
Brucella
Obligate intracellular parasite of animal and human Brucella
spp. are causative agent of
brucellosis
,
malta fever
or
undulant
fever
.
4 major human pathogens and their animal reservoirs:-
-B.melitensis
(goats & sheep).
-B.abortus
(cattle).
-B.suis
(pigs).
-B.canis
(dogs).
General characters:
-Gram negative rods, non-motile, non spore–forming & some
are capsulated.
-Brucella are obligate aerobes, grow on blood agar and enriched
media (trypticase-soy) ∕ 2-5 days showing small, convex
colonies. Virulent strains give typical smooth colonies which
tend to change to rough form if become avirulent. Serum of
susceptible animals contain globulin and a lipoprotein that
suppress growth of a virulent type and favor the growth of
virulent one.

-Only B.abortus requires 5-10% Co
2
for growth, others grow in
air and all require the presence of basic pepsin dye except
B.canis.
-Brucella utilize CHO with no acid or gas, reduce nitrate,
catalase & oxidase positive and H
2
S is produced by many
strains. They are sensitive to heat and killed by milk
pasteurization for 10 min at 60
o
C and by acidity of sour milk,
also killed by exposure to 1% phenol for 15 min.
Antigenic structure:
-The 2 lipopolysaccharide antigens A&M are present in
different proportions in the 4 spp.
-Superficial L Ag also present that resembles the Vi Ag of
Salmonellae.
Pathogenesis:
The organisms enter the body either by ingestion of
contaminated milk products or through direct contact of mucus
membrane or abraded skin in an occupational setting such as
farmers.
The organisms → localize in RES (L.N, liver, spleen and bone
marrow) many killed by macrophages, but some survive within
the cells (intracellular) protected from Abs. Granulomas may
appear which can progress to focal abscesses and caseation.
Osteomylitis or cholecystitis also occasionally occur.

-Brucellae
which
infect
human
have
differences
in
pathogenicity:
*B.abortus →mild disease without suppurative complications
and non caseating granuloma.
*B.canis →mild disease.
*B.suis →chronic disease with suppurative and caseating
granulomas.
*B.melitensis → more acute and sever disease.
- The mechanism of pathogenesis in not well defined except the
role of endotoxin in active brucellosis.
Clinical findings:
After incubation period (1-6) weeks ,non specific insidious
symptoms occur as malaise, fever, weakness, aches and sweats,
fever usually undulating (rises up then fall during night)
accompanied by drenching sweat. Enlarged lymph node, liver
and spleen are frequently found.
Following the initial infection, a chronic stage may develop,
characterized by weakness, aches, low grade fever and some
psychoneurotic symptoms.The diagnosis of chronic brucellosis
is difficult.
Laboratory diagnosis:
A-specimens include:
-Blood for blood culture during acute phase
-Biopsy material for culture of illness
-Serum for Antibody detection
B-Culture :
on trypticase – soy broth and sub culture every 3-5
days on solid media (under aerobic and 10% CO
2
), keep blood
for 4wks before being discard as negative. The colonies appear
as small, transparent and non hemolytic, Gram’s stain showing
the typical coccobacilli. Biochemically they are (oxidase
positive & urease positive). The isolated brucellae typed by H
2
S
production and agglutination by specific antisera.
C-Serology
1-Agglutination test (Rose Bengal)
For detection of IgG Ab, serial
tube dilution used, IgG titers>1:80
indicate active infection.
This test can give fales positive
because of cross reaction with other infection and fales negative
because of the presence of blocking Abs which can be
overcomed by:
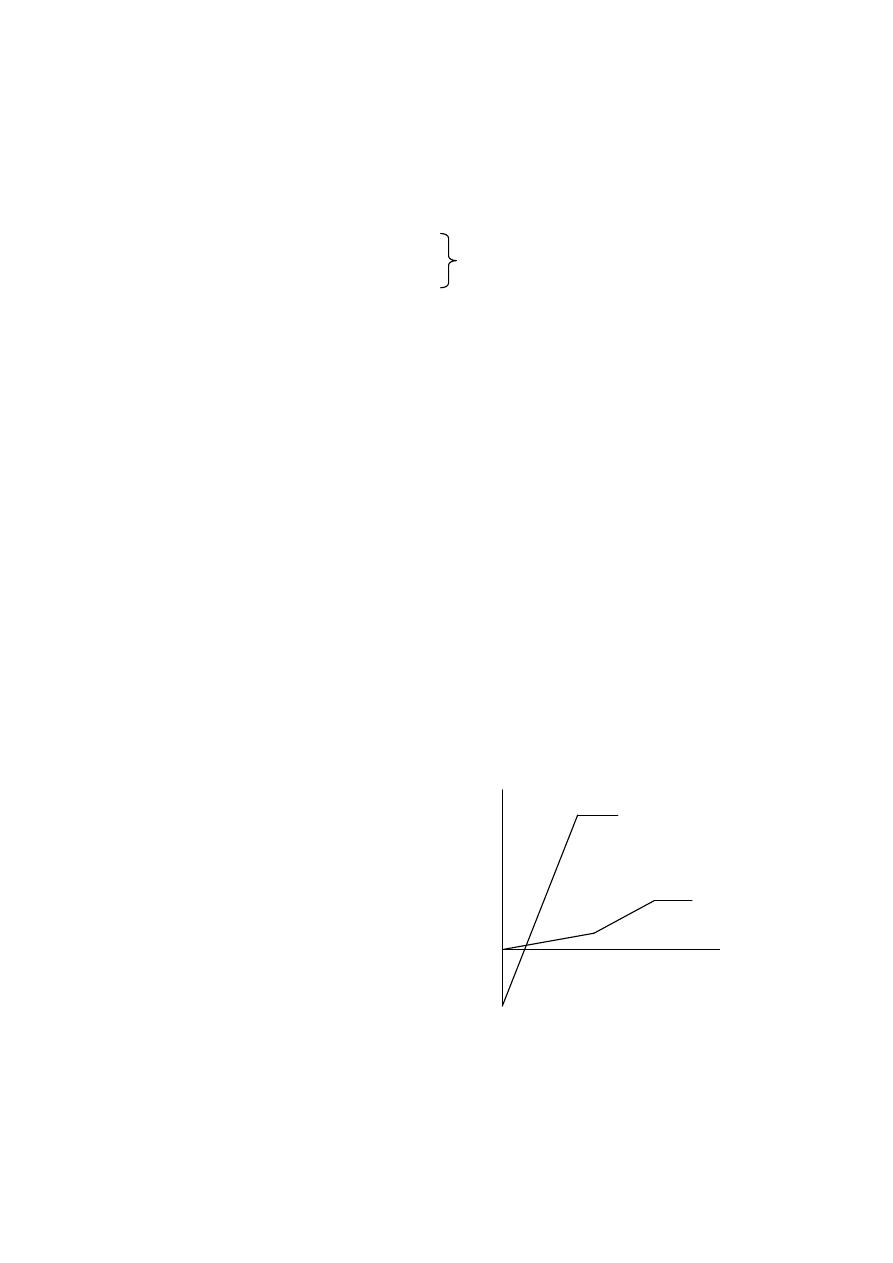
3 wk
IgM
6-8WK
3WK
IgG

a. 2- Mercaptoethanol test – the addition of 2me will destroy
IgM and leaves IgG for, agglutination reaction.
b. Blocking Ab (IgA) which appear during subacute stage and
remain for years causing a negative test in low serum dilution
,so increase
dilution and using coombs
antiglobulin
method(patient serum + Brucella antigen +Anti human globulin)
2-ELISA & EFAT
D. Brucella skin test:
Intra dermal injection of protein extract→ erythema, edema and
induration develop within 24hrs ← unreliable, & rarely used.
Treatment:
Because of Intracellular location ←for best result treatment
must be prolonged with combination of streptomycin &
tetracycline.
