
1
المحاضرةاألولى أ. صباح النجار
Parasitology
Tapeworms (cestodes)
Objectives
: to study the general characteristics of medically important
tapeworms including their morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis and laboratory
diagnosis.
General characters:
Tapeworms is a group of parasites considered to have limited distribution and
have the following characters;
- All tapeworms utilize more than one host during their life cycle except
Hymenolepis nana
in which life cycle takes place in a single host.
- They have ribbon- like shape whose bodies are made up of many similar
segments or proglottids,these segments are flattened dorsoventrally.
-
The anterior end, the
‘head’, is known as the scolex and has well developed adhesive
organ.
- Adult tapeworm inhabits the small intestine of vertebrates. While the larvae
inhabit the tissues of vertebrates & invertebrates.
- All tapeworms are hermaphrodites, they have both male and female
reproductive organs in the same segment.
- They have no gut, absorption of nutrients taking place through the outer
protective layer known as integument(body wall).
Adult tapeworms produce minimal intestinal irritation and few systemic effects. All
symptoms have been attributed to chemical effects(toxic byproducts) and

2
mechanical effects. The absorbed byproducts
which secreted by the worm may
create systemic intoxication, diarrhea and vomiting.
Mechanical action cause slight irritation in the intestinal mucosa, and
considerable disturbances in the normal function of GIT which cause chronic
indigestion. The worm utilize the host’s nutrients which lead to hunger pain &
loss of weight.
- Adult tapeworm composed of:
1- Scolex (head): the point of attachment to mucous membrane. The
scolex could be armed or unarmed depend on the presence or
absence of hooklets which are spine like structure.
2- Neck: the region just behind the head and considered as the region of
growth, from the posterior end of the neck , the process of
strobilization start.
3- Strobila: a chain of segments or proglottids composed of:
-immature proglottid posses undifferentiated sex organs.
-mature proglottid contain well differentiated sex organs of both male
and female .
-gravid proglottid ,all reproductive organs will be atrophy except the
uterus which filled with eggs .
Type of Cestodes larvae :
A - Bladder larvae :
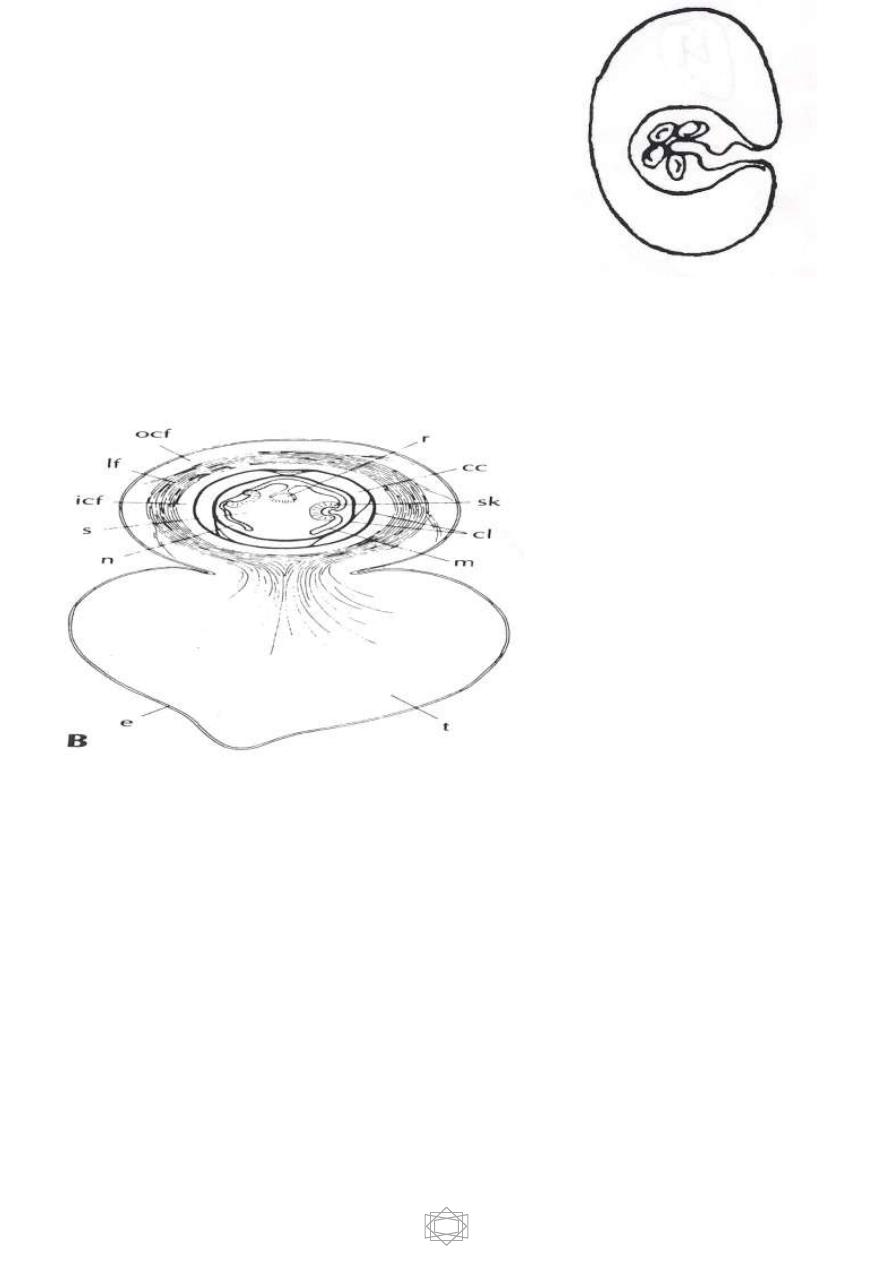
3
1. Cysticercus : a true bladder worm, It is oval
in shape, about 5x10 mm has fluid- filled
membranous bladder with invaginated scolex.
e.g. larvae of
Taenia solium
&
Taenia
saginata.
2.
Cysticercoid ;is not a true bladder worm, it
has bladder filled with parenchyma cells and invaginated scolex and a
caudal appendage . e.g
. larva of Hymenolepis spp.
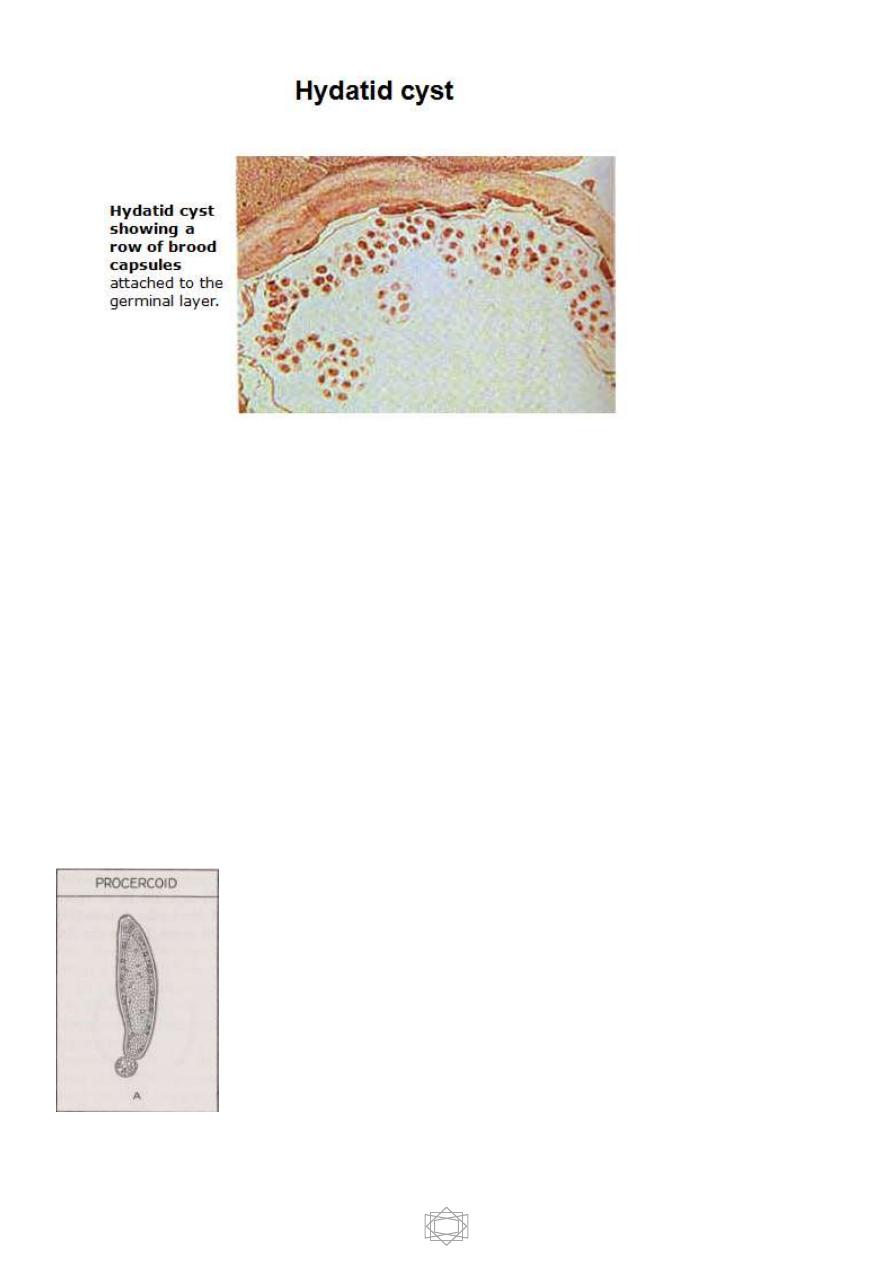
3-Hydatid cyst: large bladder composed of two layers, outer laminated and
inner germinal layers and filled with hydatid fluid . It is form multiple scolices
and numerous daughter or brood capsules. e.g. larva of
Echinococcus spp
.
4
3.Coenurus : A bladder worm resembles Cysticercus except that its bladder
generally is much larger and bears numerous scolices rather than one e.g.
larva of Taenia multiceps .
B – Solid larvae:
1. Procercoid : sac – like solid body with cephalic invagination and caudal
spherical appendage at its posterior end which contain 6 hooks e.g.
Diphylobotherium latum.
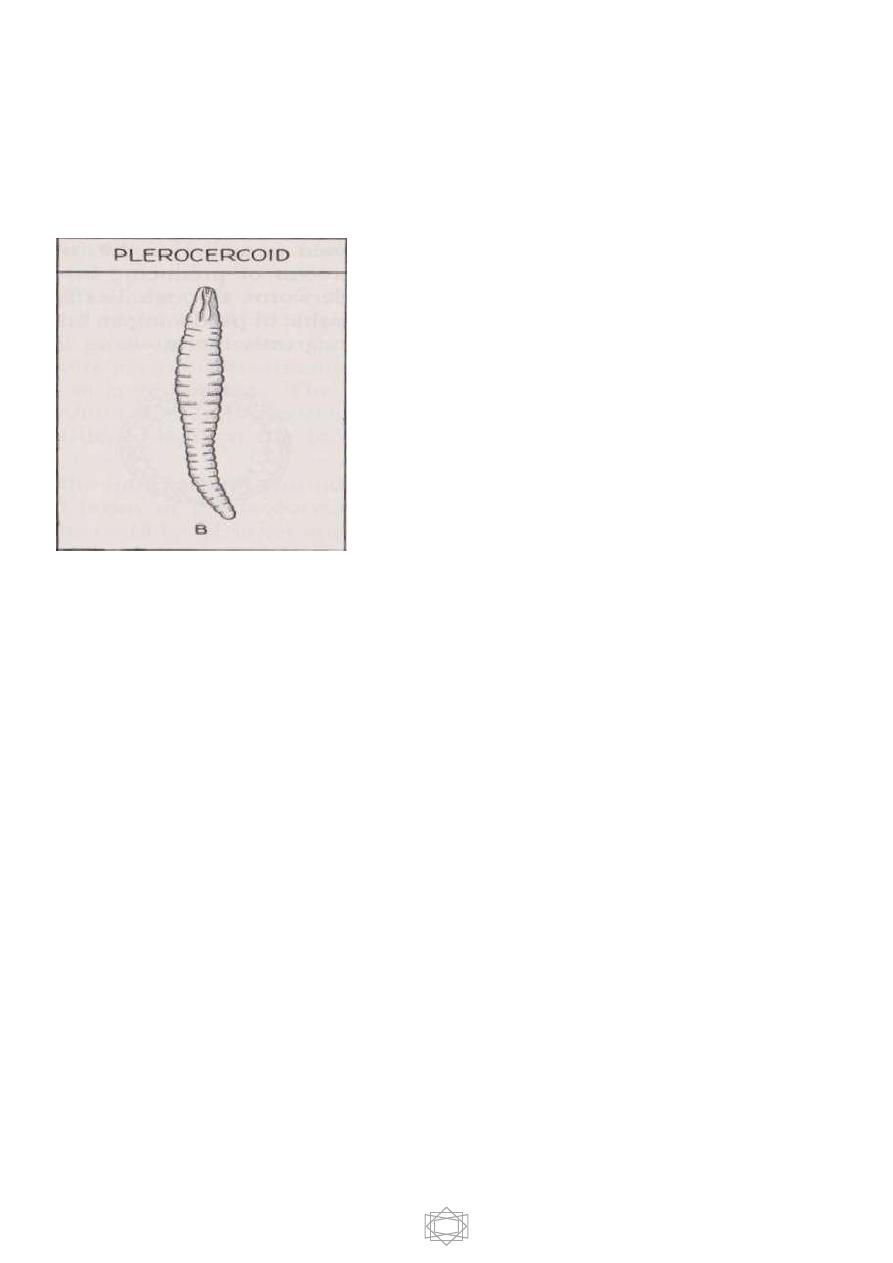
5
2-Plerocercoid : chalky white solid structure with pseudo segmentation composed
of caudal solid appendage and invaginated head in the neck
e.g.Diphyllobotherium latum.
-Diagnosis of adult tapeworm infection is achieved by finding
characteristic eggs, Proglottids or both, involved in feces. Serological diagnosis is
not helpful.
-
Classification of Cestodes:
- Class Cestoidea include 2 orders:
1- Order Cyclophyllidea
2- Order Pseudophyllidea
-
Cyclophyllidea include ;
1-
Taenia saginata
(beef tapeworm)
2-
T. solium
(pork tapeworm)
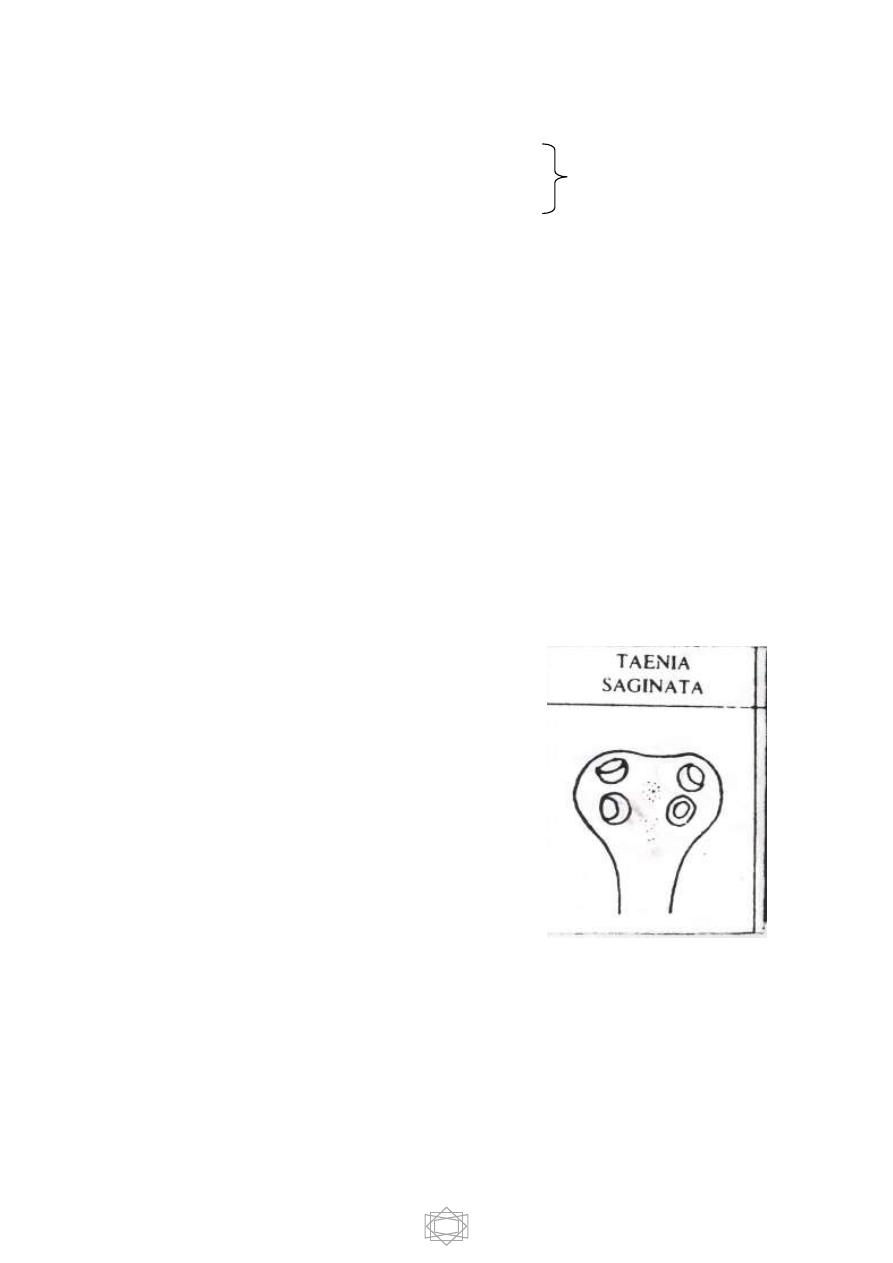
6
3-
T. multiceps
(gid worm)
4-
Echinococcus spp.
(hydatid worm)
5-
Hymenolepis
nana ( dwarf tapeworm )
parasite of rodents
6-
H. diminuta
( rat tapeworm )
parasite of rodents
7-
D. caninum
(dog tapeworm)
Pseudophyllidea:- include only one species of medical importance,
Diphyllobothrium latum
(broad or fish tapeworm
)
.
Taenia saginata
Morphology
The length of adult worm from
4-10 m , it may be over 12m in some
situations.
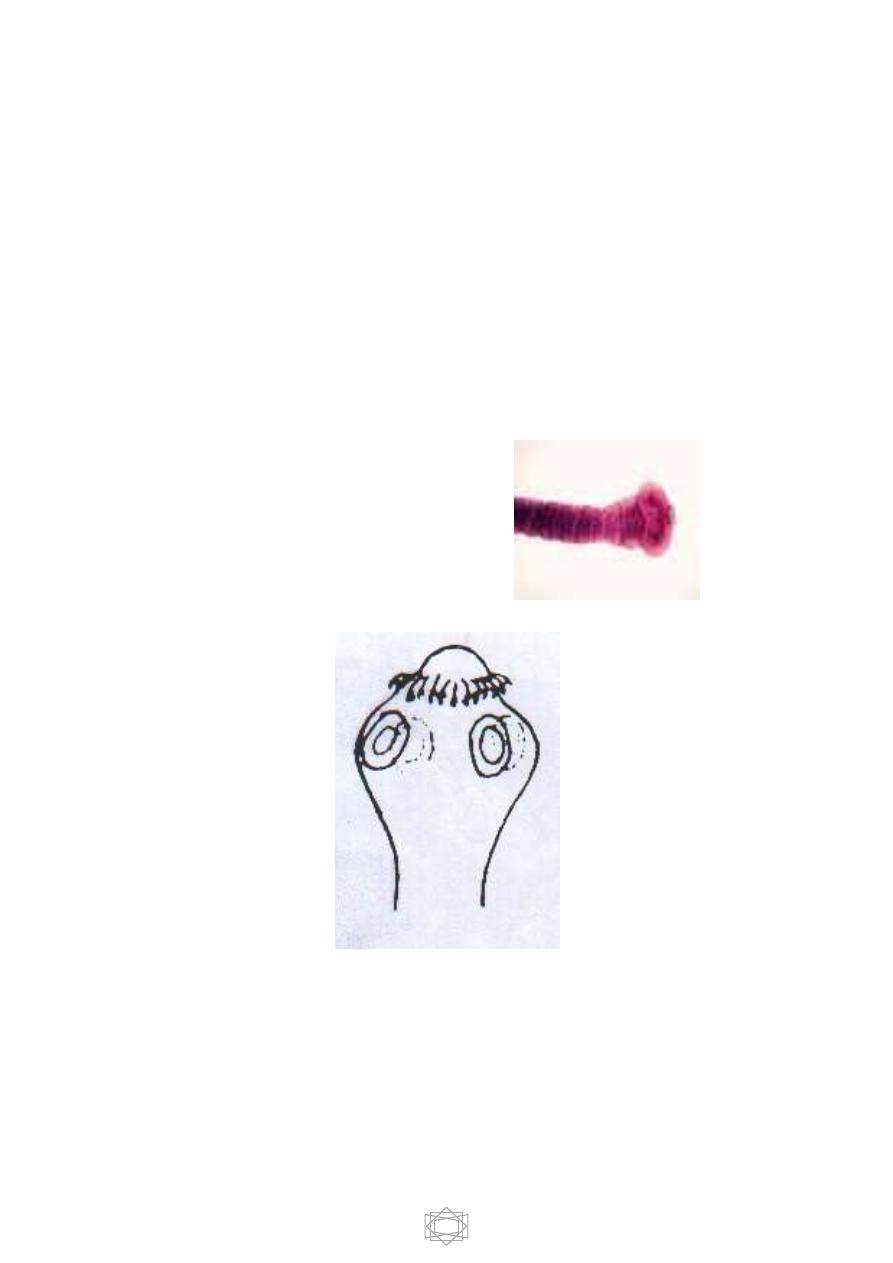
Scolex: does not have a rostellum or hooks so
it’s describe as an-unarmed scolex.
It’s quadrate in its cross section &
provided with 4 muscular suckers.
Strobila: 1000-2000 proglottids
1-immature segments ;they are small ,wider than long with not well
differentiated reproductive organs .
2-mature segments ;almost squire in shape with well differentiated sex organs
of both male and female .

7
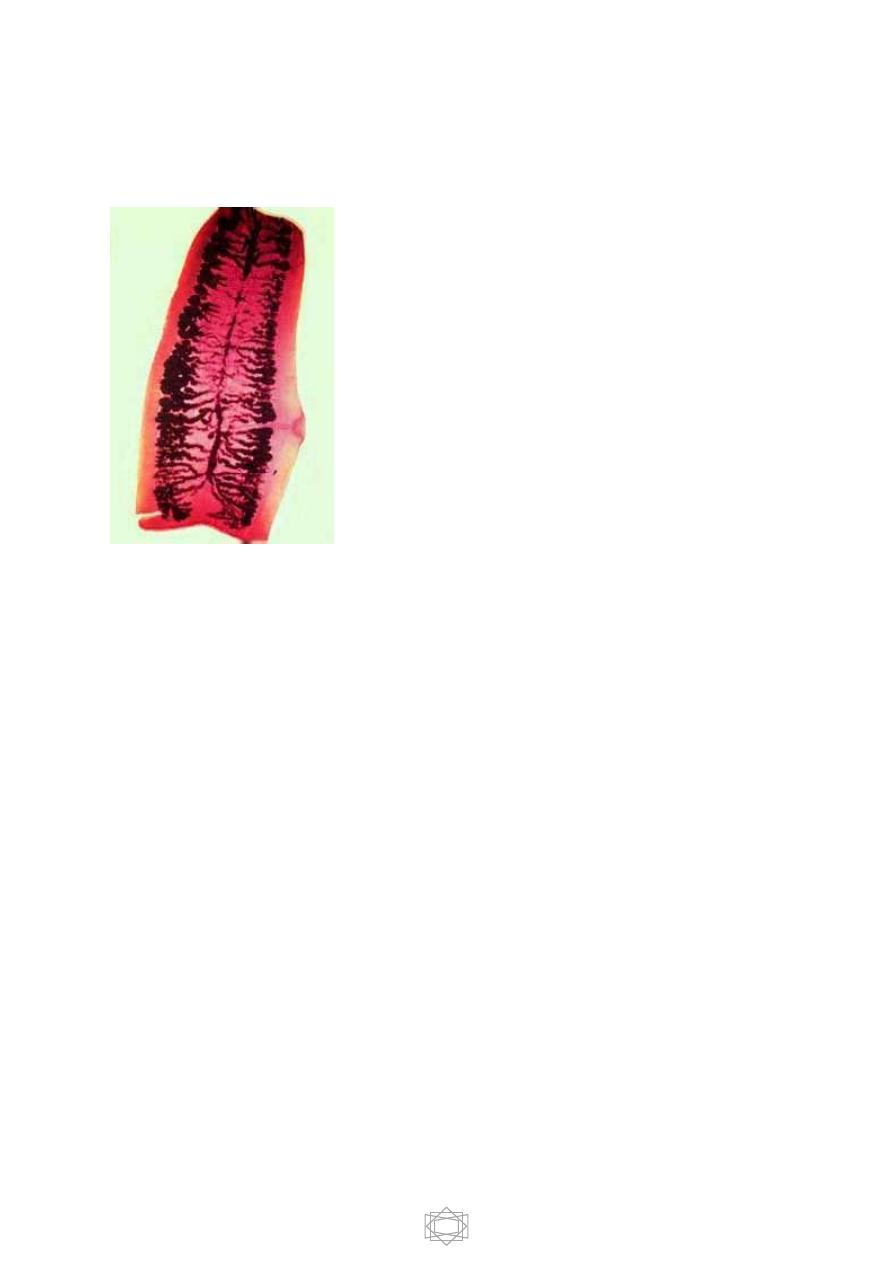
3-gravid segments ;longer than wide consist of median uterus with 15-30
lateral uterine branches with unilateral genital pore .
Gravid T.saginata segment 15-30
lateral uterine branches
Habitat ;Adult worm inhabit upper part of the small intestine of man .
Egg: if you want to describe the egg of any
helminthic parasite you should look for size, shape, color, content (SS CC)
Size ; 36 -50 micron in diameter.

8
Shape; globular or spherical
Color: yellowish-brown
Contents: hooked ball embryo (oncosphere) with 6 hooks (hexacanth embryo)
surrounded by thick, radially striated brown embryophore . The embryophore
surround by egg shell which is extremely delicate &usually lost in intestine.
Larval stage:
Cysticercus
bovis
, it is oval, fluid filled bladder larva with
invaginated unarmed scolex.
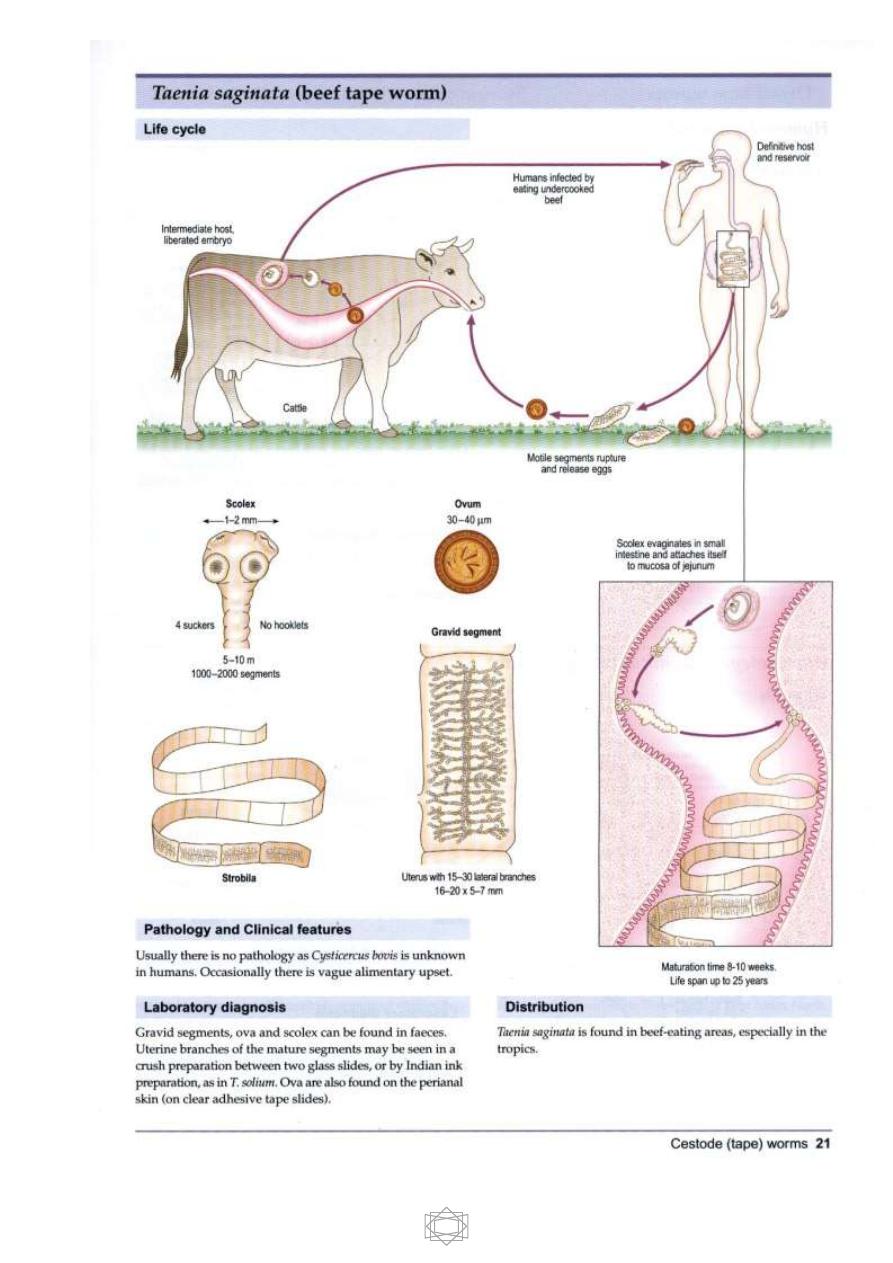
-Life cycle:
Intermediate host: cattle
Final host: man
The cattle will be infected by ingestion the eggs while grassing on contaminated
soil or contaminated drinking water. In the duodenum where the reaction is
alkaline the embryo will be liberated & penetrate the intestinal wall by means of
its hooks, then reach circulation & carried to different parts of the body & then
develop to
Cysticercus bovis
.

9
The common sites of infection in cattle are: muscle of jaw, diaphragm, heart,
shoulder and esophagus. Man will be infected by eating insufficiently cooked
meat which contain
C. bovis
.
The meat will be digested & the larva will be released & the scolex become
evaginated and attached itself to the mucous membrane & develop to an adult
worm within 3 months.
10

11
- Pathogenesis, pathology & symptomatology:
The disease is called beef tapeworm infection or taeniasis. Usually single
worm develop in the intestine of man but more than one worm has been
reported.
Beef tapeworm infection usually asymptomatic, but because of the large size
of the worm, it may responsible for acute intestinal obstruction and because
of utilizing the host’s nutrients it’s responsible for anemia and hunger pin.
Sometimes an individual segment may be lodge in the appendicial lumen &
initiate appendicitis. The absorbed byproducts may create systemic
intoxication (symptoms such as food poisoning) and diarrhea.
The most common symptom is the discomfort or embarrassment of the
patient because gravid segment will crawl out of the anus irrespective of
defection & this will result in mental worried to the patient.
-Diagnosis:
The basic diagnosis is don from a stool sample it’s difficult to differentiate
between eggs of
T.saginata
, &
T.solium
. Their eggs are morphologically
identical so they are called
Taenia
spp, eggs, also eggs can be detected by
swabbing peri-anal area or by scotch tape slide technique.
Specific diagnosis can be done by counting the number of lateral uterine
branches in gravid segment or finding the unarmed scolex with whole worm
after successful medication.
-Treatment:
The highly effective drugs are:
Niclosamide, praziquantel and mebendazole.

12
أ . صباح النجار: ةـــــــــــــيناثلا ةرضاحملا
Parasitology
Taenia solium
( pork tapeworm )
Adult worm found in upper part of small intestine of humans, larval stage infects
pigs and humans and causes cysticercosis in humans.
Normally adult worm is from 2 – 8 m.
Scolex: is globular in shape with 4 muscular suckers and two rows of hooks
and rostellum, so it is called an armed scolex.
Strobila;800-1000 proglottides.
Gravid segment
:
It is longer than broad with median uterus and 7 – 13 lateral
uterine branches.

13
Egg:
Taenia spp.
Egg Similar to that of
T. saginata
.
Larval stage: It is called
Cysticercus
cellulosae
, which has a fluid filled bladder
that is 0.5 – 1.5 cm in length with an armed invaginated scolex.
Cysticercus cellulosae of T. solium
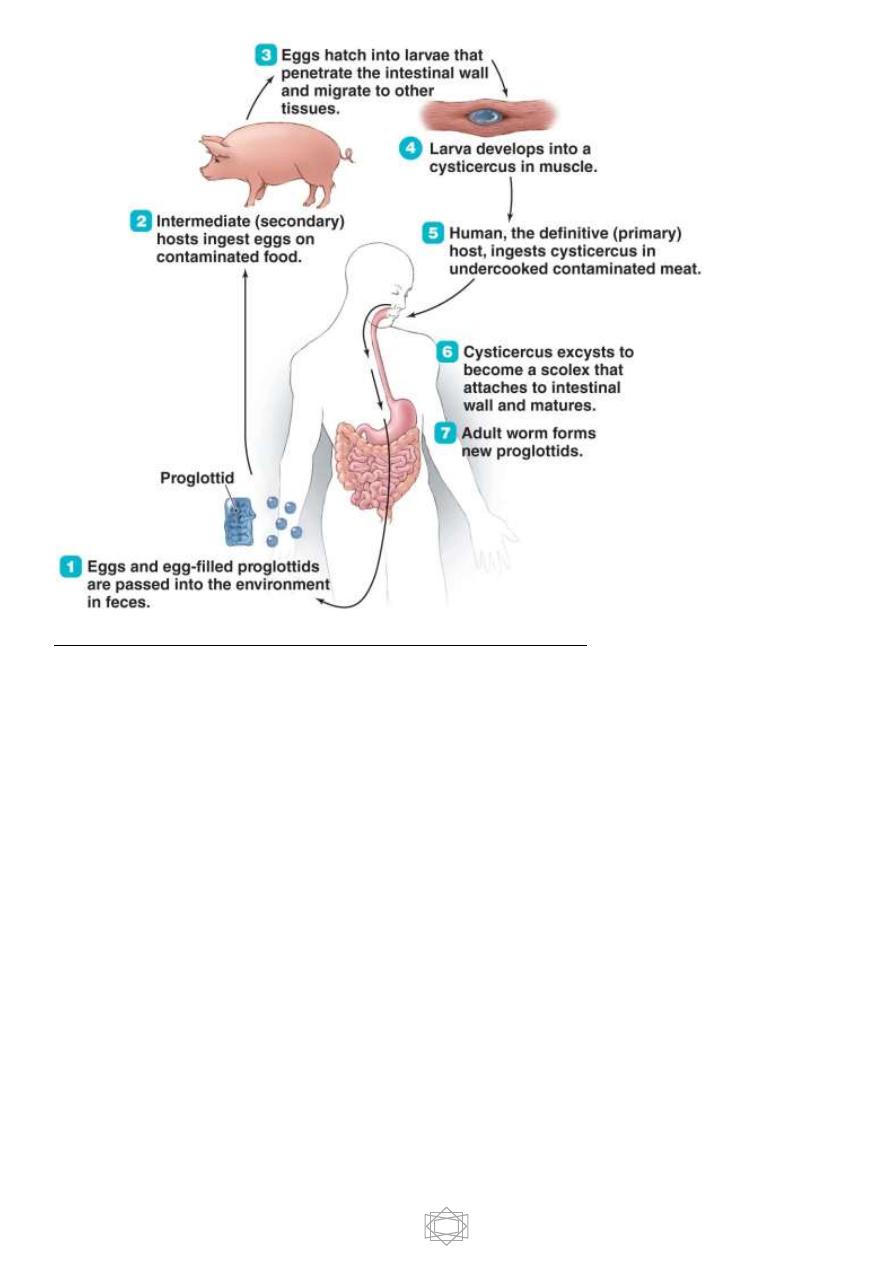
Life cycle:

14
Intermediate host is the pig, but man some time acts as intermediate host and
there will be a disease known as cysticercosis.
Pig will be infected by ingesting the eggs through contaminated food and water. In
the small intestine where the reaction is alkaline eggs will be hatches and
hexacanth embryo liberated which migrates through intestinal wall and reach
blood circulation then reach different parts of the body and then it will be develop
to
C. cellulosae
mainly in striated muscles .
Humans are infected either by ingestion of food contaminated with feces
containing eggs (
hetero – infection
) or by
auto- infection
.
Autoinfection occur when human infected with adult worm can ingest eggs
produced by that tapeworm , either through contaminated fingers ( external
autoinfection ) or possibly , from proglottids carried into the stomach by reverse
peristalsis ( internal autoinfection ) . Once eggs are ingested, oncosphere hatch
in the intestine, invade intestinal wall , and migrate to striated muscles , as well
as the brain , liver and other tissues , where they develop into
C. cellulosae .
When humans ingest undercooked pork contain cysticerci the meat will be
digested and invaginated scolex in cysticerci become evaginated and attached
itself to the mucosa and develop to adult tapeworm and after 2 – 3 months, ova
start appearing in stool sample .
15
Pathogensis, pathology and symptomatology
:
he disease is called Taeniasis or pork tapeworm infection .
Adult worm may cause slight irritation at the site of attachment in the mucosa , or
it may cause intestinal obstruction . Ordinarily the worm produces no serious
damage but at times it cause abdominal discomfort , hunger pain , chronic
indigestion , persistent diarrhea or alternating of diarrhea and constipation .
In very rare cases , the scolex may perforate the intestinal wall and will initiate
peritonitis .
Appendicitis also may occur due to migration of gravid segment in to the
appendicial lumen .

16
The most frequent and sever disease caused by
T
.
solium
is cysticercosis . The
severity of cysticercosis depends on location , size and number of the larvae in
the tissues , as well as the host immune response .
The presence of growing larvae usually promote a typical cellular reaction around
the parasite which lead to fibrosis and necrosis of the larvae and eventually
calcification of the parasite .
The most frequent locations are subcutaneous and intramuscular tissues , then
eye and brain . they also may occur in the liver , lung , heart and abdominal
cavity . The size of the cyst depends on its age and its location .
The most serious type of cysticercosis is neurocysticercosis which can lead to
epilepsy , lesion in the brain , blindness and tumor like growths .
Diagnosis :
Taenia
spp
. eggs in the stool sample diagnoses Taeniasis and not cysticercosis ,
and we cannot differentiate between
T.saginata
and
T. solium infection.
Gravid segment in the feces diagnosis
T. solium
infection , by counting the
number of lateral uterine branches ( 7 – 13 ) .
- If scolex is evacuated following medication an armed scolex differentiates this
worm from
T. saginata .
Serological tests are of little or no diagnostic value for detecting the adult worm

17
- In cysticercosis diagnosis primarily depend on confirming the presence of
hooks in the scolex of
C. cellulosae
by histopathological examination of
biopsy materials
Radiological tests e.g. X – ray , CT scans and MRI can also be used to detect the
disease .
X – rays are used to identify calcified larvae in subcutaneous and muscle tissues
and CT scans and MRI are used to find lesions in the brain and liver .
Serological tests are more helpful for identification of cysticercosis .
Taenia multiceps ( gid worm )
Adult worm , from 40 – 60 cm in length , the scolex with double circle of hooks,
it is found in the small intestine of dogs , wolves and foxes .
Larval stage is called
Coenurus cerebralis
is
found
in herbivores mammals
( sheep , goat and cattle ), man infected accidentally larval stage produce a
disease known as cerebral and ocular coenurosis .
