4th stage
Surgery(large intestine)Lec-1
Dr.Layth Q
4/18/2016
INFLAMATORY BOWEL DISEASEThe term reserved for idiopathic intestinal inflammation as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
ULCERATIVE COLITIS
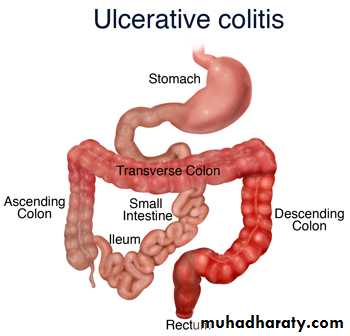
-It is disease of rectum and colon with extra intestinal manifestation .-The incidence is 10per 100000.in UK
Aetiology
The cause is unknown
Genetic contribution as 10-20-per cent of patients have first degree relative with inflammatory bowel disease .
UC more common in Caucasian than Afro-Caribbean orAsian population.
pathology
All cases start at rectum and extends proximally in continuity
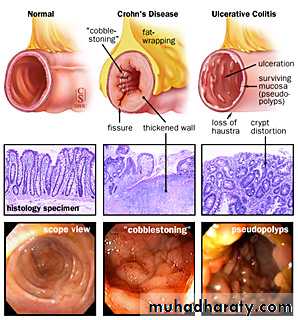
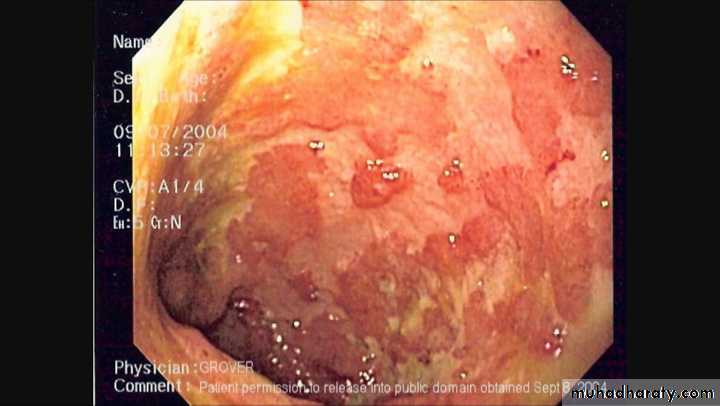
Colonic inflammation is diffuse,confluent and superficial, primarily affecting the mucosa and sub mucosa.Chronic mucosal ulceration is associated with formation of granulation tissue and regeneration ,leading to a polyp like pseudopolyposis,
Structuring in UC is very unusual and urgent assessment because of the possibility of coexisting carcinoma.A small proportion of patients with colonic dysplasia may develop irregular mucosal swelling (dysplasia-associated lesions,DALMs),highly predictive of coexisting of carcinoma.
Histological examination reveals inflammatory cells in lamina propria,walls of crypts,and there are crypt abscesses.There is depletion of goblet cell mucin .
With time,precancerous changes can develop (dysplasia).It increases with time and ranging from 2-18-per cent at 30 years Dysplasia classified into low or high grade dysplasia.High grade dysplasia is absolute indication of colectomy as 40 per cent of colectomy specimens of high grade have evidence of colorectal cancer.
Symptoms
Depends on extent of the disease and the presence of complications .
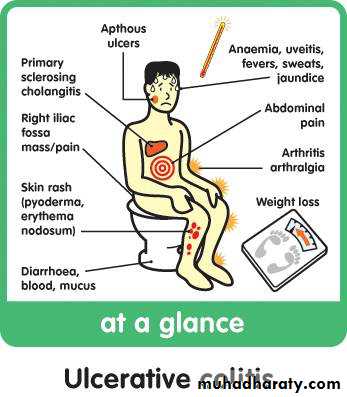
If confined to rectum usually no systemic upset and the extra alimentary manifestation are rare. The main symptoms will be rectal bleeding , and mucous discharge.Colitis always associated with bloody diarrhoea and urgency.pain is unusual. The more extensive the disease the more likely extra intestinal manifestation are to occur
Extensive colitis associated with systemic illness like, malaise,loss of appetite and fever .Bloody diarrhoea resulting in anaemia and hypo proteinemia and electrolyte disturbance .Approximately30 percent extending to sigmoid colon and spread to splenic flexure
Complications of ulcerative colitis
Acute
Toxic dilatation
Perforation
Hemorrhage
Chronic
Cancer
Extra- alimentary manefestations ,like skin lesions,eye problems and liver dis.
Classifications of colitiis severity.
Bowel motion and presence of illness.Mild: four stools with or without bleeding daily .
Moderate disease : more than four stools with few systematic illness,abdominal pain,inflammatory markers,including ESR and C- reactive protein ( CRP) are often raised .
Severe disease : more than six bloody stools,fever,tachycardia,anaemia, and raised inflammatory markers.Hypoalbuminaemia is common .
Fulminant disease: more than ten bowel movements daily,fever,tachycardia bleeding ,Hypoalbuminaemia,abdominal tenderness and distension,blood transfusion requirement ,progressive colonic dilatation ( toxic megacolon) . This is a significant finding and indication for immediate surgery if colonic perforation is to be avoided.
Extra intestinal manefestations:
Arthritis,sacroiliitis,ankylosing spondylitis more common than general population and associated with HLA-B27Sclerosing cholangitis is associated with UC can progress to cirrhosis and heptocellular failure and at more great risk of development of large bowel cancer
Skin lesions: erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum.
Eyes: affected with uveitis and episcleritis
Cancer risk in colitis
Risk increases with duration.Ten years from the diagnosis is around 1 percent.Twenty years increases to 10-15/. . Twenty per cent at 30years.Carcinoma is more likely to occur if the whole colon is involved or if the disease started early in life .Colonoscopy with multiple biopsies is advised to detect dysplasia .
Investigations:
Endoscopy and biopsy by sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy.
Radiology plain film may be valuable in toxic megacolon.Barium enema has been replaced by computed tomography. CT finding may show thickening of colonic wall .
Bacteriology:stool send for microbiology to exclude infective causes.
treatment
-Principles of management of UC:
Many patients maintained for years on medical therapy.
Toxic dilatation suspected with sever abdominal pain .
Colitis patients at risk of cancer especially pan colitis.
Multidisciplinary approach,gastroenterologist,nurses,as well as surgeon.
-Medical treatment : therapy based on anti inflammatory agents .5- aminosalicyclic acid and corticosteroids either topically or systemically.The immunosuppressive drugs azathioprine and cyclosporine maintain remission as steroid sparing agents.More recently monoclonal antibodies,(infliximab)
-Acute colitis severe type require hospitalisation in addition to steroids ,medical therapy ,supportive treatment ,fluid and electrolyte balance. The multidisciplinary approach,lastly to surgical option.
-indication for surgery:
Fulminating disease failing to respond to medical therapy
Chronic disease with anaemia,frequent stools,urgency and tenesmus
Steroid dependant
Inability of the patient to tolerate medical therapy.
Neoplastic change
Extra intestinal manefestations
Rarely,severe haemorrhage or stenosis causing obstruction.
-Operative treatment for UC:
Emergency---is subtotal colectomy and end ileostomy. the recto sigmoid is left
Long and brought as mucous fistula or closed just beneath the skin
Elective surgery----- the indications for it include:
Failure of medical treatment/ steroid dependance.
Growth retardation
Extra intestinal disease
Malignancy
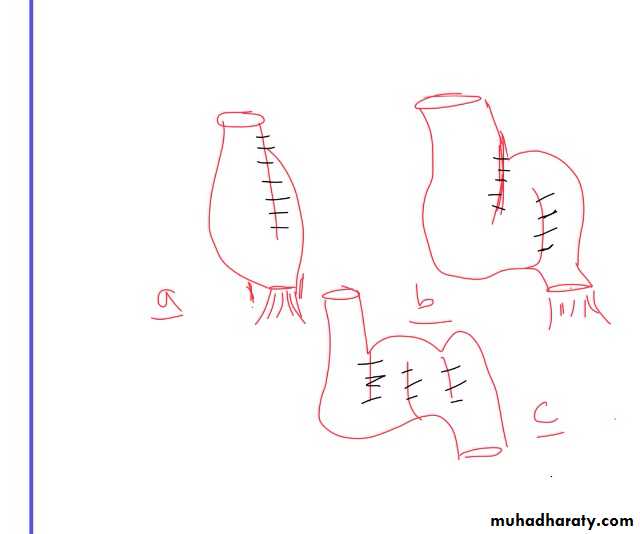
-In elective setting --->FOUR operations:
.subtotal colectomy and ileostomy
.proctocolectomy and permanent ileostomy.
.restorative proctocolectomy with ileoanal pouch.
.subtotal colectomy and ileorectal anastamosis.
INFECTIONS OF SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE
Yersinia., amebiasis, salmonella, typhoid and paratyphoid, tuberculosis, actinomycosis, and clostridium difficile.