
1
Alpha Hemolytics Streptococci
Objectives:
Upon completion of this lecture, the student will:
Analyze the diseases & pathogenicity for viridans & pneumococci.
Demonstrate the epidemiology/transmission for viridans &
pneumococci.
Outline the laboratory diagnosis for viridans & pneumococci.
State the drug of choice and prophylaxis where regularly used.
Lec.3
Dr.Sarmad Zeiny
2013-2014
BCM

2
Viridans Group Streptococci
( No Lancefield antigen classification. Members
include Streptococcus salivarius, S. sanguis, S. mitis,
S. intermedius, S. mutans, and others.)
They contain many species, they are untypable i.e. no group specific Ag, they are α-
hemolytic Streptococcus
It is present as a Commensal on mucosa of mouth, nasopharynx, and saliva.
Diseases:
1) Tooth carries: caused by S.mutans, by producing glycocalyx plaque formation.
2) Subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE):
Tooth extraction enters human body
subacute (slow) bacterial endocarditis
(SBE) in patients with abnormal heart
valves and no antibiotic prophylaxis. In
contrast, acute infective endocarditis is
caused by a staphylococcal infection, often
secondary to IV drug abuse, and is
characterized by an abrupt onset of shaking
chills, high spiking fevers, and rapid valve
destruction. See fig.4
3) Abscesses: There is a subgroup of the viridans streptococci called the
Streptococcus intermedius which are microaerophilic and are part of the normal
G.I. tract flora. Are often found in abscesses in the brain or abdominal organs. They
are found alone in pure cultures or in mixed cultures with anaerobes. A clinical
pearl is that if Streptococcus intermedius group bacteria grows in the blood you
should suspect that there is an abscess hiding in an organ.
Lab Dx:
1) Specimen: blood, gingival swab …etc
2) Grams slide: G+ve cocci, arrange in chains.
3) Culture: on Chocolate or blood Agar: α- hemolysis small (pinpointed), gray, glistening
colonies
4) Biochemical tests:
- Optochin sensitivity disc: Chocolate agar streaked with Viridans Streptococci then
apply Optochin disc no zone of inhibition around the disc (i.e. resistant to
Optochin) . This test used to differentiate S.pneumoniae from Viridans
Streptococci.
Fig 4: Viridans Streptococcus is eating heart valves
slowly, while Staphylococcus aureus is eating fast .
Lec.3
Dr.Sarmad Zeiny
2014-2015
3
- Bile Solubility test: Viridans Streptococci are resistant for bile salt which remains
intact in broth culture contains this salt, while S.pneumoniae is sensitive for bile salt
which induces the autolysis of this bacterium.
Turbid broth culture of S.pneumoniae + 10% Bile salt = Clear Broth after 10 min (+ve
result for S.pneumoniae)
Turbid broth culture of Viridans Streptococci + 10% Bile salt = No changes remains
turbid) after 10 min (+ve result Viridans Streptococci)
- API Strept: a set of biochemical test in one plastic sheet.
5) Antibiotic sensitivity test.
S.pneumoniae (Pneumococci, Diplococcus pneumoniae):
Distinguishing Features:
α-hemolytic.
Optochin sensitive.
Lancet-shaped diplococcic (cat eye).
Lysed by bile.
Reservoir:
human upper respiratory tract.
Transmission:
Respiratory droplets:
- Not considered highly communicable.
- Often colonizes the nasopharynx without causing disease.
Predisposing Factors:
• Antecedent influenza or measles infection.
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
• Congestive heart failure (CHF).
• Alcoholism.
• Asplenia predisposes to septicemia.
Virulent factors & Pathogenesis:
• Polysaccharide capsule is the major virulence factor.
• lgA protease anti IgA
• Teichoic acid.
• Pneumolysin O: hemolysin/cytolysin
- Damages respiratory epithelium
- Inhibits leukocyte respiratory burst and inhibits classical complement fixation
Capsular polysaccharide
Gram +VE diplococcus
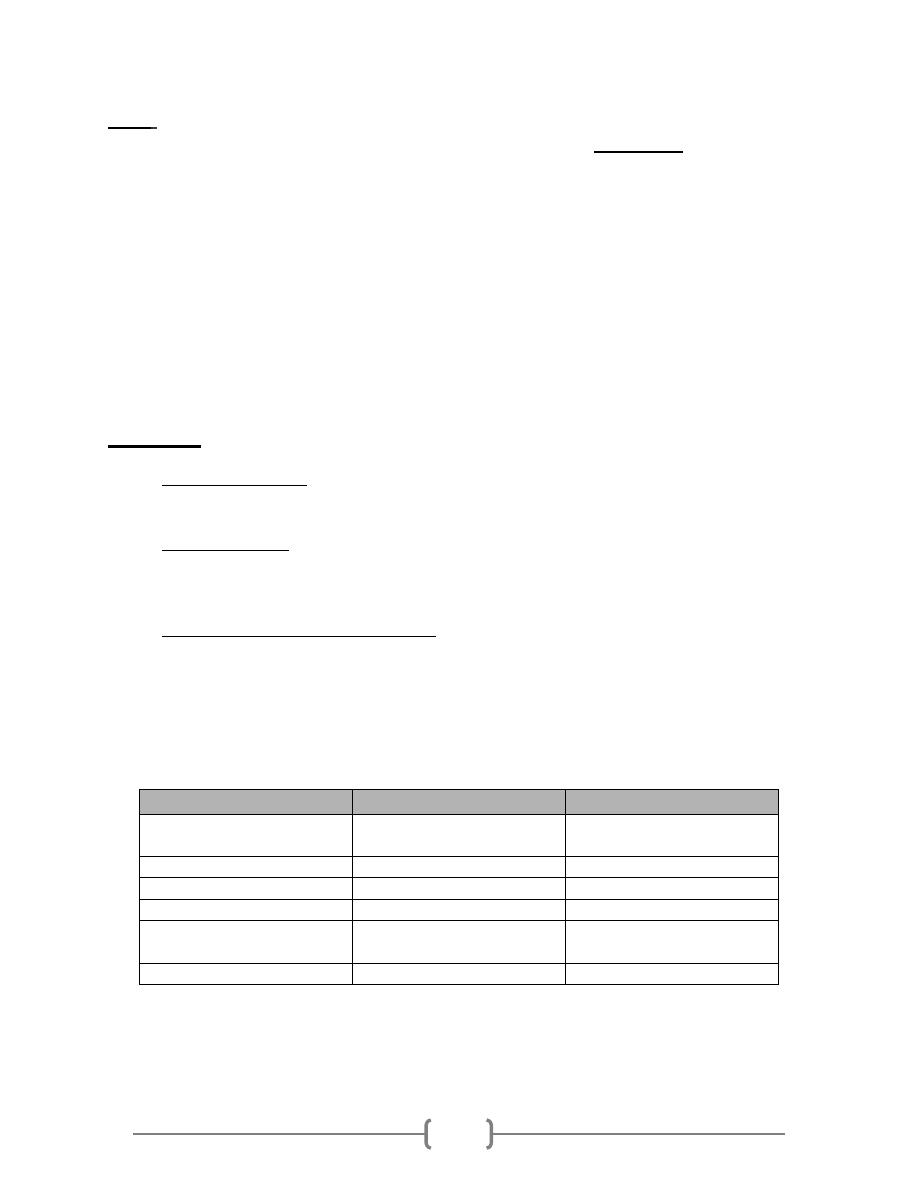
The "pneumococcal warrior." He is a mighty foe, with "capsule" armor, a
lung emblem on his shield, and a lancet-shaped diplococcus lance. The
lung emblem on his shield shows the severe lobar pneumonia caused by
this organism. Note the consolidation of the middle right lobe and the lower
left lobe, which accompany fever and shaking chills.
4
Notes
:
The Pneumococci is a very important organism because it is a major cause of bacterial
pneumonia and meningitis in adults, and otitis media in children. Pneumococcus is to Parents
while group B streptococcus is to Babies.
Pneumococci are typed to 84 serotypes according to the nature of capsular
polysaccharide antigen. In adults, types 1-8 are responsible for about 70% of
pneumococcal pneumonia and for 5% of fatalities due to pneumococcal bacteremia. In
children, type 6, 14, 19 and 23 are frequent causes.
Pneumococci are part of the normal nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal flora of
many healthy persons. The carrier rate varied widely between different groups and
among individuals of the same group from time to time (40-70%). Harmless to carrier
unless provoked by predisposing factors such as influenza or common cold, measles,
COPD, alcoholism….etc
Diseases:
a) Typical pneumonia:
- Most common cause (especially adult & elderly)
- Shaking chills, high fever, lobar consolidation, blood-tinged, "rusty" sputum
b) Adult meningitis:
- Most common cause
- Peptidoglycan and teichoic acids are highly inflammatory in the CNS.
- CSF reveals high WBCs (neutrophils) and low glucose, high protein
c) Otitis media and sinusitis in children: most common cause
As both Pneumococci and Viridans streptococci are α-hemolysis (green color) on
culture agar, we expect misdiagnosis between them. So we depend on the following
differential points:
Character
Pneumococci
Viridans streptococci
Morphology
Ovoid or lanceolate
diplococci
Rounded cocci in short or
long chains.
Capsule
Present
Absent
Optochin sensitivity
+ve
-ve
Bile solubility
+ve
-ve
Capsular swelling test
(Quellung reaction)
+ve
-ve
Virulence in mice
+ve
-ve
5
Lab Dx
of
S.
pneumoniae
:
o
Gram stain:
direct exam for sputum to differentiate from pneumonia caused by viral
infection. Direct exam reveals G+ve diplococci and many neutrophiles.
o C
ulture:
on Chocolate or blood Agar α- hemolysis small (pinpointed), gray, glistening;
colonies tend to dip in the center and resemble a doughnut (umbilicated) as they age;
colonies may be mucoid.
o Biochemical tests:
A.
Optochin sensitivity disc: Chocolate agar streaked with S.pneumoniae then apply
Optochin disc. Demonstrate a zone of inhibition around the disc. This test used to
differentiate S.pneumoniae from Viridans Streptococci.
B.
Bile Solubility test: S.pneumoniae is sensitive for bile salt which induces the autolysis
of this bacterium. While Viridans Streptococci are resistant for bile salt and remain
intact in broth culture contains this salt.
Turbid broth culture of S.pneumoniae + 10% Bile salt = Clear Broth after 10 min (+ve result
for S.pneumoniae)
Turbid broth culture of Viridans Streptococci + 10% Bile salt = No changes after 10 min (+ve
result Viridans Streptococci)
o Serology:
a)
Rapid diagnosis test for S.pneumoniae is the Quelling reaction test: Is a rapid
diagnostic test on culture. By mixing S.pneumoniae with specific anti-polysacchride
(capsule component) on microscope slide. The capsule swell due to Ag-Ab reaction.
Examined by capsular stain such as Indian ink.
b) Latex particle agglutination test for capsular antigen in spinal fluid diagnostic for
meningitis.
{S.pneumoniae + specific Ab = capsule swelling (+ve result) stain with negative stain like
India ink} diplococci surrounded by clear area with dark background.
o
Virulence in mice
: when inject Pneumococci in the mice the mice will die, while when
inject Viridans the mice will survive.
o Antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
6
Vaccine
-
Pediatric (PCV, pneumococcal capsular vaccine):
o
Seven of the most common serotypes
o
Conjugated to diphtheria toxoid
o
Prevents invasive disease
- Adult (PPV, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine):
o
23 of the most common capsular serotypes
o
Recommended for all adults
>65
years of age and any at-risk individuals
Anaerobic streptococcus: Peptostreptococcus
These streptococci grow only under anaerobic or microaerophilic conditions
and variably produce hemolysins.
They are part of the normal flora of the mouth, upper respiratory tract,
bowel, and female genital tract.
They often participate with many other bacterial species in mixed anaerobic
infections. Such infections may occur in wounds, in the breast, in
postpartum endometritis, following rupture of an abdominal viscus, the
brain, or in chronic suppuration of the lung.
The pus usually has a foul odor.
Summary
• Alpha haemolytics streptococci causing greenish discoloration on chocolate agar.
• Viridans causes SBE in suspected individuals. AB prophylaxis needed.
• Pneumococcus is capsulated and typed accordingly to 84 serotyped.
• Pneumococci are the leading cause of adult pneumonia.
• Pneumococci present in carrier state in 40-70% of healthy humans.
• Pneumococci & viridans can be differentiated by Optochin sensitivity, arrangement, bile
solubility, Capsular swelling test (Quelling reaction) and serologically.
• Pneumococci can be prevented by a Vaccine causing Ab against capsular Ag.
END
