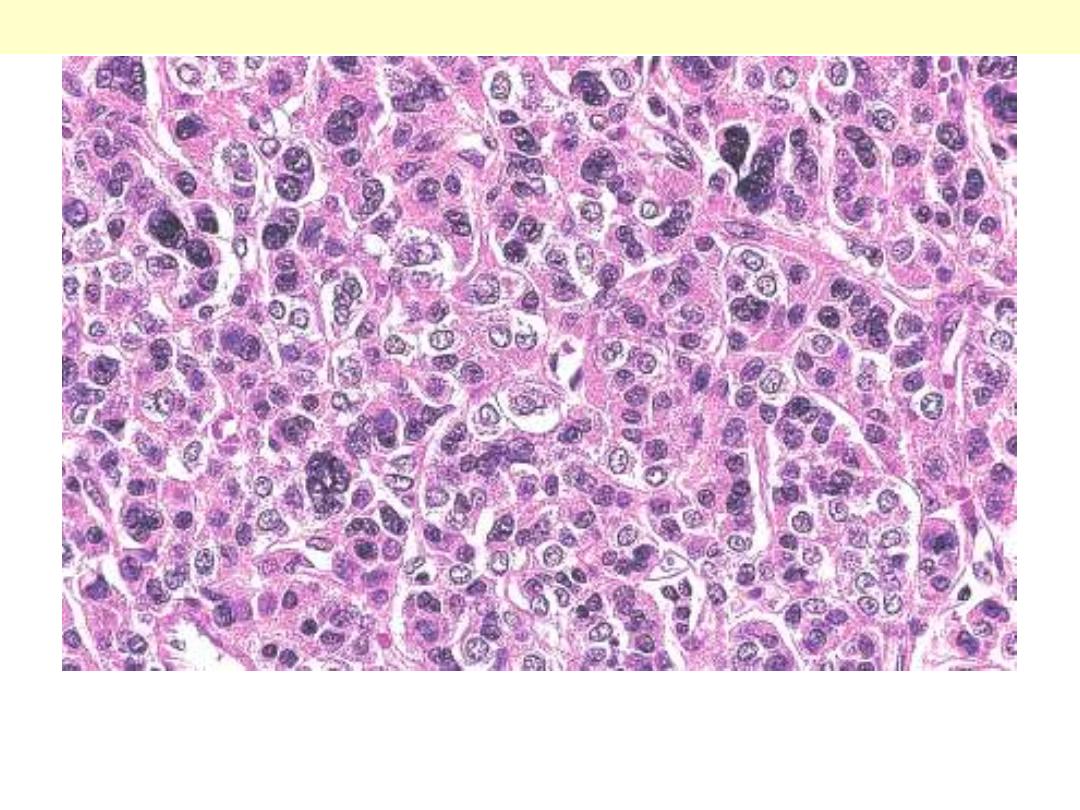
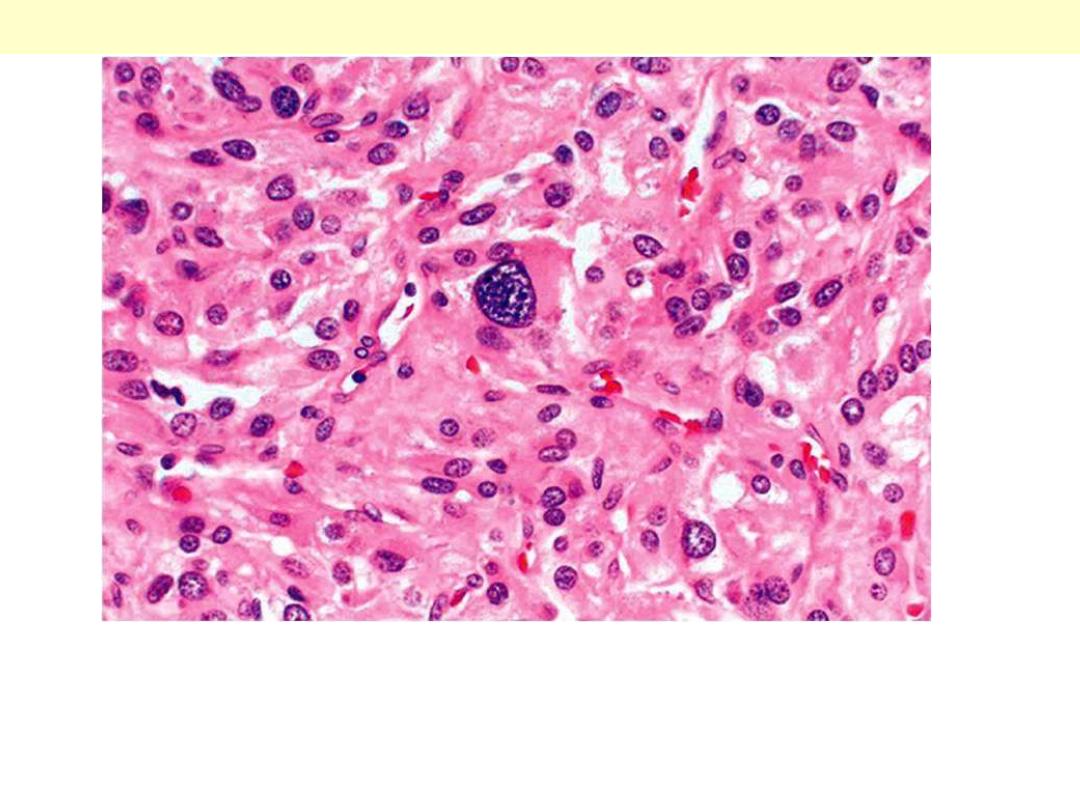
There is nuclear hyperchromasia, diffuse pattern of growth, and
mitotic activiaty.
Adrenal cortical carcinoma
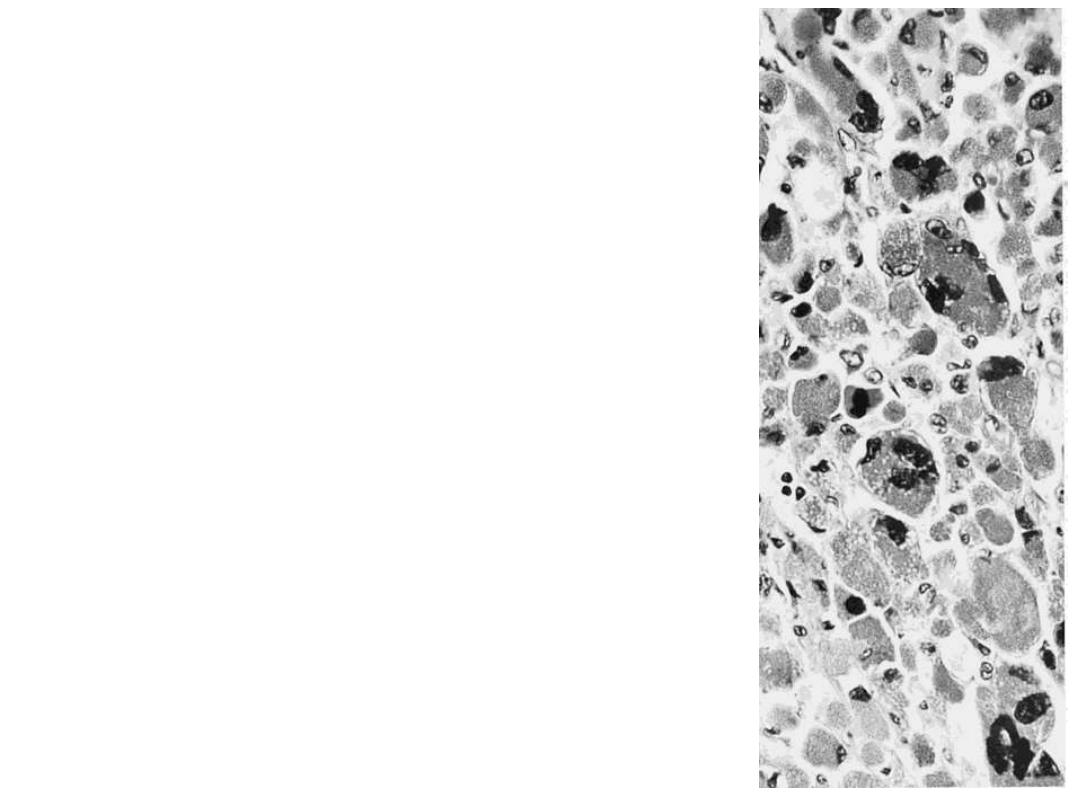
large cells with considerable variations in
size and with many bizarre nuclei. There
were tumor cells lying free within veins. This
finding was significant because 2 years after
surgical removal patient developed
pulmonary metastases.

Adrenal medulla - Tumors
The yellow-tan tumor is
enclosed within an
attenuated yellowish
cortex and demonstrates
areas of hemorrhage.
The residual adrenal is
seen below.
Pheochromocytoma
Adrenal pheochromocytoma. The
tumor shown in A has a markedly
variegated appearance.
One half of the specimen & the
lower portion of the the other half
were fixed in dichromate fixative
and have acquired the typical dark
brown color indicative of a positive
chromaffin reaction.
Pheochromocytoma
The section of tumor at the bottom has been placed into a dichromate
fixative which turns the tissue brown as the catecholamines are oxidized.
Compare to the section of pink to yellow tumor at the top which has not
been placed in dichromate fixative
*
.
Pheochromocytoma Chromaffin reaction
The section demonstrates characteristic nesting of cells ("Zellballen") with
abundant pinkish cytoplasm. It is not uncommon to find bizarre cells even
in pheochromocytomas that are biologically benign, and this criterion by
itself should not be used to diagnose malignancy.
Pheochromocytoma
The tumor is composed of large cells that are pink to mauve and
arranged in nests with capillaries in between
*
.
Pheochromocytoma Adrenal gland
The tumor shows
the typical location
above the upper
pole of the kidney,
which is
uninvolved.
Neuroblastoma adrenal
The tumor exhibits a
variegated appearance
resulting from hemorrhage
and necrosis.
Neuroblastoma showing a
variegated appearance with
extensive areas of necrosis.
The tumor shown is almost
entirely necrotic and
hemorrhagic.
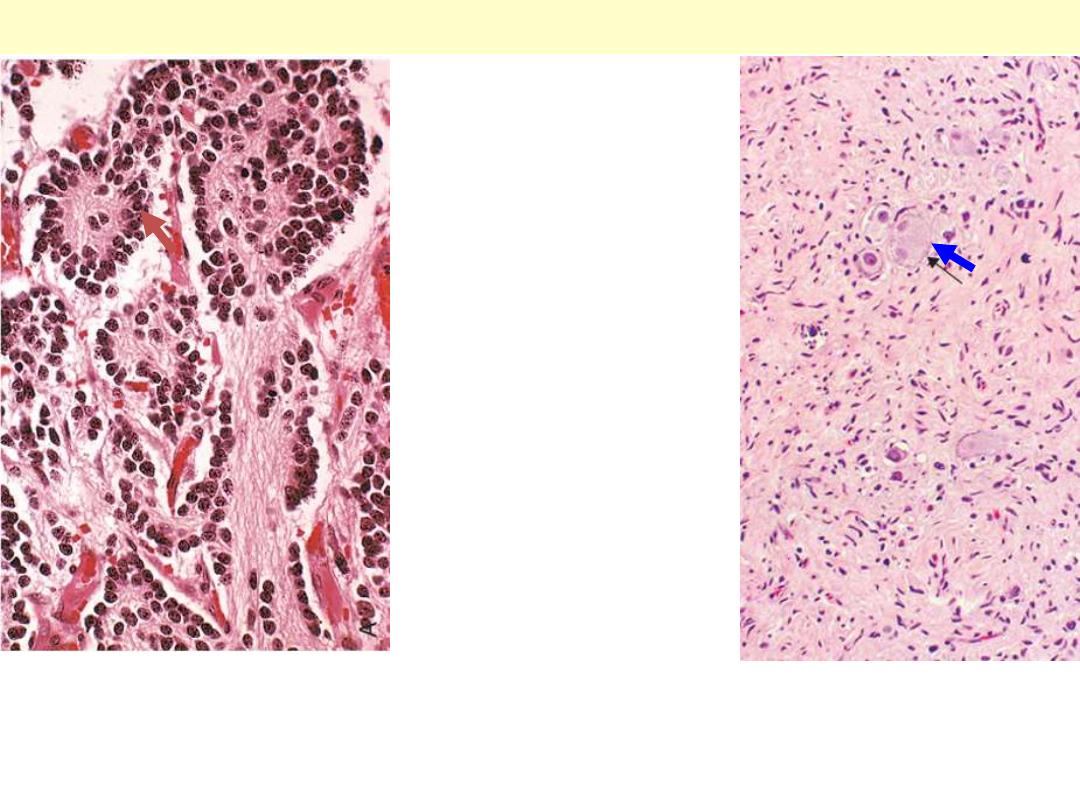
A: the tumor is composed of small cells embedded in a finely fibrillar matrix. A Homer-Wright pseudo-
rosette is seen (arrow) . B: Ganglioneuromas, arising from spontaneous or therapy-induced maturation
of neuroblastomas, are characterized by clusters of large cells with vesicular nuclei and abundant
eosinophilic cytoplasm (arrow), representing neoplastic ganglion cells. Spindle-shaped Schwann cells
are present in the background stroma.
Neuroblastoma & ganglioneuroma

Adrenals – Addison’s disease
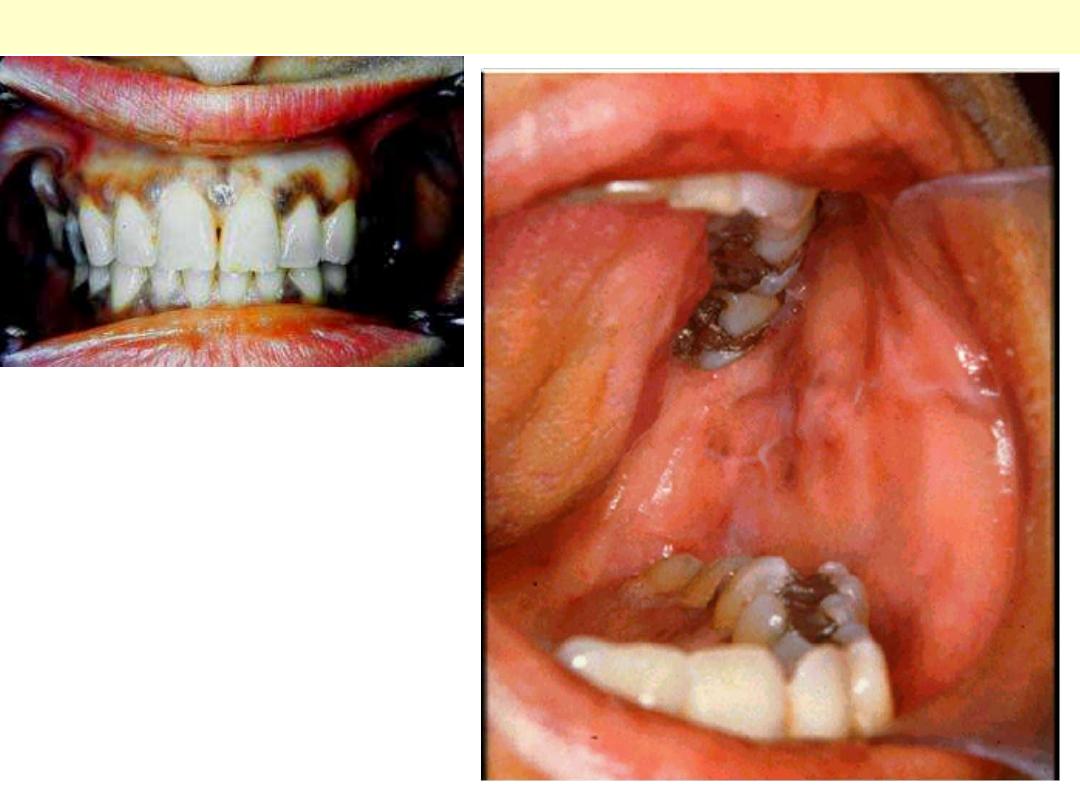
Addison disease oral pigmentation

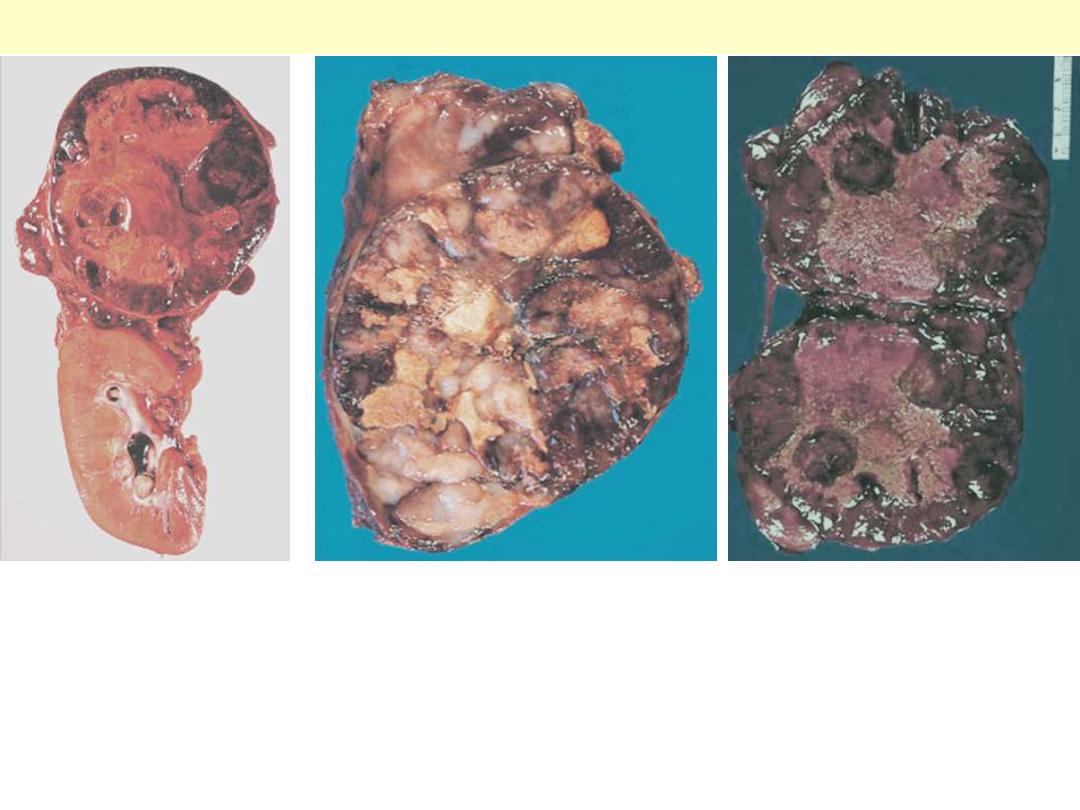
Adrenals – Metastatic tumors
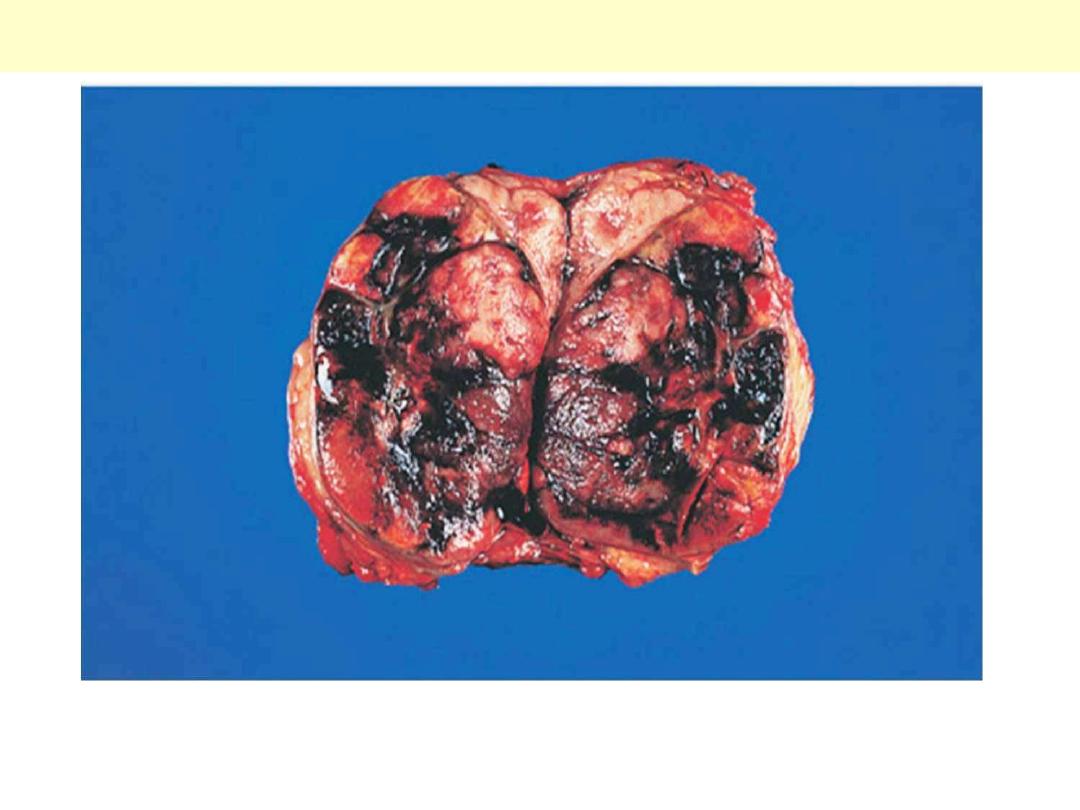
Enlargement of the gland by a markedly hemorrhagic tumor
representing metastatic breast carcinoma.
Breast carcinoma metastatic to adrenal

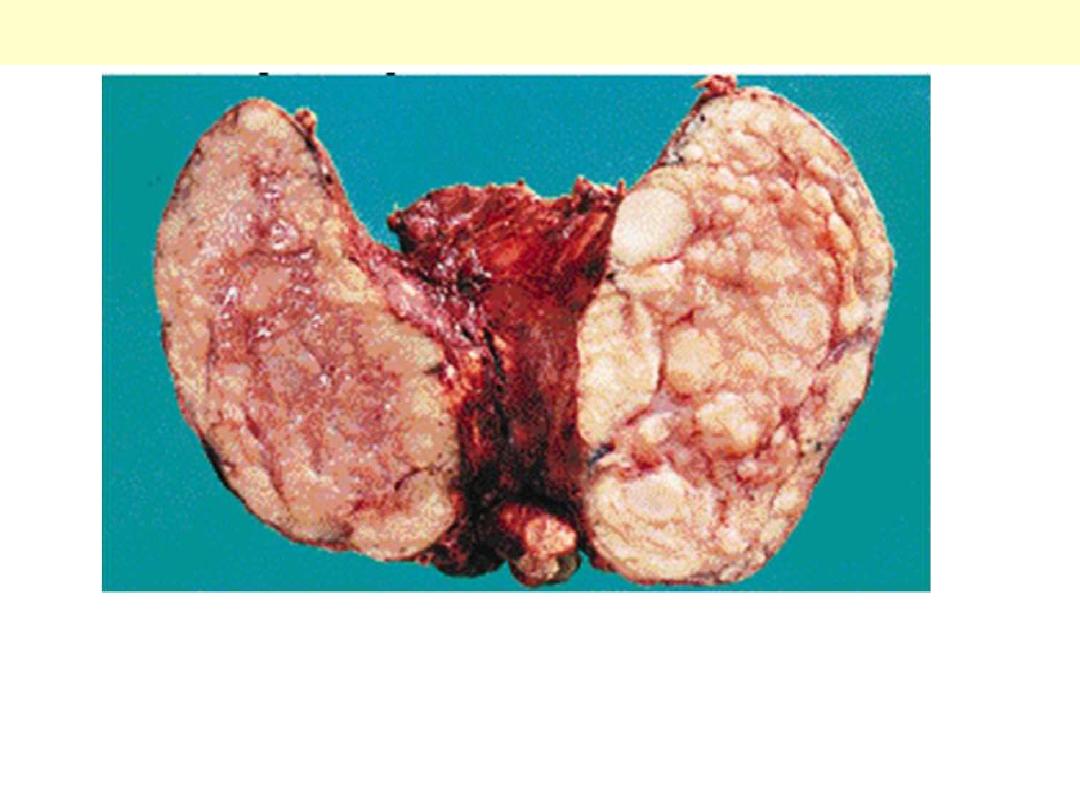
Adrenocortical hyperplasia

The pair of adrenals in the center are normal. Those at the top come from a patient
with adrenal atrophy (with either Addison's disease or long-term corticosteroid
therapy). The adrenals at the bottom represent bilateral cortical hyperplasia. This
could be due to a pituitary adenoma secreting ACTH (Cushing's disease), or Cushing's
syndrome from ectopic ACTH production, or idiopathic adrenal hyperplasia.
Adrenocortical hyperplasia
Normal

Pancreas -
Endocrine

Pancreas - Tumors
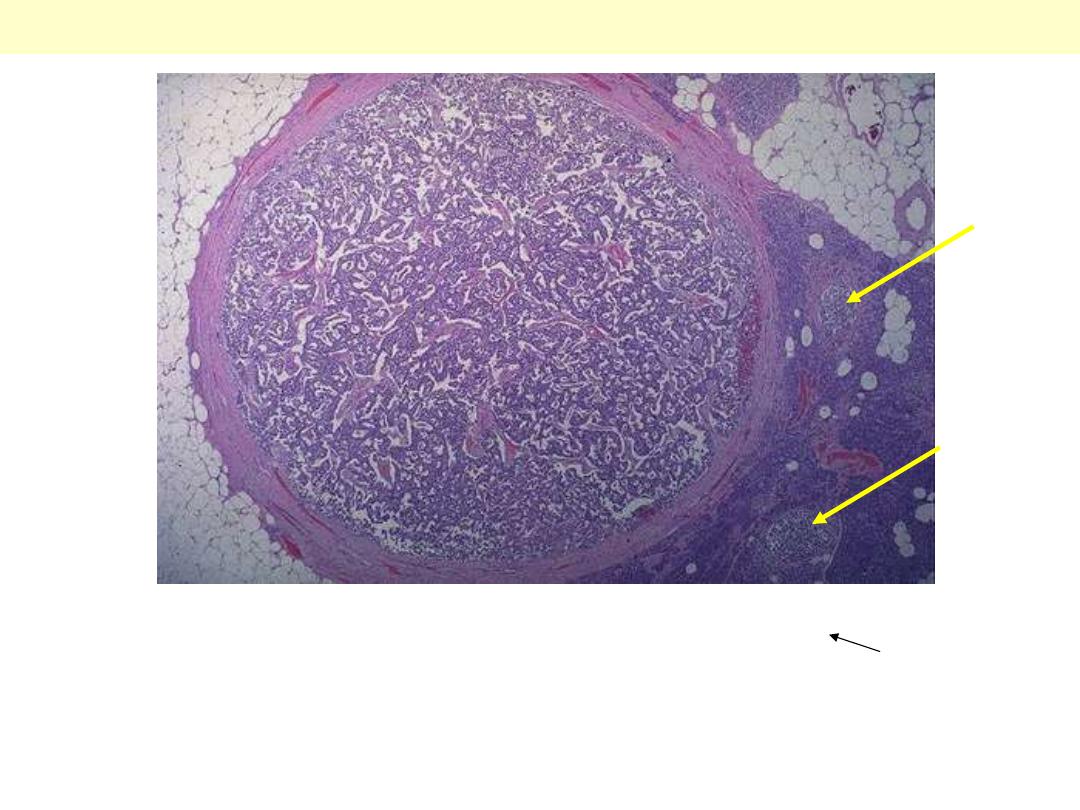
This tumor is separated from the pancreas by a thin collagenous
capsule. A few normal islets are seen in the pancreas at the right
(arrows) for comparison.
Islet cell adenoma
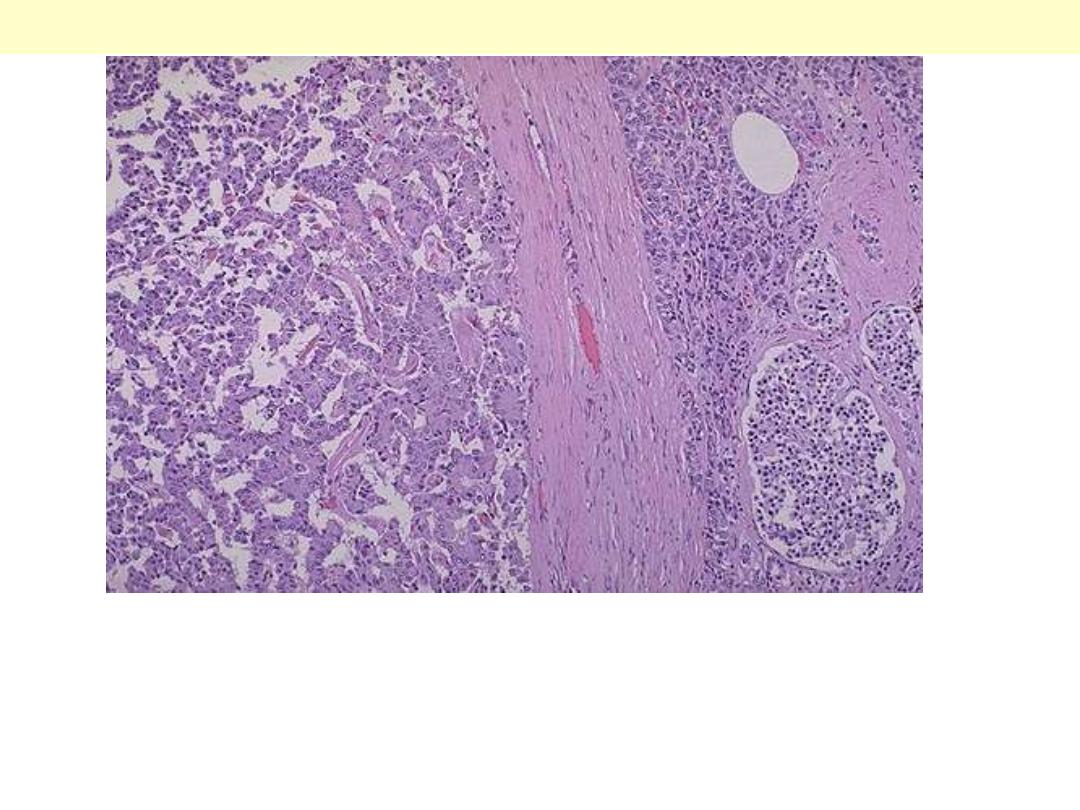
Higher magnification of the previous photo. The islet cell adenoma at the left
contrasts with the normal pancreas with islets at the right. Some of these
adenomas function. Those that produce insulin may lead to hypoglycemia. Those
that produce gastrin may lead to multiple gastric and duodenal ulcerations
(Zollinger-Ellison syndrome).
Islet cell adenoma
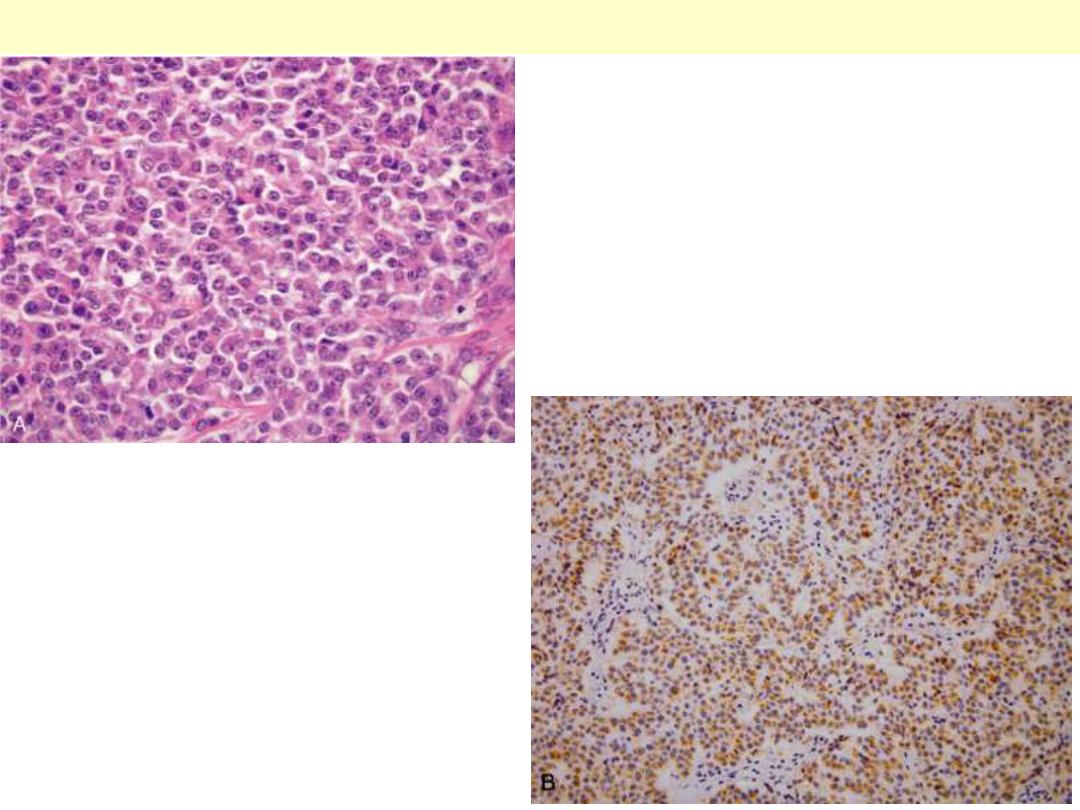
A: The neoplastic cells are
monotonous and demonstrate
minimal pleomorphism or mitotic
activity (H&E stain). B:
Immunoreactivity for insulin
confirms the neoplasm is an
insulinoma. Clinically, the patient
had episodic hypoglycemia.
Pancreatic endocrine tumor ("islet cell tumor") (insulinoma)

Pituitary gland

Pituitary - Adenoma
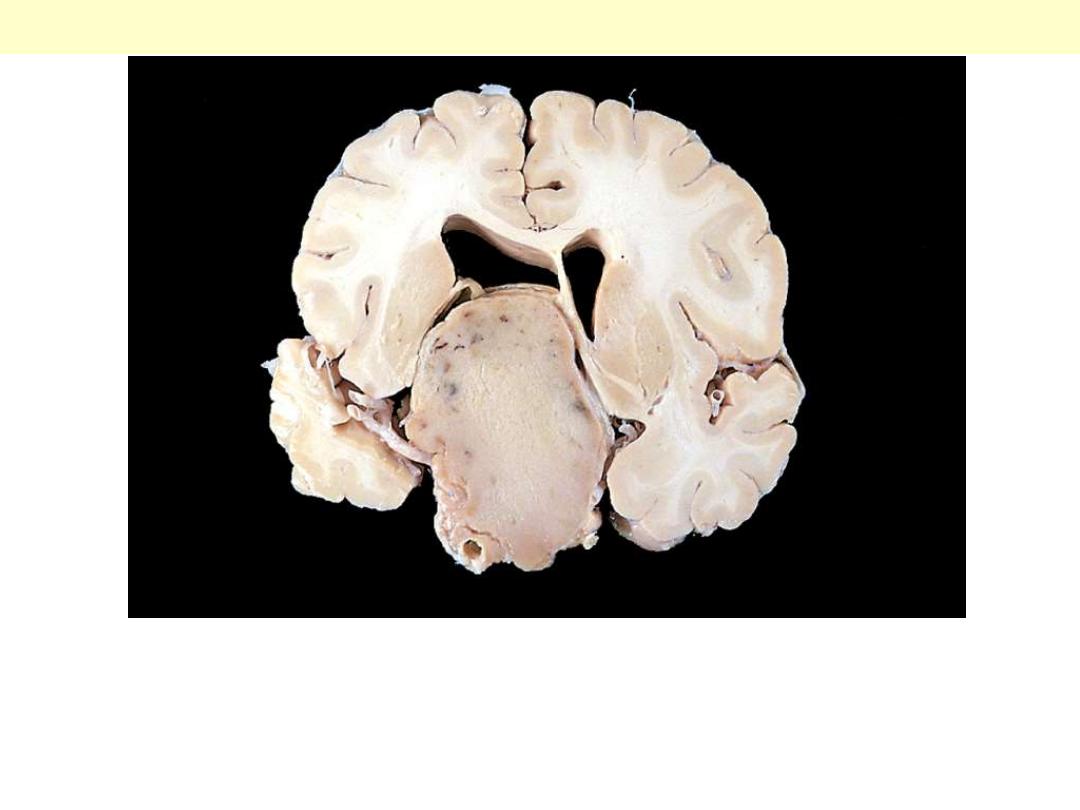
This massive, nonfunctional adenoma has grown far beyond the
confines of the sella turcica and has distorted the overlying brain.
Nonfunctional adenomas tend to be larger at the time of diagnosis
than those that secrete a hormone.
Pituitary adenoma gross
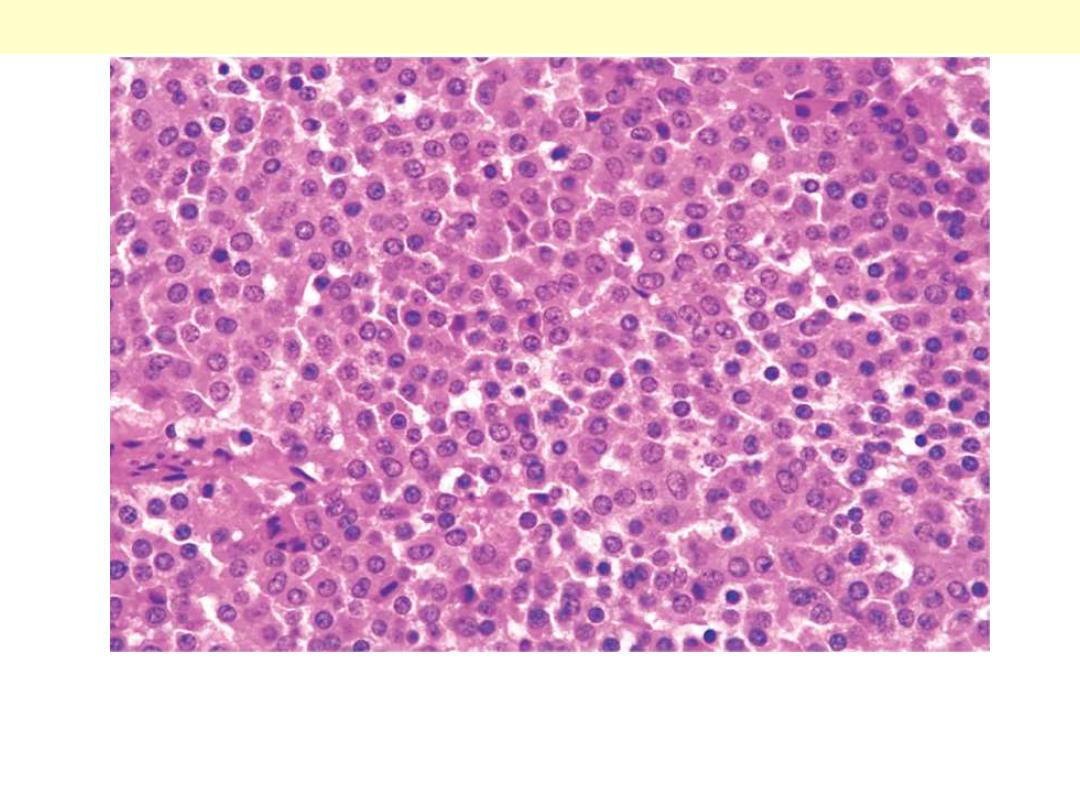
The monomorphism of these cells contrasts markedly to the mixture
of cells seen in the normal anterior pituitary. Note also the absence of
connective tissues.
Pituitary adenoma

Pituitary – Normal
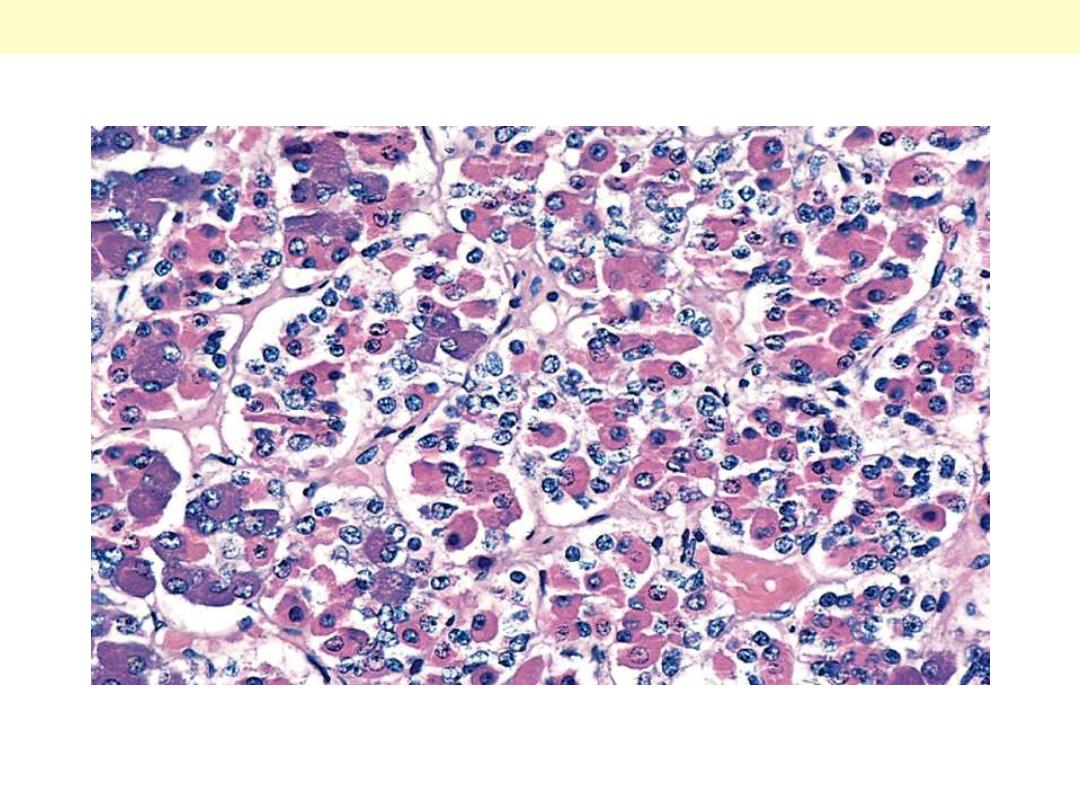
The gland is populated by several distinct cell populations containing a variety of stimulating (trophic)
hormones. Each of the hormones has different staining characteristics, resulting in a mixture of cell
types in routine histologic preparations.
Normal anterior pituitary

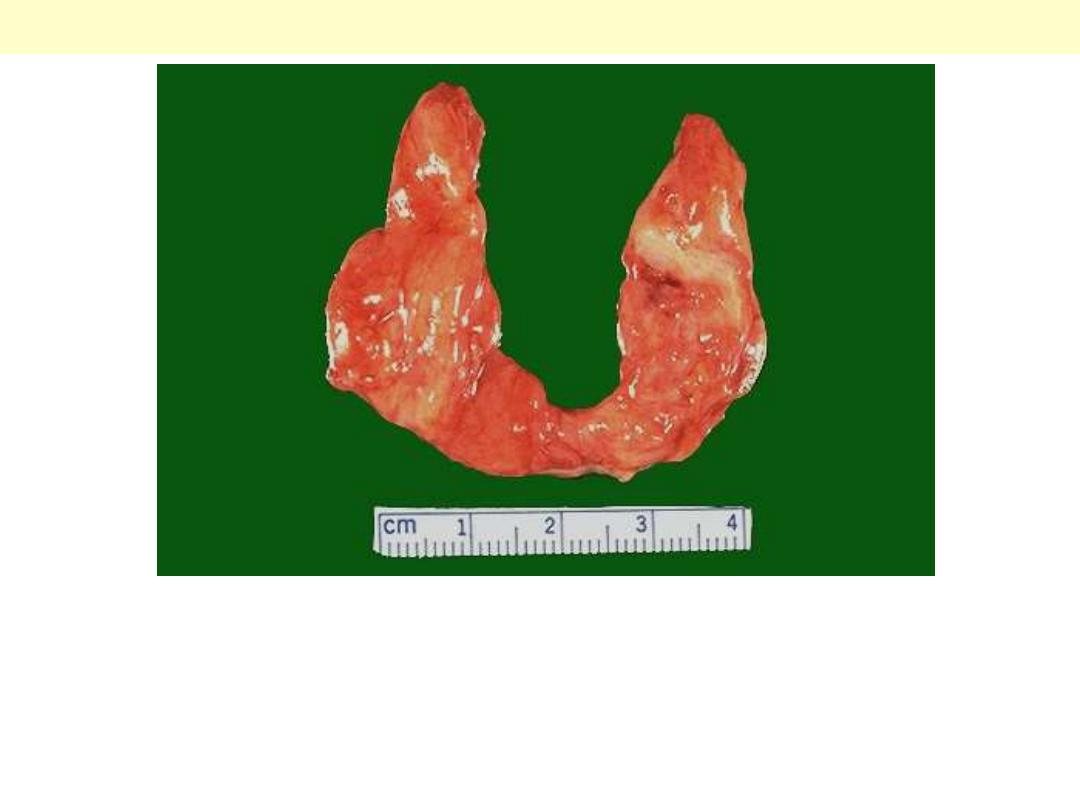
Thyroid gland

Thyroid – Chronic lymphocytic
thyroiditis( Hashimoto’s thyroiditis )
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Grossly the thyroid is usually symmetrically enlarged and firm,
with a bosselated surface. As a result of disappearance of brown
(iodine-rich) colloid, and its replacement by lymphocytes, the cut
surface is whitish rather than normal brown color.
Cut surface of thyroid involved by
Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The
appearance is reminiscent of a
hyperplastic lymph node.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
This symmetrically small thyroid gland demonstrates atrophy. This
patient was hypothyroid. This is the end result of Hashimoto's
thyroiditis. Initially, the thyroid is enlarged and there may be transient
hyperthyroidism, followed by a euthyroid state and then hypothyroidism
with eventual atrophy years later.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
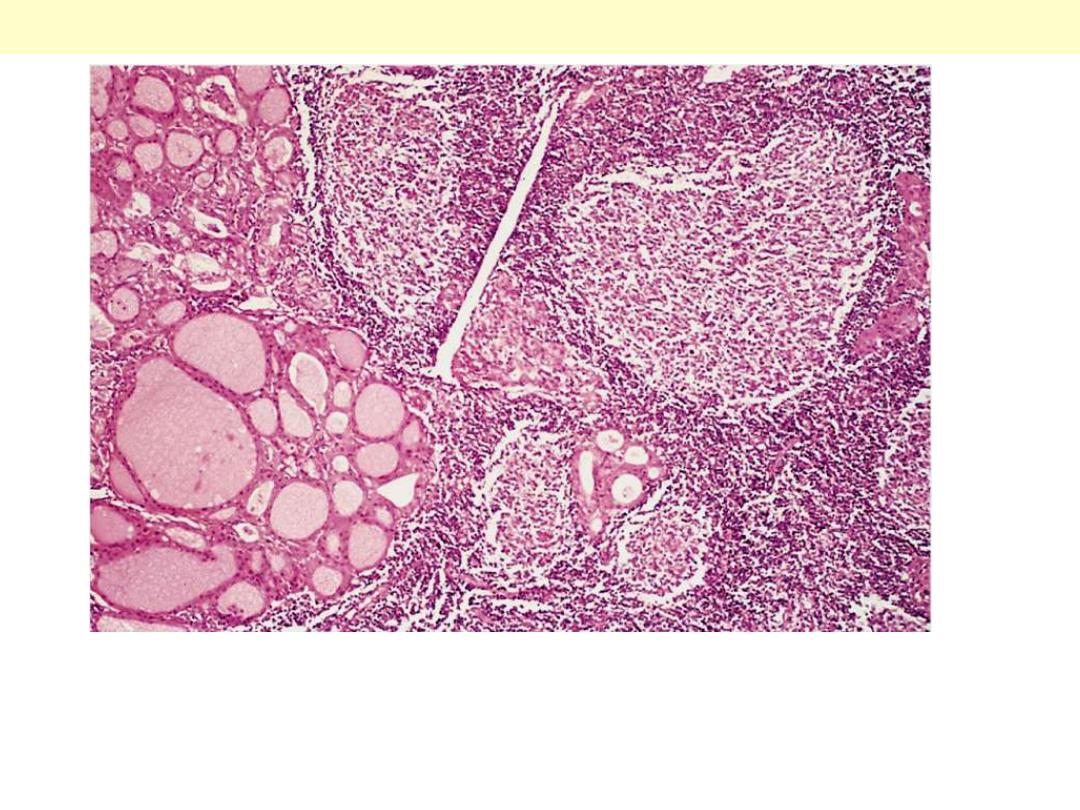
The thyroid parenchyma contains a dense lymphocytic infiltrate
with germinal centres. Residual thyroid follicles lined by deeply
eosinophilic Hürthle cells are also seen.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
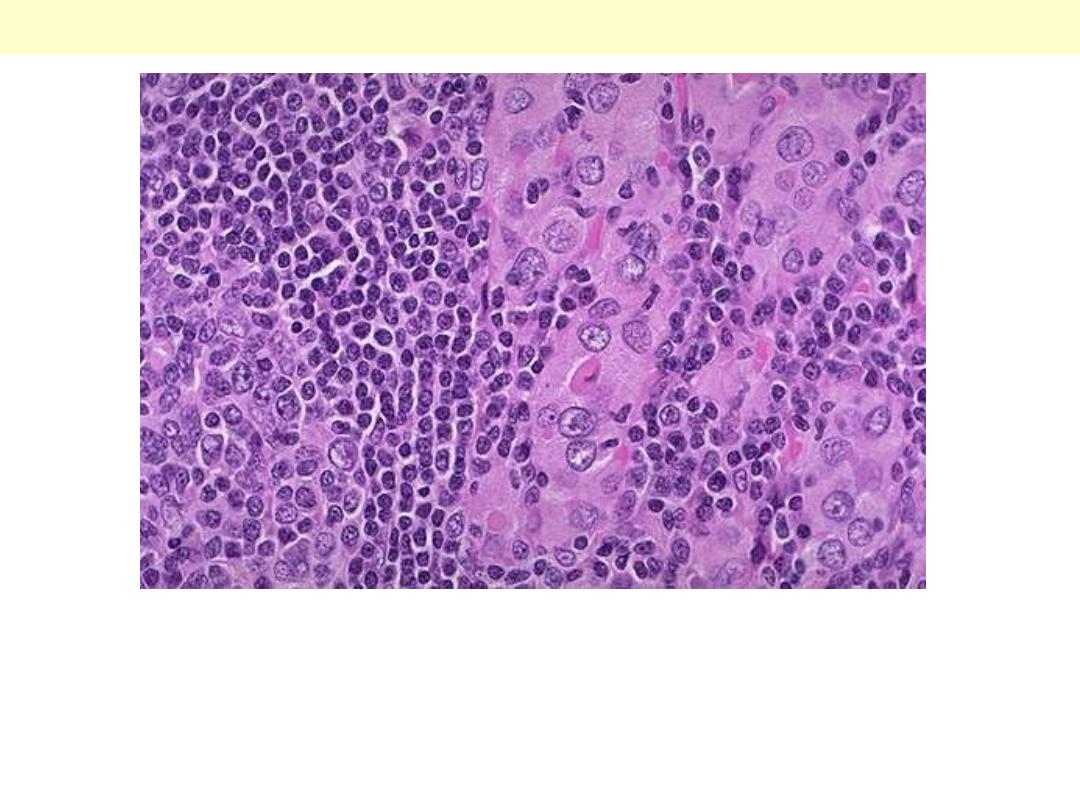
Hashimoto's thyroiditis demonstrates the pink Hurthle cells at the
center and right. The lymphoid follicle is at the left. Hashimoto's
thyroiditis initially leads to painless enlargement of the thyroid,
followed by atrophy years later.
Hashimoto thyroiditis

Thyroid - Goiters
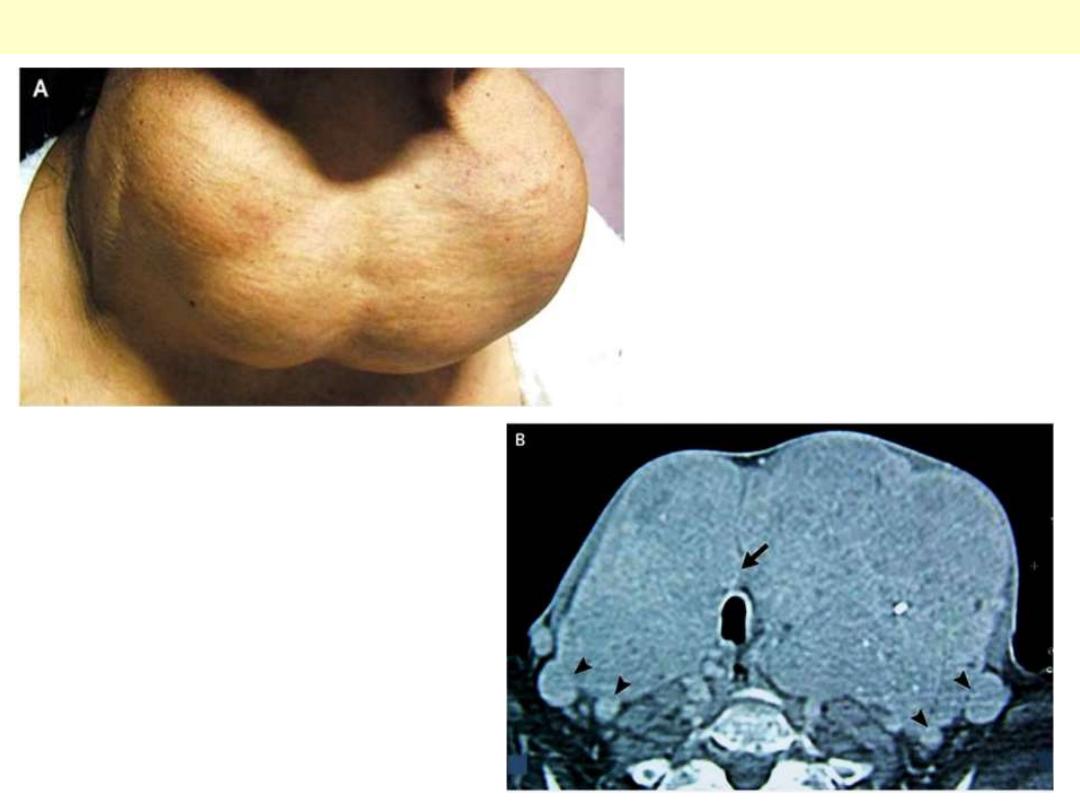
Endemic goitre
A 72-year-old woman presented for
evaluation of dyspnea. Thirty-five years
earlier, she had noticed a painless, slowly
enlarging anterior neck mass. Since she
was otherwise asymptomatic and many in
her community had the same "problem,"
she did not seek medical attention. For the
past few years, however, she has had a
sensation of suffocating a few minutes
after falling asleep. Physical examination
showed a goiter that was large, lobular,
soft, and painless, with cyanosis and
protrusion of the inferior lip (Panel A), which
was probably related to chronic respiratory
insufficiency. Serum thyrotropin and free
thyroxine levels were normal. Computed
tomography (Panel B) revealed a heterogeneous
goiter, 16 cm x 7 cm, that was in contact with
the trachea (arrow) and was displacing vascular
structures (arrowheads). Cytologic examination
of a specimen obtained by aspiration showed a
colloid goiter. Surgical treatment was
successfully accomplished early in 2007.
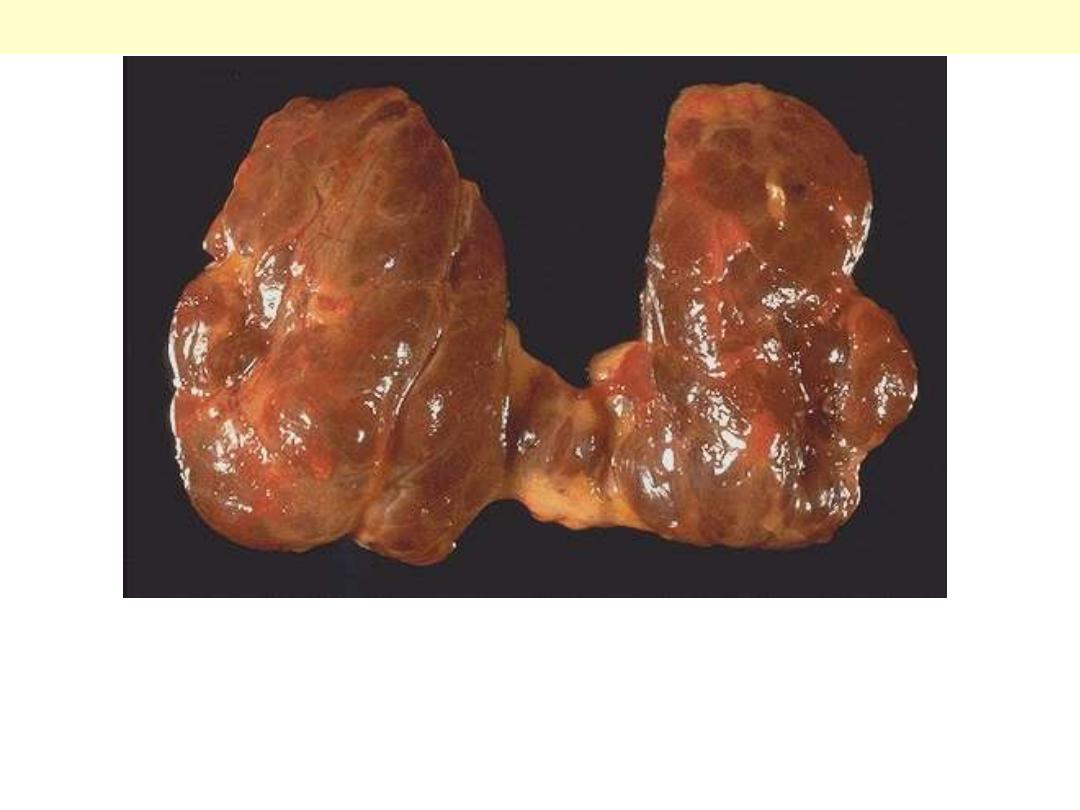
This diffusely enlarged thyroid gland is somewhat nodular. This
patient was euthyroid. This represents the most common cause for
an enlarged thyroid gland and the most common disease of the
thyroid--a nodular goiter.
Nodular colloid goiter
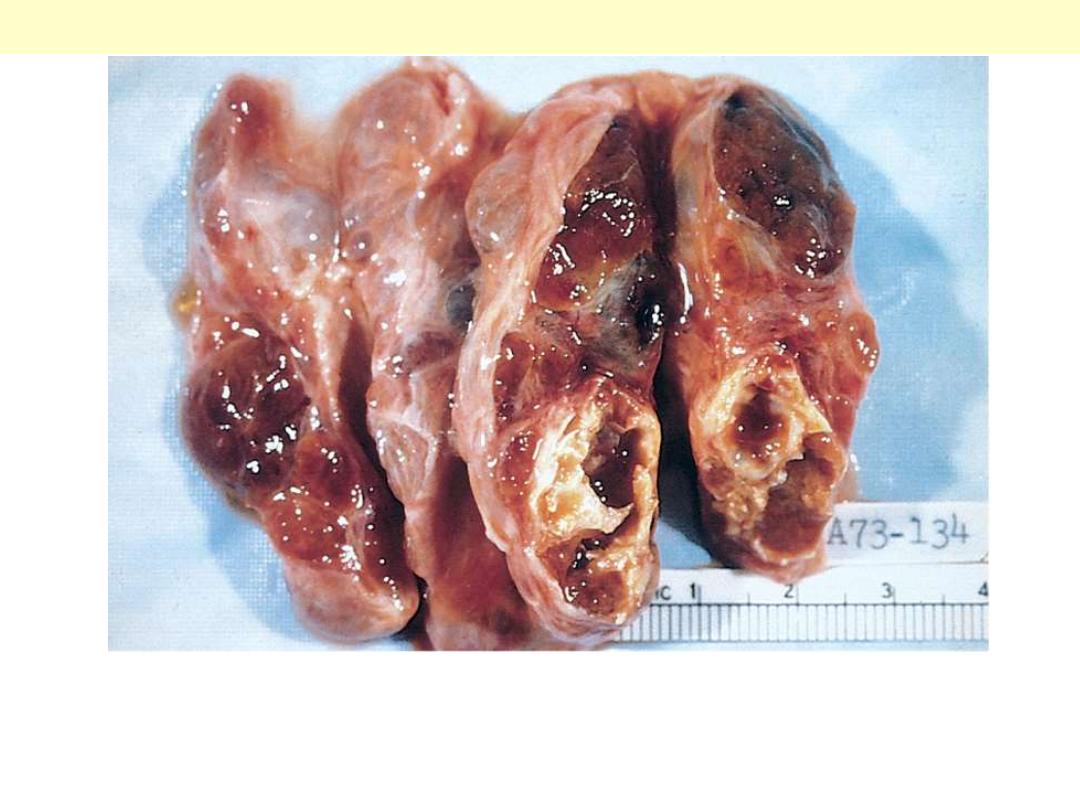
The gland is coarsely nodular and contains areas of fibrosis and
cystic change. Note the brown gelatinous colloid characteristic of this
condition ("colloid goiter").
Multinodular goiter
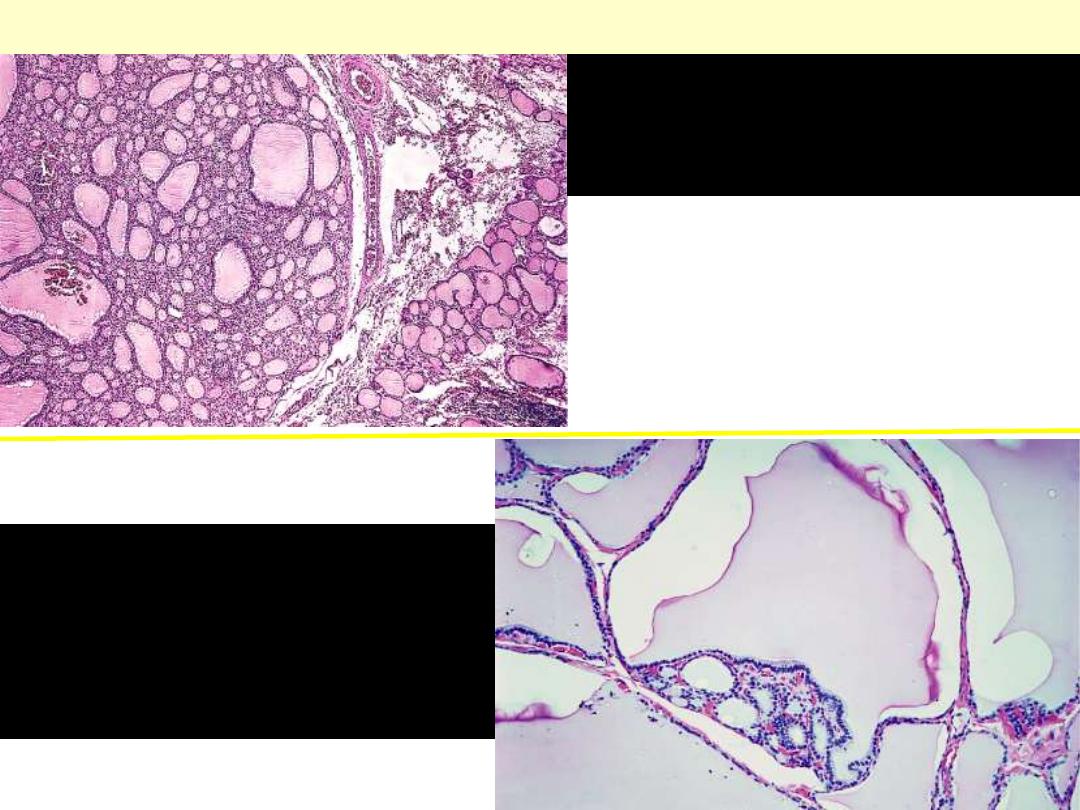
Appearance of nodular
hyperplasia. The hyperplastic
nodules lack a capsule
Nodular colloid goiter
Nodular hyperplasia
showing markedly
distended, colloid-filled
follicles

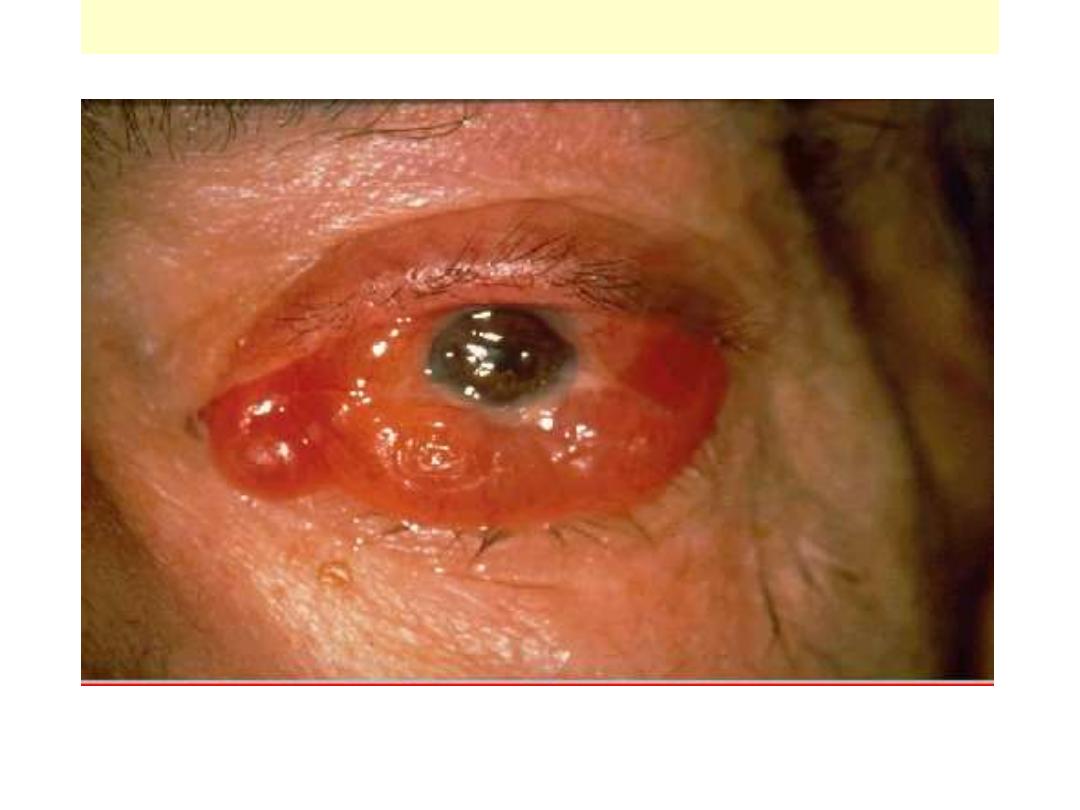
Thyroid – Graves disease

Exophalmos (protuberant, staring eyes due to
expansion of retro-orbital soft tissue)
Grave’s disease
Thyroid opthalmoplegia
Graves Disease (Diffuse thyroid hyperplasia)
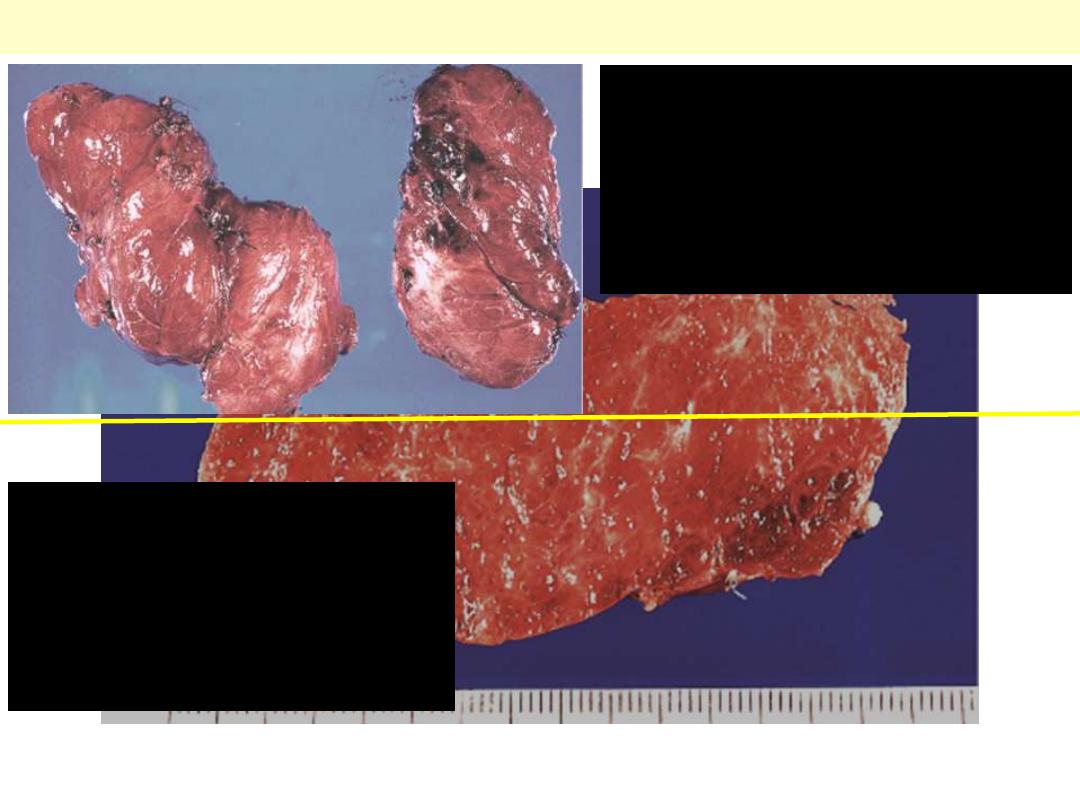
Outer aspect of diffuse
thyroid hyperplasia in a
patient with Graves’ disease.
The gland is diffusely
swollen and hyperemic.
Cut surface of thyroid
gland with diffuse
hyperplasia, showing a
hyperemic "juicy"
appearance.
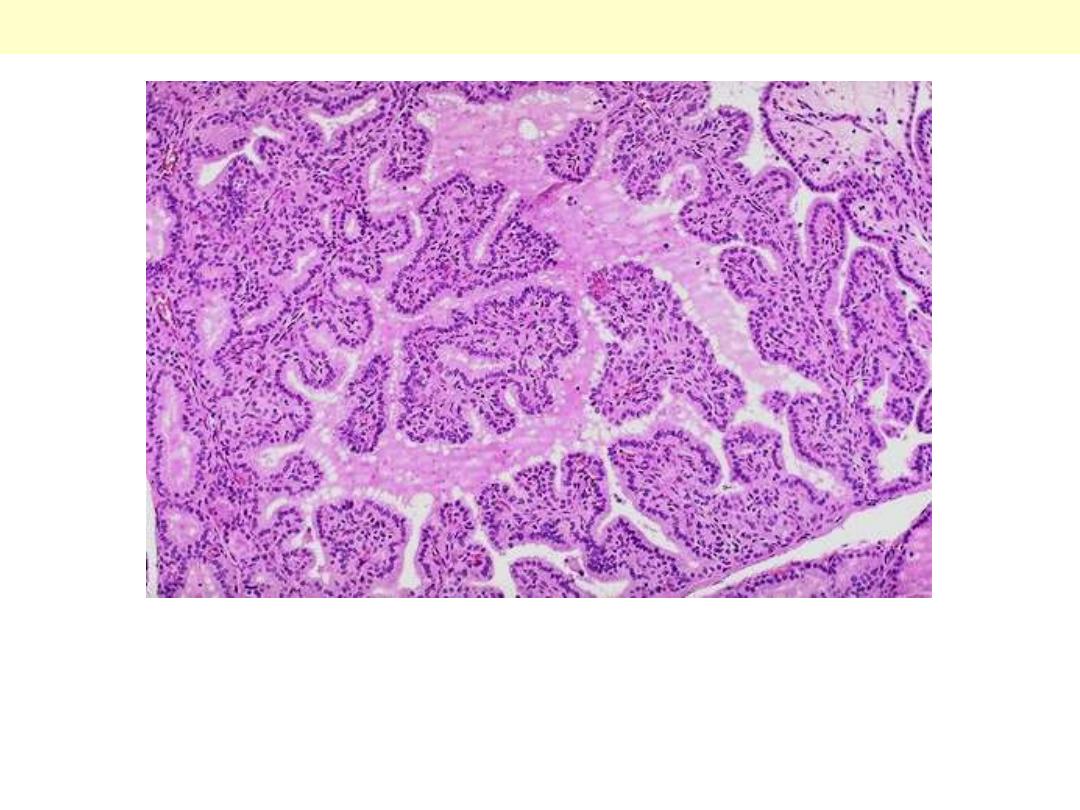
Note the prominent infoldings of the hyperplastic epithelium.
Graves disease
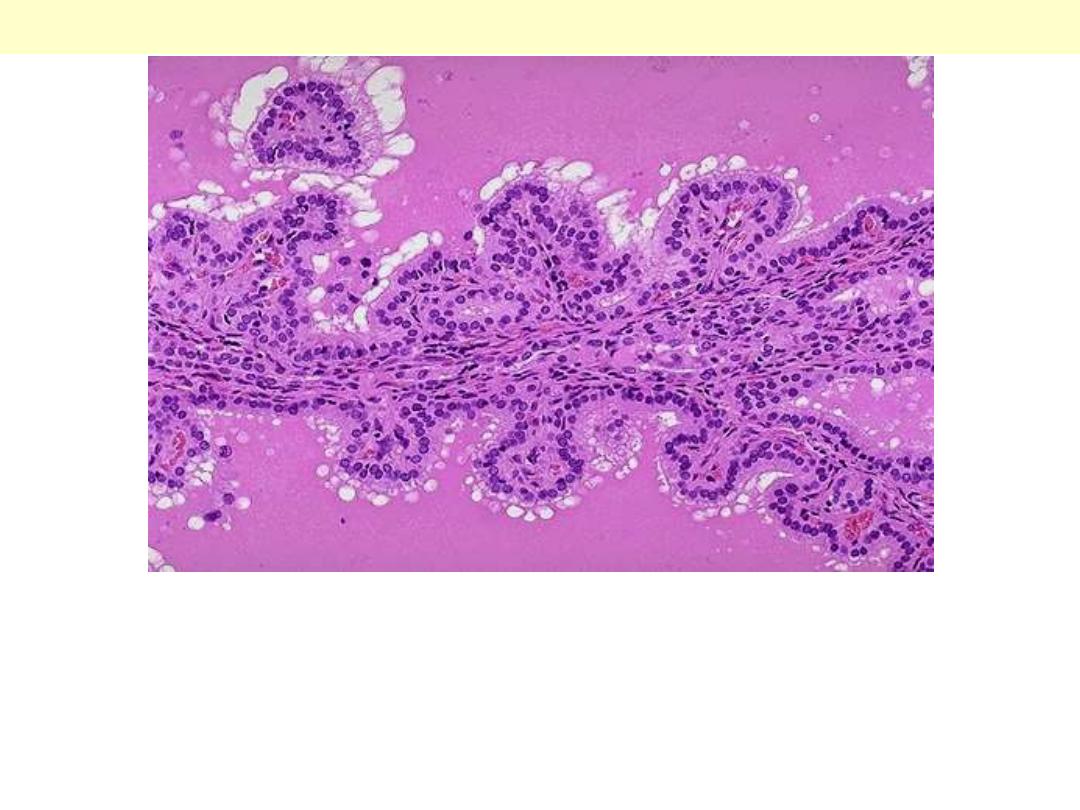
The tall columnar thyroid epithelium with Grave's disease lines the
hyperplastic infoldings into the colloid. Note the clear vacuoles in the
colloid next to the epithelium where the increased activity of the
epithelium has led to scalloping out of the colloid.
Graves disease
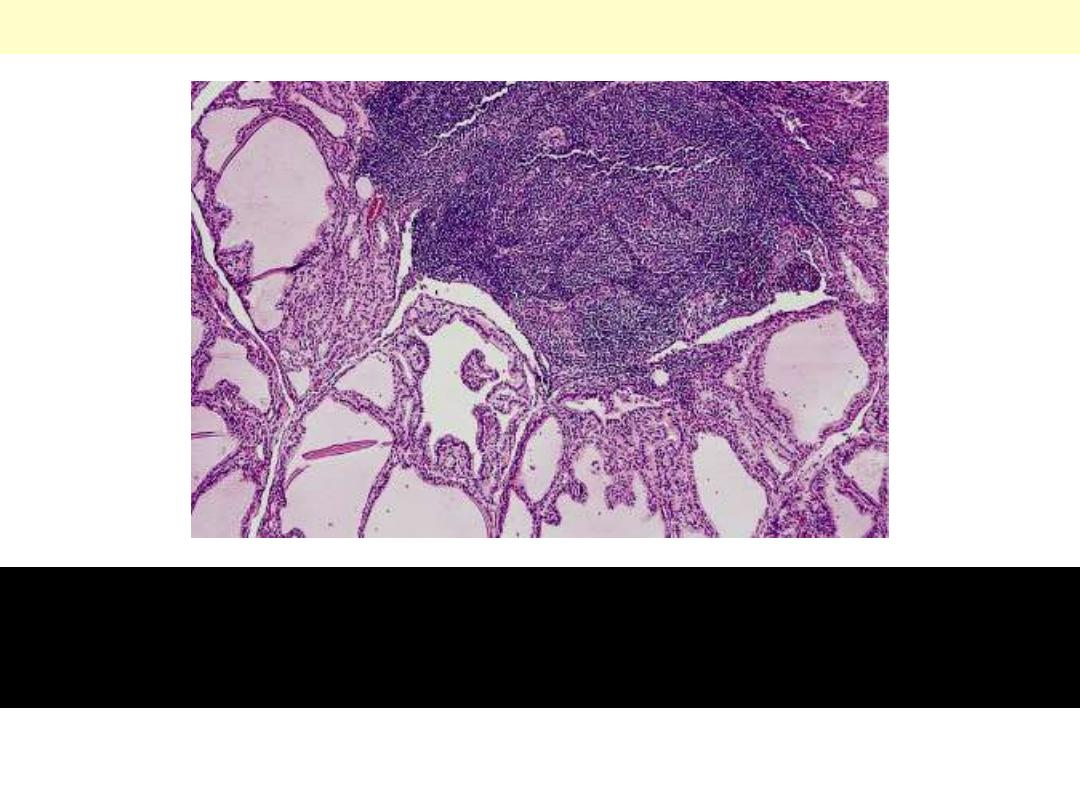
Graves disease
Lymphoid follicles with germinal centers and hyperplastic thyroid
follicles in diffuse hyperplasia. Note the pale-staining quality of the
colloid.

Thyroid – Tumors
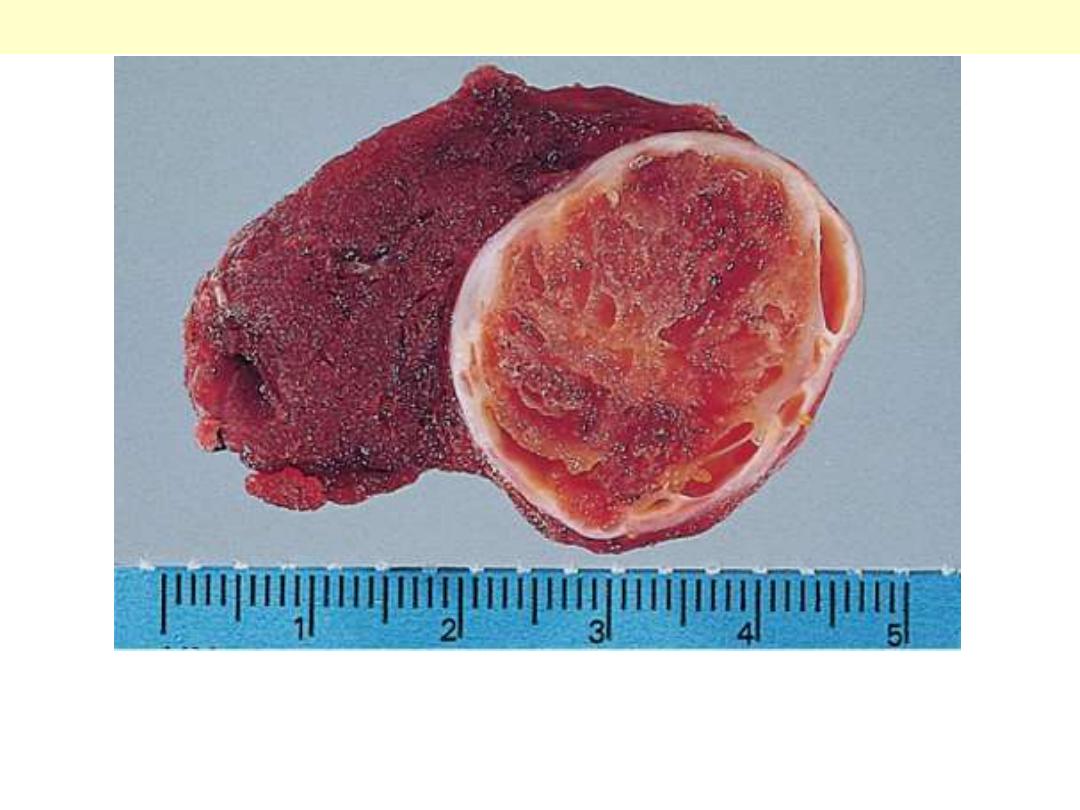
A solitary, well-circumscribed, encapsulated nodule is seen.
Follicular adenoma thyroid

Follicular adenoma G
Here is another follicular adenoma that is surrounded by a thin white
capsule. It is sometimes difficult to tell a well-differentiated follicular
carcinoma from a follicular adenoma. Thus, patients with follicular
neoplasms are treated with thyroidectomy just to be on the safe side.
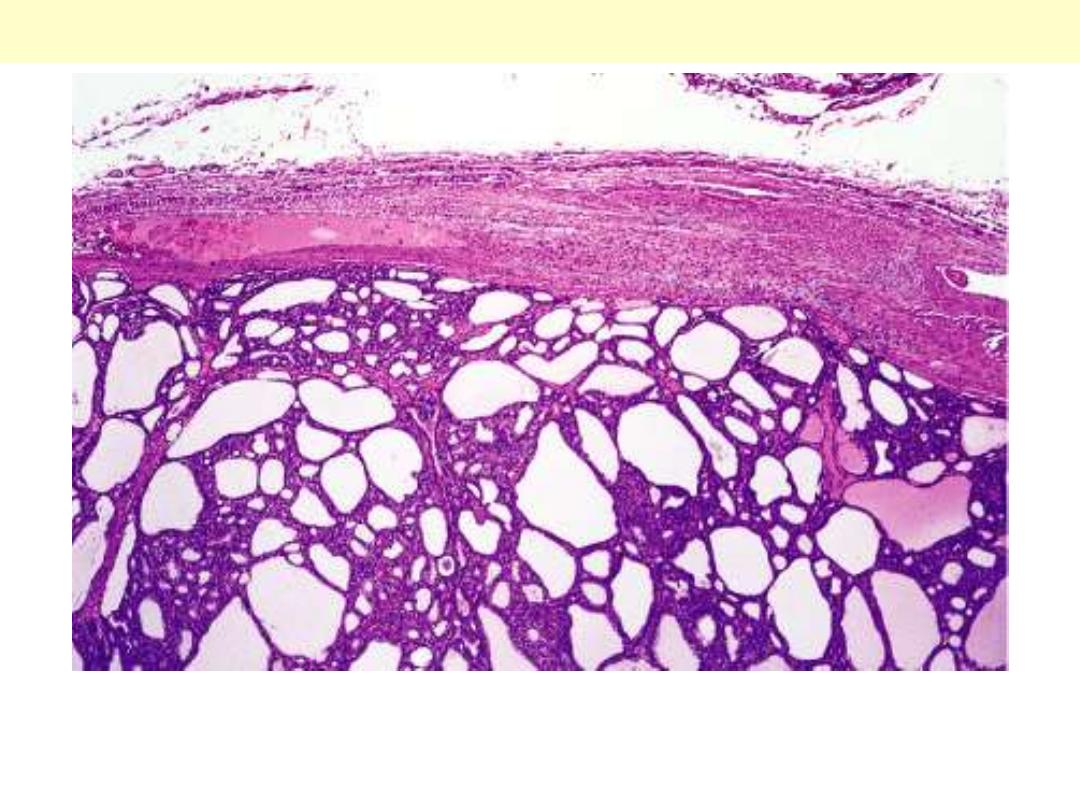
Follicular Adenoma thyroid
Intact fibrous capsule around a follicular adenoma
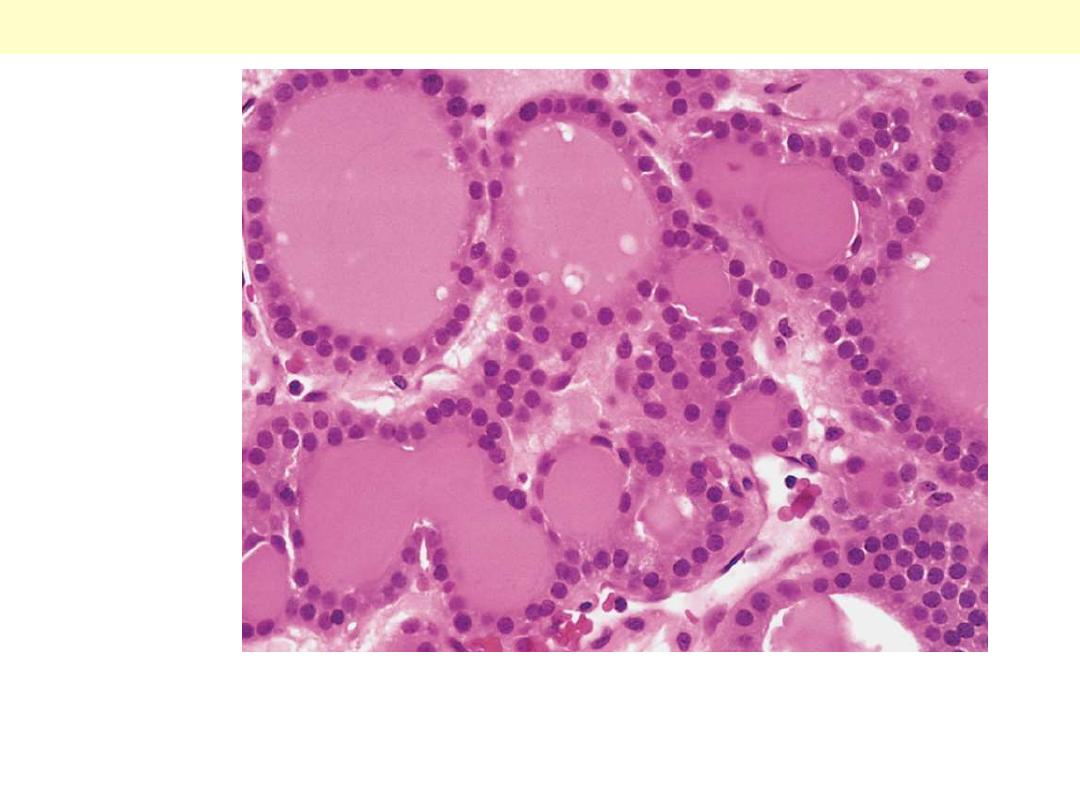
Well-differentiated follicles resemble normal thyroid
parenchyma.
Follicular adenoma thyroid
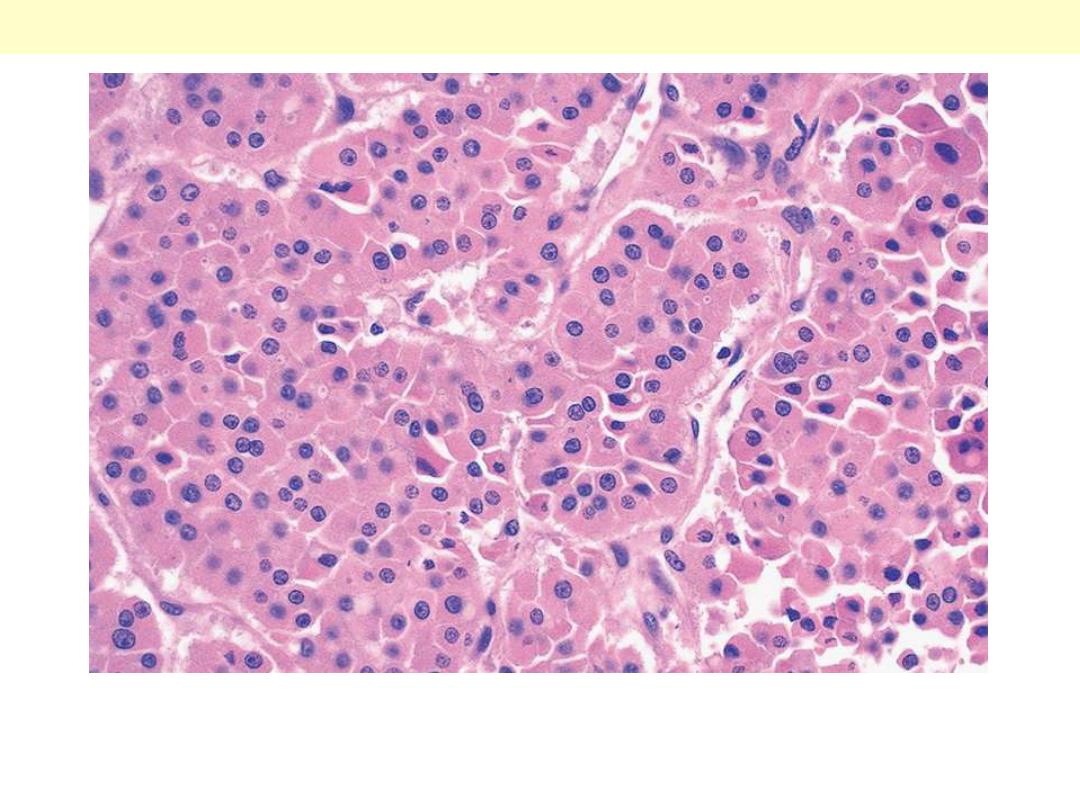
The tumor is composed of cells with abundant eosinophilic
cytoplasm and small regular nuclei.
Hürthle cell adenoma thyroid
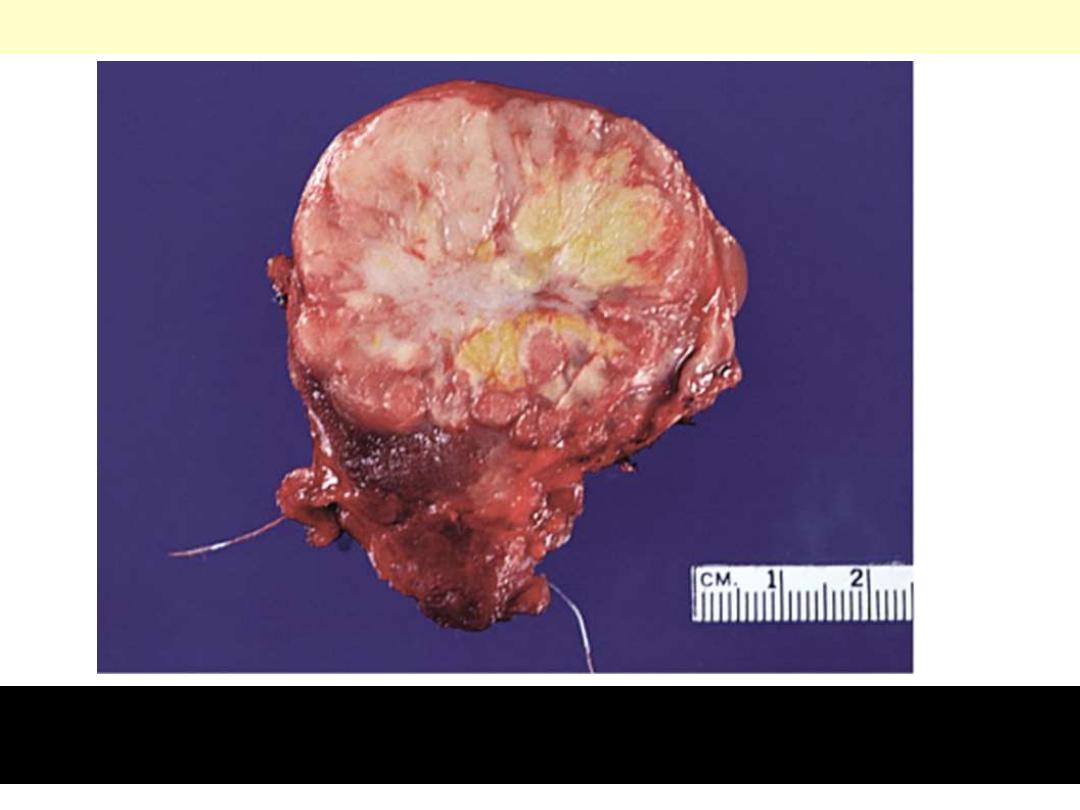
Most cases are solid, whitish, firm & clearly invasive. The tumor
shown exhibits a central area of fibrosis
Papillary ca thyroid central fibrosis
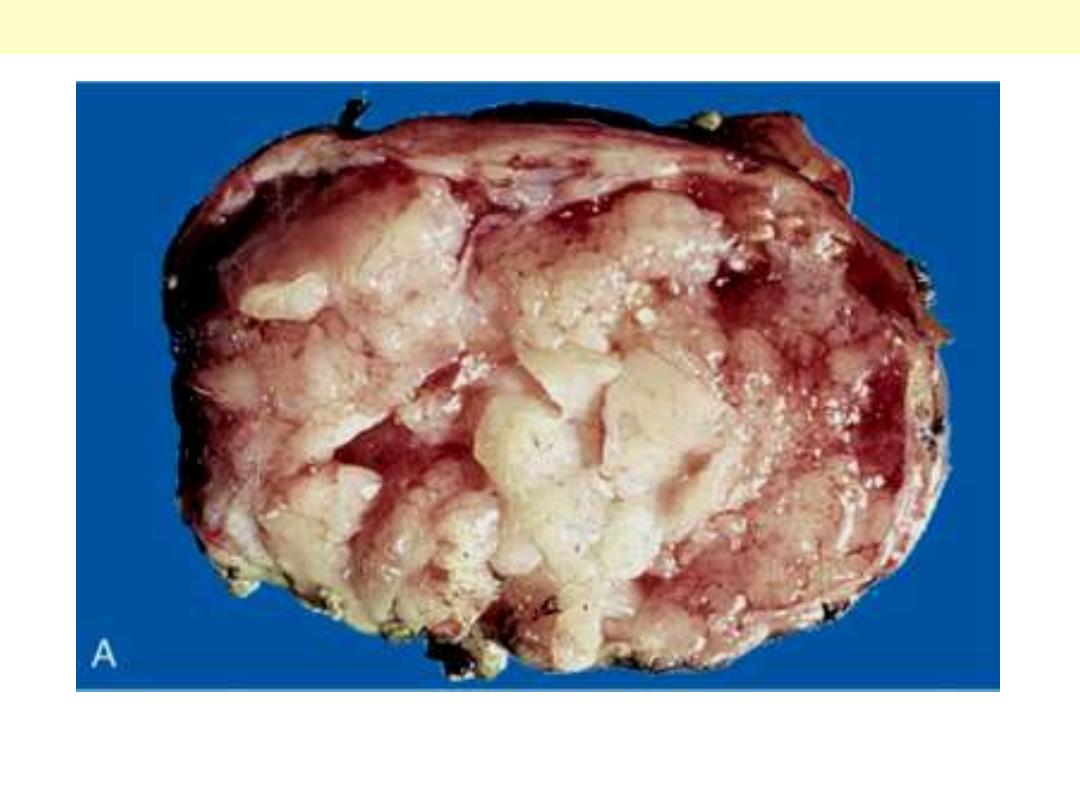
A papillary carcinoma with grossly discernible papillary structures.
Papillary carcinoma thyroid.
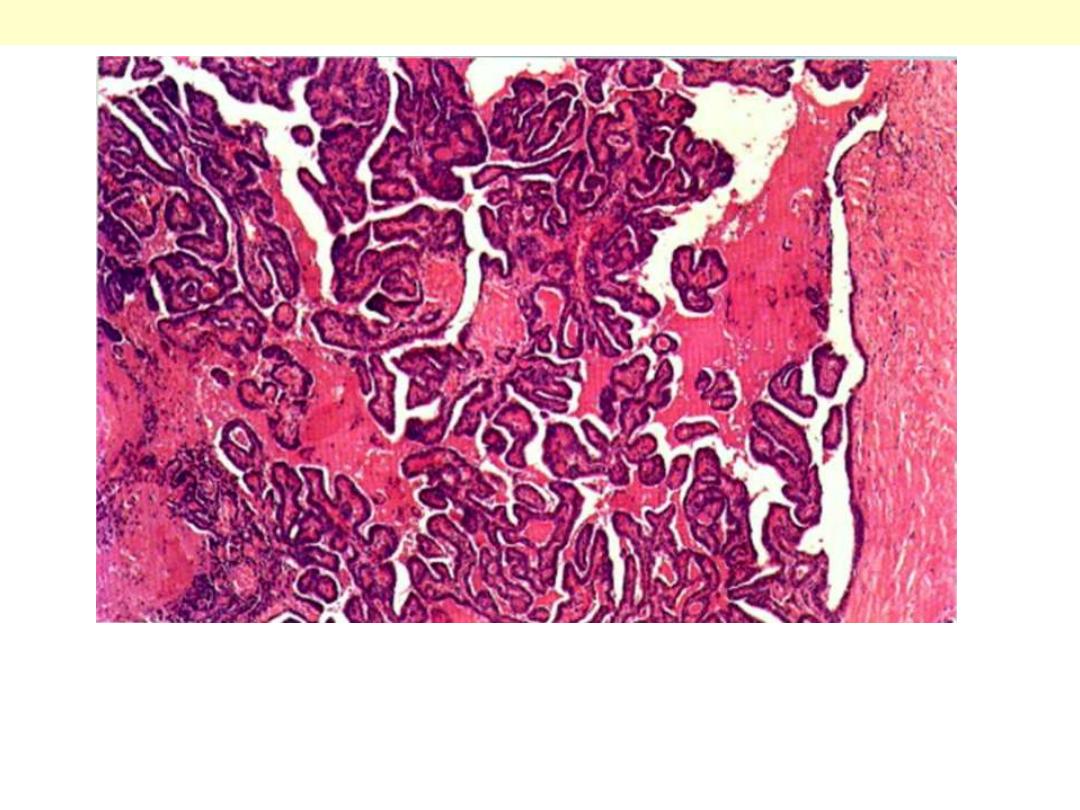
Papillary carcinoma: Thyroid
Papillary adenocarcinoma: thyroid. It is a well-differentiated papillary lesion,
lying within a cystic space. The fibrous capsule is on the right. The papillae
have a core of vascular connective tissue and are covered with cuboidal
epithelium.
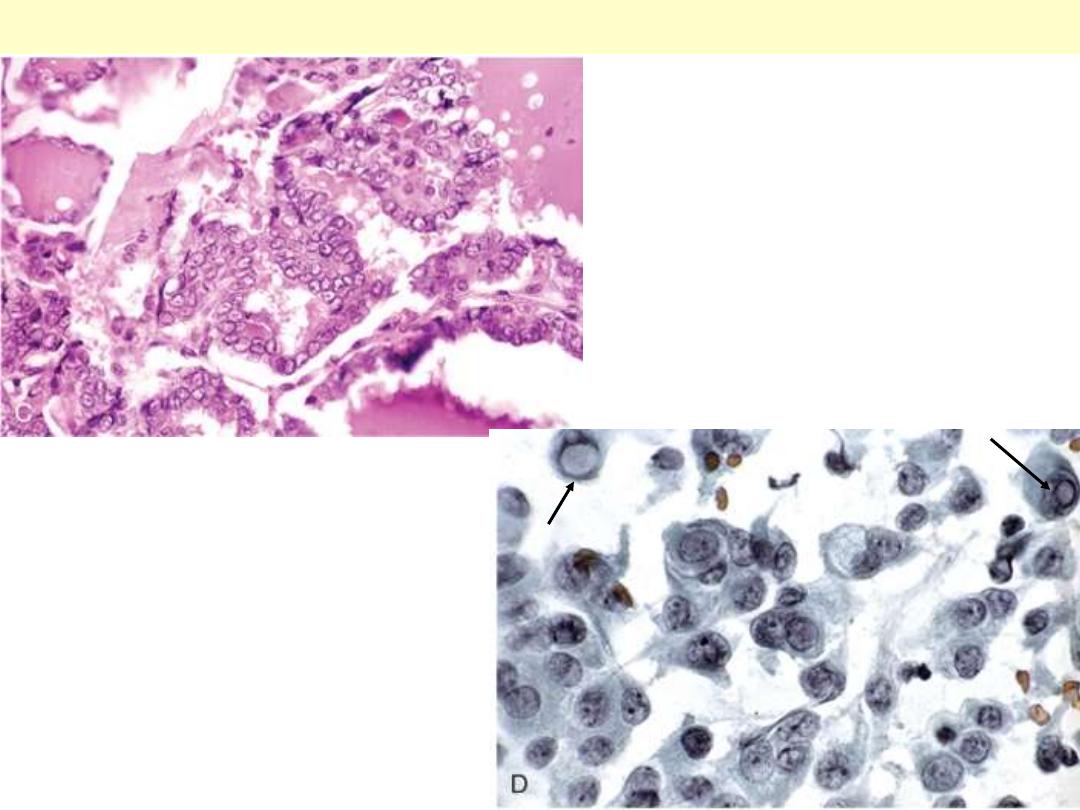
The papillae are lined by cells with
characteristic empty-appearing
nuclei, (ground glass or "Orphan
Annie eye" nuclei) (C). D, Cells
obtained by fine-needle aspiration of
a papillary carcinoma.
Characteristic intranuclear
inclusions are visible in some of the
aspirated cells.
Papillary carcinoma nuclear features
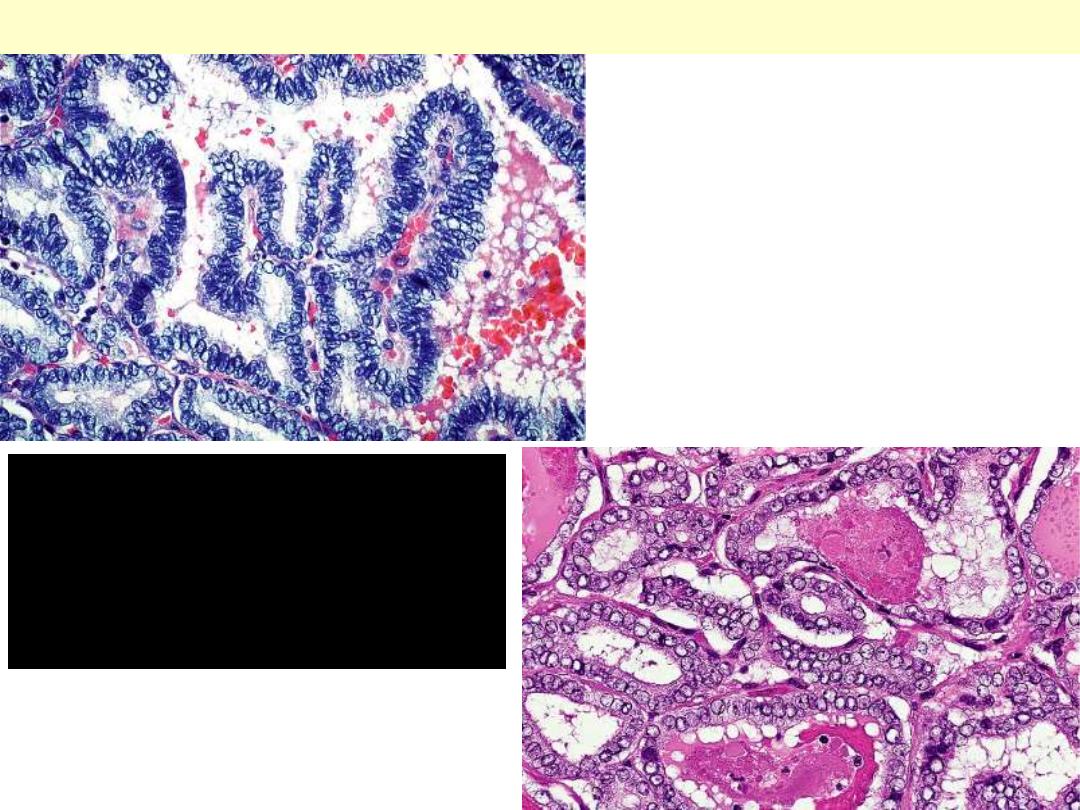
Nuclear features of
papillary carcinoma:
optically clear (ground
glass) nuclei
Papillary carcinoma thyroid ground glass nuclei
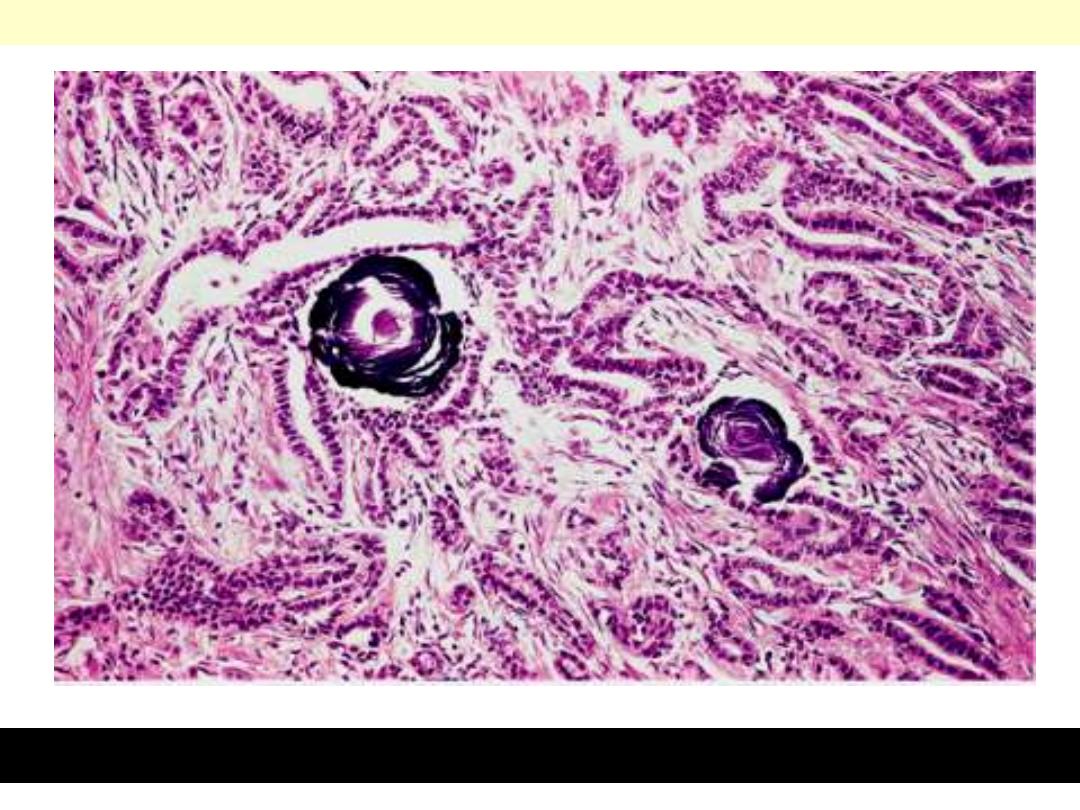
Psammoma body formation within the stroma of the tumor.
Papillary carcinoma: Thyroid
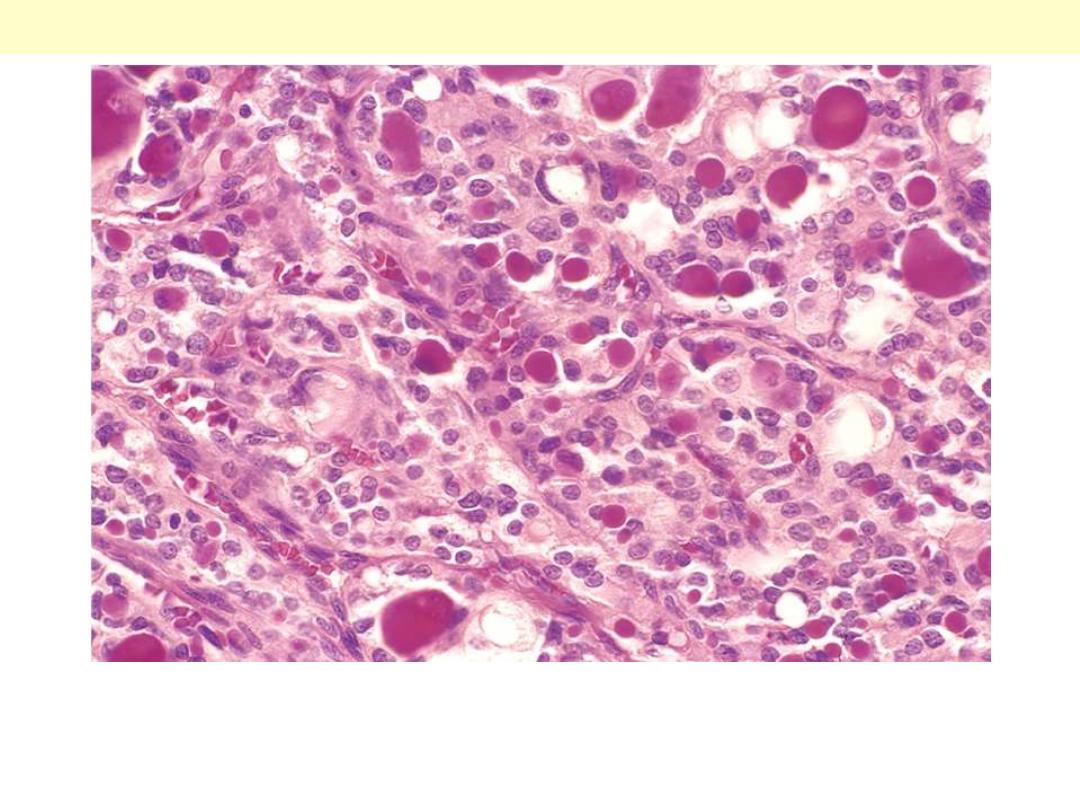
A few of the glandular lumens contain recognizable colloid.
Follicular carcinoma thyroid.
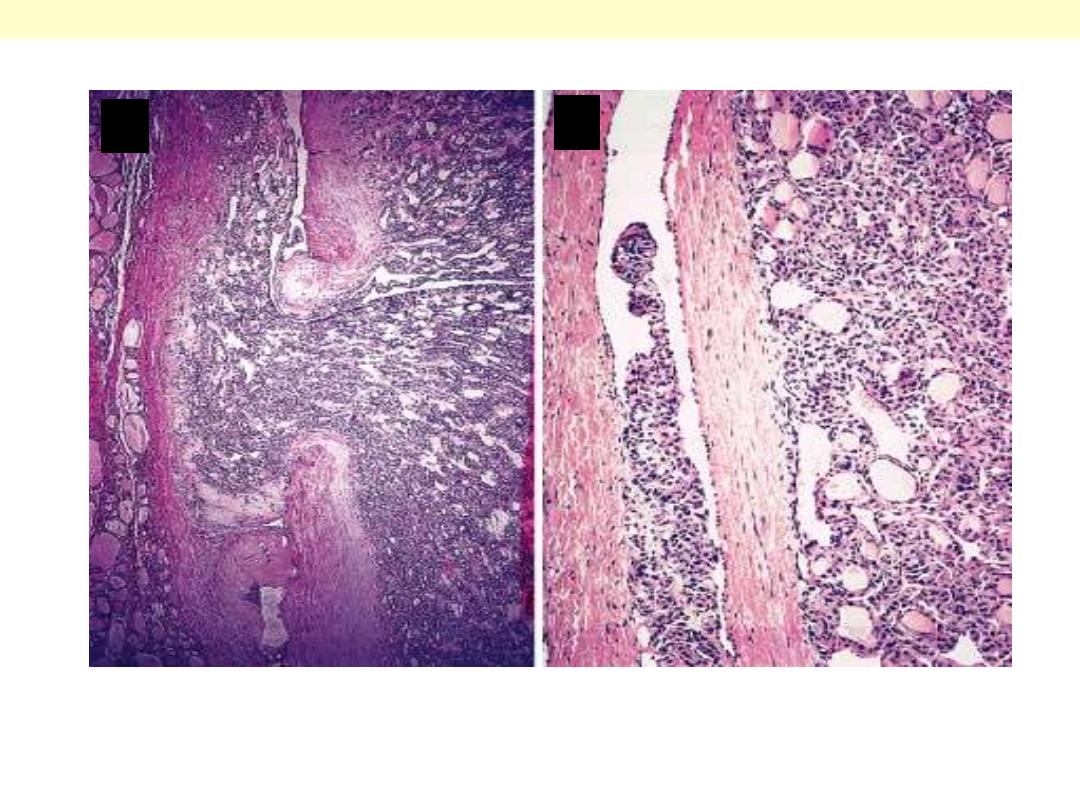
Minimally invasive follicular carcinoma: Thyroid
Capsular (A) and vascular (B) invasion in minimally invasive
follicular carcinoma.
A
B
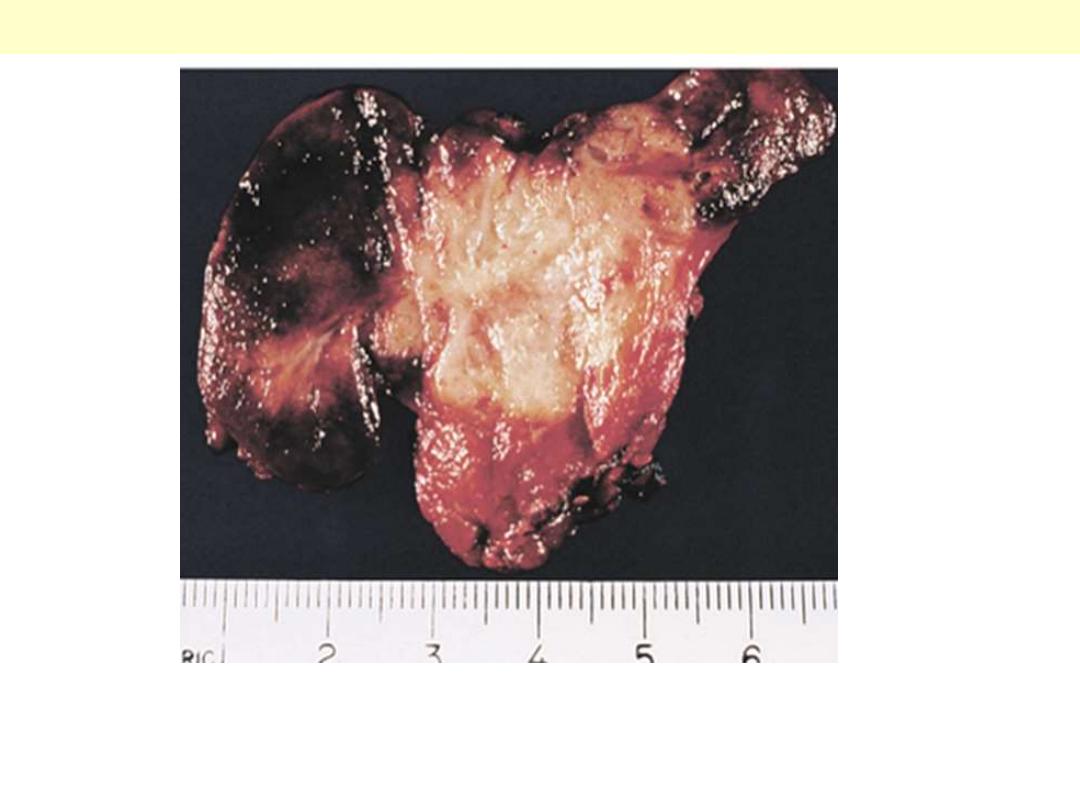
Note its unencapsulated quality, solid appearance, and
yellowish tan color
Medullary carcinoma thyroid
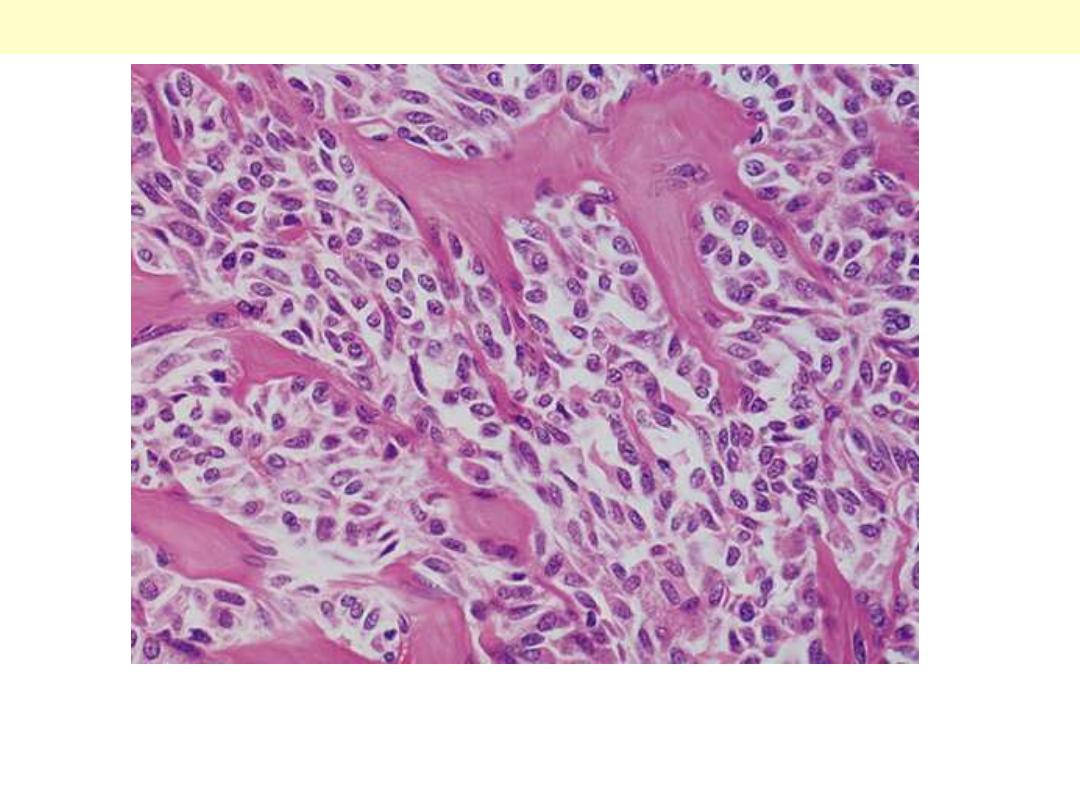
Solid pattern of growth with round & spindle cells
associated with deposition of pinkish amyloid.
Medullary carcinoma thyroid
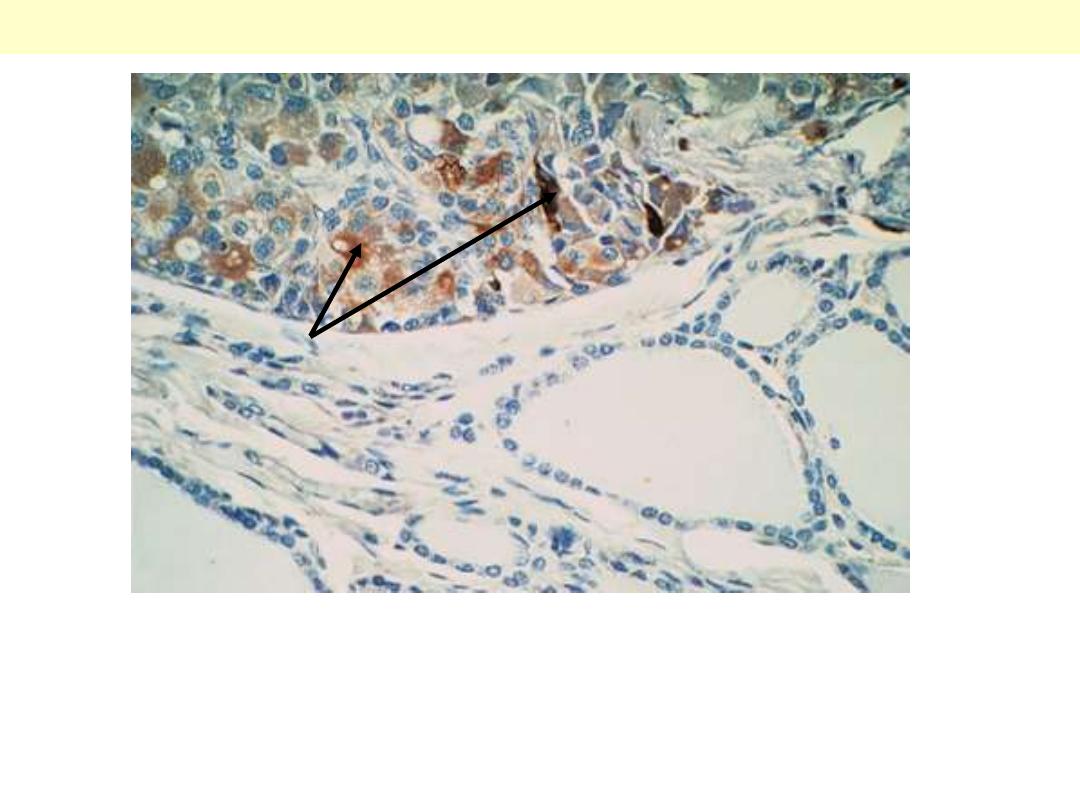
c
Medullary carcinoma
Immunocytochemical positivity for calcitonin. The
adjacent nonneoplastic thyroid follicles are negative.
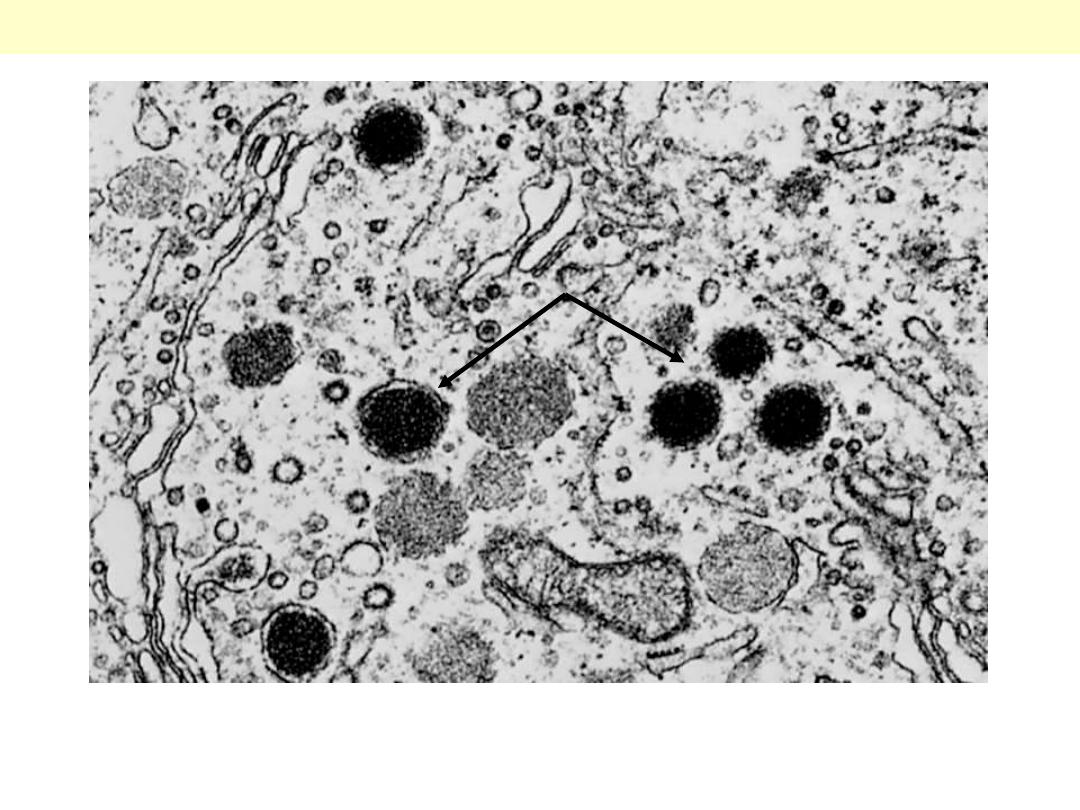
These cells contain membrane-bound secretory granules that are the sites of storage of calcitonin and
other peptides (original magnification ×30,000).
Medullary thyroid carcinoma EM
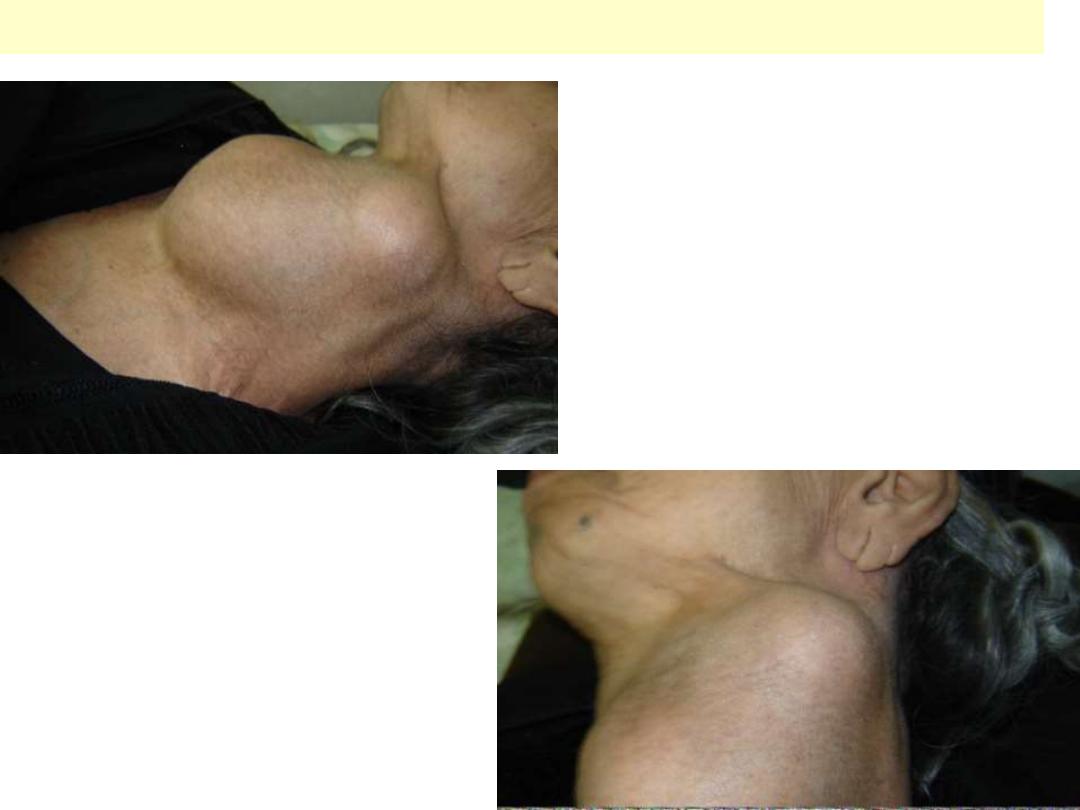
A 70-year-old Iraqi female presented with a
3-month-history of rapidly enlarging thyroid
mass with shortness of breath & dysphagia.
Anaplastic (undifferentiated) carcinoma thyroid
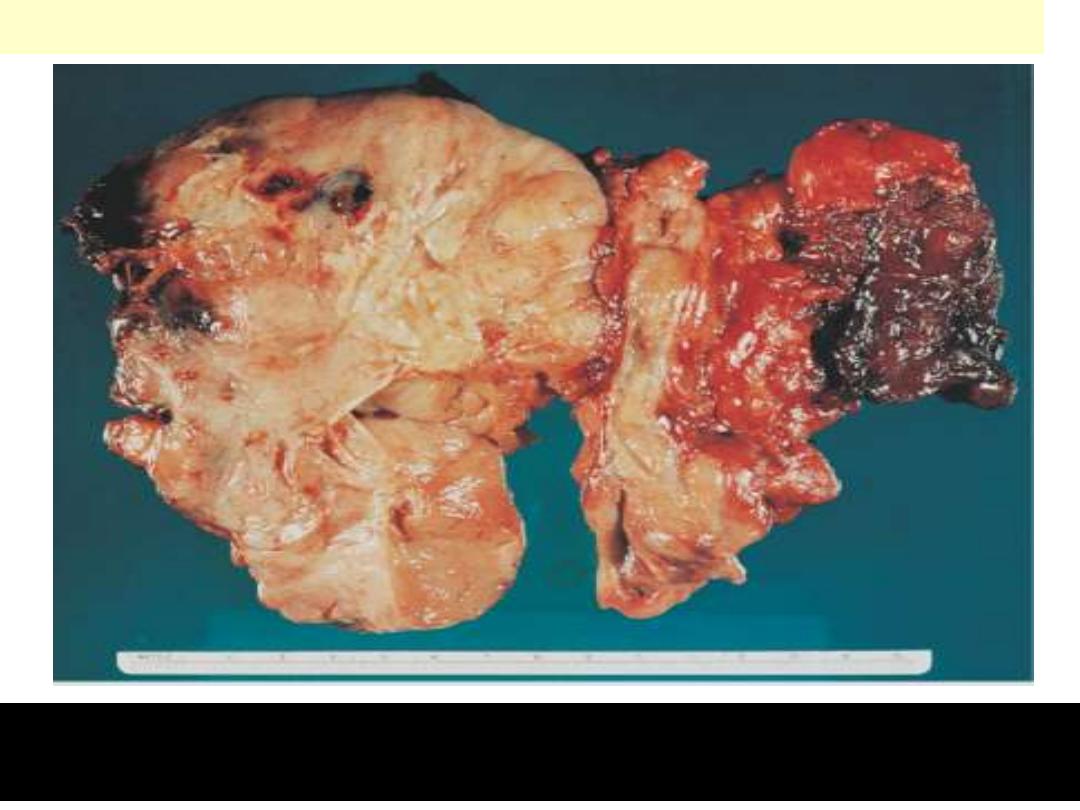
The cancer is entirely replacing the gland and extending into the
surrounding skeletal muscle.
Anaplastic (undifferentiated) ca thyroid
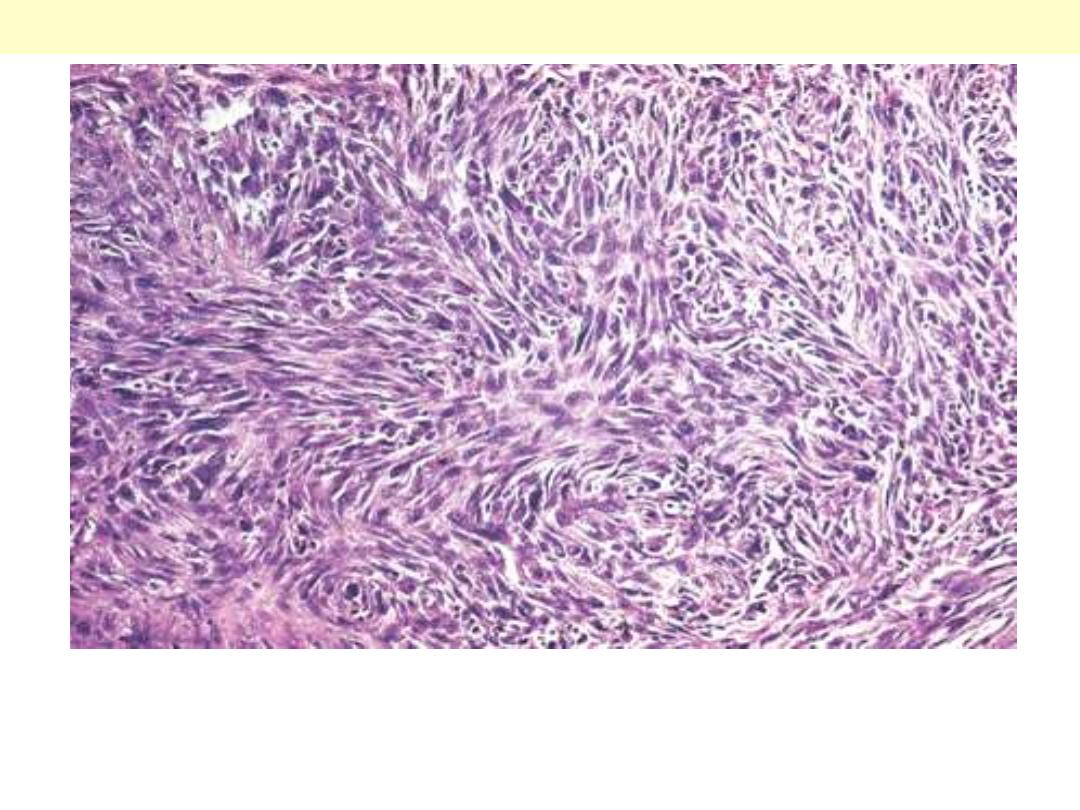
Anaplastic carcinoma of the spindle cell type. Tumor grows in
diffuse fashion around thyroid follicles. Appearance closely
simulates that of soft tissue sarcoma.
Anaplastic (undifferentiated) ca spindle cell type thyroid
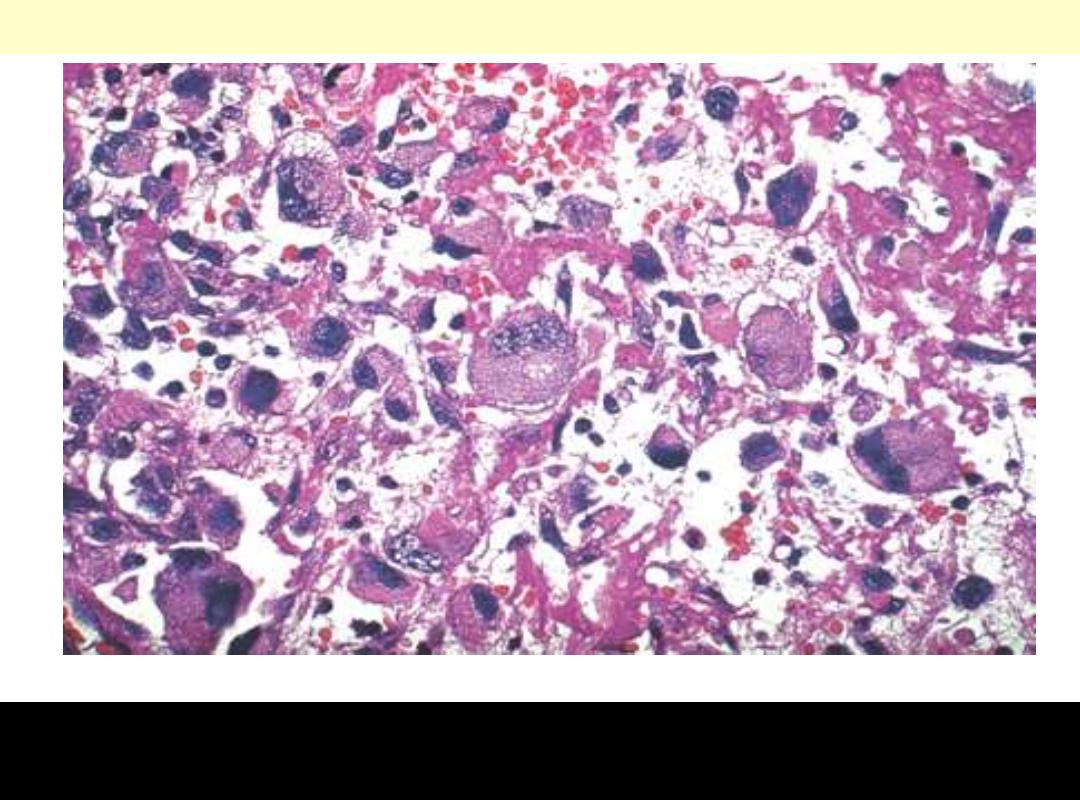
Several giant tumor cells with huge hyperchromatic nuclei are
present in solid and myxoid background.
Undifferentiated (anaplastic) carcinoma
