
1
Parasitology
Lac: 1
Lecturer: khalidah Kareem
Phylum Platyhelminthes [Flat worm]
1- Class Cestoda [Tapeworms]
2- Trematoda [Flukes]
Class cestoda [tapeworms]
Objective:
To study the causative parasites of tape worm infection,
morphology, life cycle, clinical symptoms and diagnosis for
1- Hymenolepis nana [Dwarf tape worm]
2- Hymenolepis diminuta [Rat tapeworm ]
3- Dipylidium caninum [Dog tape worm ]
4- Diphyllobothrium latum [Fish or Broad tape worm]
Phylum platyhelminthes
Class: cestoda
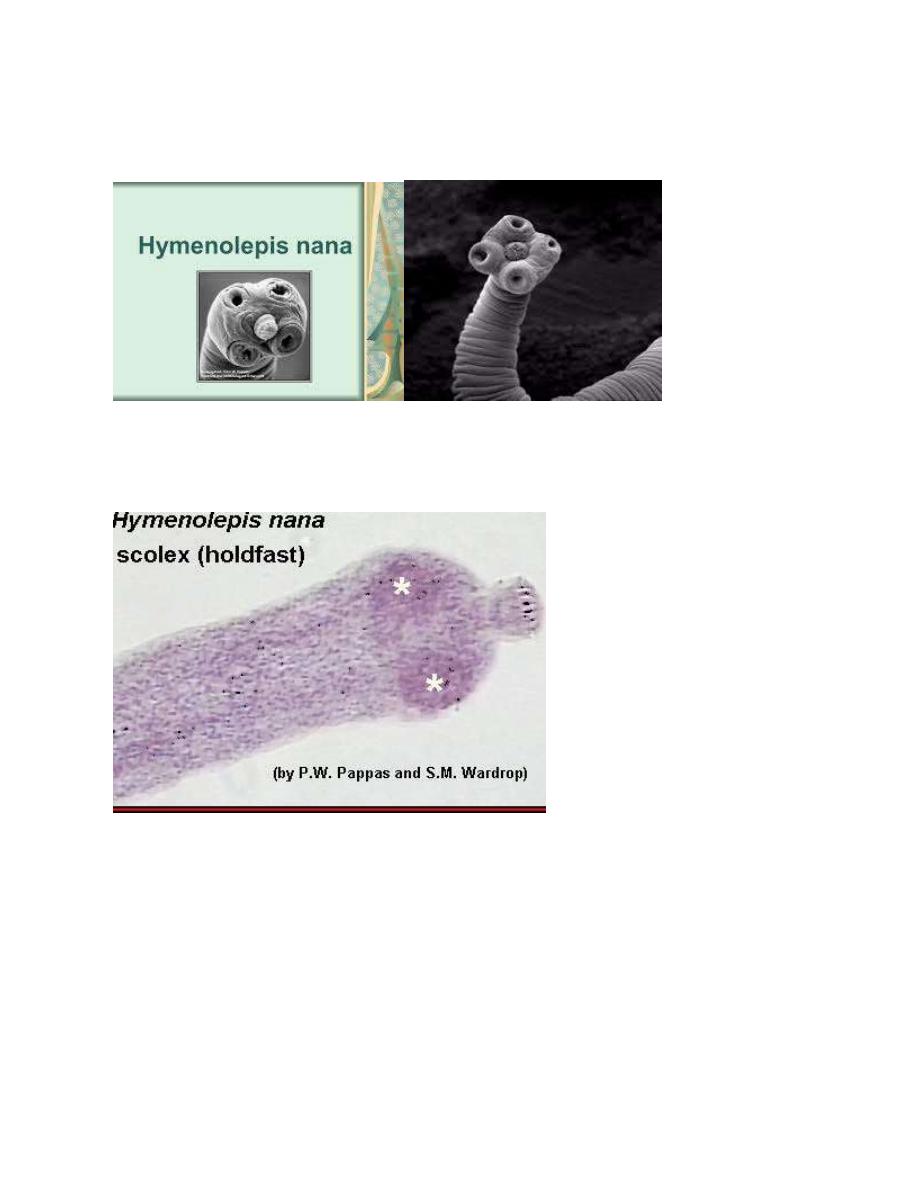
Hymenolepis nana (Dwarf tapeworm)
It causes a disease known as dwarf tapeworm infection. The infection in
humans is primarily limited to children in warm climates.
H. nana is the smallest tapeworm of man; it is 25-40mm in length, habitats of
adult worm are in the upper 3/4
th
of the ileum. The scolex is globular in shape and
provided with 4 muscular suckers and rostellum with single row of hooklets. The
strobila consists of about 200 proglottids; the proglottids are twice wider than they
are long.
2
Adult worm
Each Mature proglottid compose of one set of male reproductive organ and one
set of female reproductive organ , genital pore made lateral located on one side ,the
gravid proglottid consisted of a sac-like uterus filled with eggs .

3
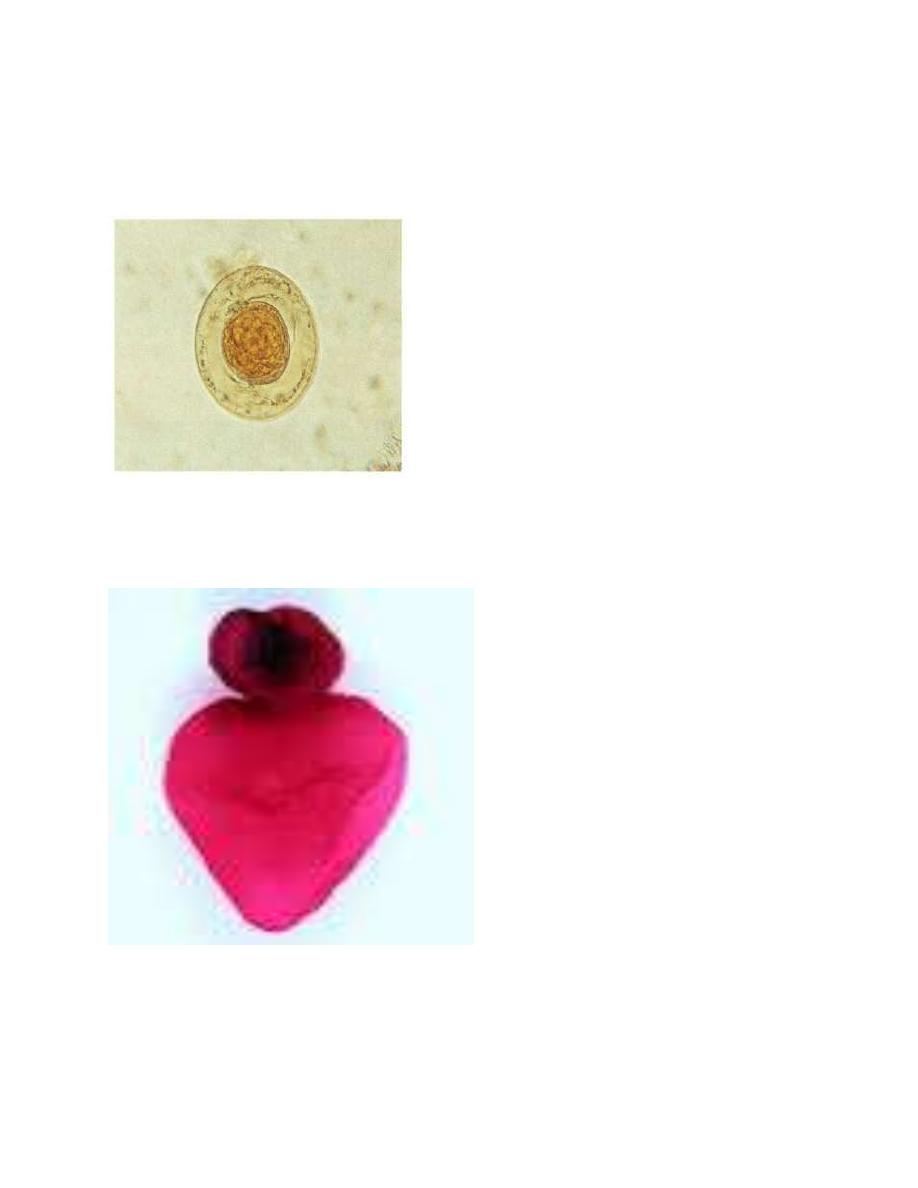
Eggs are almost spherical transparent, measures 45µm by 38µm in size,
have 2 thin membranous shells, the inner one of which has 2 polar thickenings,
each provided with 4-8 polar filaments.
Hymenolepis nana [ovum]
Cysticercoid larvae
4
-
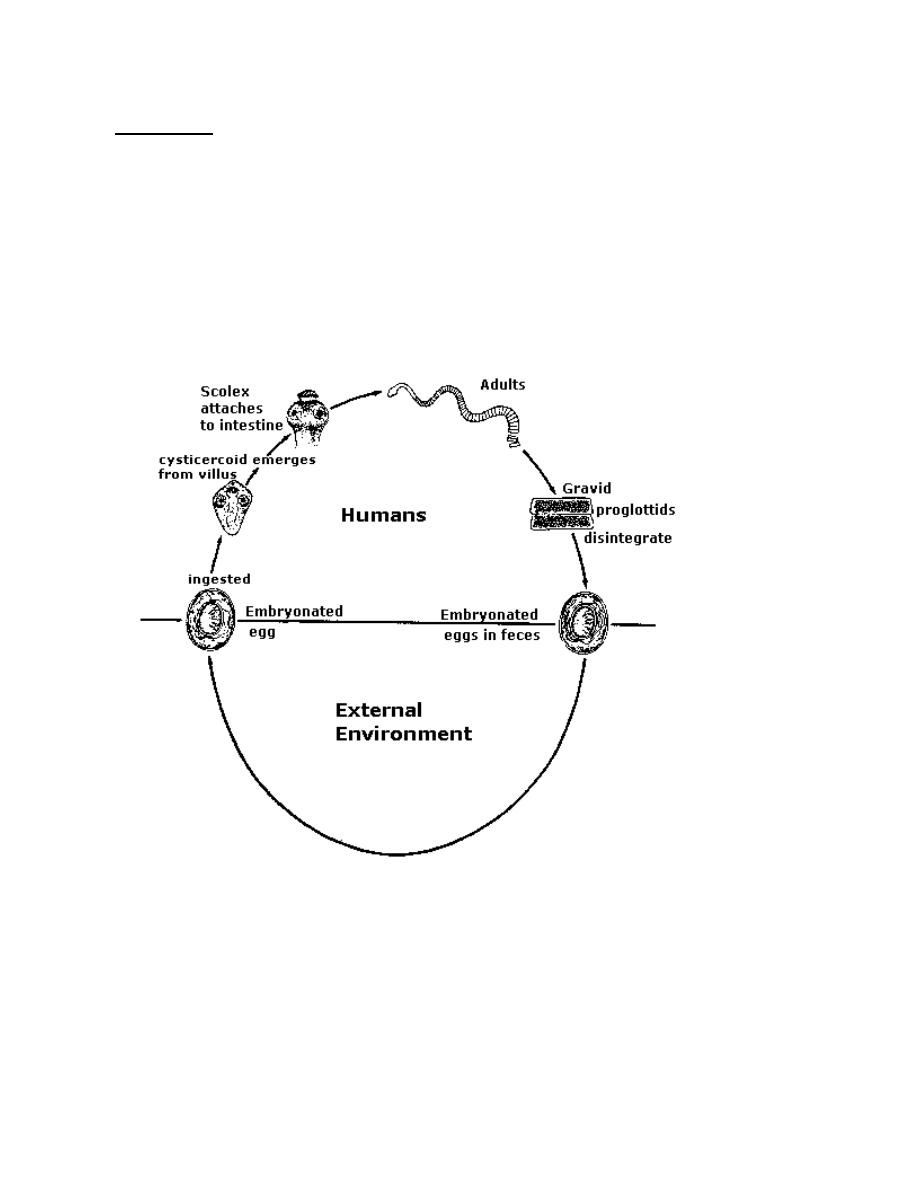
Life cycle
:
This is the only tapeworm for which human acts as definitive and
intermediate host during its life cycle, it has simple direct life cycle, when eggs
are swallowed, they hatch in the duodenum and the liberated oncosphere
penetrate the stroma of villi with the help of the hooklets, then they transform
into cysticercoids larvae.cysticercoid after maturing re-enters the lumen of
small intestine and attach to the mucosa and in about 2 weeks they developed to
complete worm.
,
H.nana: life cycle
In heavy infections, internal autoinfection may occur as a result of hatching
of eggs in the upper part of small intestine and the liberated oncospher directly
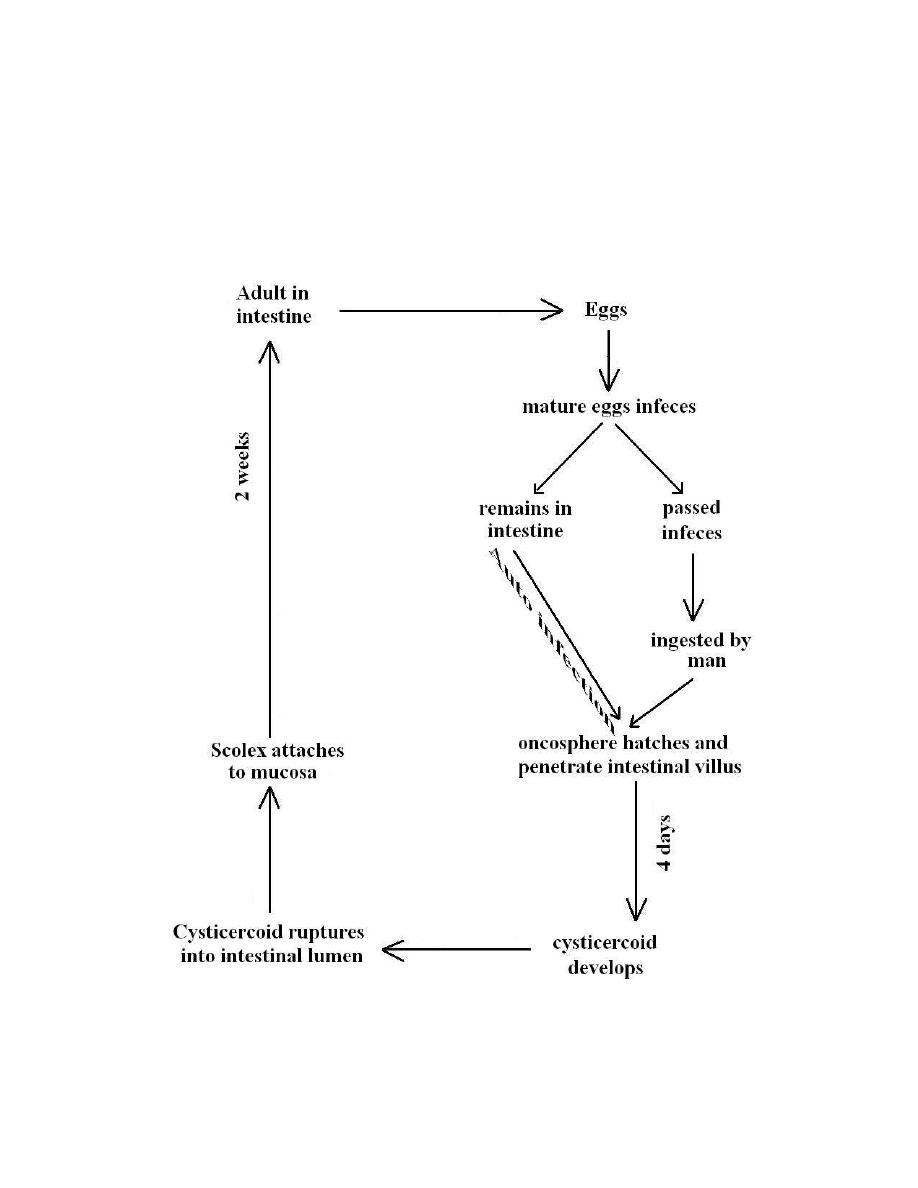
5
penetrate the villi, then they transform into cysticercoids larvae,cysticercoid
after maturing re-enters the lumen of small intestine and attach to the mucosa.
External autoinfection by ingestion of one’s own eggs is also common.H.nana
also can utilize fleas and beetles for development of the cysticercoids stage.

6
-Pathogenesis and Symptomatology
: H. nana infection cause
mechanical irritation and allergic manifestation. H.nana infection may produce
no detectable symptoms but in case of heavy infection it may cause diarrhea,
abdominal pain, anorexia and nervous disorders.
-
Diagnosis
: is based demonstration of the characteristic eggs in the stool by
general stool [examination direct microscopic examination ] or by concentration
method in case of light infection.
Medication:
Praziquontel is drug of choice; Nichlosamide is known to be on effective
alternative drug.
Parasitology
Hymenolepis diminuta (Rat Tapeworm)
It causes a disease known as rat tapeworm infection in man. It is a
parasite of rats and mice and other rodents. It has been reported from human
hosts, usually children, human infection with rat tape worm considered being
accidental zoonotic occurrence.
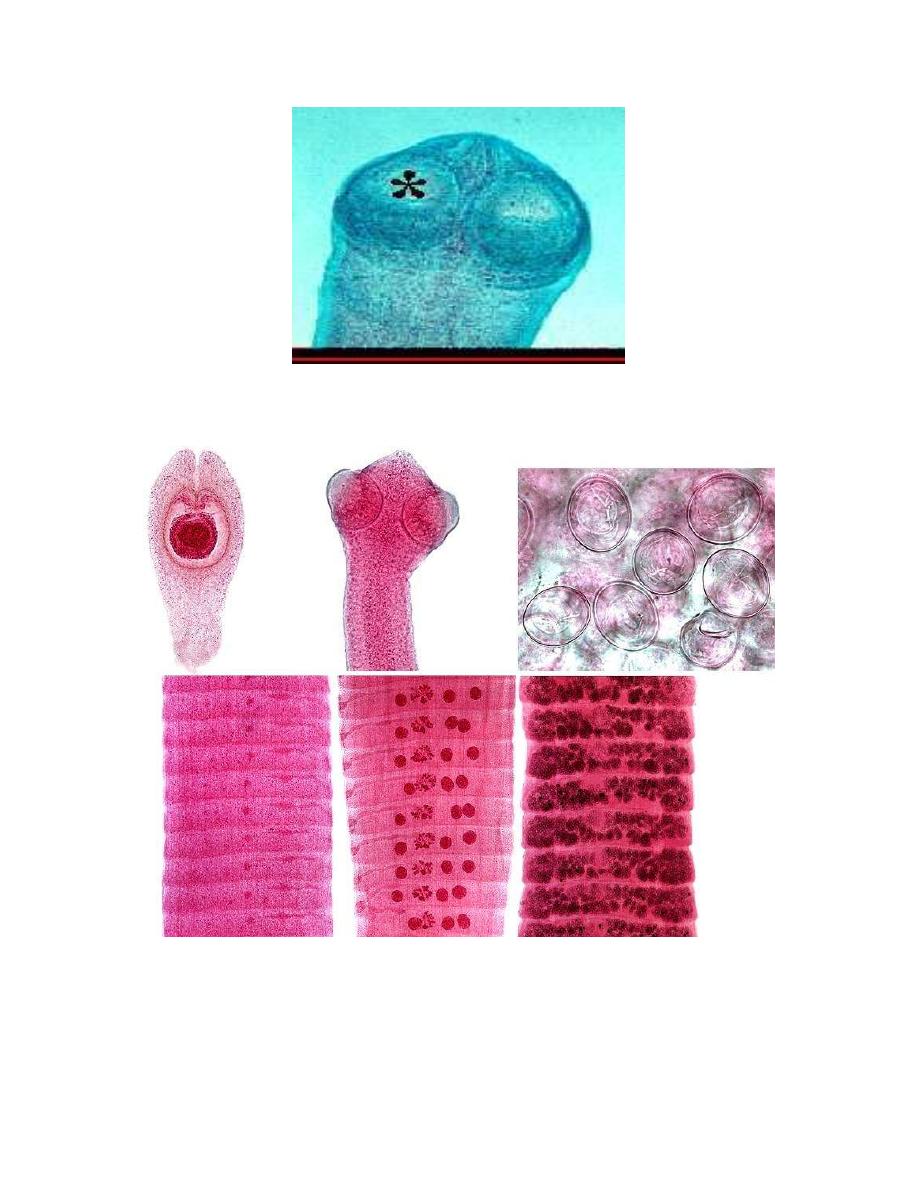
Adult worm measures 20-60cm lives in the small intestine, the scolex is
club shape d provided with 4 small suckers and rudimentary rostellum. All
proglottid are twice wider than they are long in size

7
Solex
Immature mature Gravid
H.dimiuta
8
Each Mature proglottid compose of one set of male reproductive organ and one
set of female reproductive organ , genital pore made lateral located on one side ,the
gravid proglottid consisted of a sac-like uterus filled with eggs .
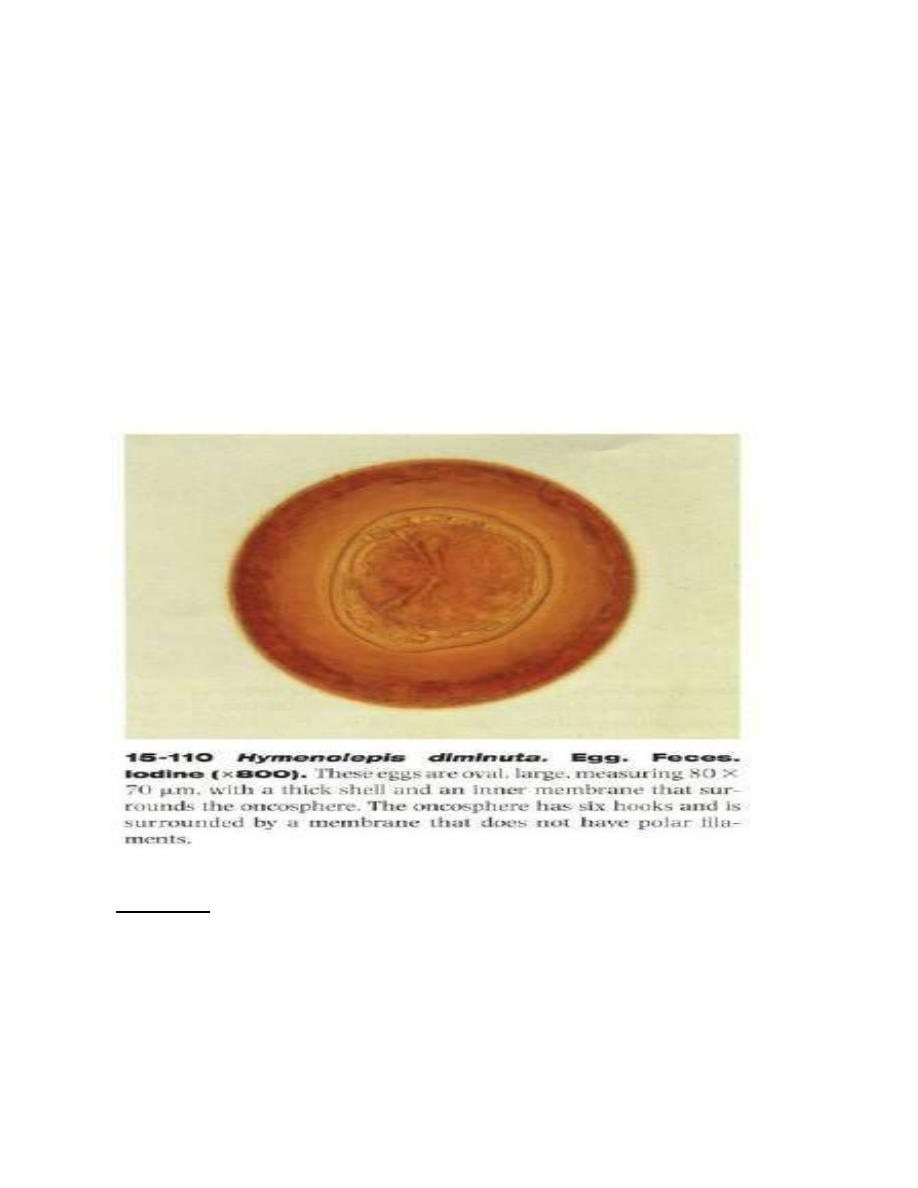
Egg: ovoid to sub-spherical in shape, yellowish brown in color, measures
55µmby 85µm in size, there is a considerable space between the striated brown
outer membrane and the hyaline inner membrane. Inner membrane is provided
with a pair of polar thickenings but lacks the polar filaments.
-
Life Cycle: when eggs voided in the feces of definitive host ingested by an
arthropod, usually larval stage of fleas and beetles, cysticercoids larva will be
develop in the arthropod, when the infected arthropod is ingested by definitive
hosts, cysticercoids is digested out of its vector host and the scolex attaches to
the small intestine mucosa and develops into adult worm.
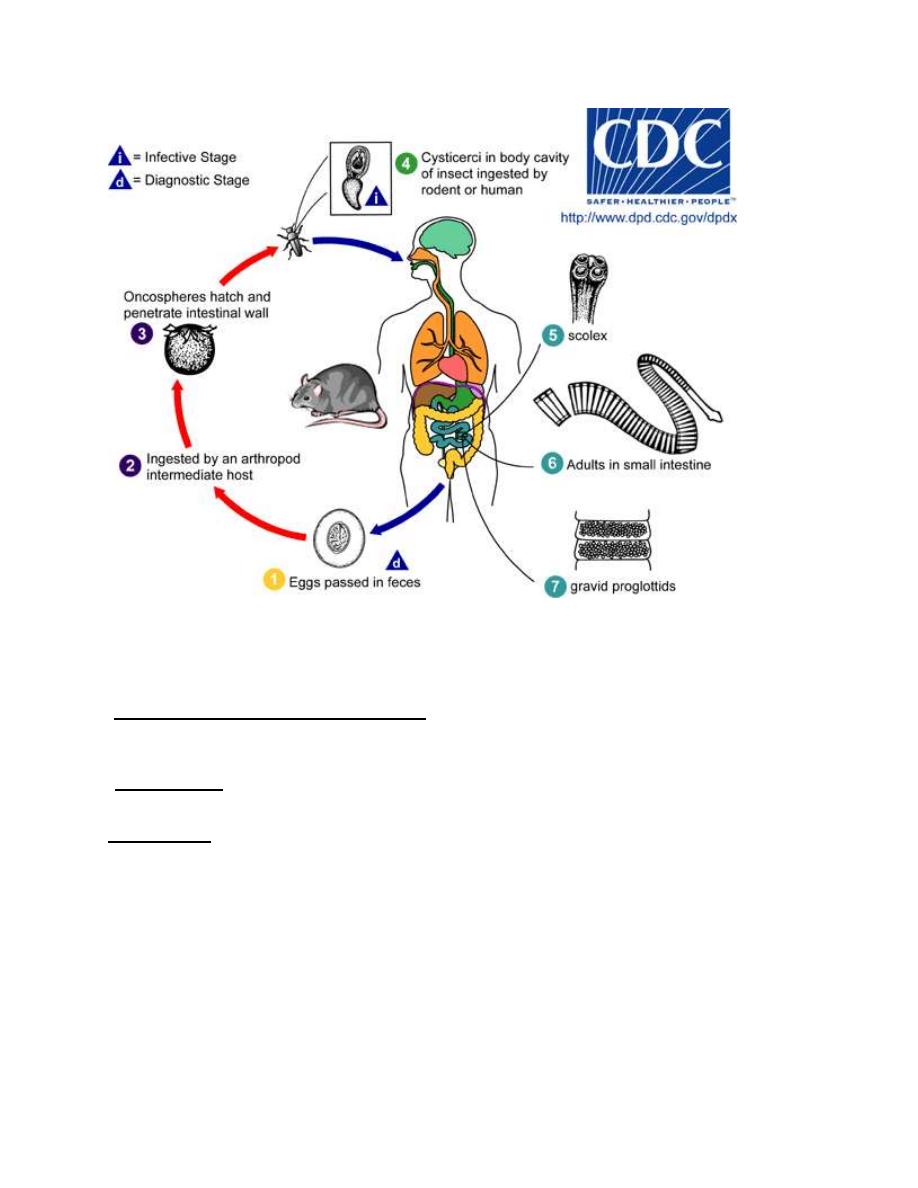
9
H.diminuta: Life cycle
-Pathogenesis and Symptomatology:
H. diminuta infection usually produces no symptoms.
-Diagnosis: ismade on the recovery of typical eggs in the stool. Direct
microscopic examination or concentration method .
Treatment: Niclosamide is drug of choice, Praziquntal is alternative therapy.
