
Some free-living amoebae (facultative) also called
opportunistic amoebae
can cause serious even
fatal disease if reach human body. These amoebae
has found to have the ability to live in the tissues
of mammals.
It can invade human nervous system, usually
result in the death of the patient.
1.Nagleria fowleri
cause
primary amoebic
encephalitis(PAM).
2.Acanthomoeba spp. Cause
granulomatous amoebae
meningoencephalitis(GAM).
*

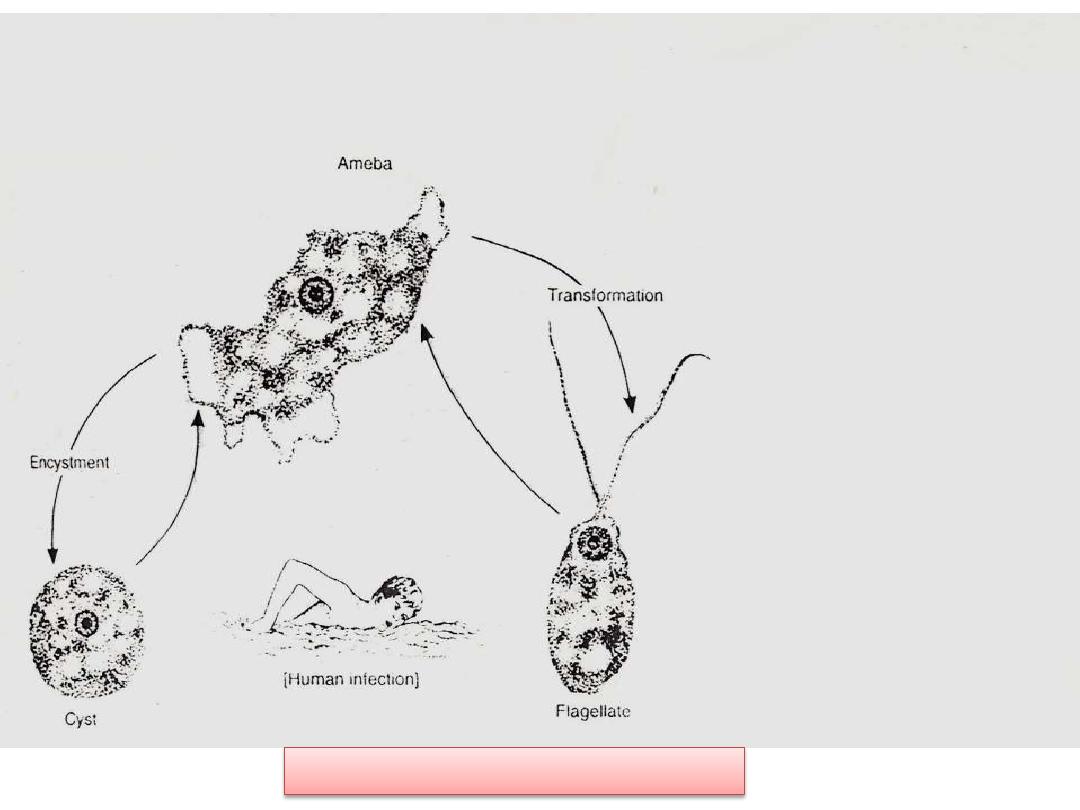
Life cycle of N.fowleri
Naegleria fowleri
occurs in three forms:
1.
a cyst,
2.
a trophozoite (ameboid) and a
3.
trophozoite flagellate. It does not form a
cyst in human tissue. Only the
amoeboid
trophozoite
stage exists in human
tissue. The flagellate form can exist in the
both
amoeboid
and
flagellates
are
infective stage.

Free – Living Pathogenic
amoebae
1.Naegleria fowleri (brain – eating amoeba)
It causes
primary amoebic meningoencephalitis
(PAM)
in humans. It is cosmopolitan, mainly in North
America, Western Europe, Africa, Japan and
Australia.
The amoebae found in warm fresh water of ponds,
lakes, pools and moist soil. rivers, and
. It is
also found in soil, near warm-water discharges of
, and in poorly
, or
or
stage. There is no evidence of
this organism living in salt water.
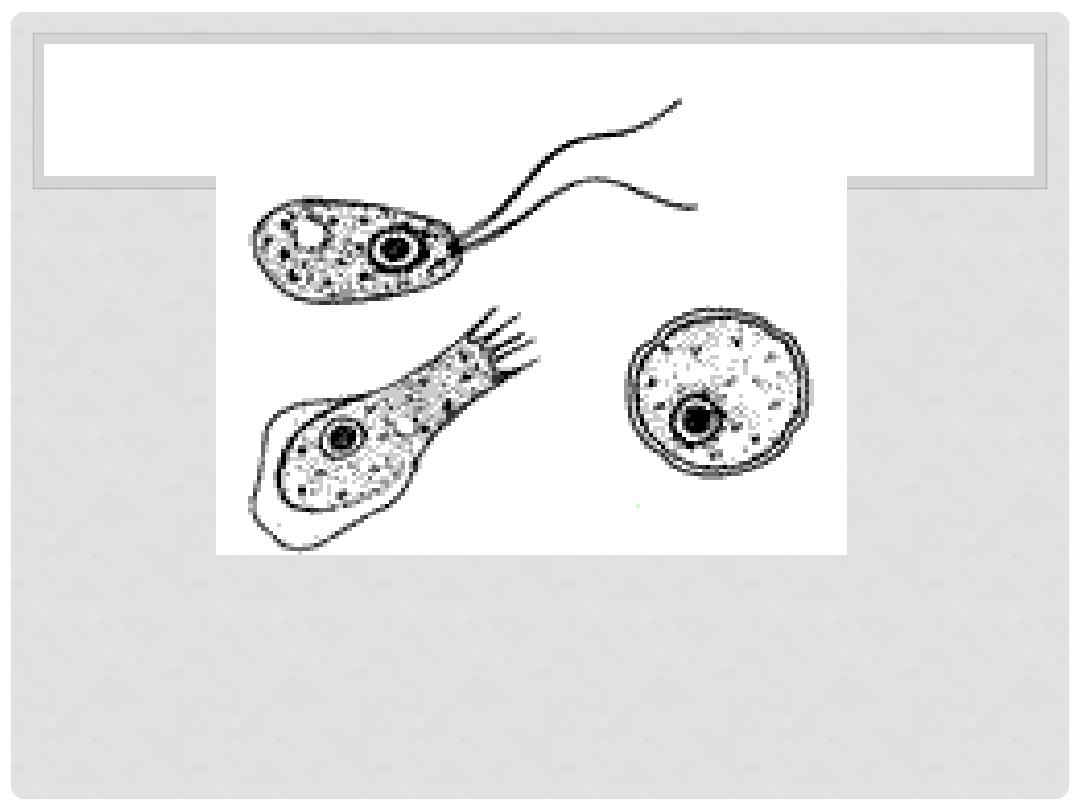
Different stages of Naegleria fowleri
1. A
MOEBOID
T
ROPHOZOITE
STAGE
:
This reproductive stage of the protozoan organism,
which transforms near 25 °C/77F and grows fastest
at around 42 °C/106.7F, proliferates by
. The trophozoites are characterized by a
nucleus and a surrounding halo. They travel by
, temporary round processes which fill
with granular cytoplasm. The pseudopodia form at
different points along the cell, thus allowing the
trophozoite to change directions. In their free-living
state, trophozoites feed on bacteria. In tissues, they
red blood cells and white blood cells
and destroy tissue.
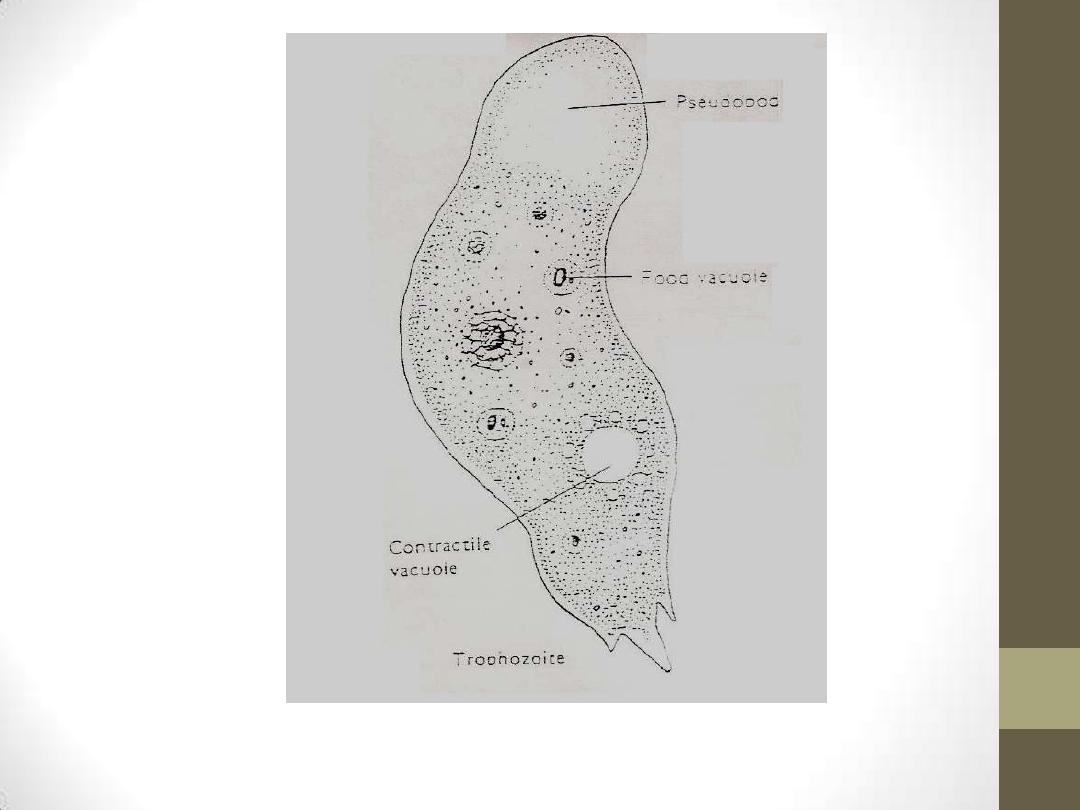
Amoeboid trophozoite of N.fowleri

2.Flagellate trophozoite stage:
•
This biflagellate form occurs when
trophozites are exposed to a change in
ionic concentration, such as placement in
distilled water. (The flagellate form does
not
exist
in
human
tissue).The
transformation
of
trophozoites
to
form occurs within a few
hours.this is transient form.
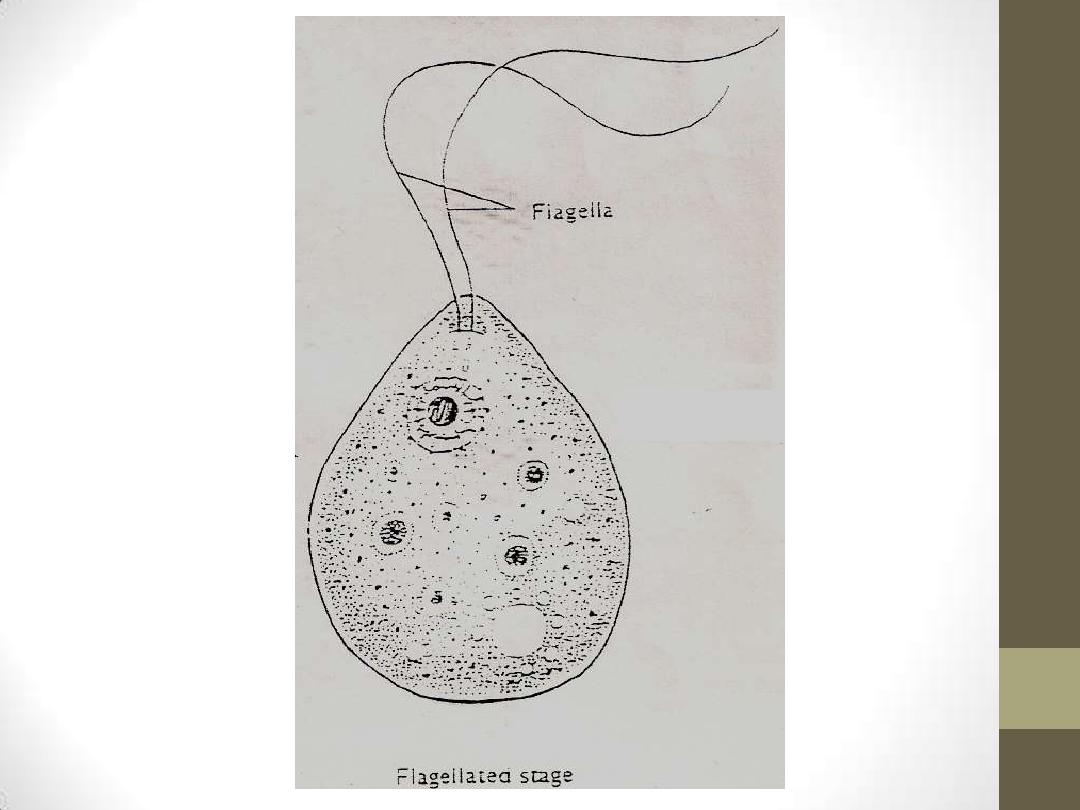

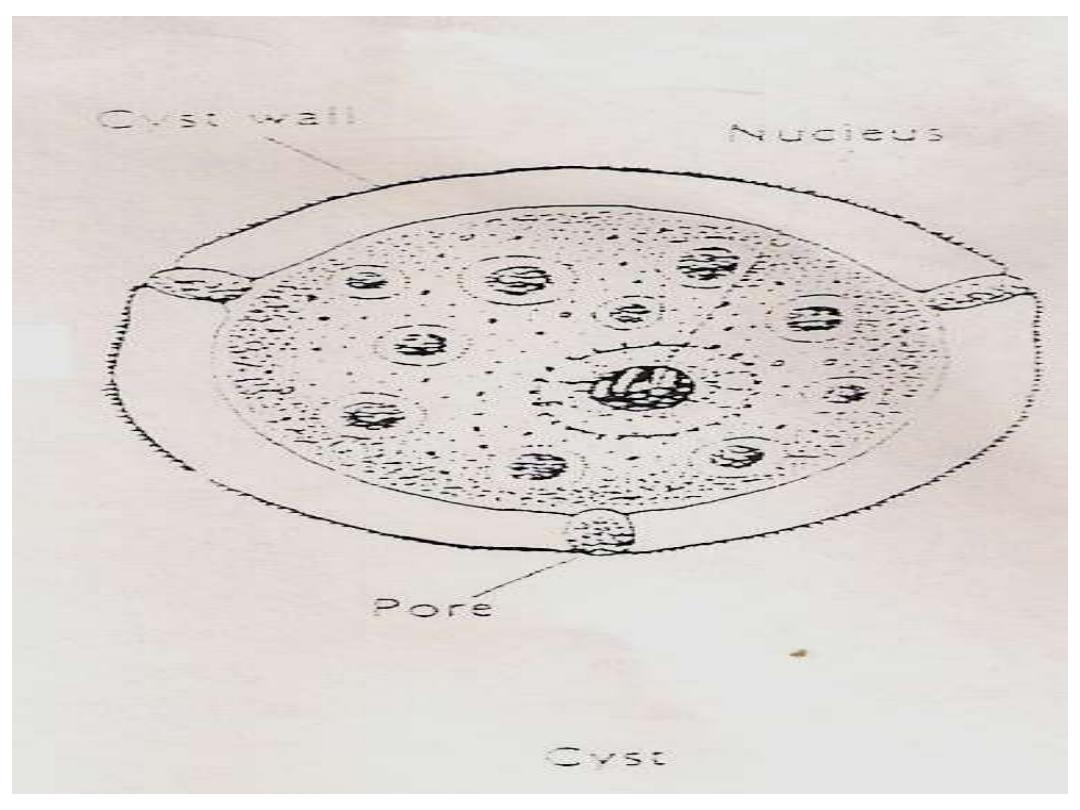
3.Cyst stage:
Trophozoites encyst due to unfavorable conditions.
Factors that induce
formation include a lack of
food, overcrowding, desiccation, accumulation of
waste products, and cold temperatures. N. fowleri
has been found to encyst at temperatures below
10 °C/50F.not found in the tissues.

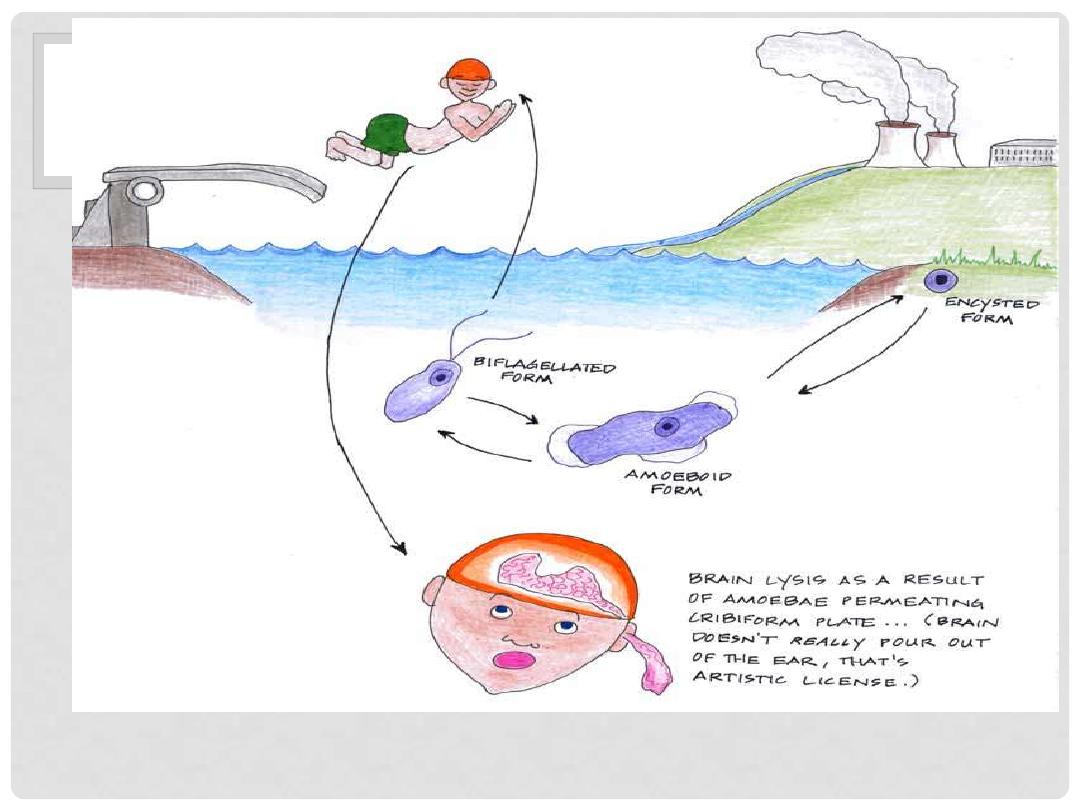
Mode of infection:
•
Humans infected by swimming in contaminated
stagnant water in lakes, ponds, stream or
swimming pools containing the infective form
(Amoeboid trophozoite)which enter human body
through nasal mucosa and often migrate to the
brain, causing rapid tissue destruction.
•

*
*
Amoeboid trophozoite
transform into
flagellated
form
in vitro after being transferred to water
from a tissue or culture. The flagellated form do
not divide but rather lose their flagella and
convert back into the amoeboid form.
Cyst
formation is known to exist only in external
environment.
LIFE CYCLE OF N.FOWLERI
Life cycle of N.fowleri

*
*
The amoebae enter nasal passages when the persons swimming or has
contact with warm water, moving along olfactory nerve, through cribriform
plate into the cranial cavity. In the brain the amoebae remain associated
with membranous covering of the brain, the meninges, where they evoke
an inflammatory response.
*
Symptomatology:
*
Early in the infection the patient complains of upper respiratory tract symptoms e.g. raning
nose, sore throat, fever and headache. Within 2 – 3 days the headache becomes more sever
and there may be vomiting, stiff neck, mental confusion, coma as a result of intracranial
pressure. Death usually with 10 days of the onset of symptoms.

Direct demonstration of motile amoebae
in unstained CSF or nasal discharge.
Stained smear of CSF.
Stained section of brain tissue at
autopsy.
Culture on non-nutrient agar medium
coated with E. coli bacteria.
Serological tests.

Detection in water is performed by
coli added, then applying the pellet
to a non-nutrient agar plate. After
several
days,
the
plate
is
microscopically
inspected
and
Naegleria cysts are identified by their
morphology.

Prevention
•
1. Public education awareness in the medical community.
•
2. Adequate chlorination of public water supply(including
swimming pools).

It
causes
granulomatous
amoebic
encephalitis(GAM)
and
amoebic keratitis
. It is
cosmopolitan but are not necessarily associated
with warm water, it is found in moist soil and in
the air and water.
It is found in only
two form
: the
trophozoite
and
cyst
, and either of these can be a source of
infection.
Amoeboid
trophozoite
has
spikey
pseudopodia and a nucleus with large, central
karyosome similar to the nucleus of Naegleria.
Acanthamoeba Spp.:
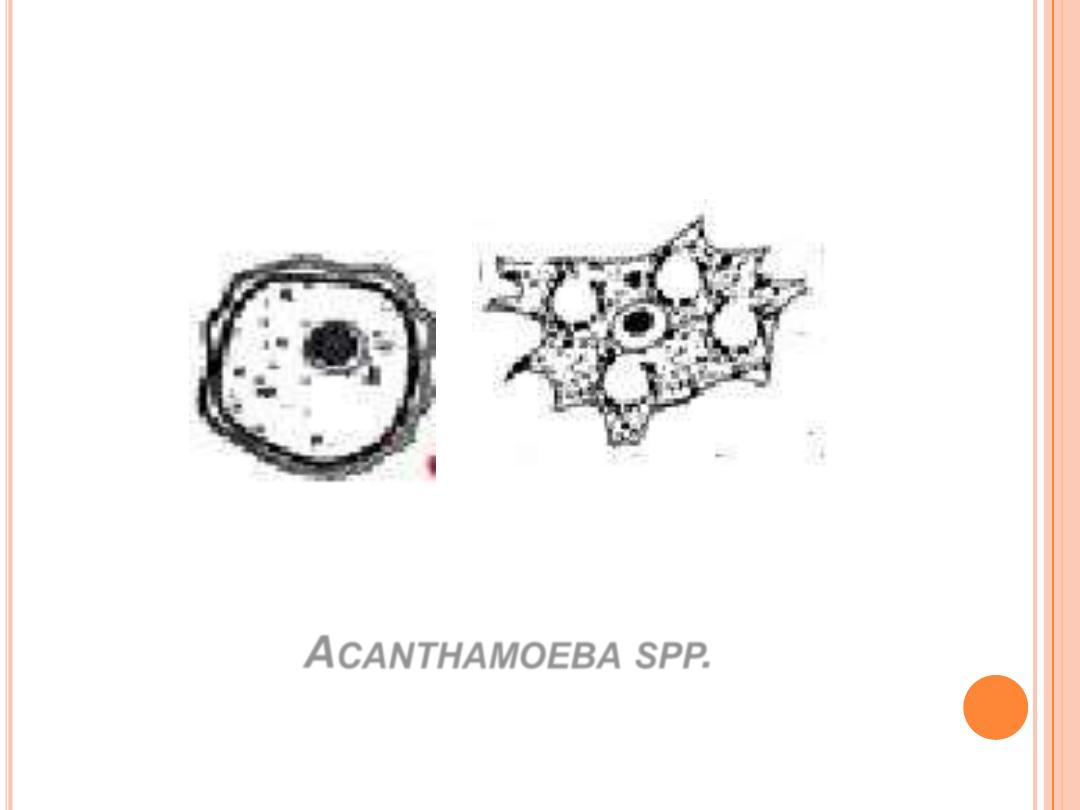
A
CANTHAMOEBA
SPP
.
Trophozoite
Cyst
Cyst :
polyconal or thicky biconvex. Acanthmoeba organisim are slightly
larger than Neglaria fowleri

Mode of infection
•
Infection can be acquired by:
•
1. inhalation., 2.ingrestion ,3.through
traumatised skin or eyes
.
•
Acanthmoeba CNS infection is not as in
Naeglaria infection ,and invasion of the CNS is
secondary to infection elsewhere in the body.
Amoebae reach the brain by way of
bloodstream, most likely from lower respiratory
tract or through ulcer of the skin or
mucosa,affected
the
immunocompromiesd
patients while keratitis affects healthy persons.

The amoebae probably enter respiratory system(R.S.), or
perhaps the skin, then migrate to CNS via the blood.
Once in the brain, it cause granulomatous encephalitis,
which means that a more or less discrete mass of
inflammatory cells and amoebae are found in the meninges
and superficial layers of the brain. The lesion develop
slowly, if treatment is not administered the progress of
disease is inexorable leading to death of the patient. Most
patients with
GAE
do not have normal immune system.
GAE has been seen in
AIDS patients
,
diabetes,
malignancies, malnutrition,
or alcoholism.

Acanthamoeba spp. Caused ulcers of the cornea of
eye in humans. Cornea is invaded when there is
trauma in the eye or the presence of amoebae in
water. In most instances, there is an association with
wearing contact lenses and a failure to clean them
properly. Corneal lesions are painful and
differentiation must be made from herpes simplex
virus.
Keratitis
affects healthy persons.
B. Amoebic Keratitis:

1.
By finding amoebae in wet mount (10%
KOH) of corneal ulcer scraping or in stained
smear.
2.
By isolation of amoebae form contact
lenses or washing solutions.
3
.Flood a culture plate with distilled water
to distinguishing between Naegleria and
Aconthomoeba species if flagellate observed
it is Naegleria spp.
:
Acanthomoebae
Diagnosis of
Lab .

Thanks for your
attention
