
Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
Lec. 3
Cholera
Wed
11 / 3 / 2015
2014 – 2015
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ

CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
1
IDENTIFICATION
An acute bacterial enteric disease characterized in its severe form by:
Sudden onset, profuse painless watery stool (rice-water stool).
Nausea and profuse vomiting early in the course of illness.
In untreated cases, rapid dehydration, acidosis, circulatory collapse,
hypoglycemia in children, and renal failure can rapidly lead to death.
Standard CASE DEFINITION by
WHO (world health organization), CDC (center of
disease control and prevention)
DISEASE UNKNOWN IN AN AREA:
Severe dehydration or death from acute watery diarrhoea in a patient aged 5 or
more.

CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
2
ENDEMIC CHOLERA:
Acute watery diarrhoea with or without vomiting in a patient aged 5 or more.
EPIDEMIC CHOLERA:
Acute watery diarrhoea with or without vomiting in any patient.
Single flagellum
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
3
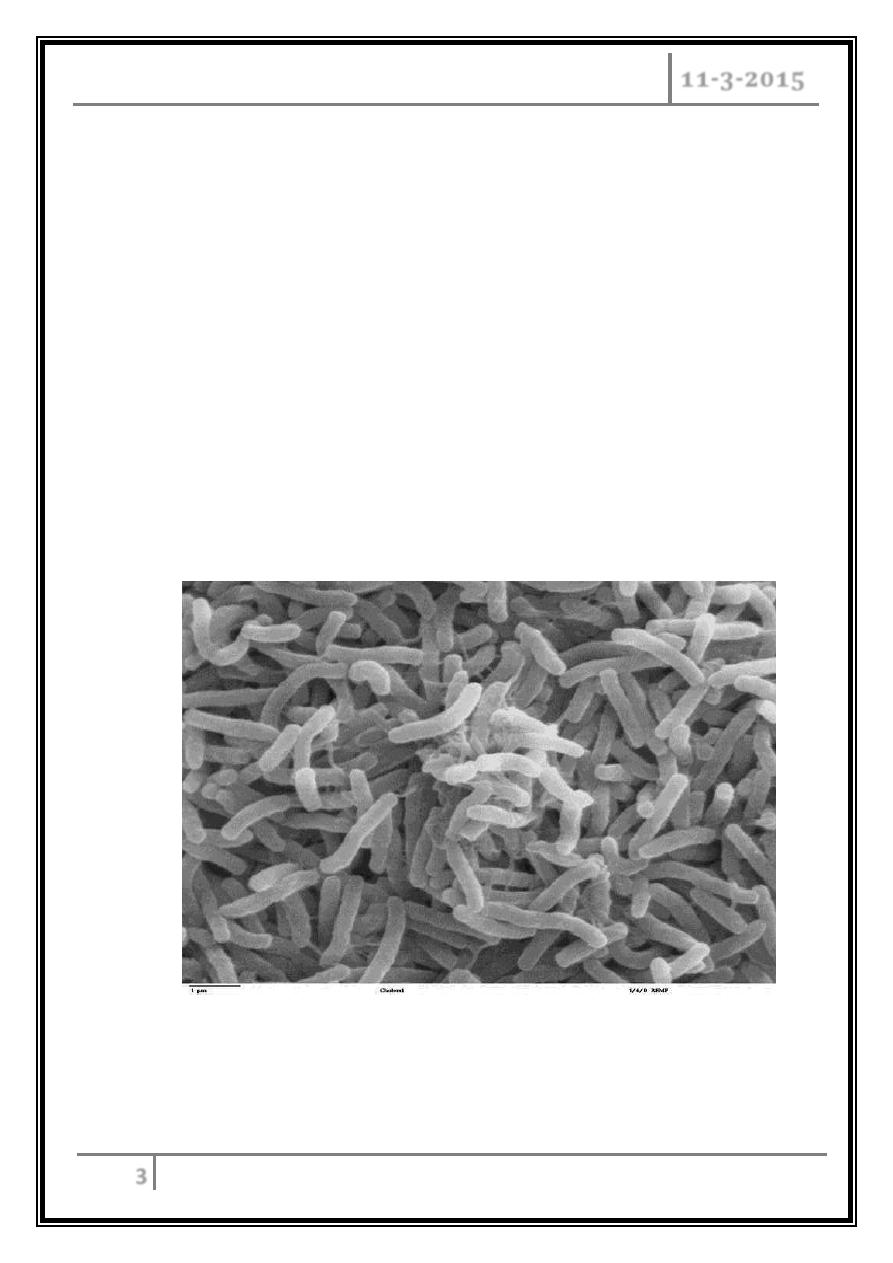
Vibrio cholerae
Gram-negative, comma-shaped bacterium.
V. cholerae is a facultative anaerobic organism and has a flagellum at one cell
pole.
During infection, V. cholerae secretes cholera toxin, a protein causes profuse,
Two sero-groups, O1 and O139, cause outbreaks of cholera.
O1 causes the majority of outbreaks, while O139 – first identified in Bangladesh
in 1992 – is confined to South-East Asia.
Scanning electron microscope image of Vibrio cholerae
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
4
CHOLERA SYNDROM
ENZYMATIC DIARRHOEA
Vibrionaceae Family: four genera.
Cholera: 139 strains.
01 of Classical type & ELTOR biological type are the causes. Now O139 is
blamed to cause the 8
th
pandemic.
Some other causes of a brief enzymatic diarrhoea are: NAG, NCV & NVC.
- NAG (non-agglutinable vibrios): Short sporadic diarrhoea by non-O1
vibrios especially V. parahemolyticus group 6.
- NCV (non-cholera vibrios): Diarrhoea by Aeromonas, Plasiomonas
genera.
- NVC (non-vibrio cholera): Other enzymatic diarrhoea by non-vibrio
microorganisms e.g. E.coli.
NB:
Vibrios of non-O1 group might cause septicemia, wound infection, otitis
media…etc.
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
5
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
6
CHOLERA: CLINICAL
Subclinical / A symptomatic / mild: common
Florid causes Loss water & electrolytes > One liter/hour.
I.P = 1 - 5 days usually 12 – 48 hours.
Abrupt onset of painless, odourless, effortless diarrhoea of up to 40 bowel
motion/day, followed by profuse vomiting.
Early signs of collapse.
Loss of skin turger, washer – woman hand.
Dehydration 12% is fatal.
Major cause of death in adults: acute renal failure, in children: hypokalemia.

CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
7
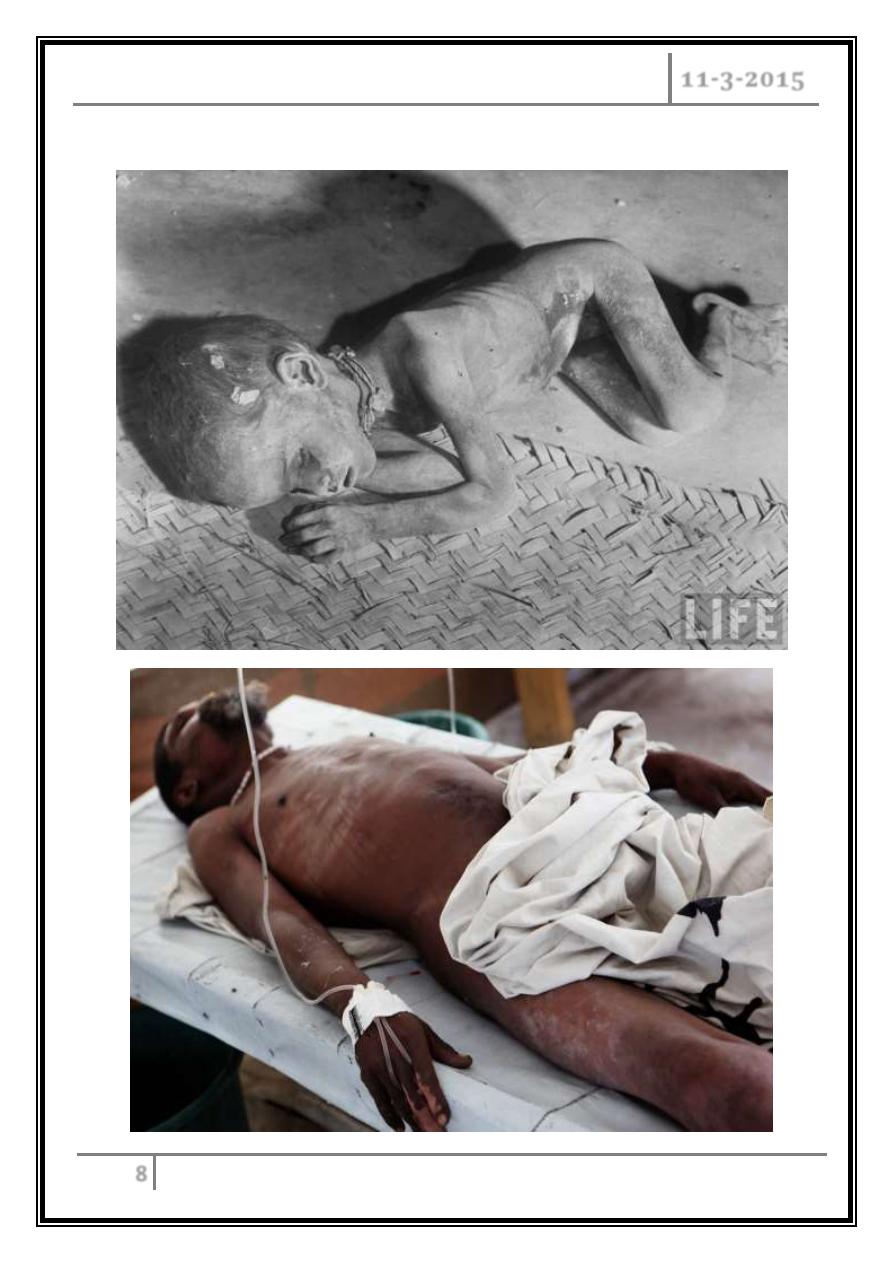
Diarrhoea "rice water" in nature and may have a fishy odor.
An untreated person with cholera may produce 10 to 20 liters (3 to 5 US gal) of
diarrhoea a day with fatal results.
For every symptomatic person, 3 to 100 people get the infection but remain
asymptomatic.
Cholera has been nicknamed the "blue death" as victim's skin turns bluish-gray
from extreme loss of fluids.
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
8
CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
9

CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
10
FACTORS FAVORING ERADICATION
o V. cholerae is a fragile microorganism.
o Large doses are required for infection, 1 billion m.o. Vs 1 million for S. typhi &
100 m.o. for shigellosis.
o No bacteremia.
o Lack of person-person transmission.
o Short incubation period.
o Impact of non-specific control measures.
o Public motivation.

CHOLERA Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
11-3-2015
11
FACTORS IMPEDING ERADICATION
Persistence of V.cholerae in the aquatic environment.
Increase in the population density.
Non-existence of an adequate vaccine.
Limited protection from natural immune system.
Failure of other traditional public- health measures e.g. Chemoprophylaxis,
quarantine, trade embargo.
Rapid development of microbial resistance and lack of effective treatment.
Flexibility & variety of microbial toxigenic strains.
… the end …
