
Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
Lec. 4
Staphylococci
Wed
11 / 3 / 2015
2014 – 2015
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
1
Staphylococci
General Characteristics
Common inhabitant of the skin and mucous membranes.
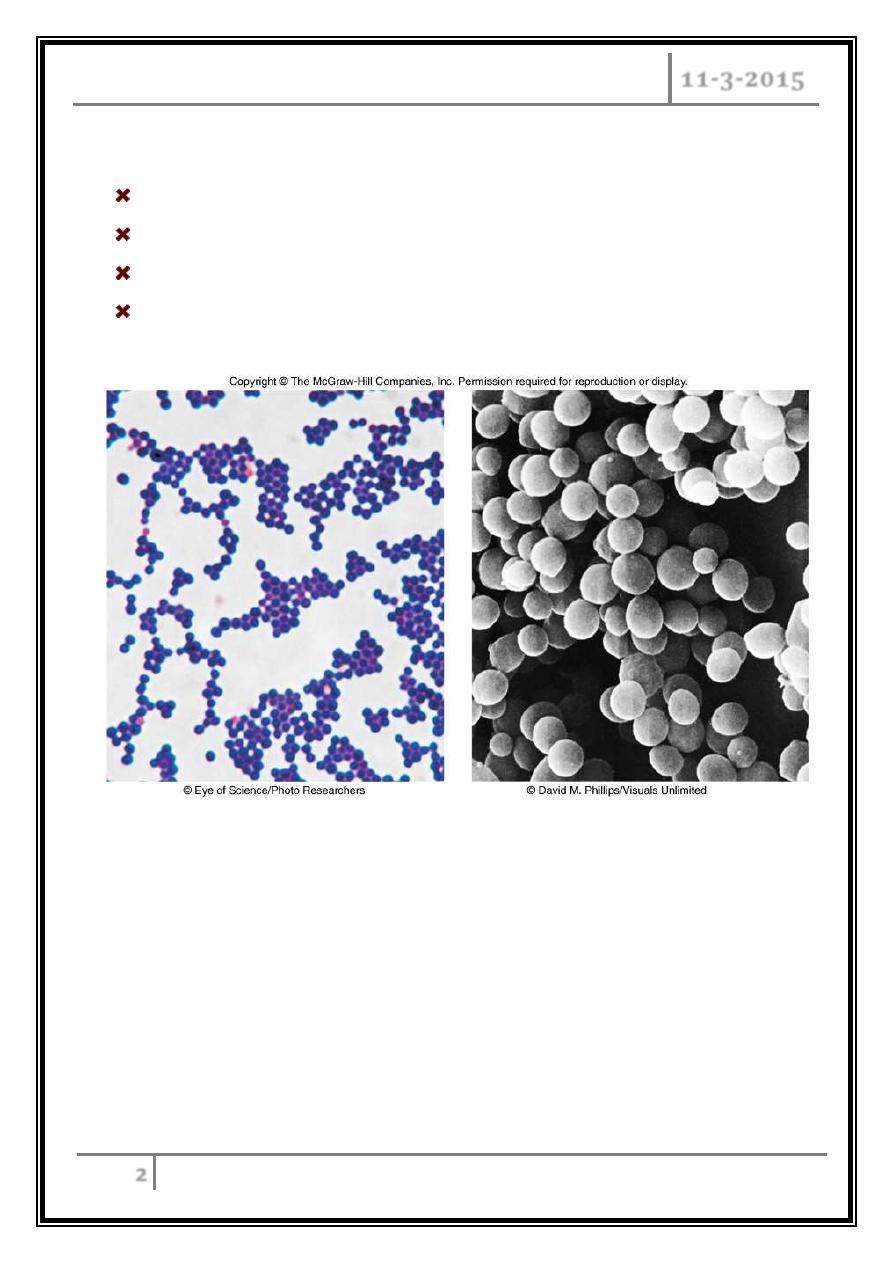
G+ Spherical cells arranged in irregular clusters.
Lack spores and flagella.
May have capsules.
31 species.
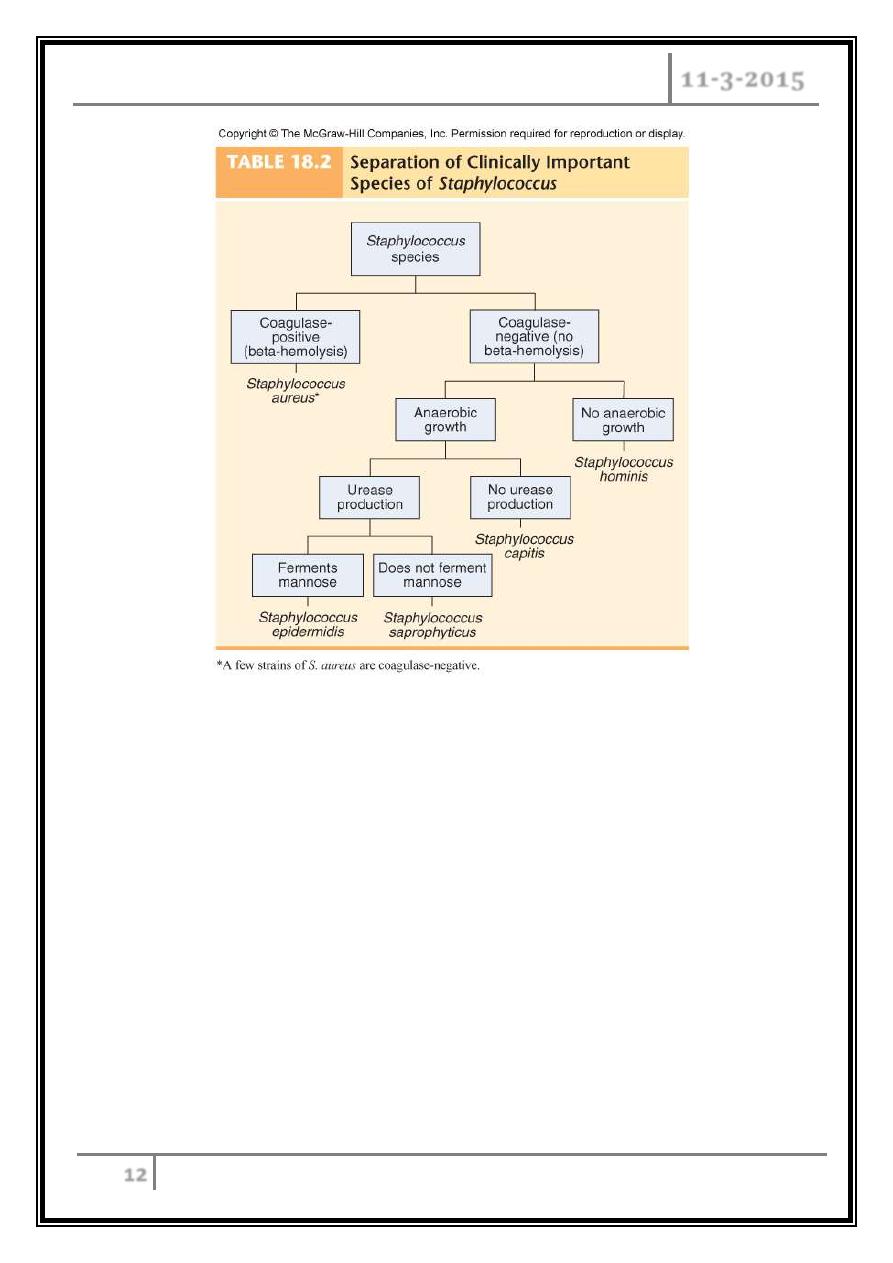
Classification
Are divided into pathogenic and non-pathogenic, based on possession of the
enzyme coagulase
- Coagulase +ve, are usually pathogenic, example, S. aureus.
- Coagulase –ve, frequently involved in nosocomial and opportunistic infections,
like S. epidermidis, and are less invasive.
S. epidermidis
– lives on skin and mucous membranes; causes
endocarditis, bacteremia, UTI.
S. hominis
– lives around apocrine sweat glands.
S. capitis
– lives on scalp, face, external ear.
*
All 3 may cause wound infections by penetrating through
broken skin.
S. saprophyticus
– infrequently lives on skin, intestine, vagina; UTI.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
2
Staphylococcus aureus
Grows in large, round, opaque colonies.
Optimum temperature of 37
o
C.
Withstands high salt, extremes in pH, and high temperatures.
Produces many virulence factors.
S. aureus morphology

STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
3
Blood agar plate, S. aureus
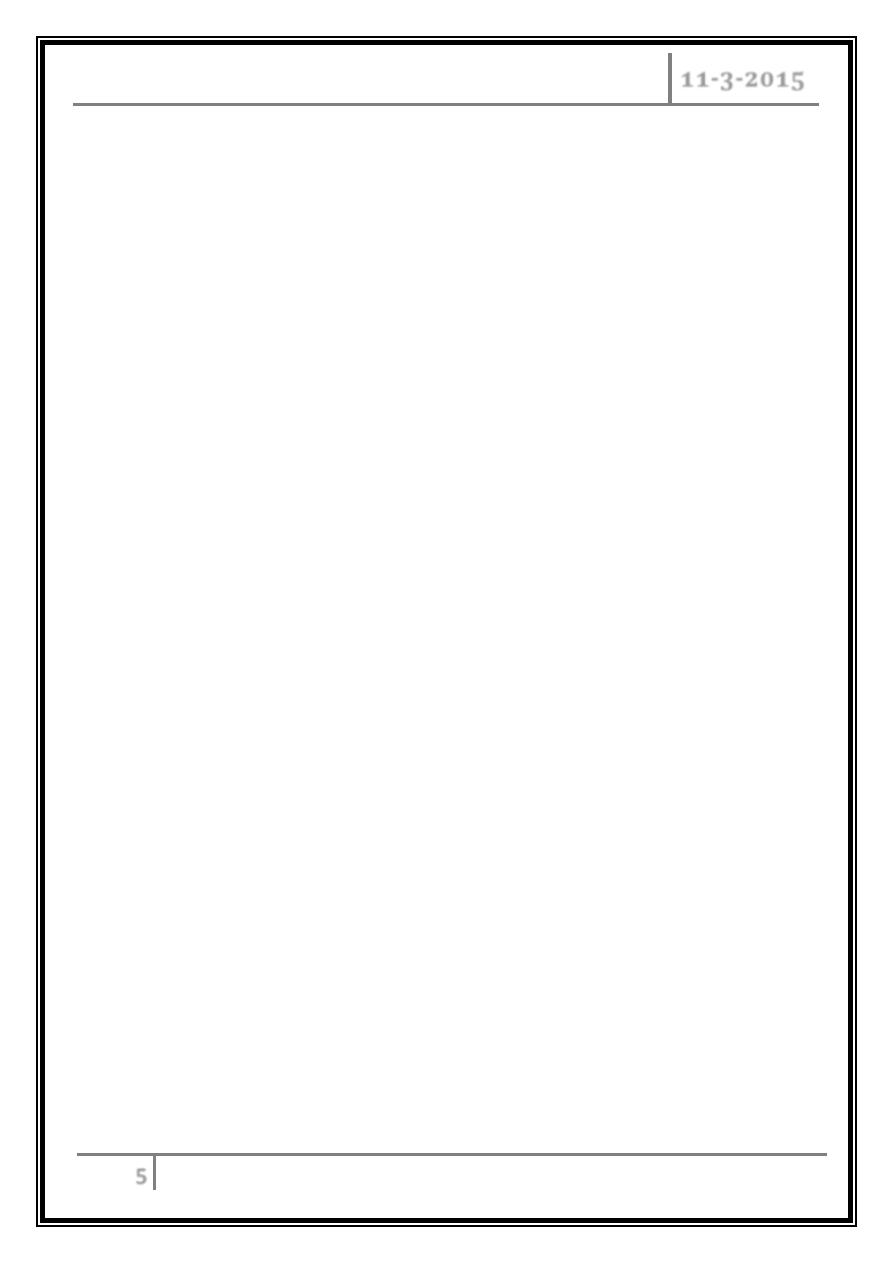
Virulence factors of S. aureus
Enzymes:
Coagulase – produced by 97% of human isolates; diagnostic.
Hyaluronidase – digests connective tissue.
Staphylokinase – digests blood clots.
DNase – digests DNA.
Lipases – enhances colonization on skin.
Penicillinase – inactivates penicillin.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
4
Toxins:
Hemolysins (α, β, γ, δ) – lyse RBC.
Leukocidin – lyses neutrophils.
Enterotoxin – induces GIT distress.
Exfoliative toxin – separates the epidermis from the dermis.
Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST) – induces fever, vomiting, shock,
systemic organ damage.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
5
Pathogenesis
Carriage rate is 20-60%.
Mostly in anterior nares, skin, nasopharynx, and intestine.
Predisposition to infection:
Poor hygiene and nutrition, tissue injury, preexisting primary infection,
diabetes, immunodeficiency.
Increase in community acquired methicillin resistance - MRSA.
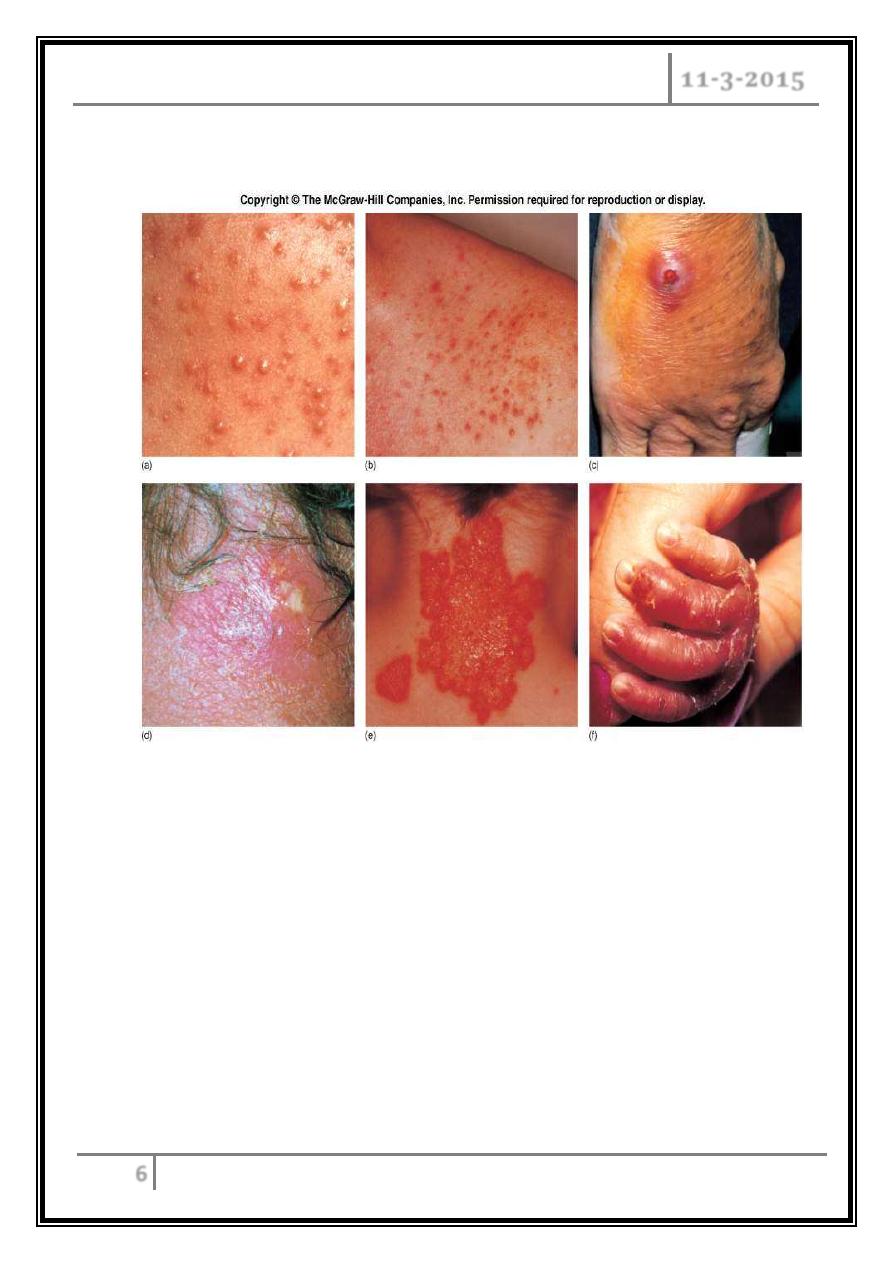
Staphylococcal Disease
Localized cutaneous infections
: invade skin through wounds, follicles, or
glands:
o Folliculitis – superficial inflammation of hair follicle; usually resolved with
no complications but can progress.
o Furuncle – boil; inflammation of hair follicle or sebaceous gland progresses
into abscess or pustule.
o Carbuncle – larger and deeper lesion created by aggregation and
interconnection of a cluster of furuncles.
o Impetigo – bubble-like swellings that can break and peel away; most
common in newborns.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
6
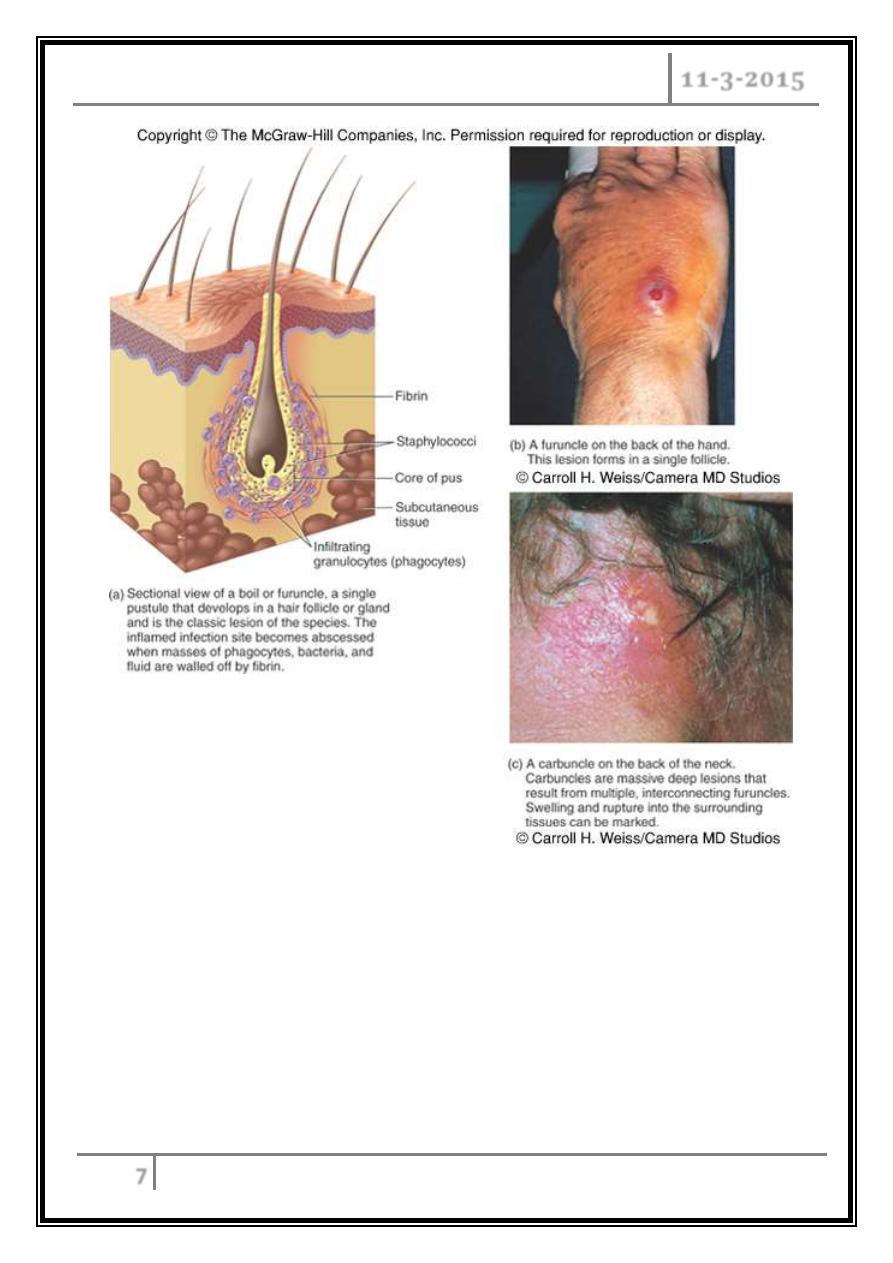
Furuncle
Deep folliculitis (infected hair follicle)
Staph. Impetigo
Superficial
folliculitis
Carbuncle
Multiple
abscesses
Around
many hair
follicles
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
7
Cutaneous lesions of S. aureus
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
8
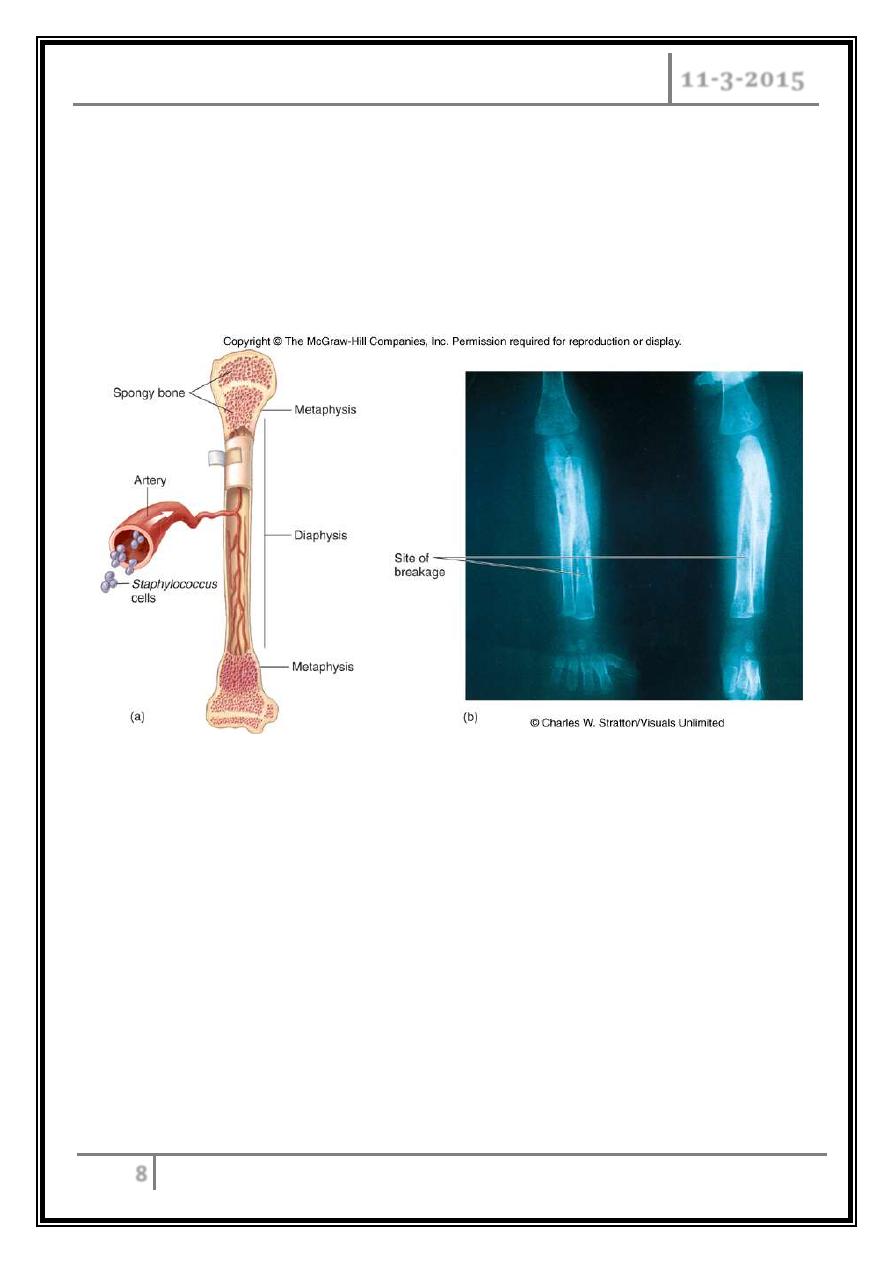
Systemic infections:
o Osteomyelitis – infection is established in the metaphysis; abscess forms.
o Bacteremia – primary origin is bacteria from another infected site or
medical devices; endocarditis possible.
Staphylococcal osteomyelitis in a long bone
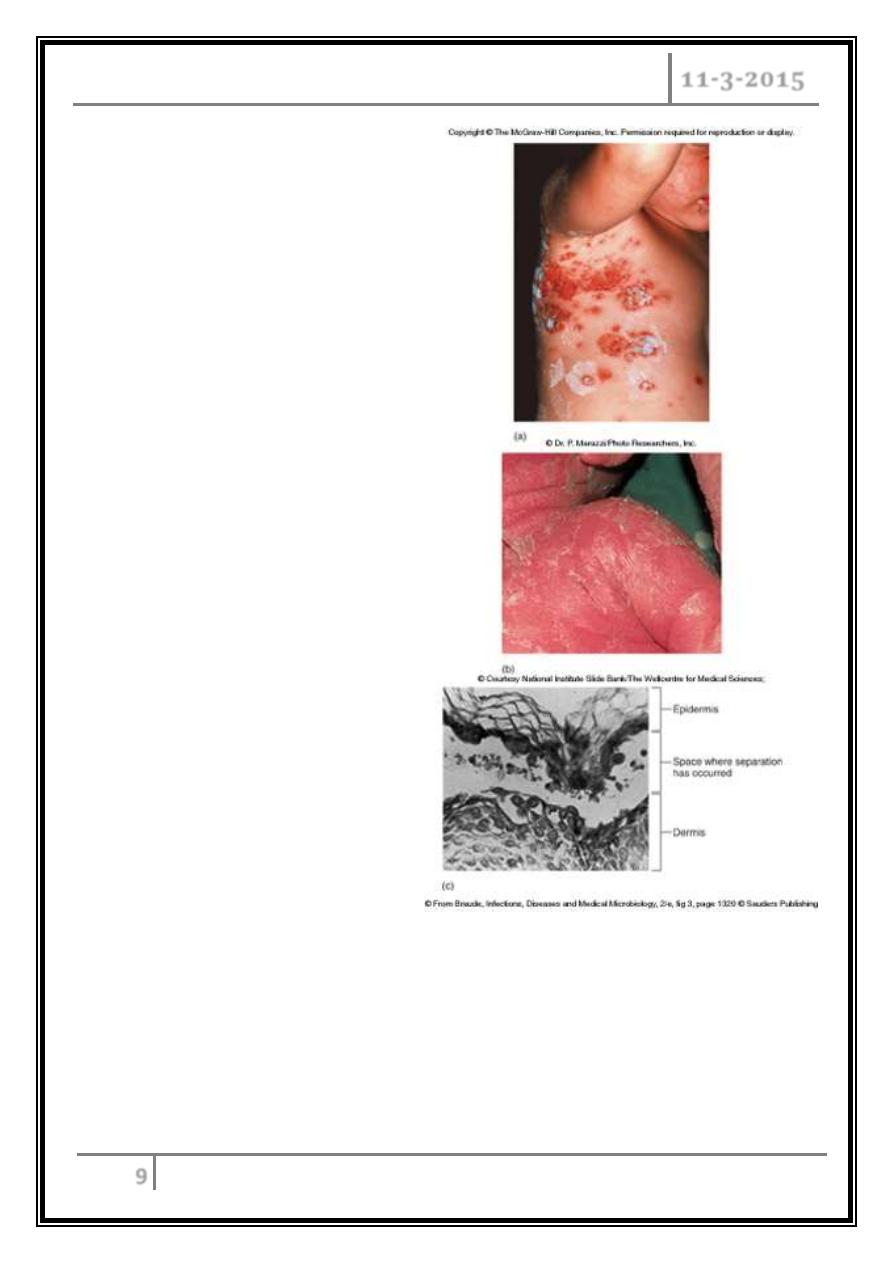
Toxigenic disease
o Food intoxication – ingestion of heat stable enterotoxins.
o Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome – toxin induces bright red flush,
blisters, then desquamation of the epidermis.
o Toxic shock syndrome – shock and organ failure.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
9
Effects of
staphylococcal
toxins on skin
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
10
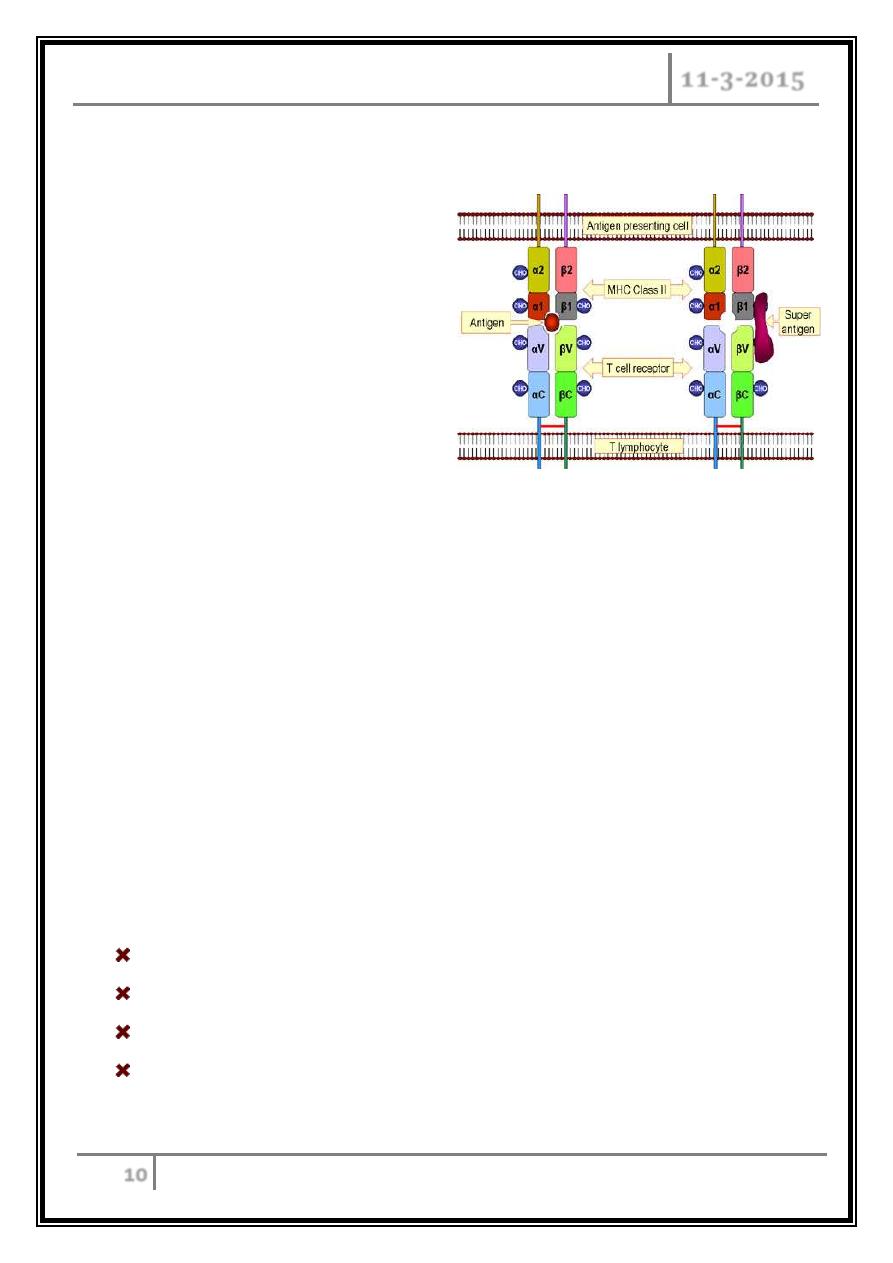
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin
Superantigen.
Non-specific binding of toxin to
receptors triggers excessive
immune response.
TSS Symptoms
8-12 h post infection.
Fever.
Susceptibility to endotoxins.
Hypotension.
Diarrhea.
Multiple organ system failure.
Erythroderma (rash).
TSS Treatment
Clean any obvious wounds and remove any foreign bodies.
Monitor and manage all other symptoms, e.g. administer I.V. fluids
Flucloxacillin or vancomycin I.V.
For severe cases, administer methylprednisone, a corticosteriod inhibitor of
TNF-a synthesis.
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
11
Identification of Staphylococcus in Samples
Frequently isolated from pus, tissue exudates, sputum, urine, and blood.
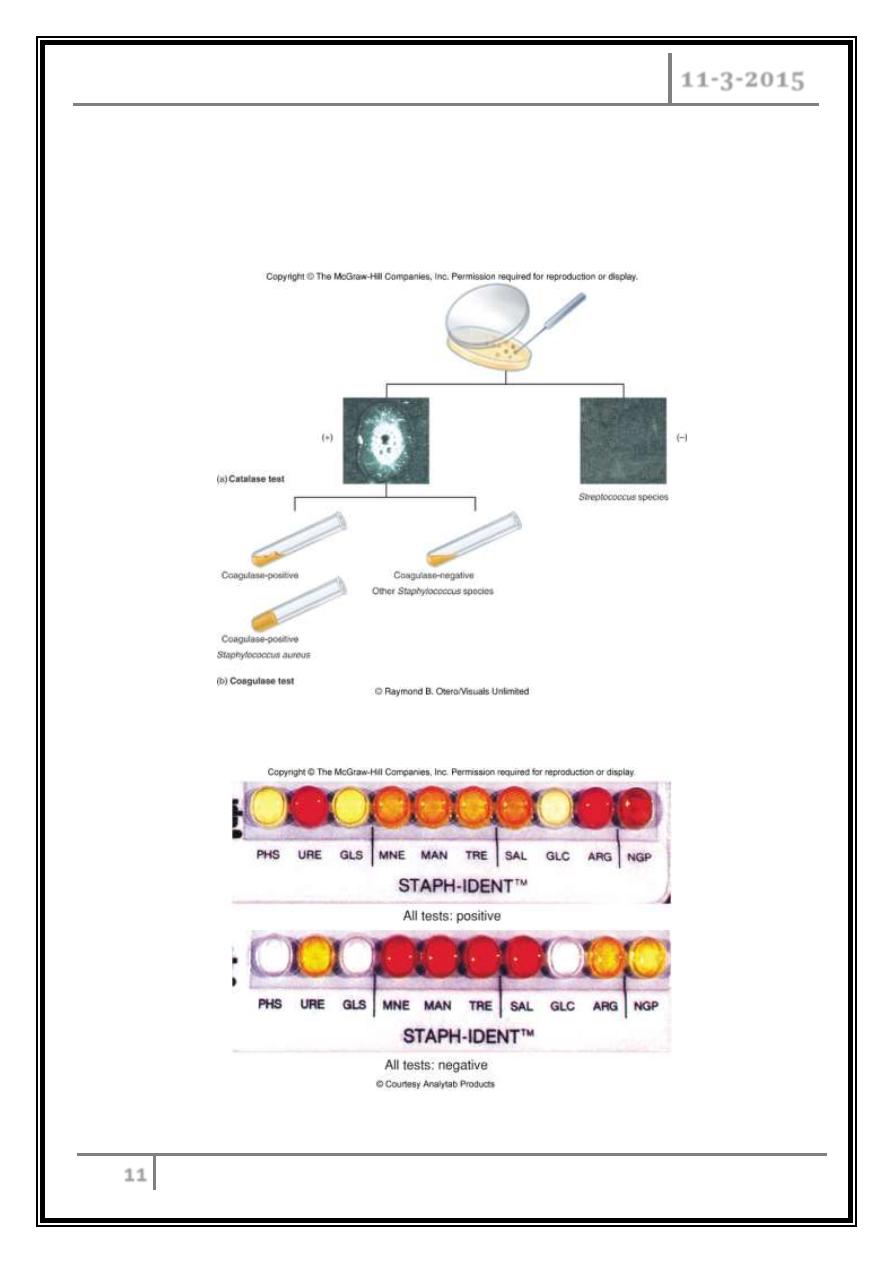
Cultivation, catalase, biochemical testing, coagulase.
Catalase test
Test system to identify Staphylococcus
STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
12
Clinical Concerns and Treatment
95% have penicillinase and are resistant to penicillin and ampicillin.
MRSA – methicillin-resistant S. aureus – carry multiple-resistance.
Some strains have resistance to all major drug groups except vancomycin.
Prevention of Staphylococcal Infections
o Universal precautions by healthcare providers to prevent nosocomial
infections.
o Hygiene and cleansing.
… The end …

STAPHYLOCOCCI Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
13
