
Lab.2
3
rd
-year class
Practical Pharmacology
2010-2011

Dosage Forms
Dr. Mohammed Qasim
&
Dr. Huda Ibrahim

I.Oral
1.Tablets:-
the most common preparation for oral use . Is
made by compressing the drugs & inert
binders as starch or lactose into hard mass
which disintegrate in water . A tablet before
being absorbed should disintegrate into
granules& then dissolute into primary drug
particles

The active substance in an oral solid dosage
form such as tablet represents only a small
proportion of the total weight
• .
These include:-
diluents(Lactose, Calcium, Sulphate), binding
agents(bentonile), lubricants(talc), disintegrating
agents (starch , mixture of sodium bicarbonate &
tartaric acid), coating formulation . material
(sugar), special
Different manufacturing procedures may result in
the production of different physical forms of the
active drug(e.g. compression force & tablet
hardness).

Coated tablets:-
a common type is a sugar coated tablet.
The coat is an additional physical barrier
for disintegration.
1-Coatings are used to mask the unpleasant
tastes & odors.
2-To protect the tablet ingredients from
decomposition in drug storage.
3-To improve the appearance of the tablet


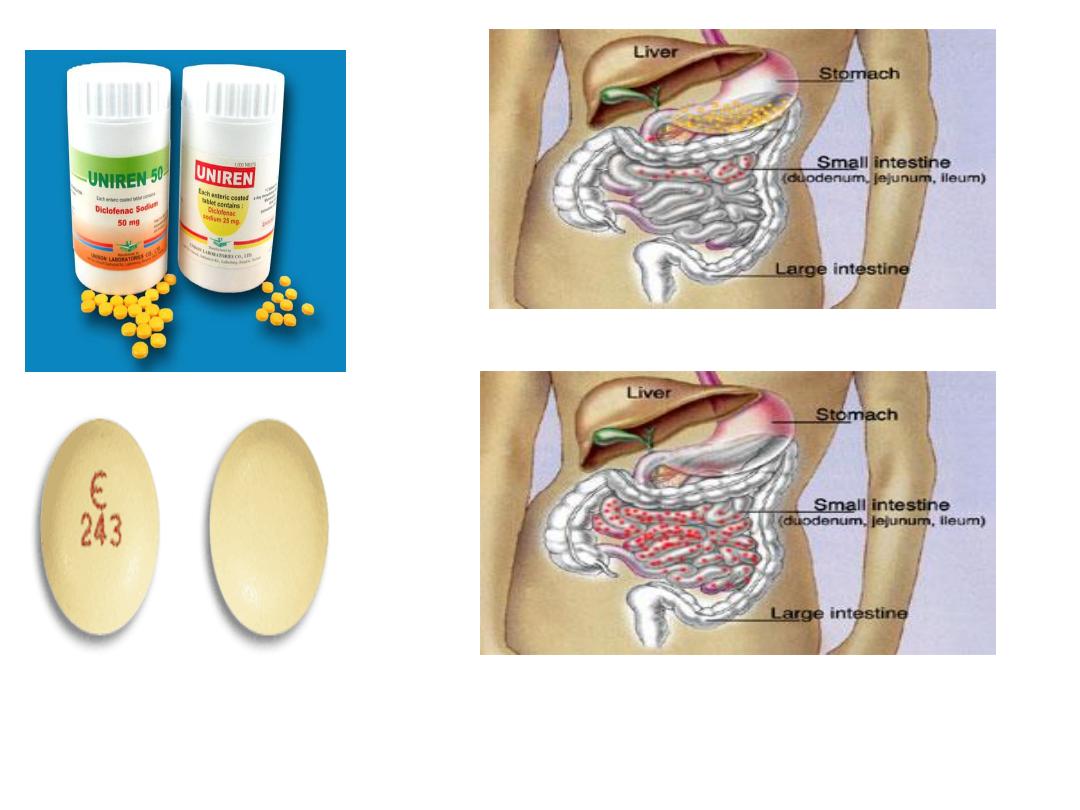
Enteric-coated tablet:-
a special film coat
designed to resist gastric fluid & disrupt or
dissolve in the intestine
1-They are used to protect a drug from
degradation in the stomach.
2-To minimize gastric irritation caused by
some drugs

Sustained-release tablets(SR)
this is designed to release their
contents over extended period of
time.

Advantages:
to eliminate the need for multiple dosage
regimens , particularly for these drugs
requiring reasonably constant blood level
over a long period of time , or drugs which
need to be given in high doses , but too
rapid release is likely to cause
undesirable side effect
(e.g. potassium chloride tablets)

2.Capsules:-
a drug formulation encapsulated in a hard
gelatin shell .Drug particles in the capsule
are not subjected to high compression
that tend to compact the powder & to
reduce the effective surface area. However,
drug bioavailability from capsule isn't always
better than a tablet.

Advantages:
1.Protection from light.
2. Mask the taste or odour of their components.
3. Attractive appearance.
4. Ease to identify.
5. Controlled release.


Spansule:
capsule containing drug granules with
special pharmaceutical formulation to be
disintegrated and dissolved in different times
for prolonged action (theophyllin)

3.Granules:-
all irregular particles of drug, sugar & inert
adjuvant stirred in water before taking

4.Effervescents tablet or
granules:-
the basis of the effervescence is a mixture
of citric acid & tartaric acid with sodium
bicarbonate . When dissolve in water , the
acid & bicarbonate react together to
produce carbonic acid . The carbonated water
partly disguises the unpleasant taste of
drug & has refreshing properties.


5.Syrup:-
is a concentrated aqueous solution of sugar ,
useful vehicle for water soluble drugs act
both as a solvent & flavoring agent .
Advantages:
1. Immediately available for absorption. 2.
Useful for children or in swallow difficulties
(elderly).


6.Elixir:-
is a sweetened hydro alcoholic solution
that contains approximately 25%. It is a
suitable vehicle for drugs soluble in either
water or dilute alcohol.


7.Linctuses:-
are viscous liquid oral preparations that are
usefully prescribed for the relief of cough

II.Topical:-
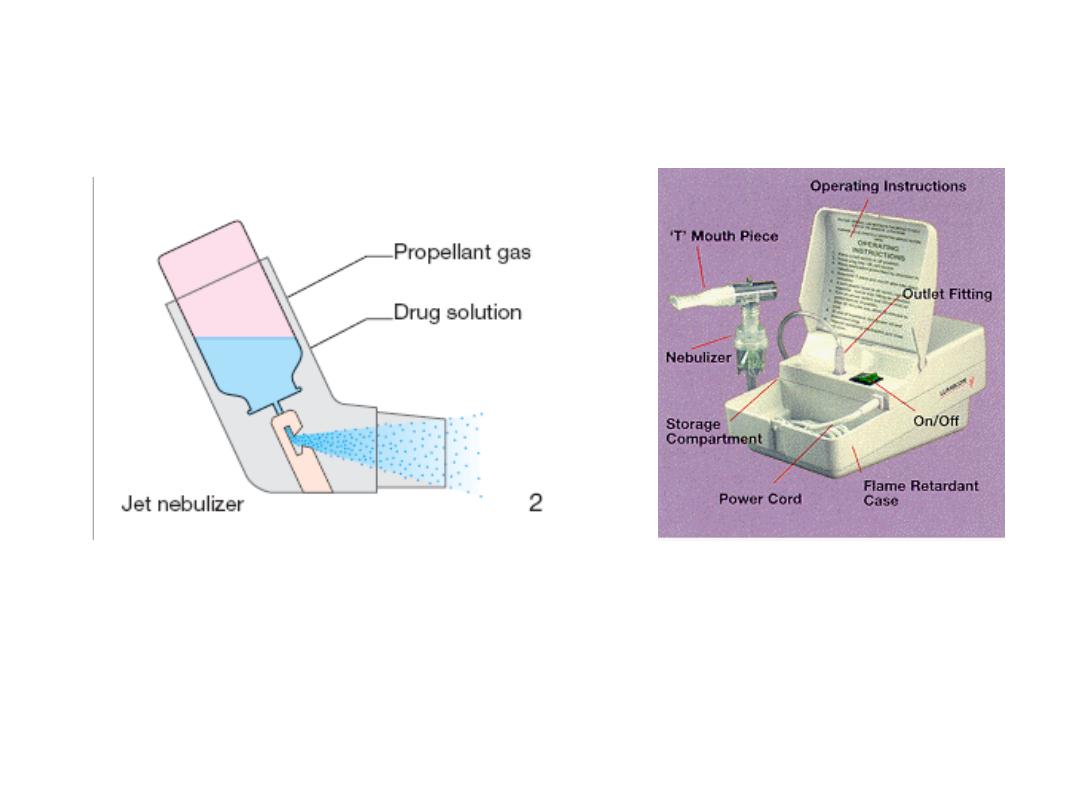
1.Aerosols:-
they are suspensions of fine solid or liquid
particles in a gas . They are used to the
respiratory tract or skin . The sprays used to
treat respiratory diseases are atomized in
devices known as nebulizers

2.Gargles:-
they are aqueous solutions used to treat or
prevent throat infections, usually dispensed
in concentrated form to be diluted in warm
water before use

3.Drops:-
could be to the eye, ear, nasal or oral drops.
Nasal drops are usually aqueous because oily
drops inhibit movement of cilia in the nasal
mucosa & if used for a long time , they may
reach the lungs & cause lipoidal pneumonia

4.Ointments:-
are semisolid, greasy preparations for
application to the skin , rectum . The base is
usually anhydrous & contains the medicament in
solution or suspension.
5.Cream:-
they are semisolid solution for external use. They
are 2 kinds:-1. aqueous cream 2. oily cream.
In which the emulsions are oil in water or water in
oil respectively
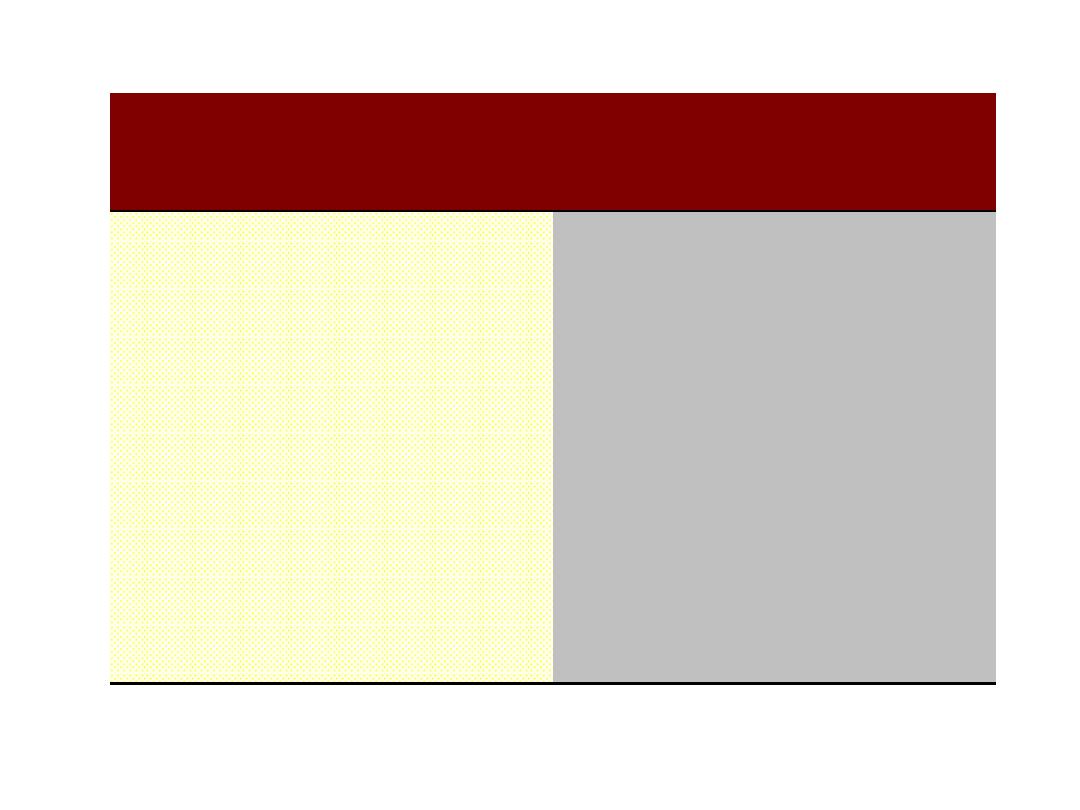
Ointment
Cream
1-greasy
1-relatively not greasy
2-semisolid anhydrous
2-semisoilid emulsion(oil +
water)
3-less skin penetration
3-more skin penetration
4-used for dry, chronic skin
lesion
4-used for wet lesions of
skin
5-applid to skin & rectum
Applied to skin only

6.Lotions:-
aqueous preparations for external
application without friction . They are
rubbed on skin or applied on the suitable
dressing

7.Suppositories:-
are conical or ovoid solid preparations for
insertion into the rectum, where they exert
local or less often systemic effect. Their base is
fat, wax or glycerol gelatin
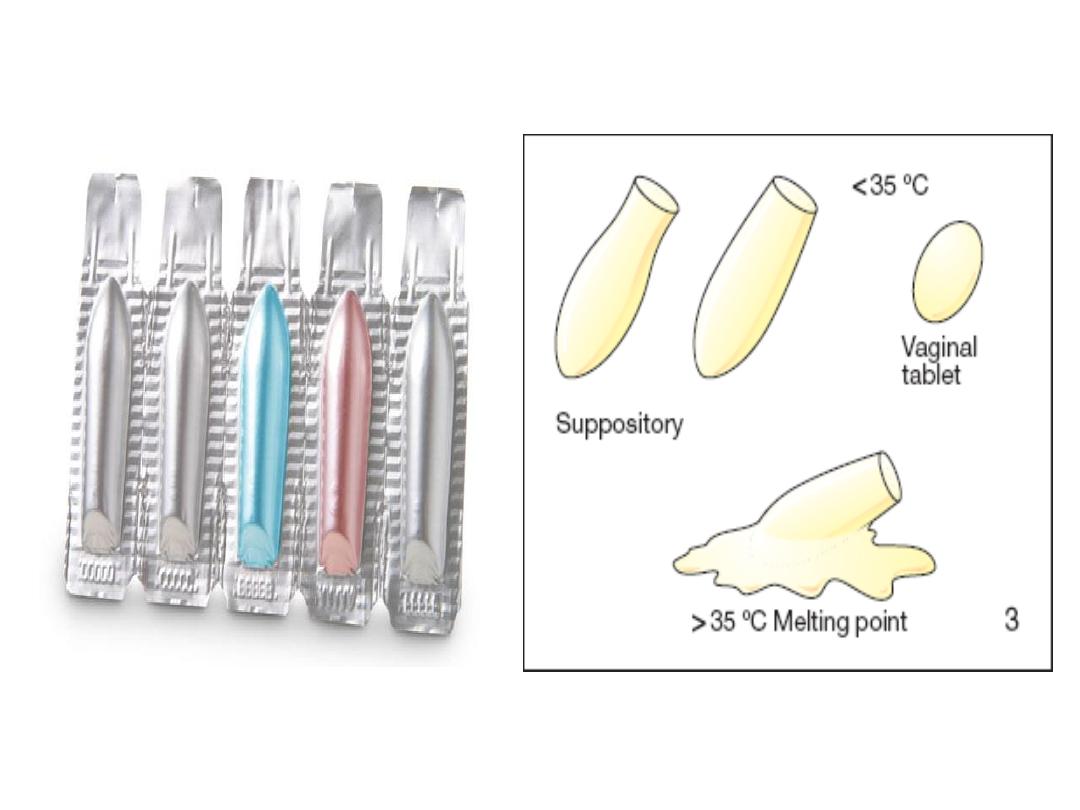

8.Pessaries:-
solid medicated preparations for
introduction into vagina where they melt or
dissolve & exert a local action

III.Injections:-
drugs given by injections act more rapidly &
reliably, thus more useful for emergency
situations . They require some technical
skills, aseptic technique & suitable
equipments

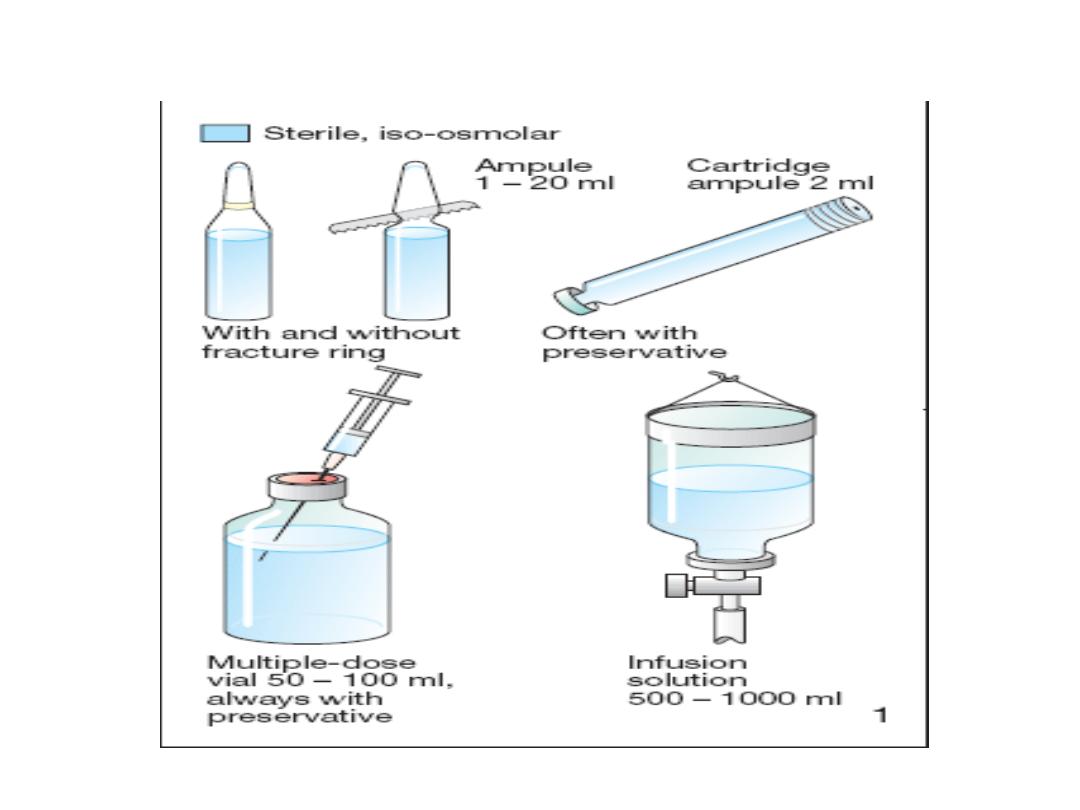
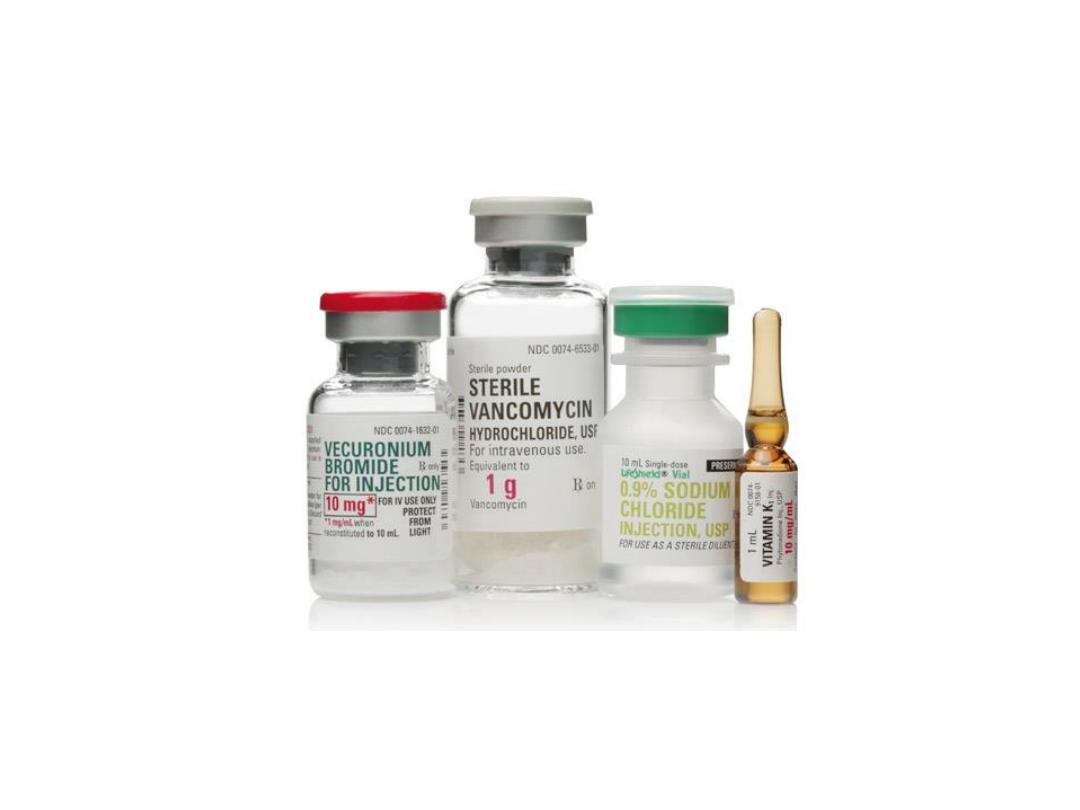
a. Injection:
highly purified & sterile dosage form either in
ampoules or vials (for multidose)
.
b. Intravenous Admixture:
(i.v. fluid) large volume injection intended to be
administered by i.v. infusion , for fluid replacement ;
electrolytes balance restoration; supplementary
nutrition; & as vehicle for other drug substance
(G/W, Albumin, Dopamine).
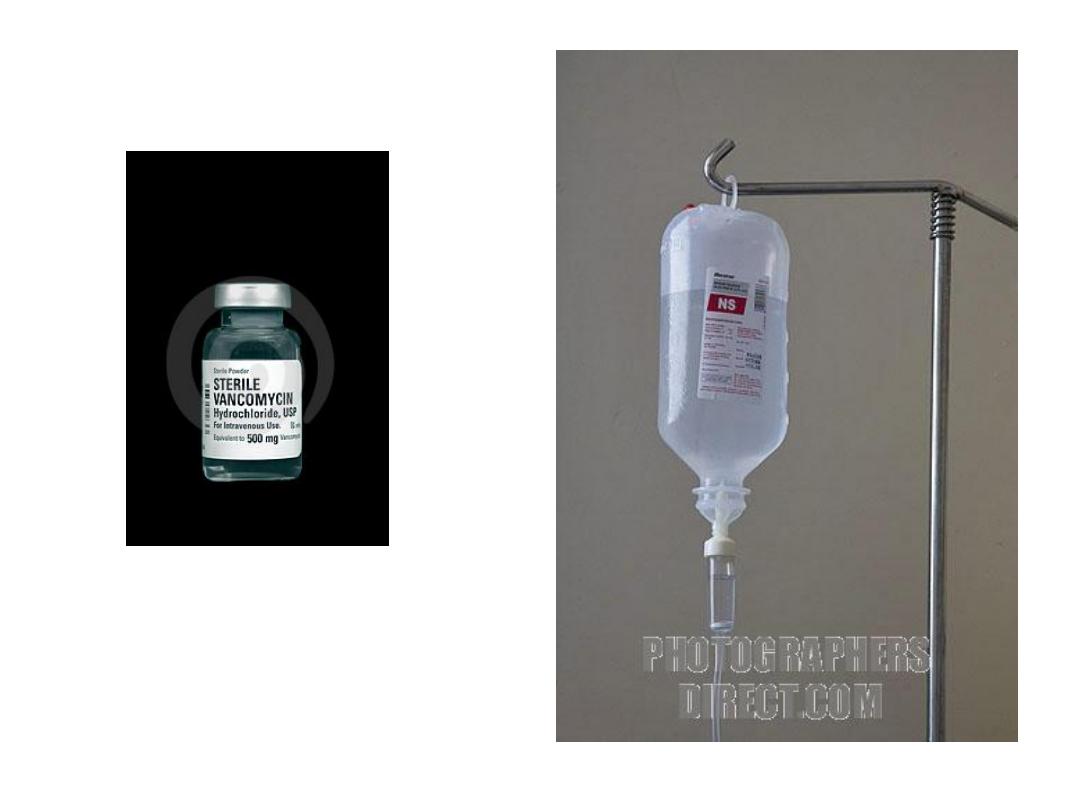

There are 2 types of injections
preparation:-
1-Ampoule:-
which contains sterile drug
solution & used once when opened.
2-Vial:-
which is designed to contain one or
multiple doses & having a rubber cover to
avoid contamination.
IV.Some pharmaceutical preparations:-
1.Extract:-
are concentrated preparations containing
active principles of vegetable or animal drugs. The
drugs are extracted with suitable solvents & the
product is concentrated to a liquid, soft or dry extract.
2.Tinctures:-
are alcoholic or hydro alcoholic solution of
the active principles of drugs. They are medicated or
non-medicated. The latter is used as flavoring agent.
3.Waters:-
aromatic waters are saturated aqueous
solutions of volatile oils, used as vehicle for water-
soluble substances

• Enema:
a clyster or injection; a liquid injected
or to be injected into the rectum (e.g.
hydrocortisone enema), & barium enema
(barium meal).
• Powder:
e.g. antacid.
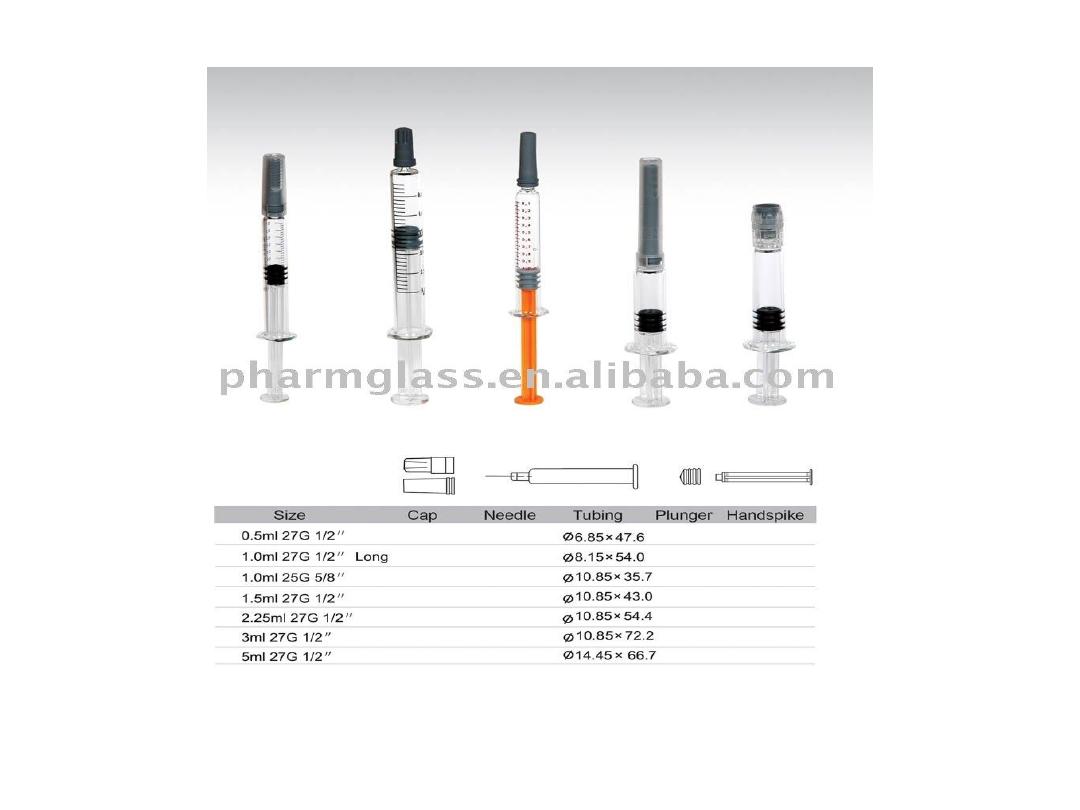
• Prefilled syringe
: e.g.enoxaparn.
• Pen
:
e.g. mixtard insulin

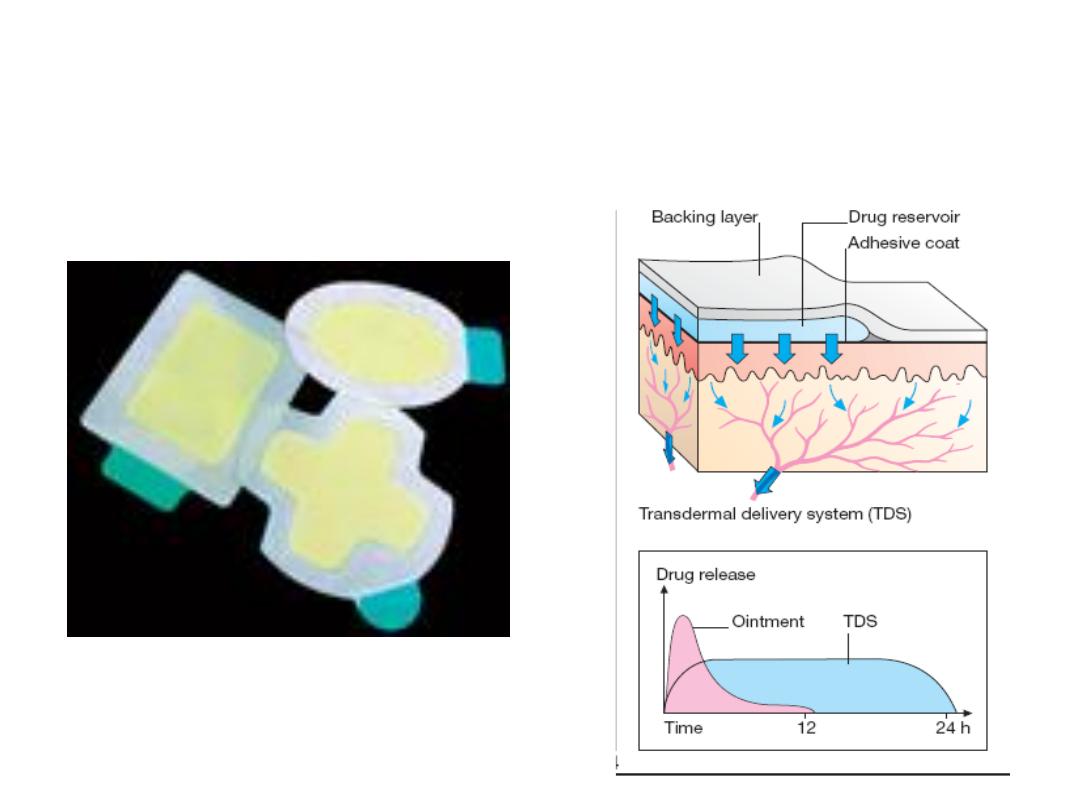
Transdermal delivery system (TDS):

