
Sunday 9 / 11 / 2014
@Ali Kareem 2014-2015
Name
:
______________________________
Class
:
_______________________________
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
ANGINA PECTORIS
Lecture 2
Total lectures NO. 14
Dr. Mohammed Rashad

2
Angina Pectoris
Def. : Imbalance between O
2
supply and requirement due to spasm or obstruction of
coronary B.V lead to sudden , severe pressing substernal chest pain .
Types :
1- Stable angina (during effort ) .
2- Unstable angina (at rest ) .
3- Vasospastic or variant angina .
4- Mixed form of angina .
Classification of antianginal drug :
1- Nitrates :
Short acting : GTN ( Nitroglycerine ) .
Long acting : Isosorbide dinitrate , Mononitrate , S.R
Erythritol tetranitrate , Amylnitrate
2- B- blockers :
Propranlol , Atenolol , Metoprolol
3- Ca
++
channel blockers :
Verapamil , Deltiazem ,Nifidipin , Amlodipin .
4- K
+
channel opener : Nicorandil .
• Organic nitrates
• They are nitric and nitrous acid esters of alcohol and they are effective in all types of
angina .
•
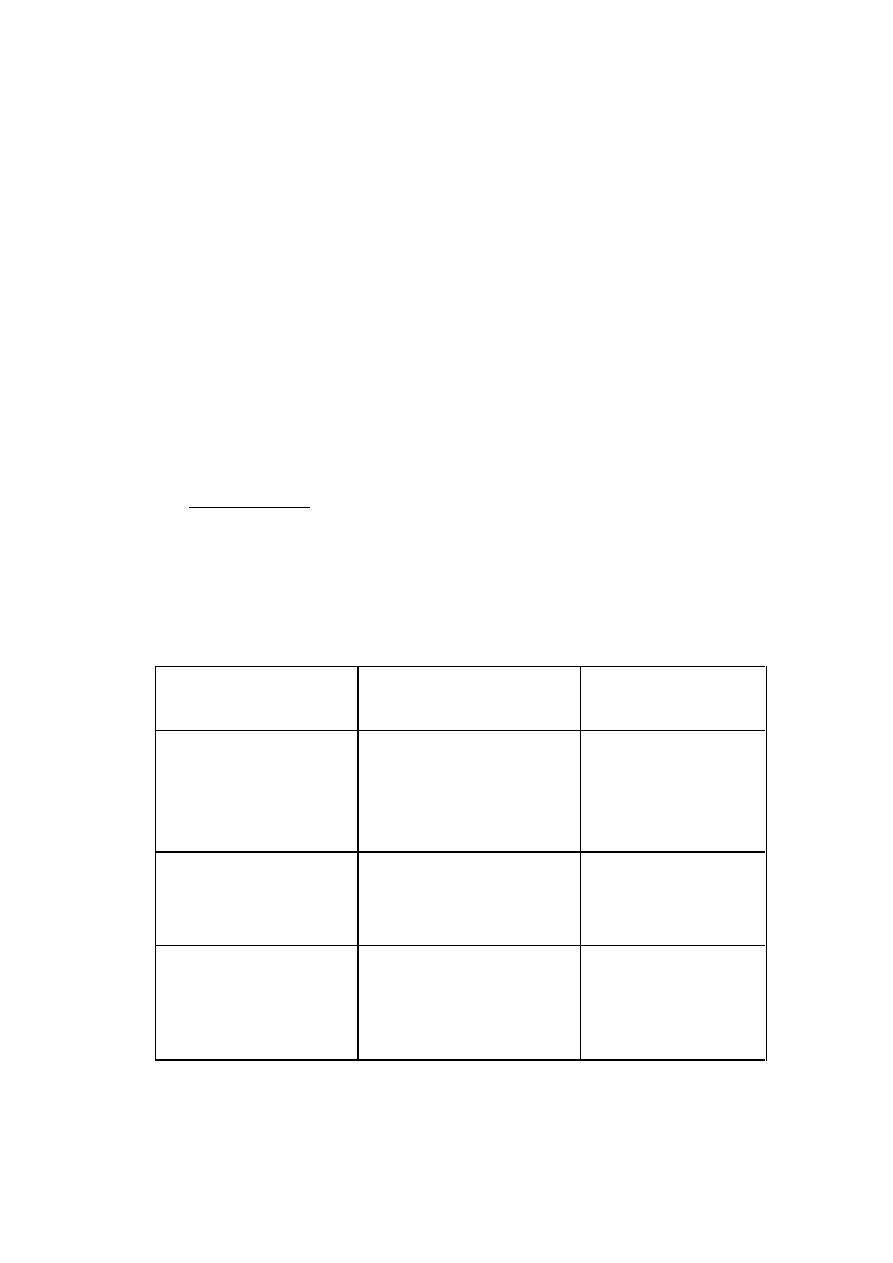
• Mechanism of action:
• Administered nitrates ⟶ ⇧ Nitrite ⟶
• Nitric oxide (NO) ⟶ ⇧ cGMP ⟶
• dephosphorylation of Myosin light chain ⟶
3
• vascular s.m relaxation .
• Effects on the cardiovascular system :
• 1- V.D of veins : ⇩ Preload ⟶ ⇩ work
• 2- V.D of coronary a. : ⇧Blood supply
• 3- V.D of arterioles (Large dose) : ⇩ After load
• Effects on the other system :
• 1- Relaxation of s.m of : Bronchi , GIT , Biliary , GUT.
• 2- ⇩ Platelet aggregation .
• Pharmacokinetics
• Organic Nitrates : Volatile , destroyed by heat .
• Bioavailability of GTN is very low because of significant 1
st
pass metabolism due to
high hepatic nirate reductase , so sublingual (S/L) ( avoid 1
st
pass) route is preferred
Duration of action
(Ms or hours)
Speed of onset (Ms)
Organic Nitrates
< 30 m
< 30 m
24 h.
1 - 4
1 - 4
30
GTN
S/L
Spray
Transdermal
4 – 8 h.
8 – 12 h.
30 – 40
Slow
Iso. Dinitrates
Oral tabs
S.R tabs
6 – 12 h.
12 – 24 h.
30 – 40
Slow
Iso. Mononitrate
Oral tabs
S.R tabs

4
Amyle nitrate : flammable , volatile , liquid used by oral inhalation .
Therapeutic uses :
1- Angina pectoris ( all types )
2- Hypertonsive emergency I.V
3- CHF & LVF
4- M.I : I.V ⟶ reduce early mortality .
5- Interventional cardiac procedure as percutaneous coronary angioplasty ( PCA )
6- Biliary colic.
7- Esophageal spasm .
8- Peripheral vascular disease .
9- Cyanide poisoning .
HB
Na−nitrite
→
Met HB
Cyanide(CN)
→ Cyano-Met HB
Na+−thio−SO4
→
MetHB + Na
+
- thiocyanate ( NaOCN ) ⟶ excreted in urine .
Adverse effects
1- Headache: the most common 30 – 60%.
2- Postural hypotension: high dose.
3- Facial flushing.
4- Tachycardia: reflex ⟶ V.D .
5- Methomoglobinemia : ⇩ O
2
of blood .
6- Tolerance : develops rapidly .
Avoided by ⟶ Nitrate free interval.
7- Cross tolerance: among all Nitrates.

5
Workers in explosive factories:
Nitrate exposure (repeated fixed dose) ⟶
⇩ response (tolerance)
years
→ dependence V.D
withdrawal days
→
coronary spasm ⟶ M.I
8- Tolerance & dependace .
Calcium channel blockers
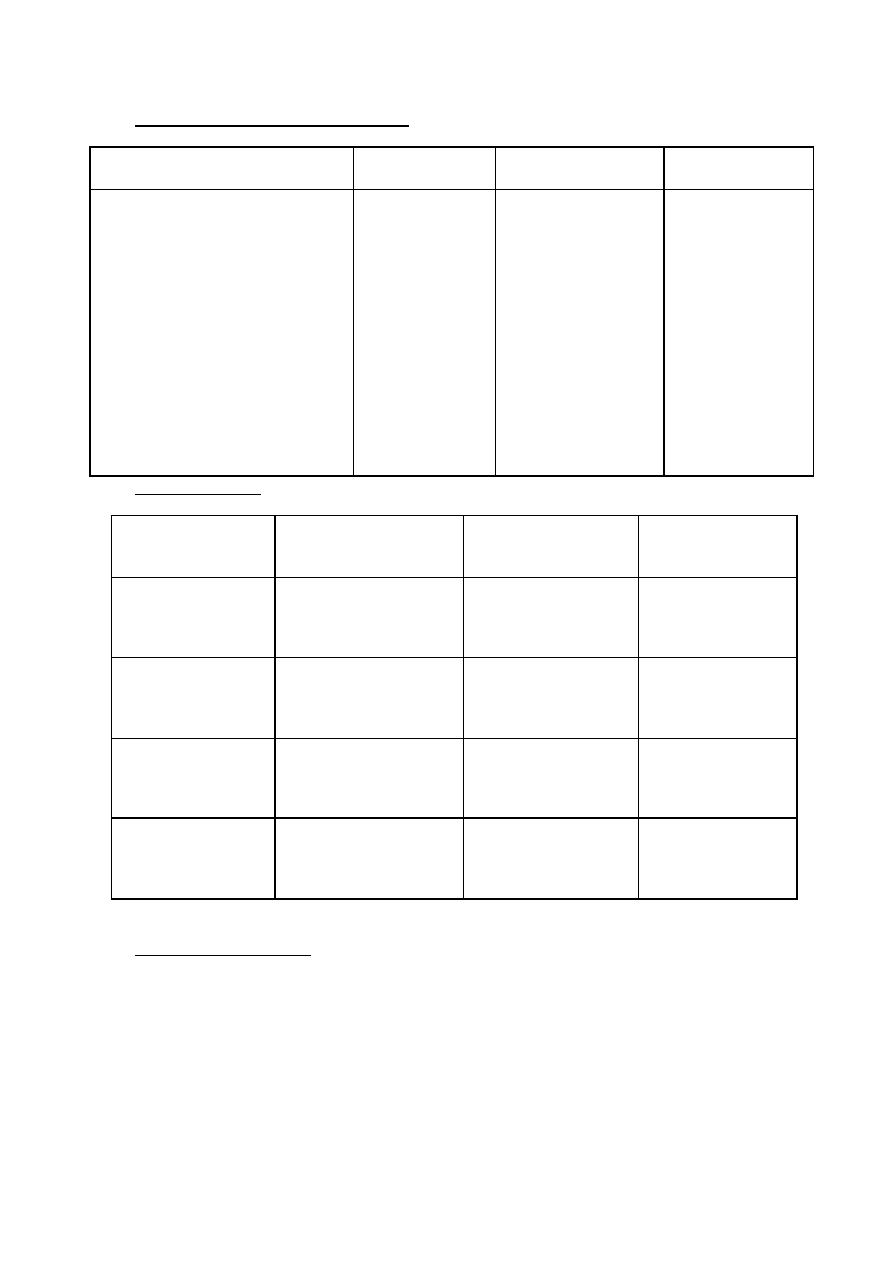
Mechanism of action :
Calcium channel blockers bind to L type calcium channels ⟶ block Ca
++
entrance into heart
& smooth m. of :
- Coronary ⟶ V.D
- Mainly arterioles ⟶ V.D
Pharmacological action :
1- ⇩ TPR ⟶ ⇩ afterload .
2- ⇩ CVP ⟶ ⇩ preload .
3- V.D of coronary ⟶ ⇧ O
2
supply .
4- Inhibit secretion of chatacoleamines .
5- -ve ( chronotropic , inotropic , dromotropic ) & effects on myocardial function.
6
Pharmacological action of CCBs on CVS :
Diltiazem
Nifedipine
Verpamil
⇩ , __
⇩
⇧
⇩ ,
⇧
__ ,
+
(Reflex)
⇧
__
⇧
⇧
+++
⇩
⇩⇩
⇩
__ ,
__ , ⇩
++
A) Heart
Heart rate
A-V conduction,velocity
Contractility
Output
B) Blood V.s
Relaxation ( V.D )
Pharmacokinetics:
T
1/2
(hr.)
Active
metobdo
Bioavailability
4 - 6
Yes
15 – 30 %
Verpam
5 - 6
Yes
40 - 60 %
Diltiazem
2 - 5
Minor
30 – 60 %
Nifedipine
35 - 45
Non
60 – 65 %
Amlodipim
Therapeutic uses of CCBs:
1- Angina pectoris : all types .
2- Hypertension : ± Angina , Asthma , Diabetes , &/or P. vascular disease (PVD) .
3- Arrhythmia: Verpamil & Diltiazem , highly effective in PSVT .
4- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
Verpamil ( -ve inotropic effect )
7
5- Other uses :
- Premature labour (Nifedipine)
- Nocturnal leg cramps (Verpamil)
- Reynaud's disease (DHPs)
- Migrain prophylaxis .
- Esophageal spasm .
- Following subarachnoid Hge (Nimodipine)
Adverse effect :
1- Headache & flushing (V.D)
2- Hypotension & fatigue .
3- Tachycardia (Nifedipine),bradycardia (Verpamil)
4- Ankle edema & Gum hypertrophy (Nifid)
5- Constipation (Verpamil).
B- Adrenocepter blocking Agents:
Rate & force contraction CO
B.P
O2 demand work .
• Determinant of arterial pressure :
• - B.P = CO x TPR
• CO (1- SV 2- HR 3- V Ret )
• TPR ( 1- caliber 2- elasticity 3- viscosity )
• - Work = B.P x SV
• CO = HR x SV
• - Mean ABP = DBP + (SBP – DBP )/3
8
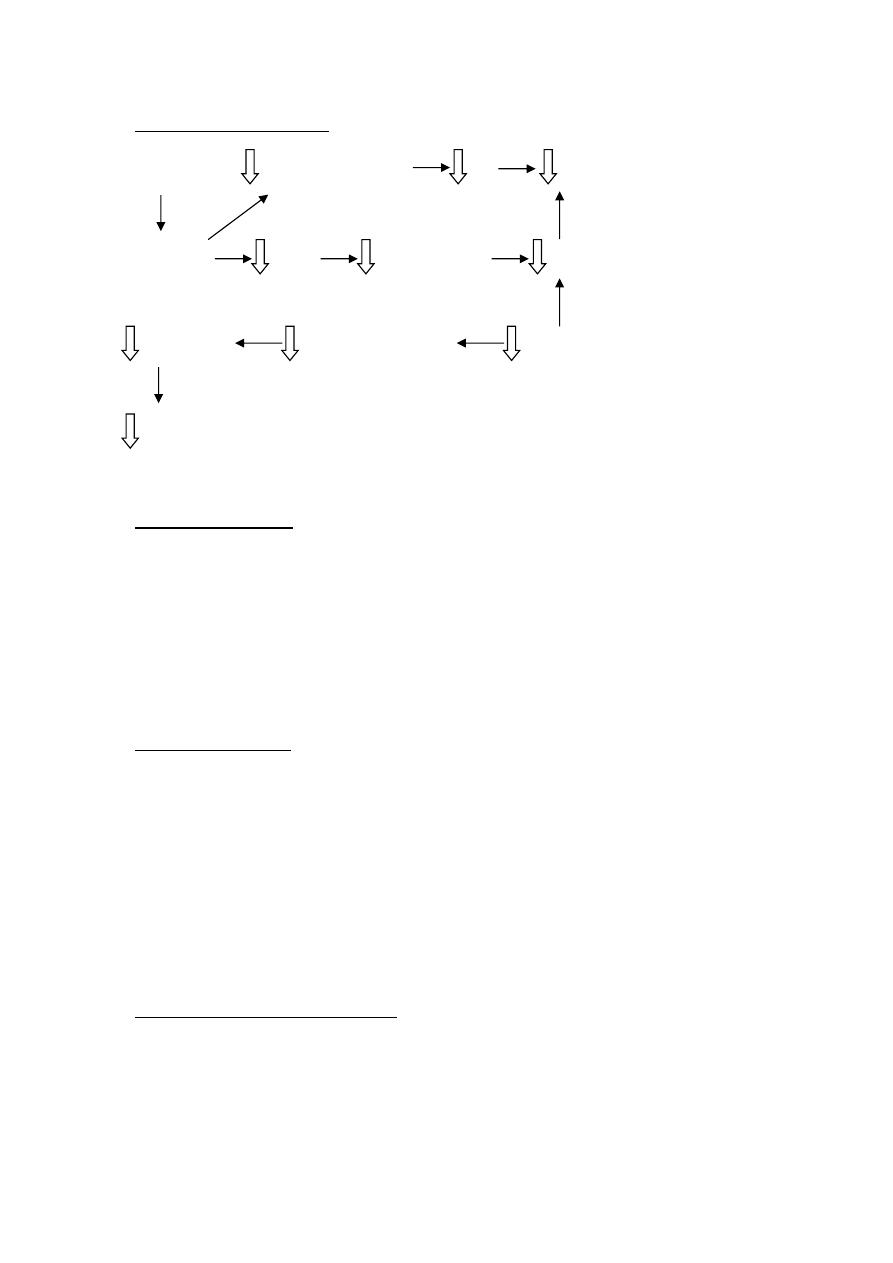
Mechanism of action :
B-blockers ontractility&rate CO B.P
Blocks B
1
Rinin Angiotensin II TPR
B. volume Na&H
2
O retention Aldosterone
B.P
Therapeutic uses :
1- Hypertension : in white & young .
2- Hypertension with concomitant diseases
SVT , MI , Angina , Chronic Ht failure .
3- Angina pectoris : except variant .
Contraindication :
1- Asthma .
2- Diabetes .
3- Severe bradycardia .
4- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
5- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Adverse effect off B-blockers :
A) Common : Bradycardia , Hypotension , Fatigue lethargy ,
Insomnia , Depression , ⇩ Lpids (⇩ compliance )
B) Alteration in serum lipid patterns ( ⇩ HDLC & ⇧Triacylglycerol ) .

9
C) Drug withdrawal:
Abrupt withdrawal ± (in pt. with IHD) ⟶ Angina , MI , sudden death .
- The dose must be tapered over 2-3 weeks .
K
+
channel openers:
Eg. : Nicorandil
K
+
channel activator ⟶ V.D as nitrates without No tolerance.
Uses : Angina .
Heart failure .
Asthma .
S/E : as nitrates .
