Sexuality and Gender
Maha S YounisProfessor of Psychiatry
Gender
Gender- the psychological aspects of being male or female.Gender roles - the culture’s expectations for masculine or feminine behavior, including attitudes, actions, and personality traits associated with being male or female in that culture.
Gender typing - the process of acquiring gender role characteristics.
Gender identity - the individual’s sense of being male or female.
LO 10.2 Gender
Menu
Biology and Learning Influences on Gender
Biological influences - hormones and chromosomesEnvironmental influences - parenting, surroundings, and culture on the formation of gender identity.
LO 10.3 Influence of biology and learning on gender development
Menu
Gender Roles
Social learning theory - gender identity is formed through reinforcement of appropriate gender behavior as well as imitation of gender models.Gender schema theory - theory of gender identity acquisition in which a child develops a mental pattern, or schema, for being male or female and then organizes observed and learned behavior around that schema.
LO 10.4 Theories on gender role learning
Menu
Gender Stereotyping
Stereotype - a concept held about a person or group of people that is based on superficial, irrelevant characteristics.Gender stereotype - a concept held about a person or group of people that is based on being male or female.
Sexism - prejudice about males and/or females leading to unequal treatment.
Benevolent sexism - acceptance of positive stereotypes of males and females that leads to unequal treatment.
LO 10.5 Gender stereotyping
Menu
Androgyny
Androgyny - characteristic of possessing the most positive personality characteristics of males and females regardless of actual sex.LO 10.6 Androgyny
Menu
Other Male and Female Differences
Cognitive differences - male advantage in mathematical and spatial skills and a female superiority in verbal skills (decreasing differences).
Emotional expression - males tend to talk with each other in a “report” style, whereas females tend to talk to each other in a “relate” style.
LO 10.7 Gender differences in thinking, social behavior, and personality
Menu
Intersexed Infants
Hermaphroditism - the condition of possessing both male and female sexual organs.Intersex - alternate term for hermaphroditism.
Intersexed, intersexual - a person who possesses ambiguous sexual organs, making it difficult to determine actual sex from a visual inspection at birth.
LO 10.8 Controversy of treatment of intersexed infants
Menu
Stages of Human Sexual Response
Excitement – beginning of sexual arousal.Plateau – physical changes beginning in first stage continue.
Orgasm - a series of rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the vaginal walls or the penis, also the third and shortest phase of sexual response.
Seminal fluid - fluid released from the penis at orgasm that contains the sperm.
LO 10.9 Bodies of men and women during sexual intercourse
Menu
Stages of Human Sexual Response
Resolution - the final phase of the sexual response in which the body is returned to a normal state.
Refractory period - time period in males just after orgasm in which the male cannot become aroused or achieve erection.
LO 10.9 Bodies of men and women during sexual intercourse
MenuMasters and Johnson Study
Used volunteers, some of whom were prostitutes, and both observed and measured their physiological responses during all phases of sexual intercourse.LO 10.10 Masters and Johnson and the human sexual response
MenuKinsey Studies
Series of sexual behavior surveys in the late 1940s and early 1950sRevealed some highly controversial findings about the kinds of sexual behavior common among people in the United States, including:
Homosexuality
Premarital sex
Extramarital sex
LO 10.11 Kinsey’s study of human sexual behavior
Menu
Sexual Orientation
Sexual orientation - a person’s sexual attraction preference for members of a particular sex.Heterosexual - person attracted to the opposite sex.
Homosexual - person attracted to the same sex.
Bisexual - person attracted to both men and women.
LO 10.13 Sexual orientations and how they develop
Menu
Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction - a problem in sexual functioning.Organic or stress-induced dysfunction - sexual problem caused by physical disorder or psychological stress.
Hypoactive sexual desire, sexual aversion, female sexual arousal disorder, male erectile disorder, male orgasmic disorder, female orgasmic disorder, premature ejaculation, vaginismus, and dyspareunia.
LO 10.14 Sexual dysfunctions causes by physical problems or stress
MenuDisorder of sexual perversionsparaphilia's
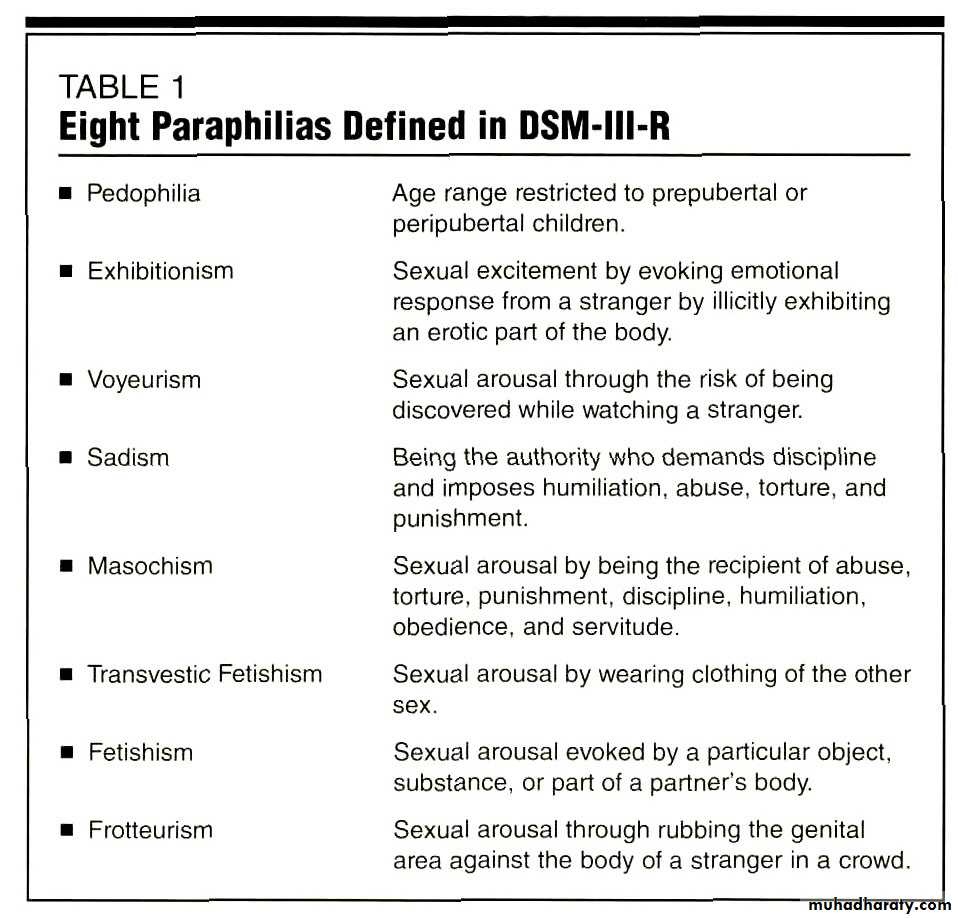
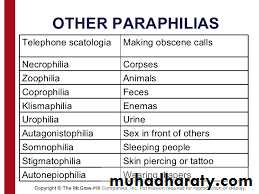
Paraphilias
Paraphilia - a sexual disorder in which the person’s preferred method of sexual arousal and fulfillment is through sexual behavior that is unusual or socially unacceptableMost common types.
Pedophilia - deriving sexual arousal and pleasure from touching or having sexual relations with prepubescent (nonsexually mature) children or fantasizing about such contact.
Pedophile - a person who has recurring sexual thoughts, fantasies, or engages in sexual actions toward prepubescent (nonsexually mature) children.
LO 10.15 Sexual dysfunctions called paraphilias
Menu