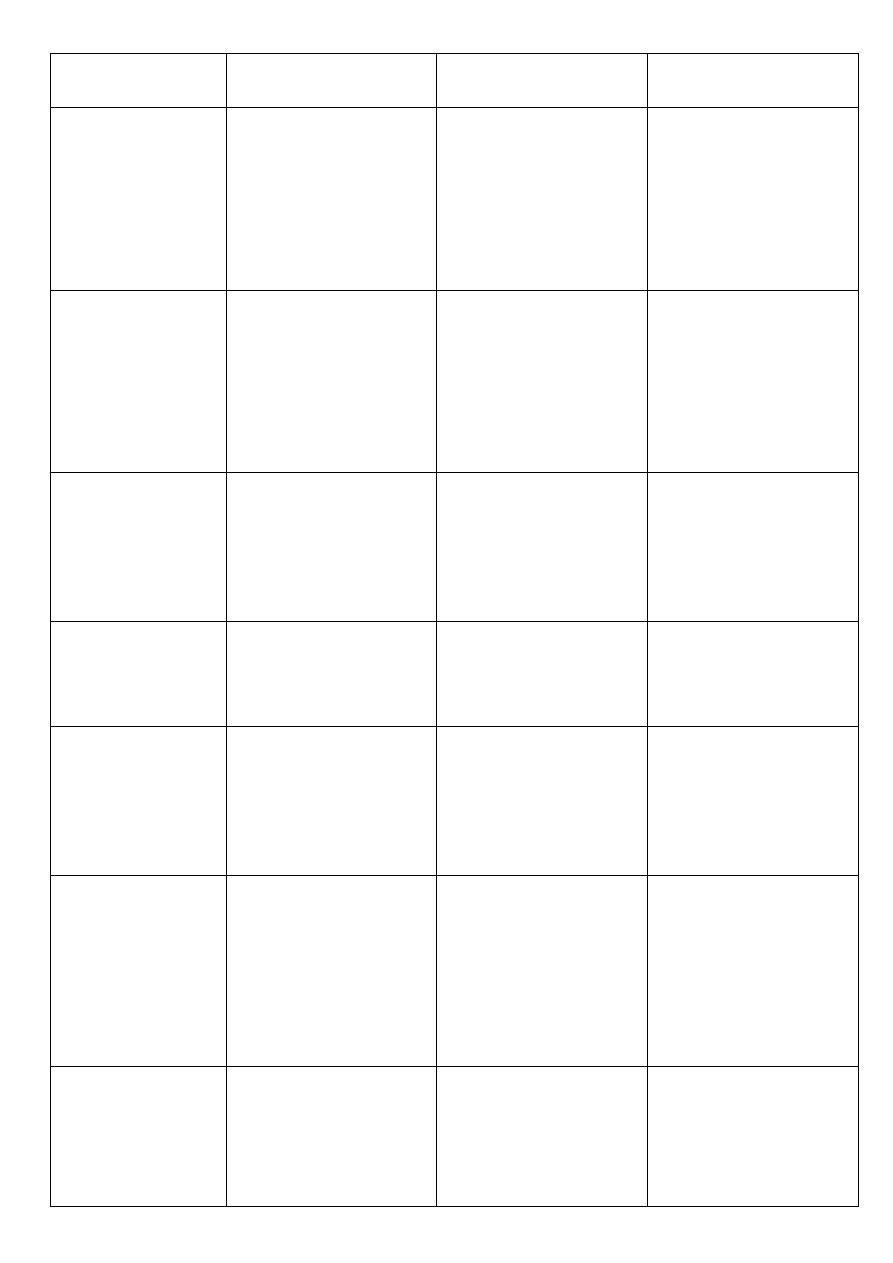
Nor Adrenalin
Isoprenaline
Adrenalin
Effect on :
decreases heart rate due to
increased blood pressure
that induces a reflex rise in
vagal activity by stimulating
the baroreceptor
s
If atropine is given before
Noradrenaline, or the vagas
is cut ,or the patient is in
shock then there will be
tachycardia
.
increase heart rate.
increase heart rate.
1. Heart rate
increase contractility and
stroke volume.
The reflex compensation
doesn't affect the positive
entropic effect of
Noradrenaline
.
increase
contractility and
stroke volume
increase
contractility and
stroke volume.
2. Force of
contraction
little or no effect on
cardiac output (due
to weak beta
1
effect)
increase cardiac
output .
increase cardiac
output .
3. Cardiac
output :
Increase
(least with
Noradrenaline).
Increase
Increase
4. Myocardial
oxygen
consumption
Increased
Increased
Increased
5. Conductivity
causes constriction
(i.e. increase total
peripheral
resistance TPR)
through αlpha
action .
dilate vessels going to
the skeletal muscles &
liver
the effect, therefore, is
a decreasing in total
peripheral resistanc
e
more evident with
Iso. (β₂ action).
dilate vessels going to
the skeletal muscles &
liver
the effect, therefore, is
a decreasing in total
peripheral resistanc
e
(β₂ action)
6.Blood vessels
of skeletal
muscles :
constrict skin and
mucus membrane
arterioles (αlpha
action).
has no effect
because there are
no beta receptors in
the skin& mucus
membrane
constrict skin and
mucus membrane
arterioles (αlpha
action).
7. Skin blood
vessels:
Comparison of effect of Adrenaline , Isoprenaline , Noradrenaline
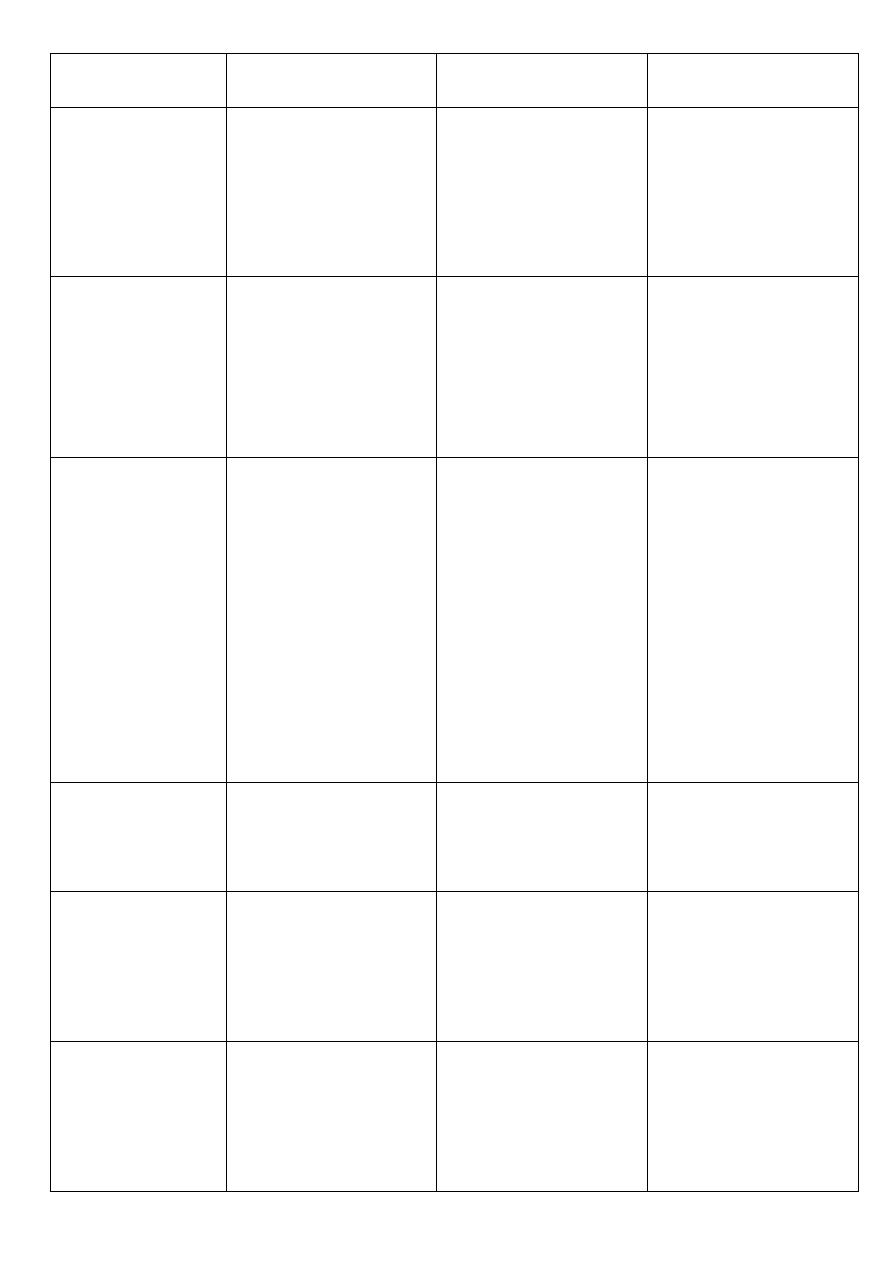
Nor Adrenalin
Isoprenaline
Adrenalin
Effect on :
Constrict
arterioles (αlpha
action
The same of the
skin.
has no effect
because there are
no beta receptors
The same of the
skin
Constrict
arterioles (αlpha
action)
The same of the
skin.
8. Renal blood
vessels :
produce
venoconstriction
which leads to
increased venous
return .
produces dilation of
veins which leads to
decreased venous
return.
produce
venoconstriction
which leads to
increased venous
return .
9. Veins
increases systolic
and diastolic blood
pressure (alpha
action).
Isoprenaline may
increase systolic
pressure slightly but it
greatly reduces the
diastolic pressure & the
mean arterial pressure
.
Adrenaline increases
systolic blood pressure
(Beta1) with slight
decrease in diastolic
blood pressure (Beta2
vasodilation)
.
The mean blood pressure
(MBP) = (diastolic + 1⁄3 pulse
pressure) may be slightly
increased because the increase
in systolic pressure is much
more than the decrease in
diastolic pressure. So
Adrenaline increases the mean
blood pressure but the
increase is less with
Noradrenaline
.
10. Blood
pressure :
have no effect
have no effect
reduces capillary
permeability due to
widening of the
endothelial cells that
decreases the pores
.
11. Capillaries:
has no effect.
(Because there are
no αlpha receptors
in the bronchiolar
smooth muscles)
.
cause powerful
bronchiodilation
(β₂ effect).
cause powerful
bronchiodilation
(β₂ effect).
12. Bronchiolar
smooth muscle
cause relaxation .
(αlpha₂ action)
cause relaxation .
(βeta₂ action)
cause relaxation .
(alpha₂ and beta₂
action)
13.
Gastrointestinal
Tract:
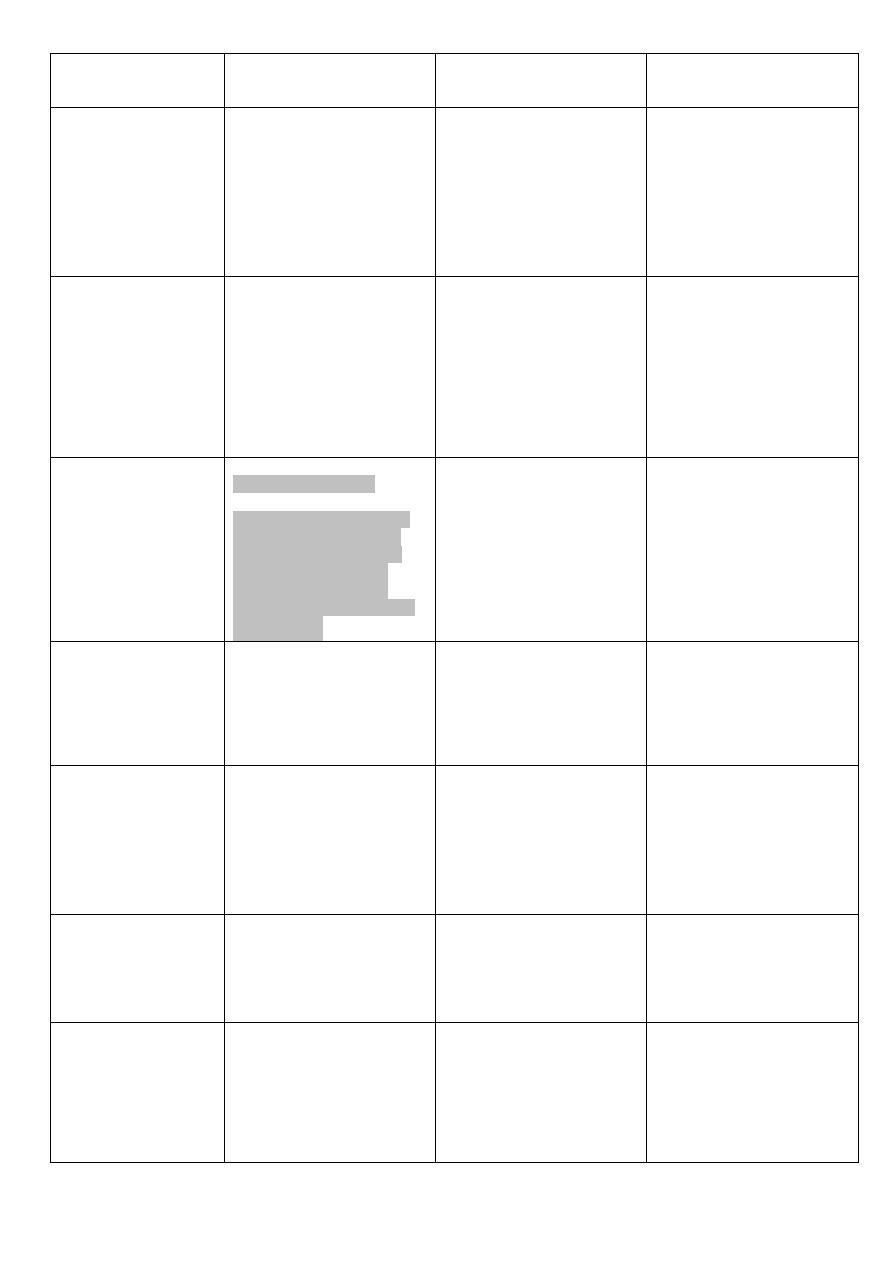
Nor Adrenalin
Isoprenaline
Adrenalin
Effect on :
(alpha action )
causes contraction.
(beta₂ action)
causes relaxation
(beta₂ action)
causes relaxation
14. Pregnancy
uterus :
has little effect
because it is not
absorbed (causes
severe
vasoconstriction).
has no effect.
(alpha₁ action)
causes contraction
of radial muscles
(mydriasis).
15. Radial
muscles of the
iris
may increase blood
suger.
cause increase in
blood suger (β₂
effect).
has significant
hyperglycemic effect
because it :
- increases glycogenolysis
in the liver (beta₂ effect)
- increases the release of
glucagon (beta₂ effect)
- Decreases the insulin
(alpha₂ effect on Beta cells
of Pancreas)
.
16. Blood
glucose:
(increased by
all)
least increased by
Noradrenaline
The increased
Lipolysis induced
by Isoprenaline is
not clinically
significant
initiates Lipolysis
(through its agonist
activity on BETA₃
receptors).
17.Lipolysis:
may cause
hyperkalemia
through alpha₁
effect.
l
ead to hypokalemia
because the biochemical
pump that shifts k into
the cells is activated by
beta₂ agonists
l
ead to hypokalemia
because the biochemical
pump that shifts k into
the cells is activated by
beta₂ agonists
.
18. Serum
pottasium k:
less with
Noradrenaline.
cause muscle
tremor (beta₂
effect)
cause muscle
tremor (beta₂
effect)
19. Muscle
tremor :
has no effect
The release is
inhibited (beta₂
effect
The release is
inhibited (beta₂
effect)
20. Release of
mediators from
mast cells :
