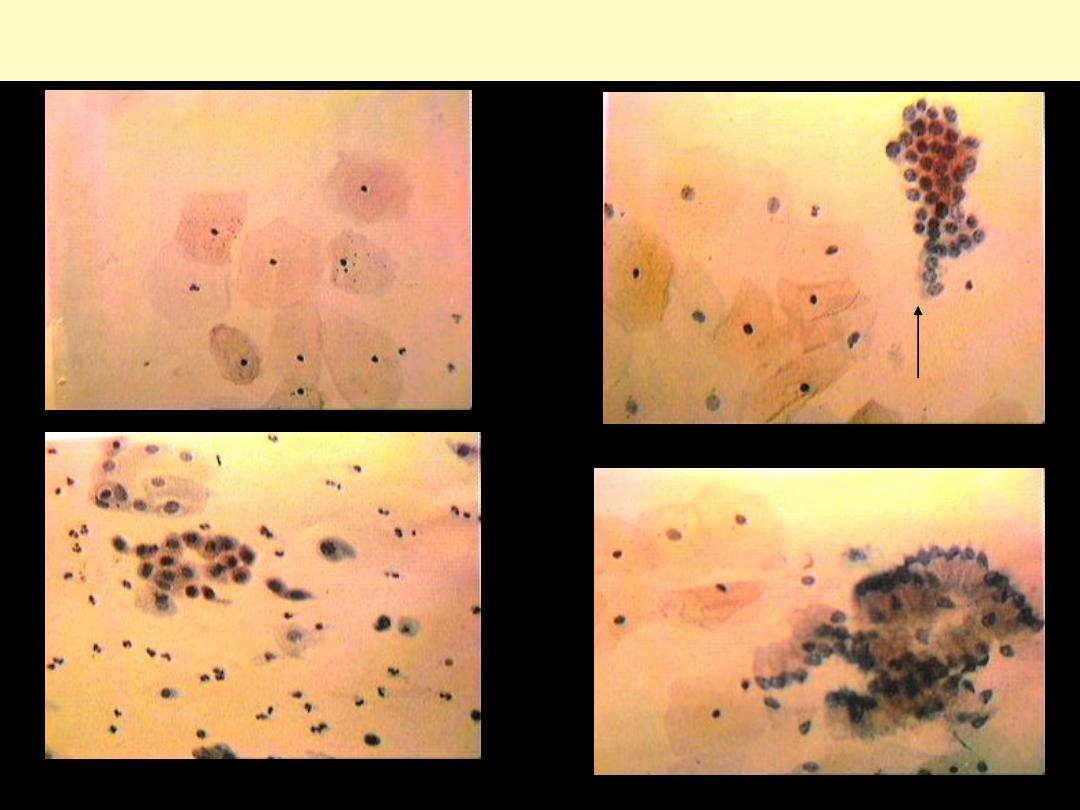
Cervix cytology-normal
superficial cells
parabasal cells
immature sq. cells
endocervical cells en face
endocervical cells-profile
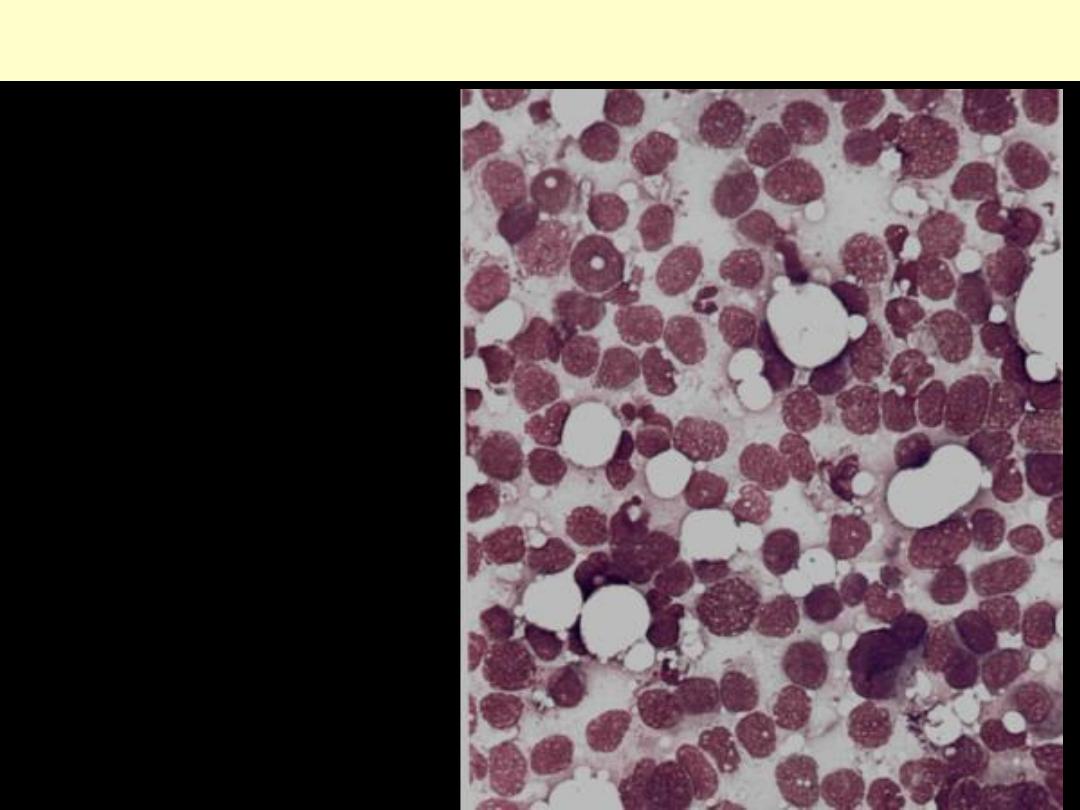
Carcinoma breast FNA
Note: The aspirate is hypercellular
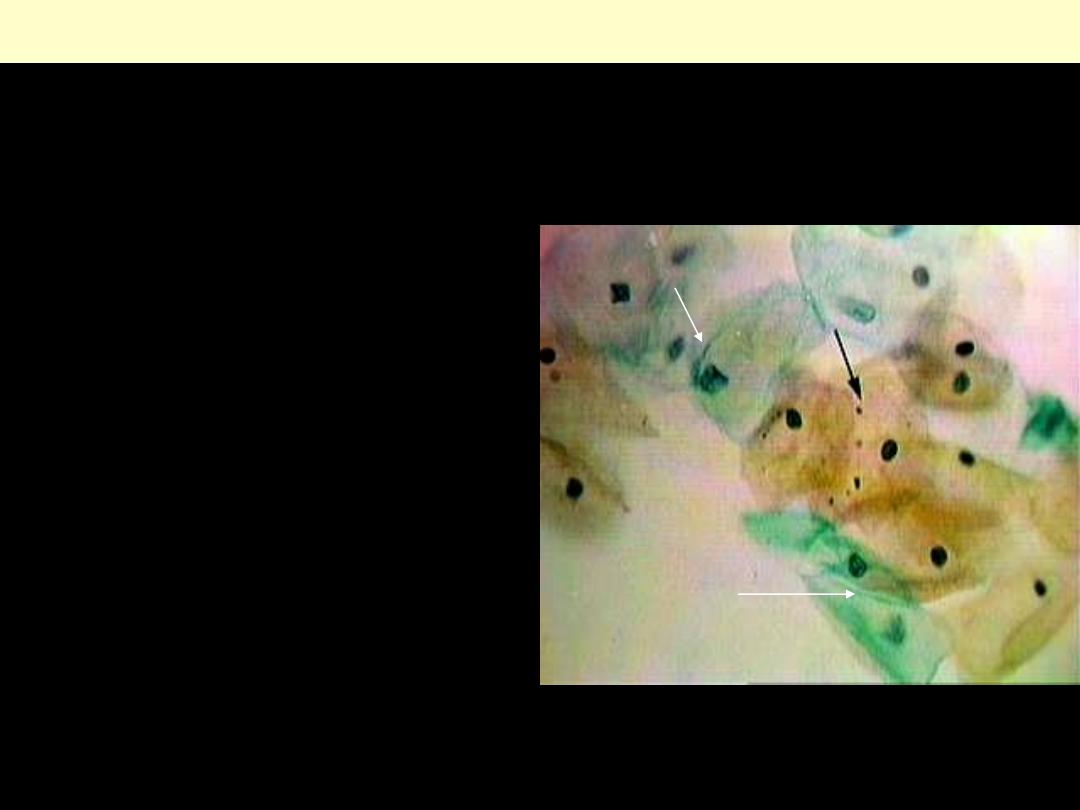
Postovulatory smear
•
This shows the effect of progesterone
produced by the corpus luteum after
ovulation.
•
Superficial cells with pyknotic nuclei and
keratohyaline granules are still seen (black
arrow), but there are increased numbers of
intermediate squamous cells with vesicular
nuclei showing a fine chromatin pattern.
•
There is some clumping of the cell with
folding of the cytoplasm (white arrow).
•
If vaginal wall smears are taken daily, it is
possible to identify the time of ovulation by
sudden change of pattern from that seen in
(estrogen effect) to that seen in this
photograph.
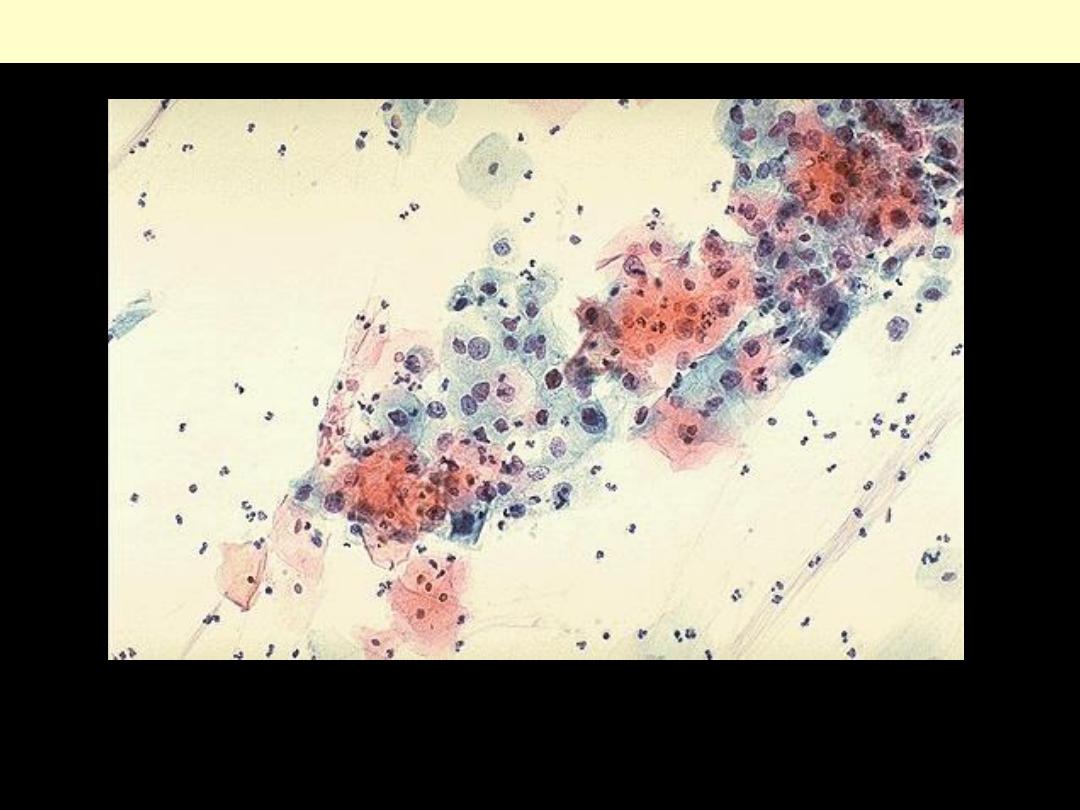
Pap smear (cervix): dysplasia
The cytologic features of normal squamous epithelial cells can be seen at the center top and bottom,
with orange to pale blue plate-like squamous cells that have small pyknotic nuclei. The dysplastic cells
in the center extending to upper right are smaller overall with darker, more irregular nuclei.
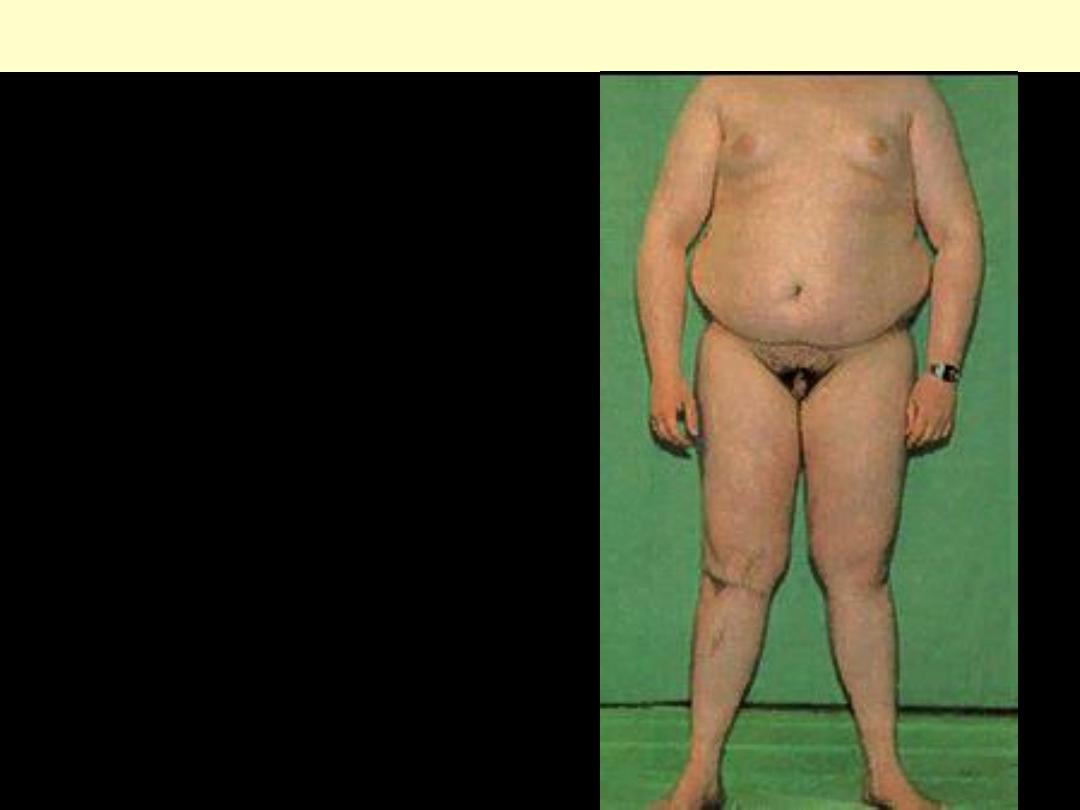
Klinefelter’s syndrome
The patient is phonotypically male, but have two or
more X chromosomes-most commonly 47 XXY. He is
eunuchoid with small, firm testes, gynecomastia and a
female distribution of body hair, and he may be
unusually tall.
