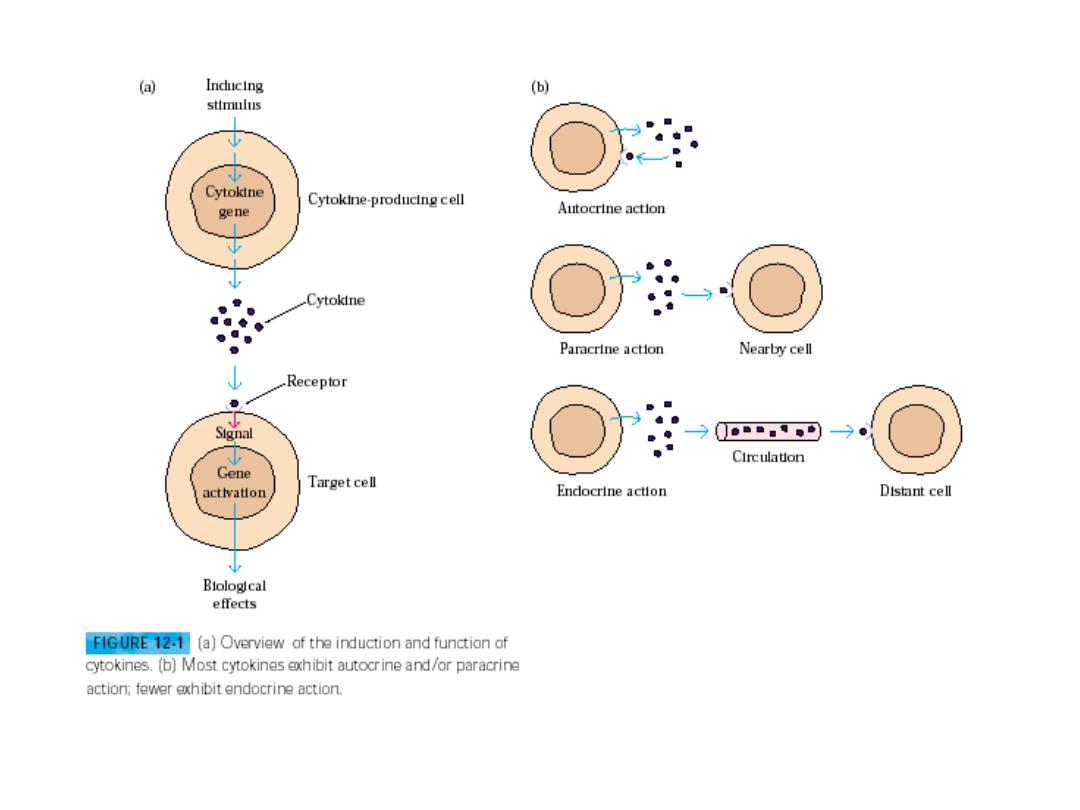
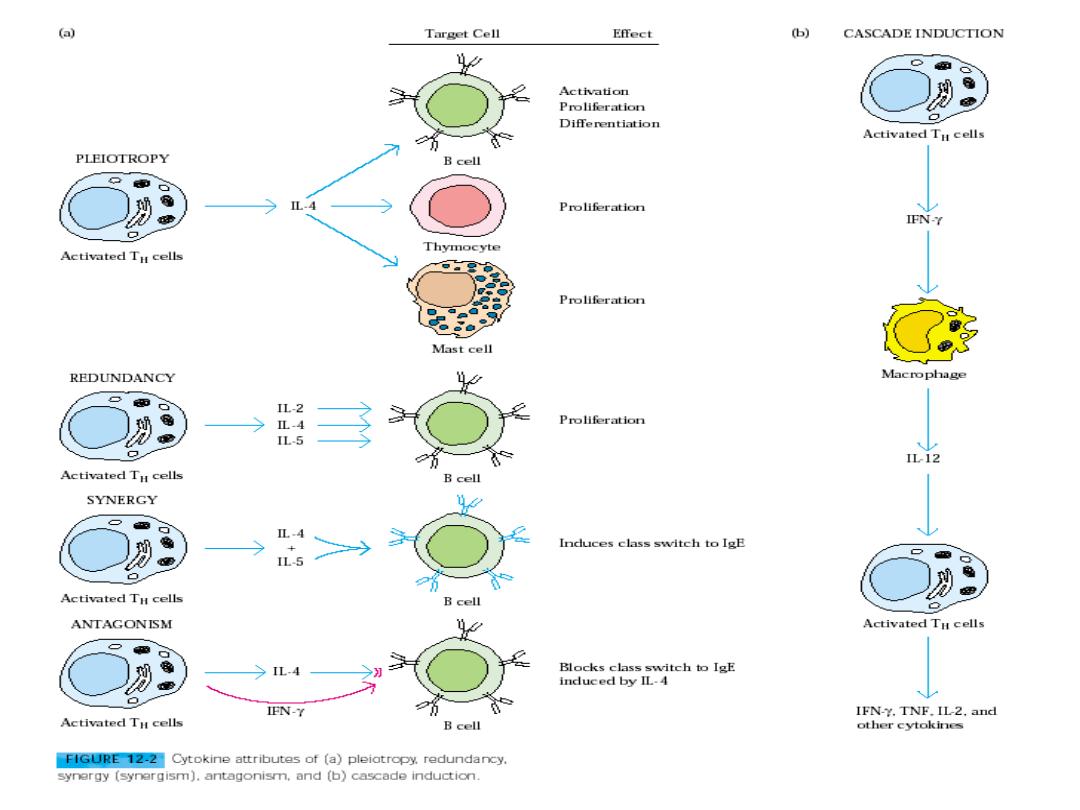
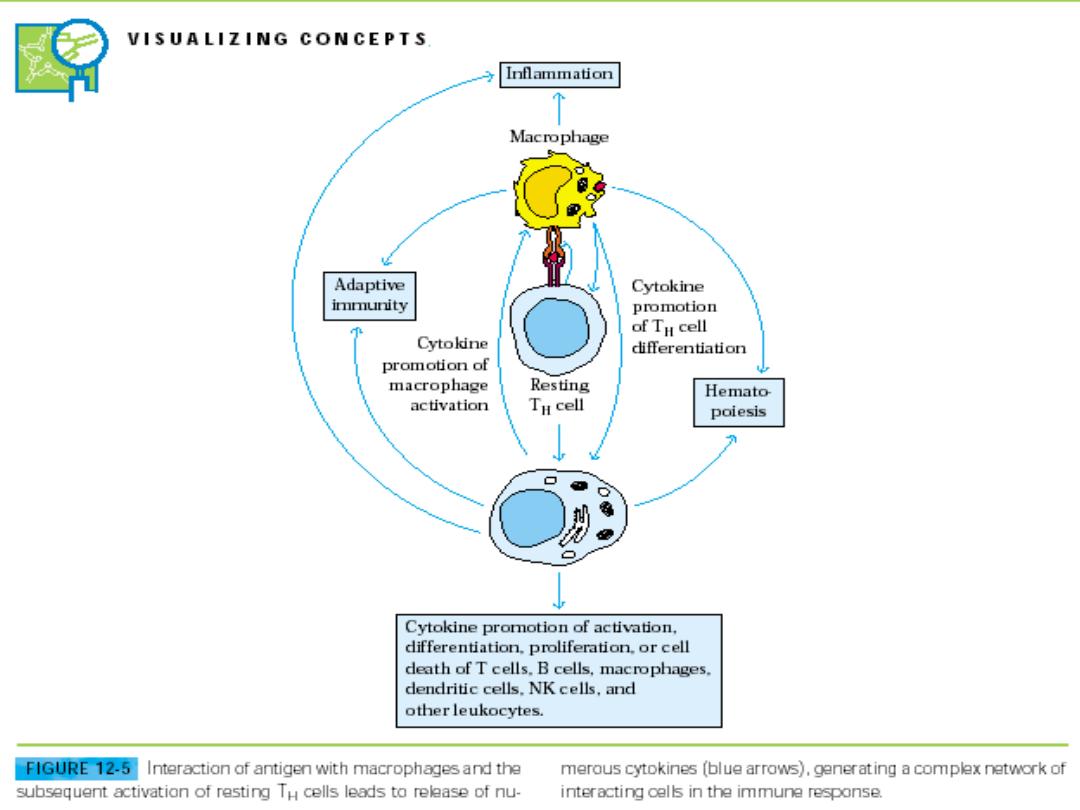
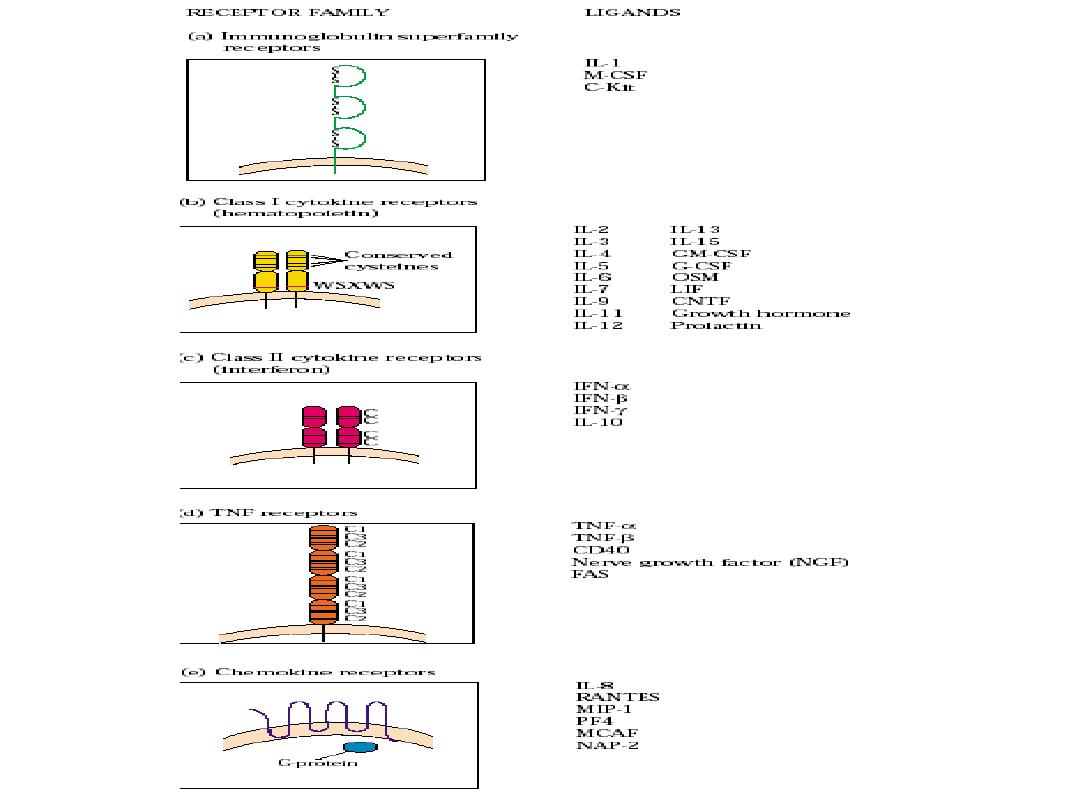
Immunity to infectious disease
ا
.
م
.
د وفاق محمود علي الوتار

Infection could be:
• Viral
• Bacterial
•
• Parasitic
•
• Fungal

Types of immune response:
• Non-specific immune response
• Mechanical: as Skin ,saliva ,tears, ciliary
movement, mucus ,
• Cellular :NK, macrophages ,complement
lysis,commensals
• Specific immune response.

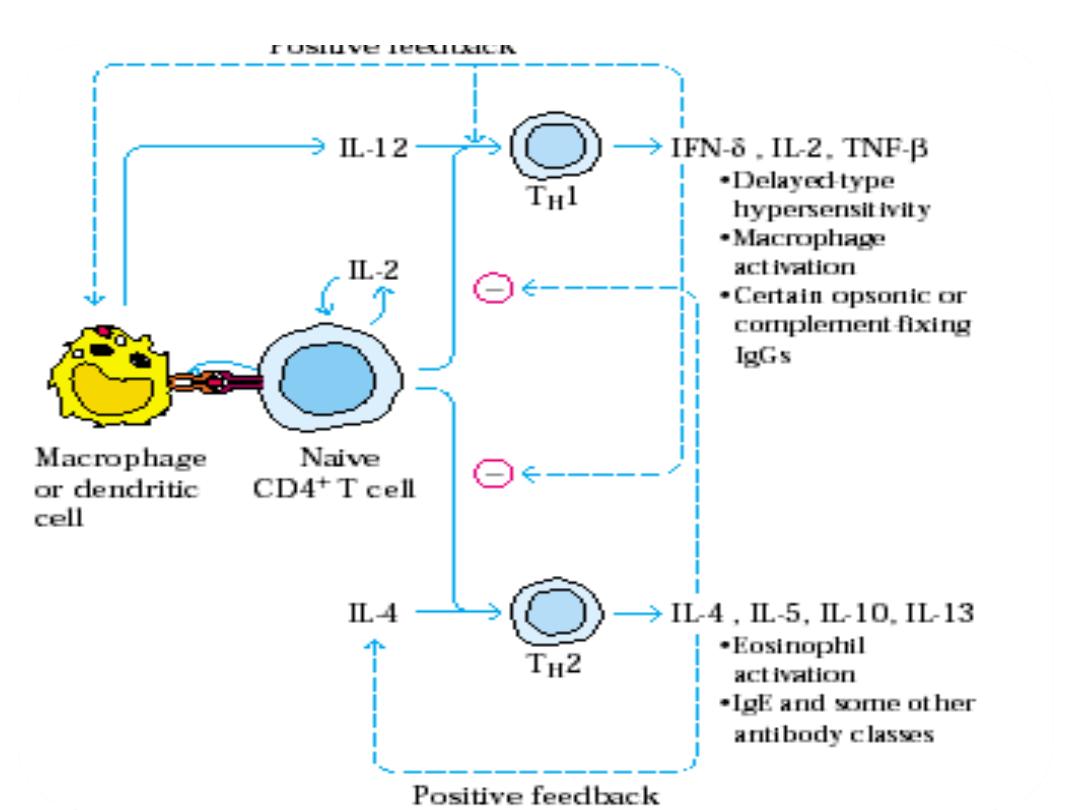
The types of immune response
• Cellular:
• Mediated by the
lymphocytes and
cytokines.
• Th-1,Th-2,Th-Del
• Humoral
• Mediated by
antibodies like IgG
• ,IgM,
• IgE,
• IgA,
• IgD.

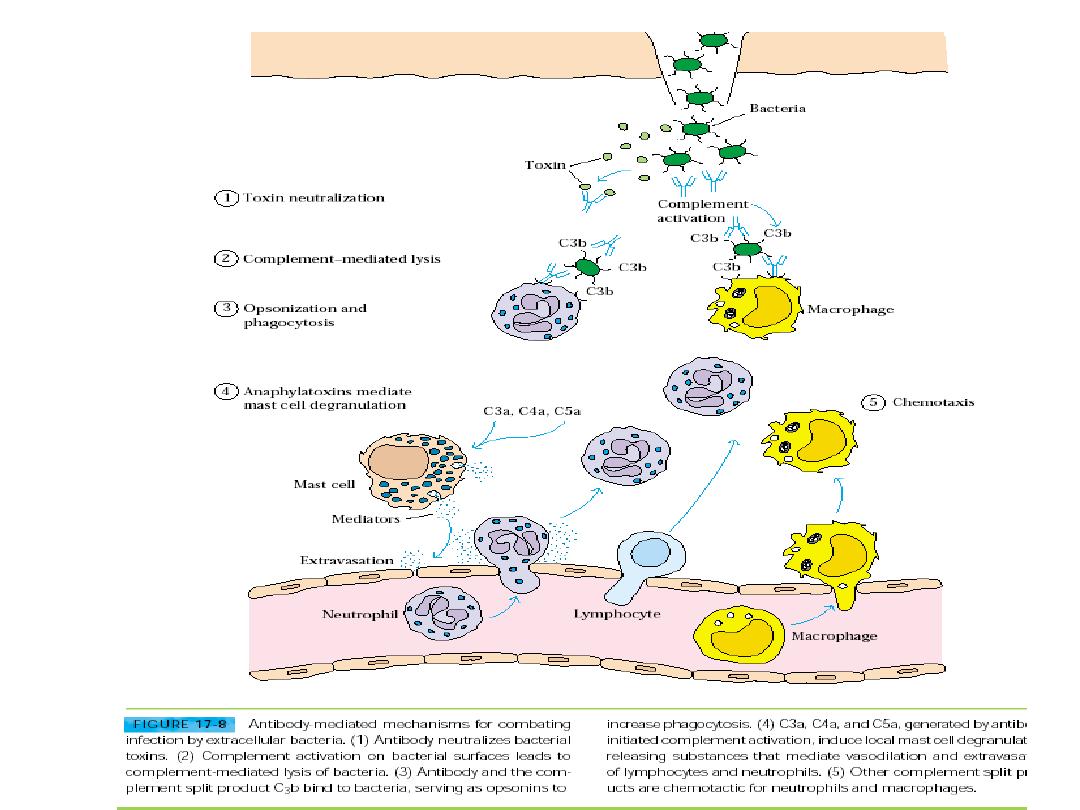
Immune response against bacteria
• Cellular or humeral
• The function of ab could be
• Opsonizing
• Complement fixing
• Haemolysing
• Agglutinating
• Surface receptors as IgD
• Secretory IgA

Immunity to viruses
• Obligate IC pathogen
• Invasion ,replication, evasion of immune system.
• Antiviral response is a complex process
• Alpha ,beta, gamma INF,as 1
ST
two interfere
with viral replication ,stimulate the MHC -1 to
make it recognizable to T-LC ,and activate NK
cells to kill infected cells
• By ADCC
• NK produce gamma INF----act macrophage
• Complement damage the envelope of some
viruses

Role of humoral immunity
• Neutralizing antibodies
• IgG the most active combine with viral antigen
on cell surface leading to ------attachment of
NK,Macr,PMNs --- damage to viral infected cells
ADCC
• IgA protect epithelial & mucosal surfaces
• Agglutination of viral particles IgM
• complement activation, promoting phagocytosis
by macrophage
• Opsonization
• Inhibition of viral enzymes

TYPES OF HOST INFECTION
• Or locally as rhinovirus
• If there is
entry
local invasion---- followed by
haematogenic
spread----- target organ
infection
e.g
measles ,poliomylitis hepatitis
.
• Or local entry-----neurological spread e.g
rabies.
• Some others remaine dorminant as HSV
• Some are latent as HIV ,CMV,EBV.

Cellular immune response
• After infection cell mediated immunity is
the main eliminator of virally infected cells
• CD4+,CD8+.
• CD4+--------effective antibody
• Cytokine production
• Excess macrophage activation
• CD8+ are generated early ,can recognize
the virally infected cells +MHC 1

Immunity to bacteria
• G+ve
• Thick peptidoglycan
• Teichoic
acid,CHO,protiens
• Resist cell lysis by
complement
• IR: spesific
Ab,opsonine,phagcytosis
by PNC
• IgG,IgM, & OR C3b
• Cell wall stimulate
alternative pathway---
opsonine--- inflamatry IR
• G-ve
• Thin inner &outer cell
membrane.
• LPS endotxines can
directly activate the
ulternative pathway
• C3aC5a--chemotactic
• C3b
• Spesific antibody
• Phagositic cells

Special bacteria
• mycobacteria
• spirochets

Immunity to parasites

Immunity to fungi

Bacterial evasion of immune
response
• Capsule
• Toxins
• Antigenic variation
• IC survival
• Immune system suppression
• Extacellular enzymes
• Expression of antibody binding protiens

Viral escape

Parasitic escape
site, size, migration,