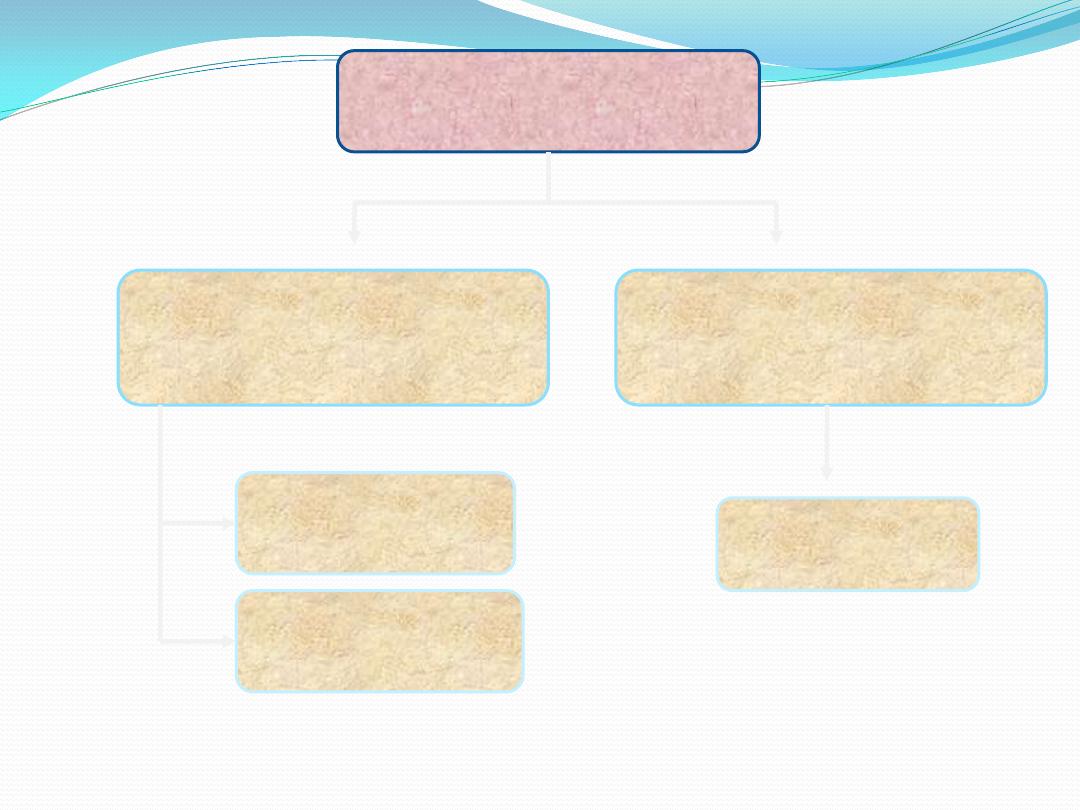
Helminthology
Platyhelminthes
(Flat worms)
Nematohelminthes
(Round worms)
Trematoda
(Flukes)
Ceastoda
(Tape worms)
Nematoda
Continue


GENERAL CHARACTERS
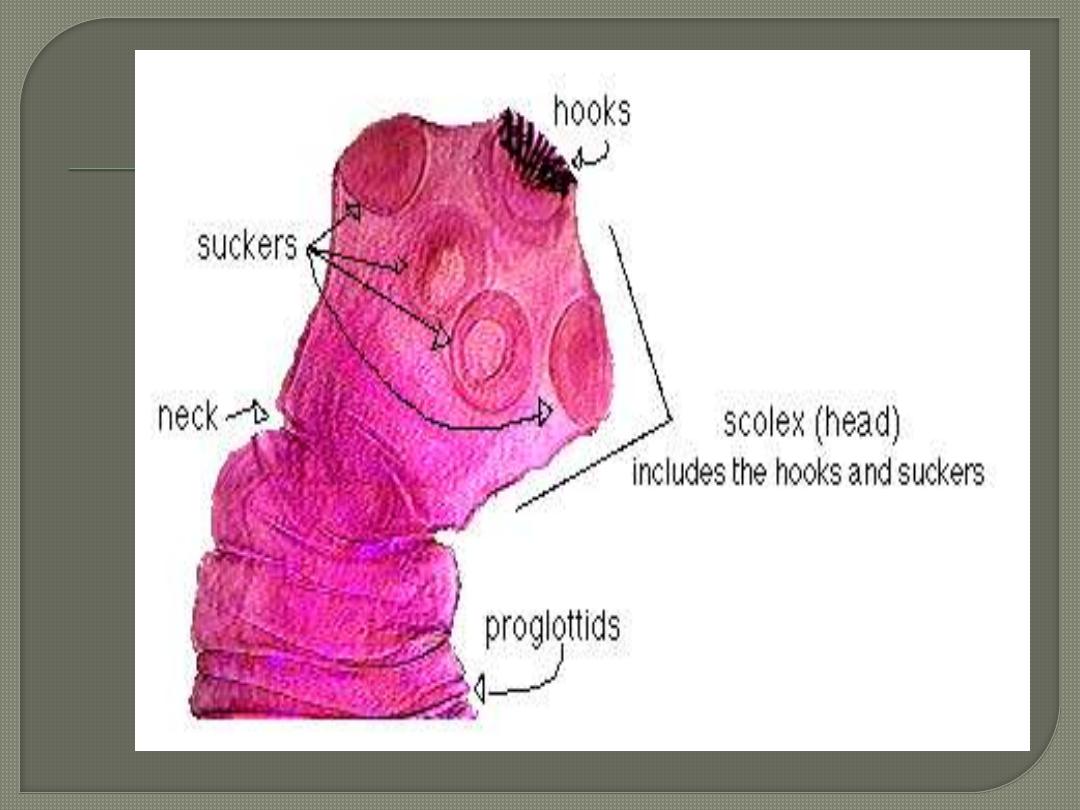
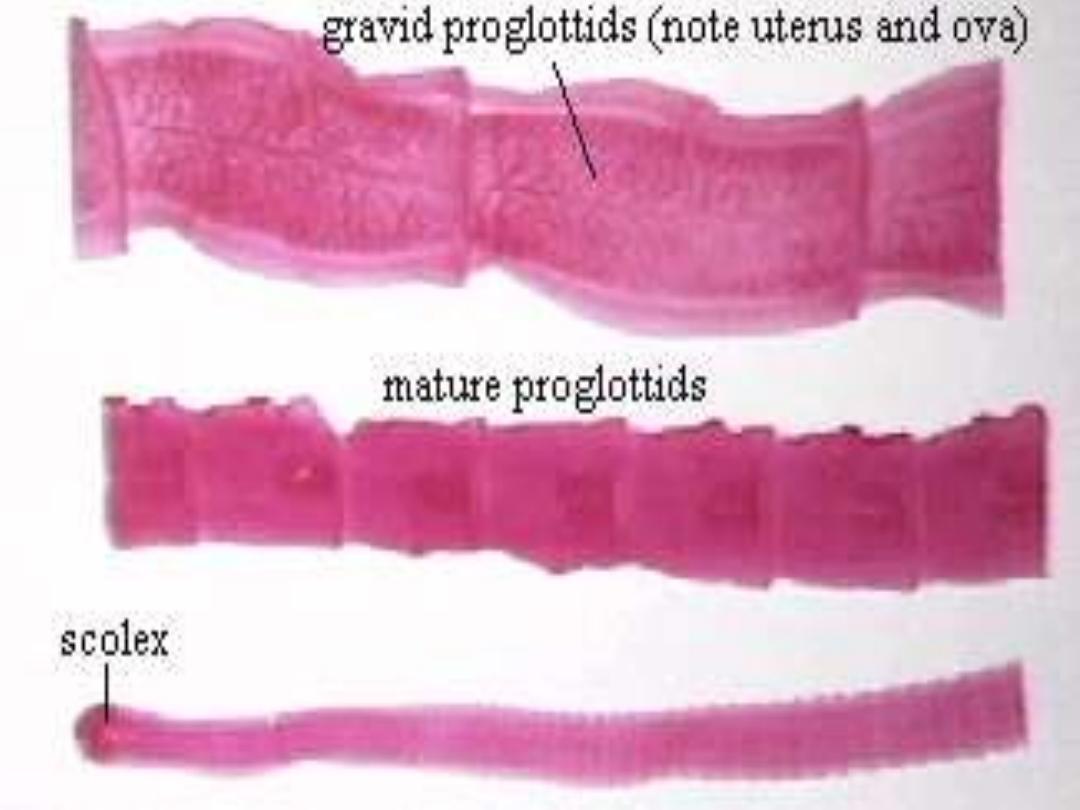
Ribbon or tape shaped.
Adult worm composed of:-
a.
Rounded scolex with appendages for
attachment (e.g. Suckers or hooked
rostella).
b.
Neck (region of growth).
c.
Strobillum (composed of 3- 4000
segments [proglottide]).
Length varies between 3mm-10m.
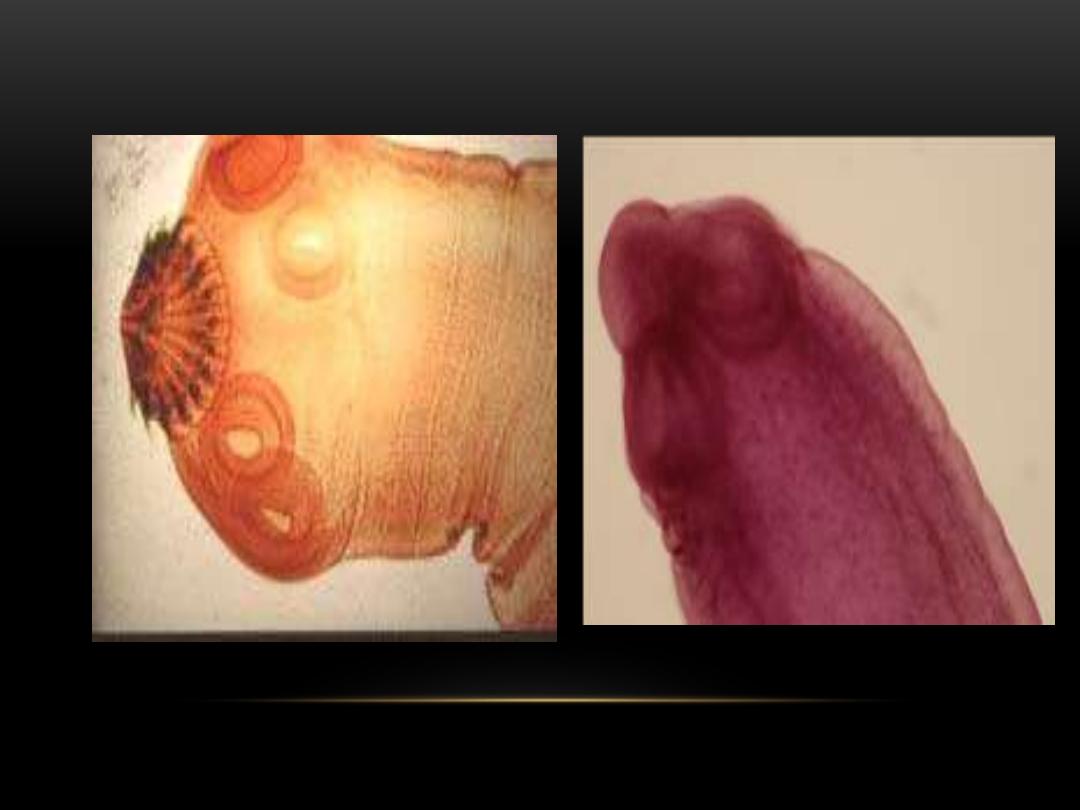
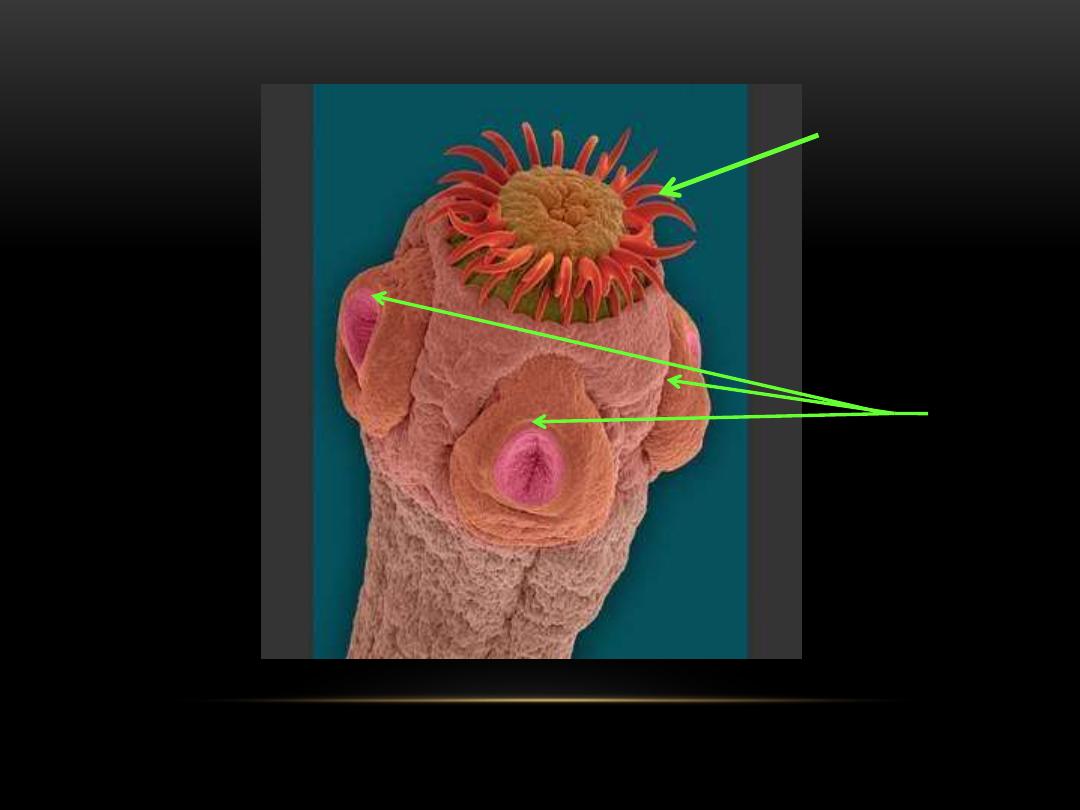
Hooked
scolex
Sucker
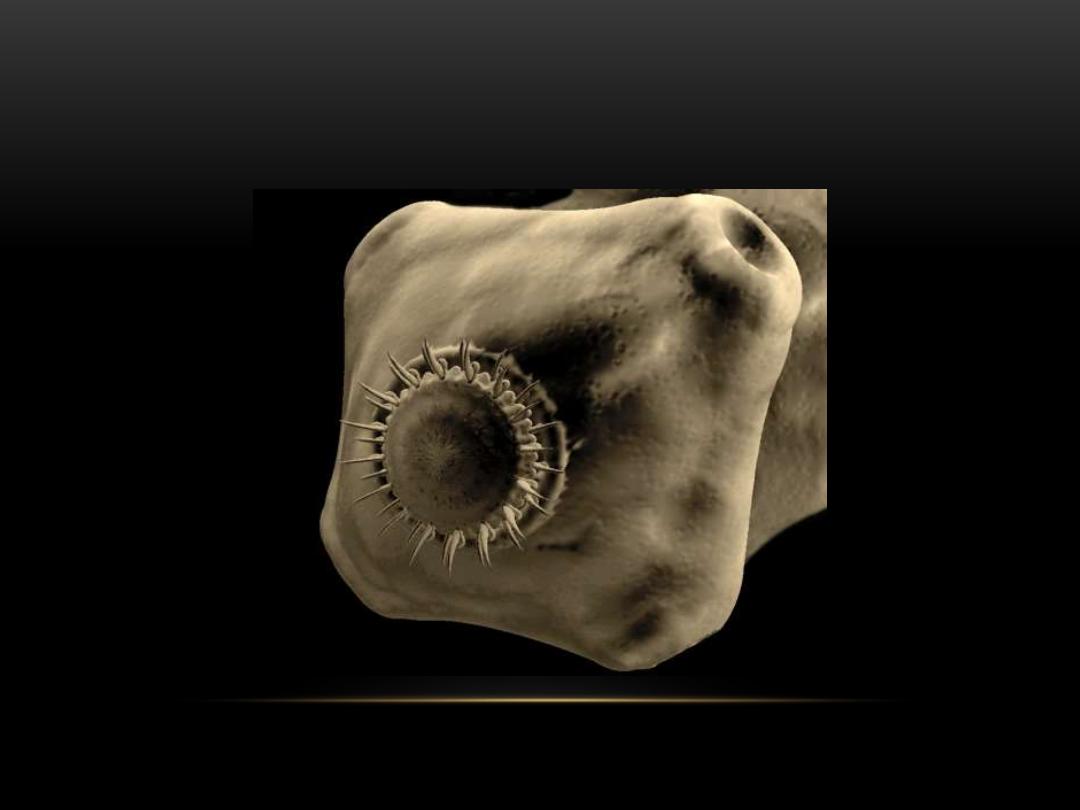
T.solim scolex

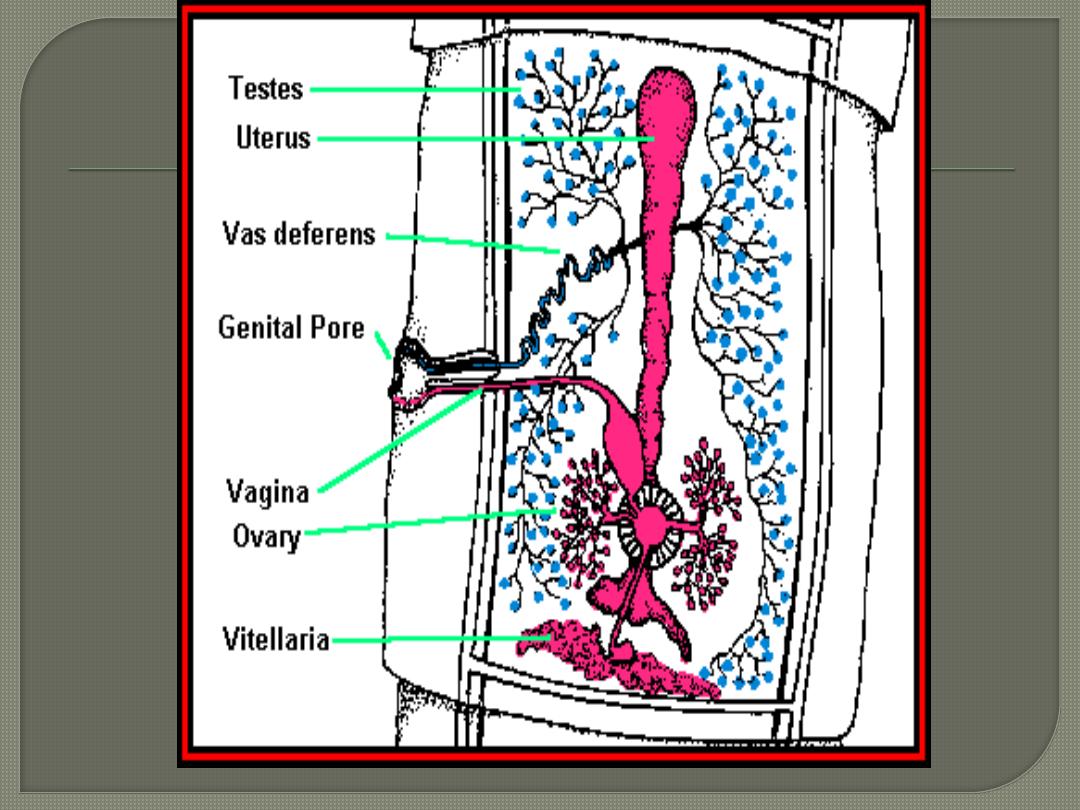
All cestodes are hermaphrodite
(Each segment contains male & female
reproductive system).
No body cavity.
No digestive tract.
No vascular system.
Continue
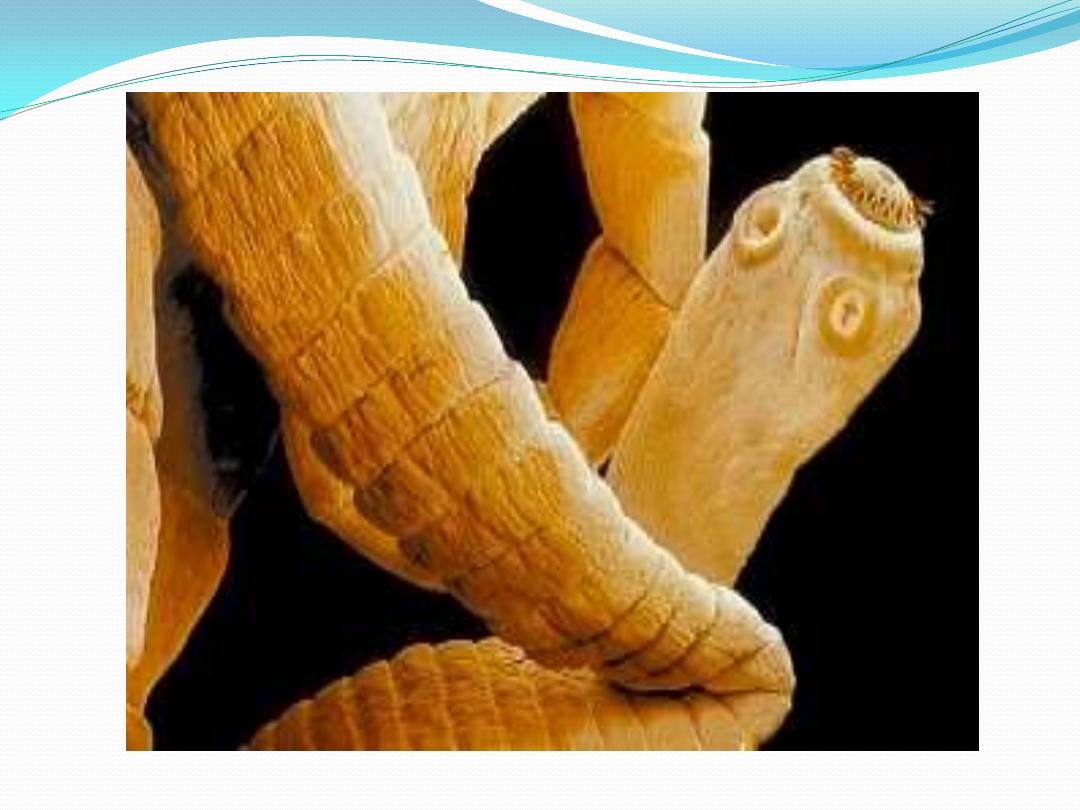

Continue
[1] [2]
[1]
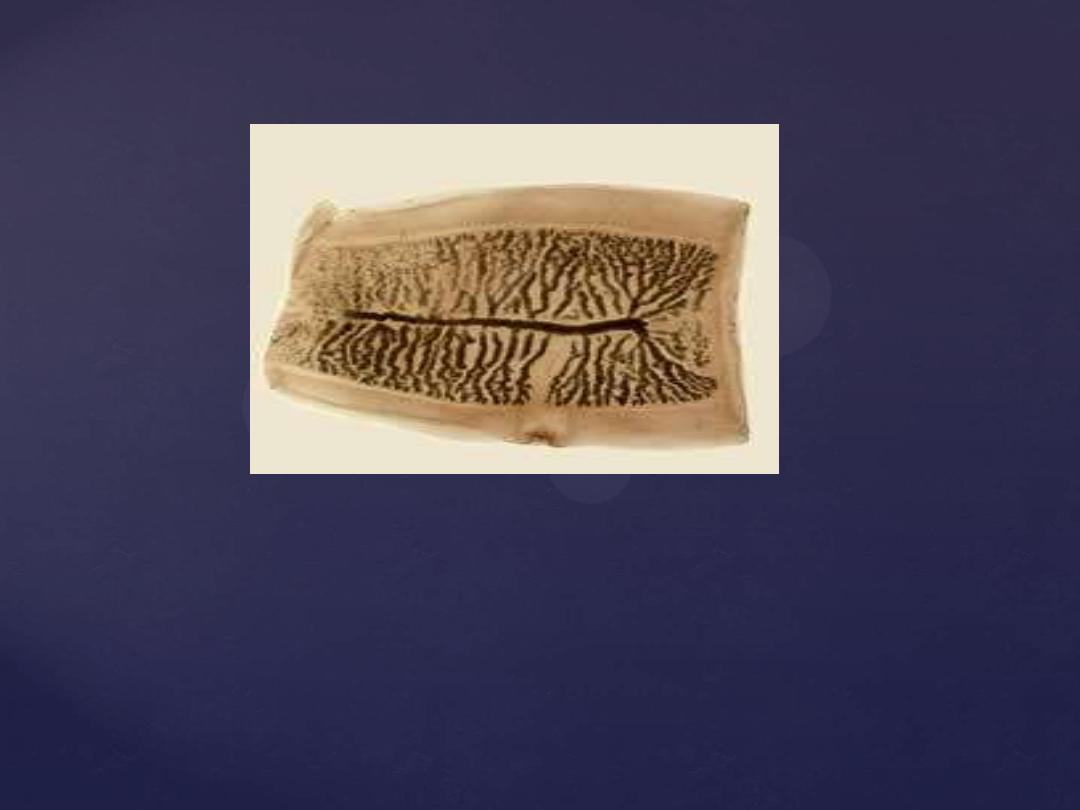
T. solium has 7 to 13 branches.
[2]
T. saginata has 15 to 20 branches.


Habitat:
a.
Adult worms live in small
intestine of their definitive hosts.
b.
Larval stage found in intermediate
hosts tissues.
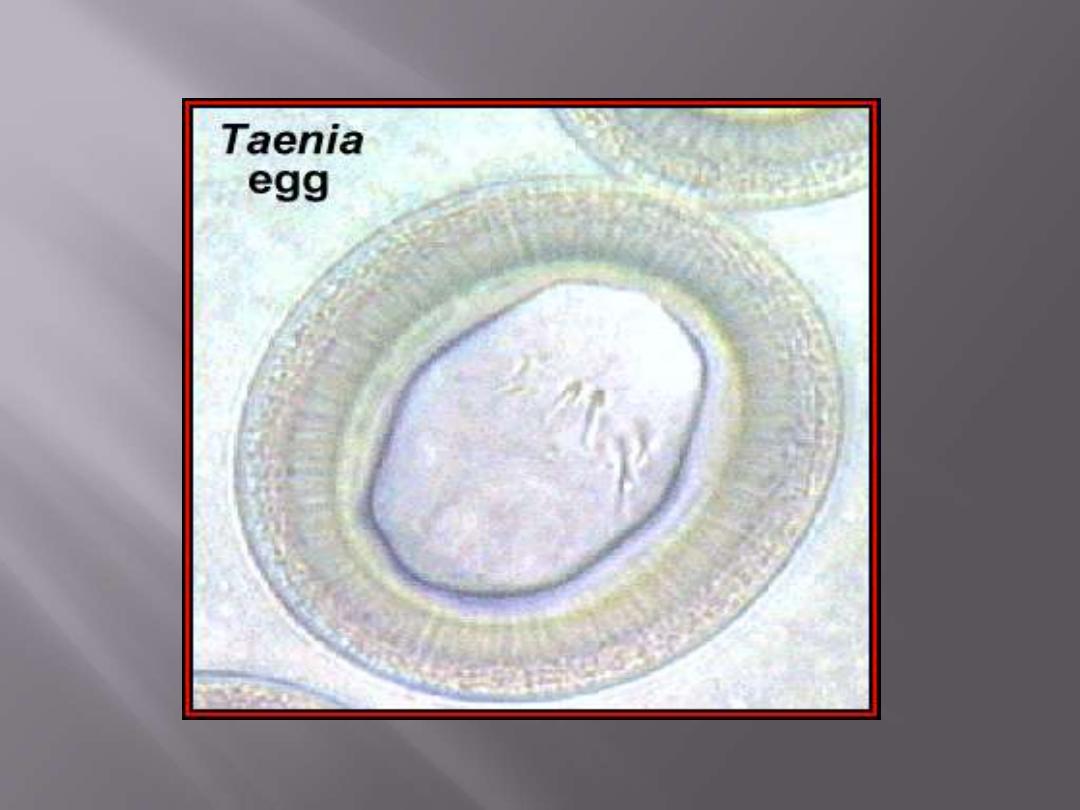
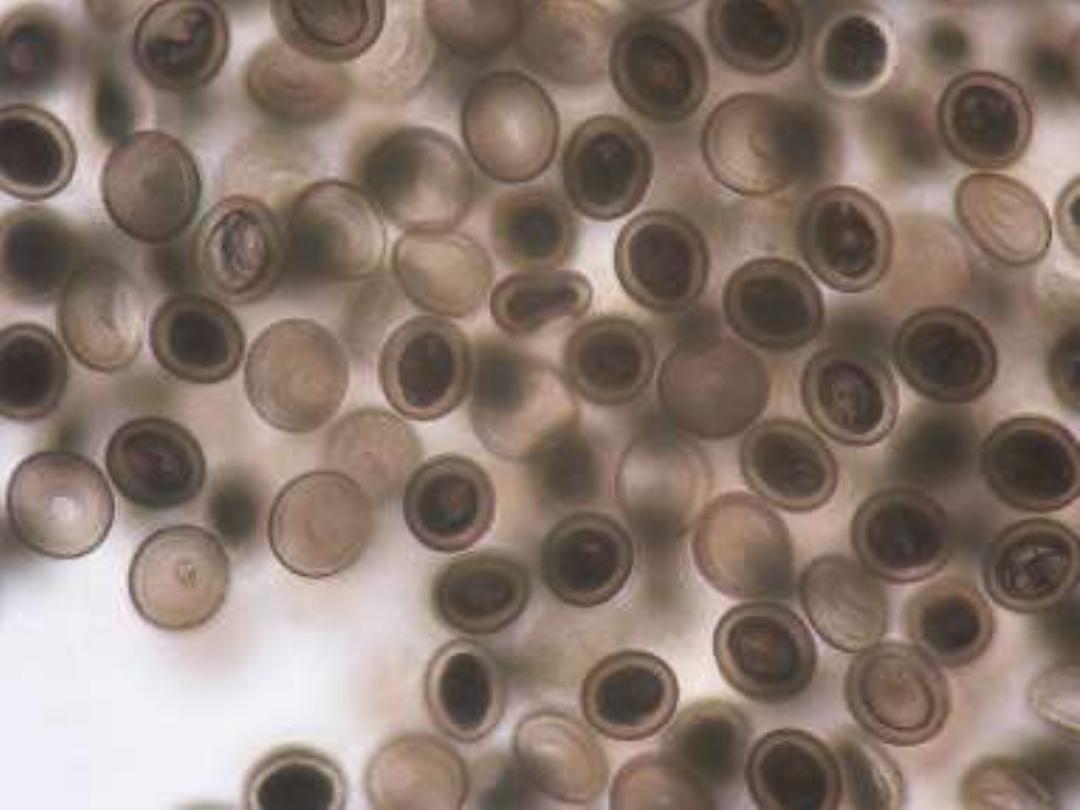
Eggs are diagnostic stage
(Spherical, with shell embryonic
membranes for embryo protection;
the embryo [onchosphere] carries 6
elongated hooks [hexacanth])
Continue

Replication is either by self-fertilization or by cross
fertilization.
Usually the presence of adult worms in the host
intestine does not produce serious symptoms, but
severe and sometimes fatal symptoms may occur due
to presence of the larval stage in the host tissues
(
e.g. Tainea solium & Echinoccus granulosus
).

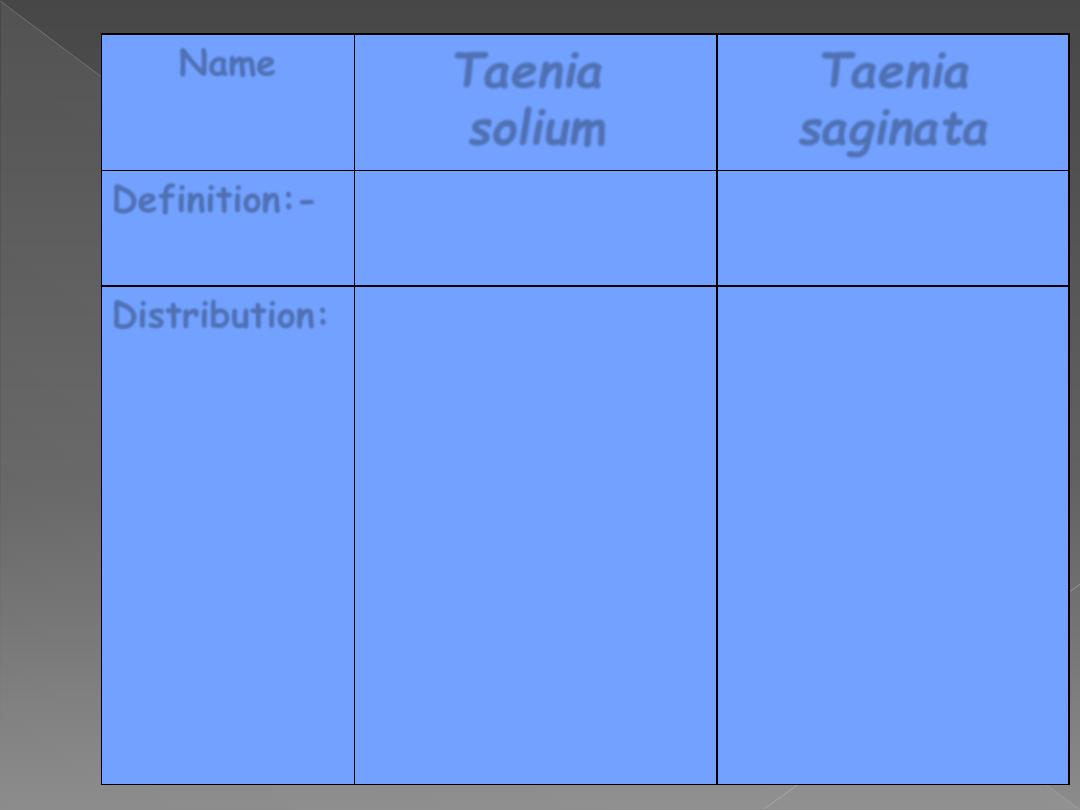
Name
Taenia
solium
Taenia
saginata
Definition:-
Pork
tape worm
Beef
tape worm
Distribution:
World wide
•
Depends
on
the
access
of
pigs
to
human feces and to
consumption of raw
& undercooked pork .
•
More endemic in
Asia, South Africa
and East Europe.
World wide
•
Depends
on
the
access of cattle to
human feces.
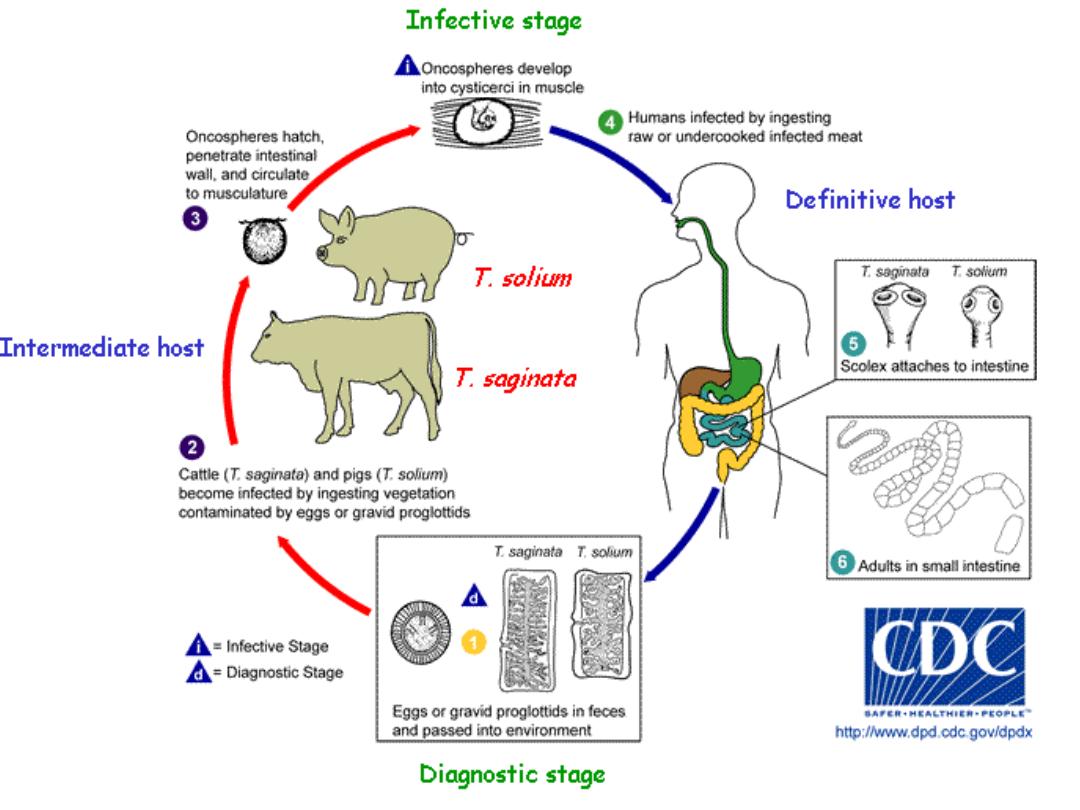
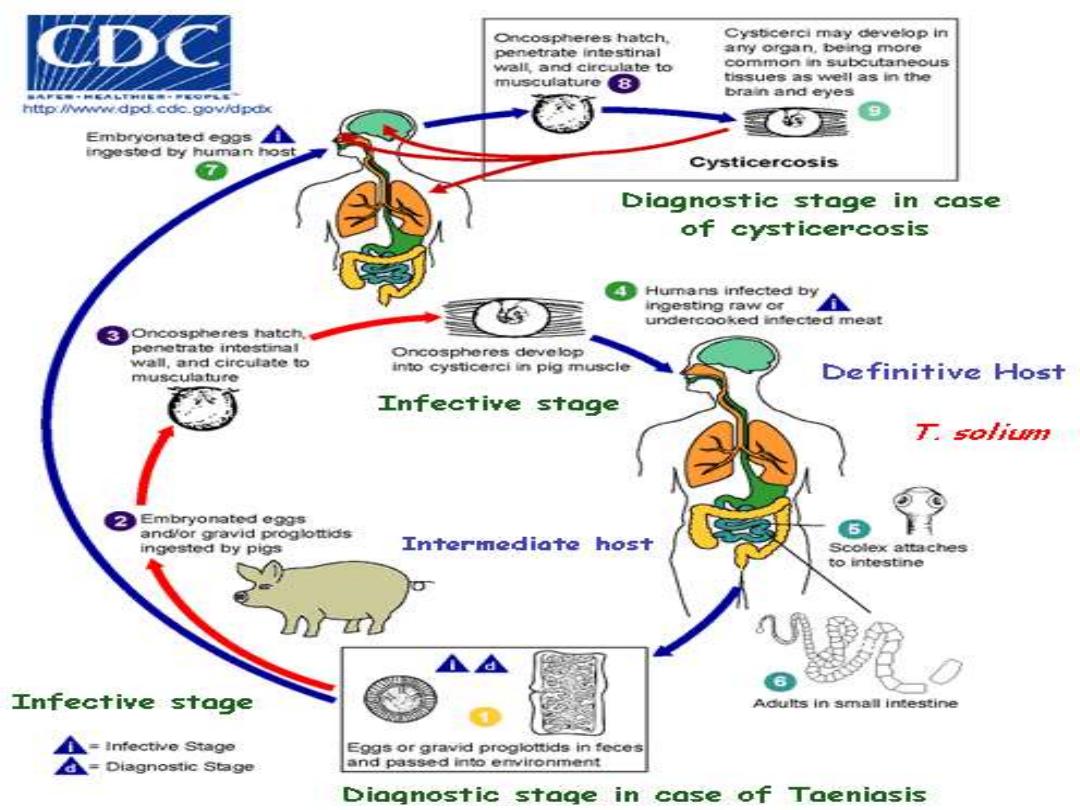
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Disease:
•
Taeniasis
•
Cysticercosis
•
Taeniasis
Habitat:
•
Adult:
Small intestine of
man
•
Larva:
As cysticercus in
pigs muscles or in
human tissues.
•
Adult:
Small intestine of
man
•
Larva:
As cysticercus in
beef muscles.
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Definitive
host:
Human
Intermediate
host:
Pigs
(human is also
a dead end
intermediate
host)
Cattle, sheep
& various
herbivores
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Diagnostic
stage:
In case of Taeniasis:
*
Eggs
and
active gravid
segments in
stool.
Eggs
•
Spherical
•
Hexacanth embryo
•
Radially
striated
embryophore
Gravid Segments
*Appears
•
in stool
•
perianal regions
•
underclothing
*Disintegrate to liberate
egg

Taenia solium
Taenia
saginata
Diagnostic
stage:
•
In
case
of
Cysticercosis:
*
By radiography of the
calcified larvae.
1.
In skeletal muscles.
2.
Visualization
in
eye
orbit.
* CT “computed
tomography” & MRI
“magnetic resonance
Imaging” for
neurocysticerosis.
------------------
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Infective
stage:
•
Taeniasis:
Larval
stage
encysted in raw or
undercooked
pork.
•
Cysticercosis:
Eggs.
Larval
stage
(cysticercus bovis)
encysted in raw
or
undercooked
beef.
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Treatment:
•
In case of
Cysticercosis:
Surgical removal.
----------
Prevention:
•
Proper disposal
of
human
sewage.
•
Proper hygiene.
•
Proper cooking
of pork.
•
Proper disposal of
human sewage.
•
Proper cooking of
beef.
•
Preservation of
beef meat by
freezing at -10
0
c
for 5 days.

Presence of the adult worm in small
intestine of human, symptoms are not
significant and thought to be psychic due
to vision of active proglottides in stool,
these symptoms may be
abdominal
discomfort and intestinal irritation.
Taeniasis
larvae development occurs in 2 months
to give a fluid filled bladder with armed
scolex [a cysticercus].
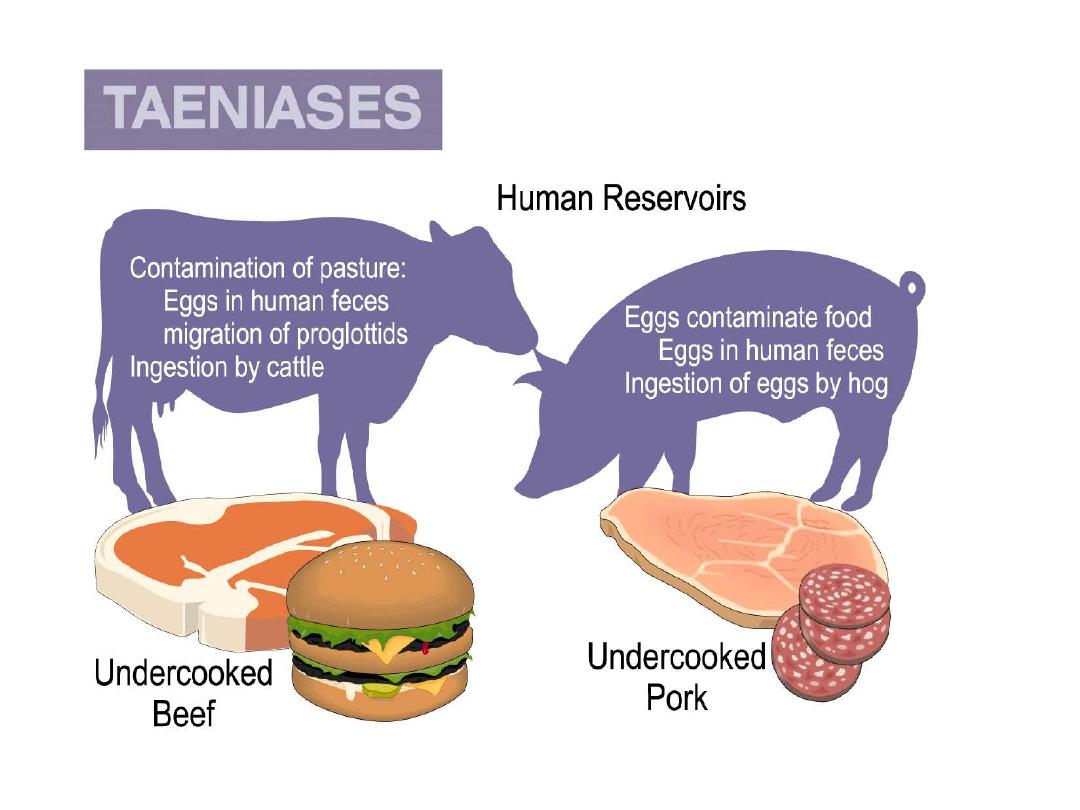
T. solium eggs ingested by
human
hatch in the intestine, penetrate
mucosa & enter blood circulation
resident in liver, skeletal muscles, brain
or eye.


Usually no immune response as the
larvae are alive but when they die, the
larvae are classified after an inflammatory
response and symptoms begin to appear.
•
In muscles:
Fever, swelling, atrophy &
fibrosis.
•
In brain:
Symptoms resembling brain
tumors, epilepsy, ataxic gait or
mental confusion
(Neurocysticerosis).
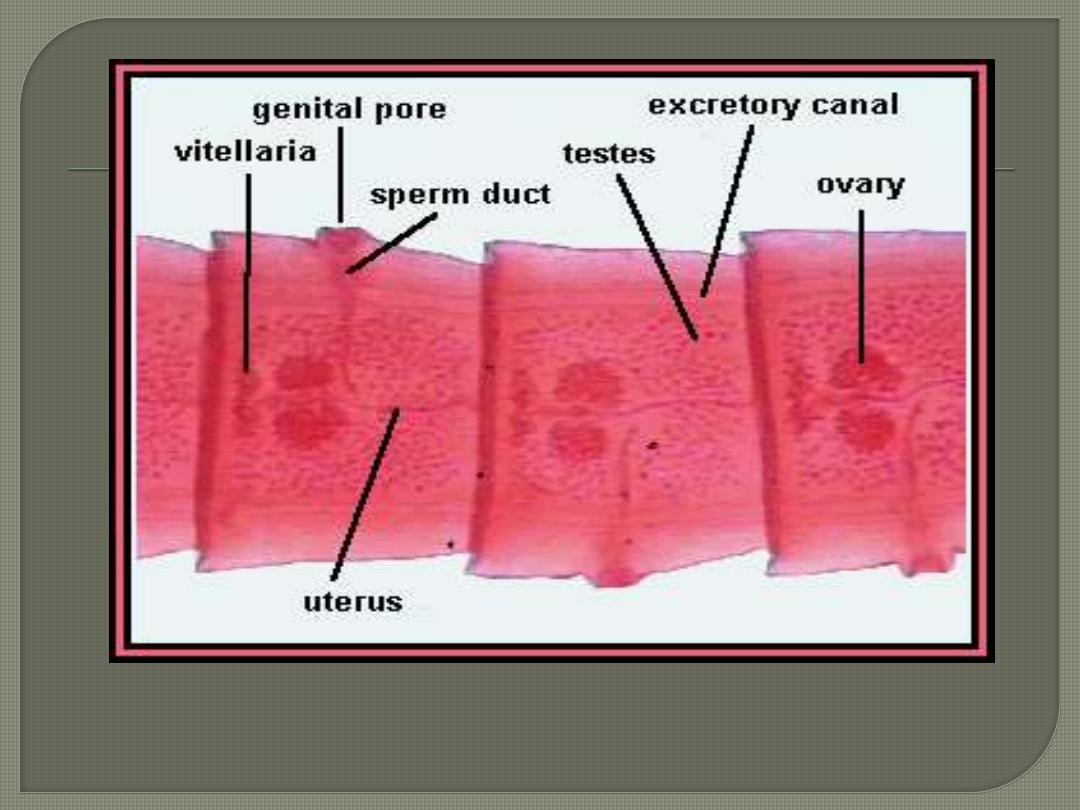
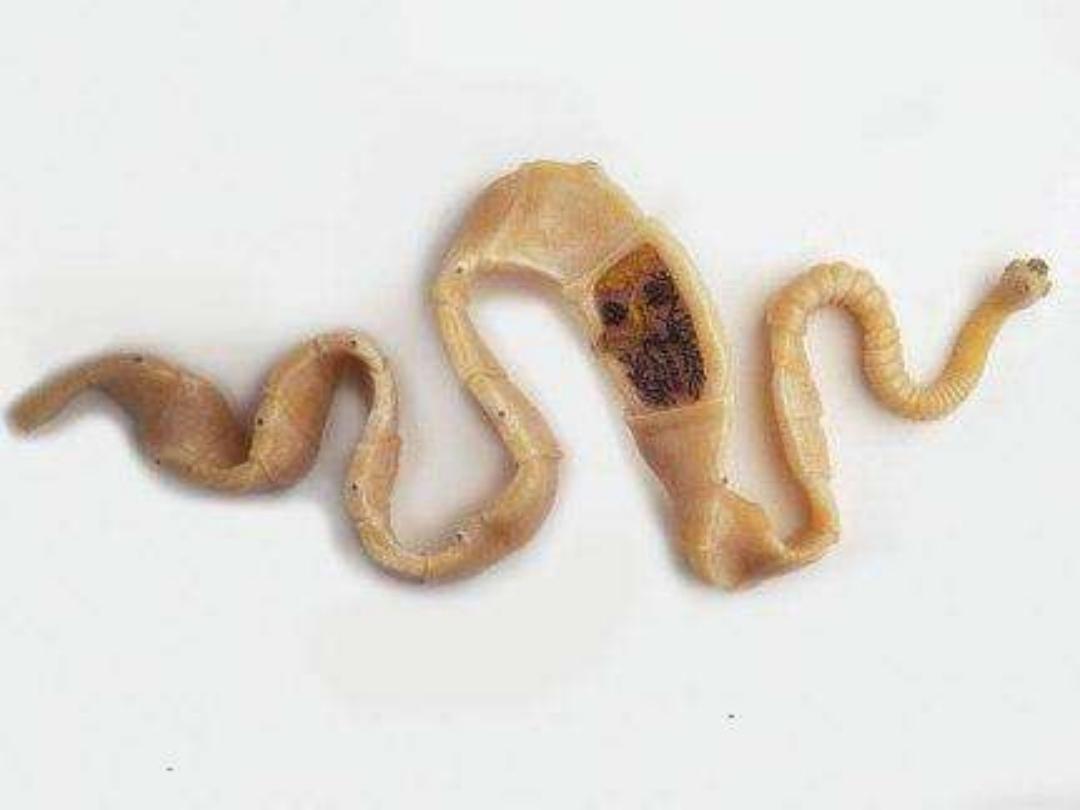
This slide shows the gravid segment
; contains
male & female reproductive system).
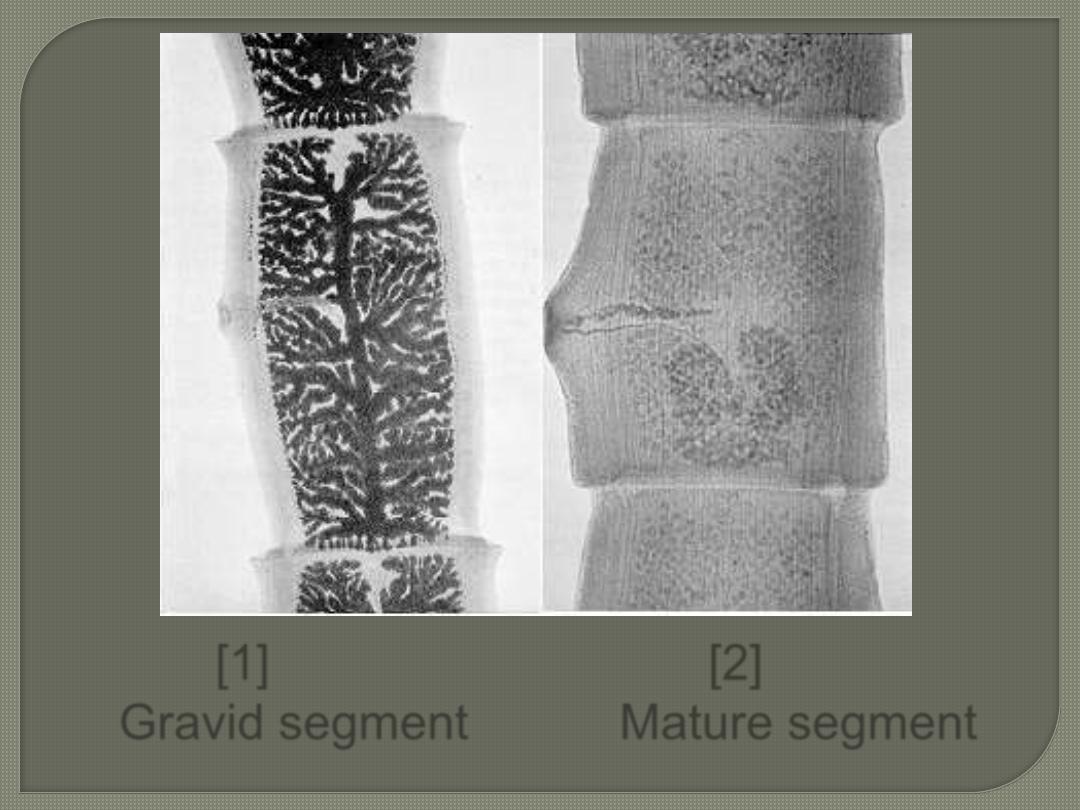
[1] [2]
Gravid segment Mature segment

