
Genus Streptococcus
G
G
r
r
a
a
m
m
’
’
s
s
p
p
o
o
s
s
i
i
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
,
,
C
C
a
a
t
t
a
a
l
l
a
a
s
s
e
e
n
n
e
e
g
g
a
a
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
Department of Microbiology
College of Medicine
University of Baghdad
Lec2, 2014-2015
Dr.Sarmad M.H Zeiny

O
O
b
b
j
j
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
s
s
:
:
U
U
p
p
o
o
n
n
c
c
o
o
m
m
p
p
l
l
e
e
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
o
o
f
f
t
t
h
h
i
i
s
s
l
l
e
e
c
c
t
t
u
u
r
r
e
e
,
,
t
t
h
h
e
e
s
s
t
t
u
u
d
d
e
e
n
n
t
t
w
w
i
i
l
l
l
l
:
:
v
Outline the
me dically important
stre pto cocci s pecie s.
v
Classification
of ge nus streptococci.
v
Des cribing the
mo rpholo gy & physiology
for streptococci.
v
Determine the
virule nce facto rs
fo r stre ptococci.
v
Analyze the
diseases & pathogenicity
for stre pto cocci.
v
Demons trate the
e pidemiology/ trans mission
for stre ptococci.
v
Outline the
laboratory diagnosis
for s treptococci.
v
State the
drug of choice and prophylaxis
where reg ularly use d.
G
G
r
r
a
a
m
m
p
p
o
o
s
s
i
i
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
S
S
t
t
r
r
e
e
p
p
t
t
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
C
C
a
a
t
t
a
a
l
l
a
a
s
s
e
e
-
-
v
v
e
e
S
S
t
t
a
a
p
p
h
h
y
y
l
l
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
C
C
a
a
t
t
a
a
l
l
a
a
s
s
e
e
+
+
v
v
e
e
General characteristic for genus streptococci :
—
G
G
+
+
v
v
e
e
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
,
,
a
a
r
r
r
r
a
a
n
n
g
g
e
e
i
i
n
n
c
c
h
h
a
a
i
i
n
n
s
s
o
o
r
r
p
p
a
a
i
i
r
r
s
s
.
.
—
S
S
o
o
m
m
e
e
s
s
t
t
r
r
a
a
i
i
n
n
s
s
a
a
r
r
e
e
c
c
a
a
p
p
s
s
u
u
l
l
a
a
t
t
e
e
d
d
—
M
M
a
a
j
j
o
o
r
r
i
i
t
t
y
y
a
a
r
r
e
e
f
f
a
a
c
c
u
u
l
l
t
t
a
a
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
a
a
n
n
a
a
e
e
r
r
o
o
b
b
i
i
c
c
,
,
f
f
e
e
w
w
a
a
r
r
e
e
o
o
b
b
l
l
i
i
g
g
a
a
t
t
o
o
r
r
y
y
a
a
n
n
a
a
e
e
r
r
o
o
b
b
i
i
c
c
.
.
—
C
C
a
a
t
t
a
a
l
l
a
a
s
s
e
e
–
–
v
v
e
e
—
N
N
o
o
n
n
m
m
o
o
t
t
i
i
l
l
e
e
.
.
—
N
N
o
o
n
n
s
s
p
p
o
o
r
r
e
e
f
f
o
o
r
r
m
m
i
i
n
n
g
g
—
F
F
a
a
s
s
t
t
i
i
d
d
i
i
o
o
u
u
s
s
m
m
i
i
c
c
r
r
o
o
o
o
r
r
g
g
a
a
n
n
i
i
s
s
m
m

G
G
e
e
n
n
u
u
s
s
S
S
t
t
r
r
e
e
p
p
t
t
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
u
u
s
s
H
H
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
β
β
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
S
S
.
.
P
P
y
y
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
e
e
s
s
S
S
.
.
a
a
g
g
a
a
l
l
a
a
c
c
t
t
i
i
a
a
e
e
α
α
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
S
S
.
.
P
P
n
n
e
e
u
u
m
m
o
o
n
n
i
i
a
a
e
e
V
V
i
i
r
r
i
i
d
d
a
a
n
n
s
s
S
S
t
t
r
r
e
e
p
p
t
t
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
i
i
γ
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
S
S
.
.
b
b
o
o
v
v
i
i
s
s
L
L
a
a
n
n
c
c
e
e
f
f
i
i
e
e
l
l
d
d
(
(
s
s
e
e
r
r
o
o
l
l
o
o
g
g
y
y
)
)
S
S
e
e
r
r
o
o
g
g
r
r
o
o
u
u
p
p
s
s
(
(
c
c
e
e
l
l
l
l
w
w
a
a
l
l
l
l
p
p
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
a
a
c
c
c
c
h
h
a
a
r
r
i
i
d
d
e
e
A
A
g
g
)
)
G
G
r
r
o
o
u
u
p
p
A
A
S
S
.
.
P
P
y
y
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
e
e
s
s
8
8
0
0
S
S
e
e
r
r
o
o
t
t
y
y
p
p
e
e
s
s
,
,
(
(
M
M
-
-
p
p
r
r
o
o
t
t
e
e
i
i
n
n
)
)
G
G
r
r
o
o
u
u
p
p
B
B
S
S
.
.
a
a
g
g
a
a
l
l
a
a
c
c
t
t
i
i
a
a
e
e
G
G
r
r
o
o
u
u
p
p
D
D
S
S
.
.
b
b
o
o
v
v
i
i
s
s
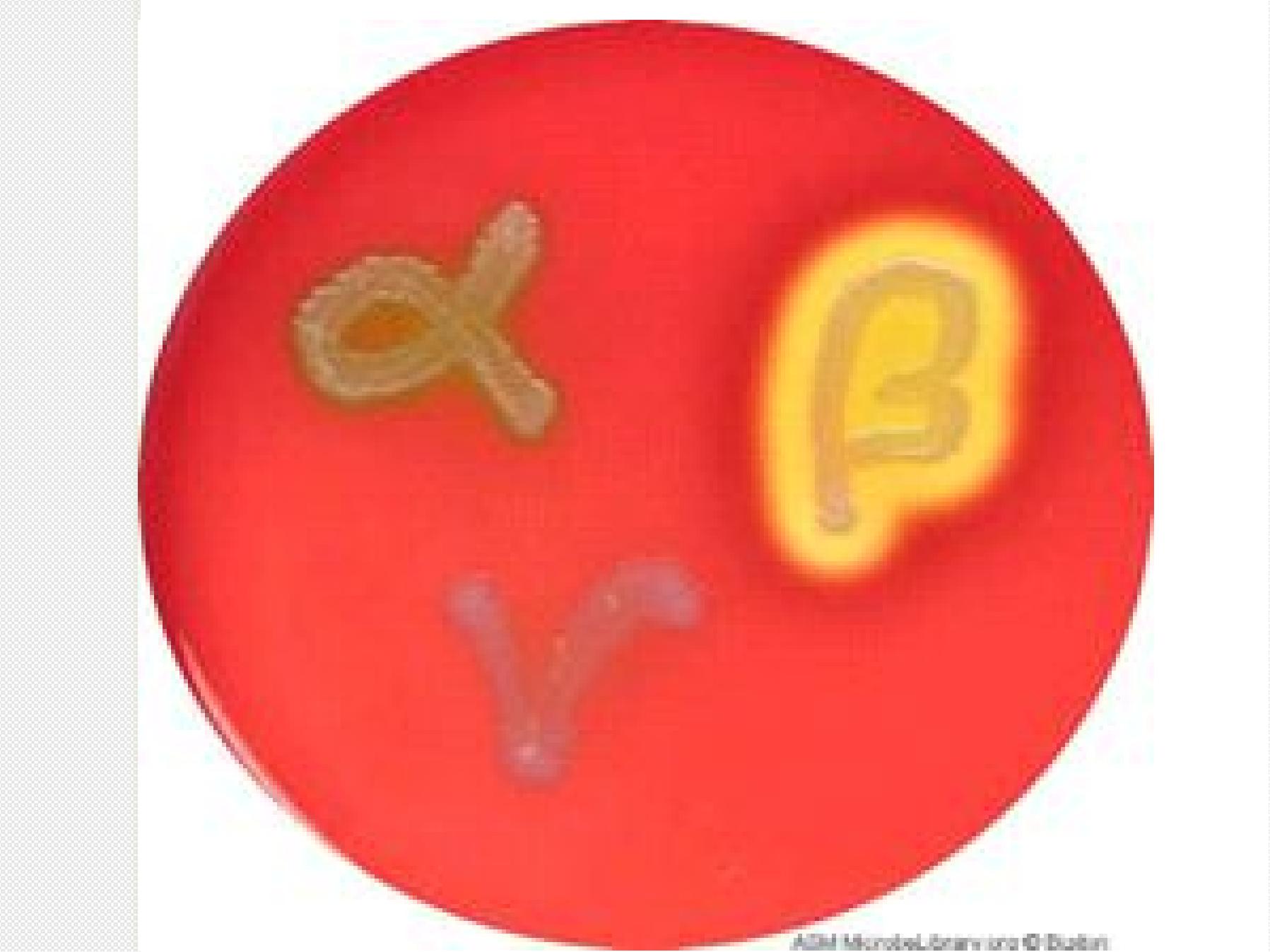
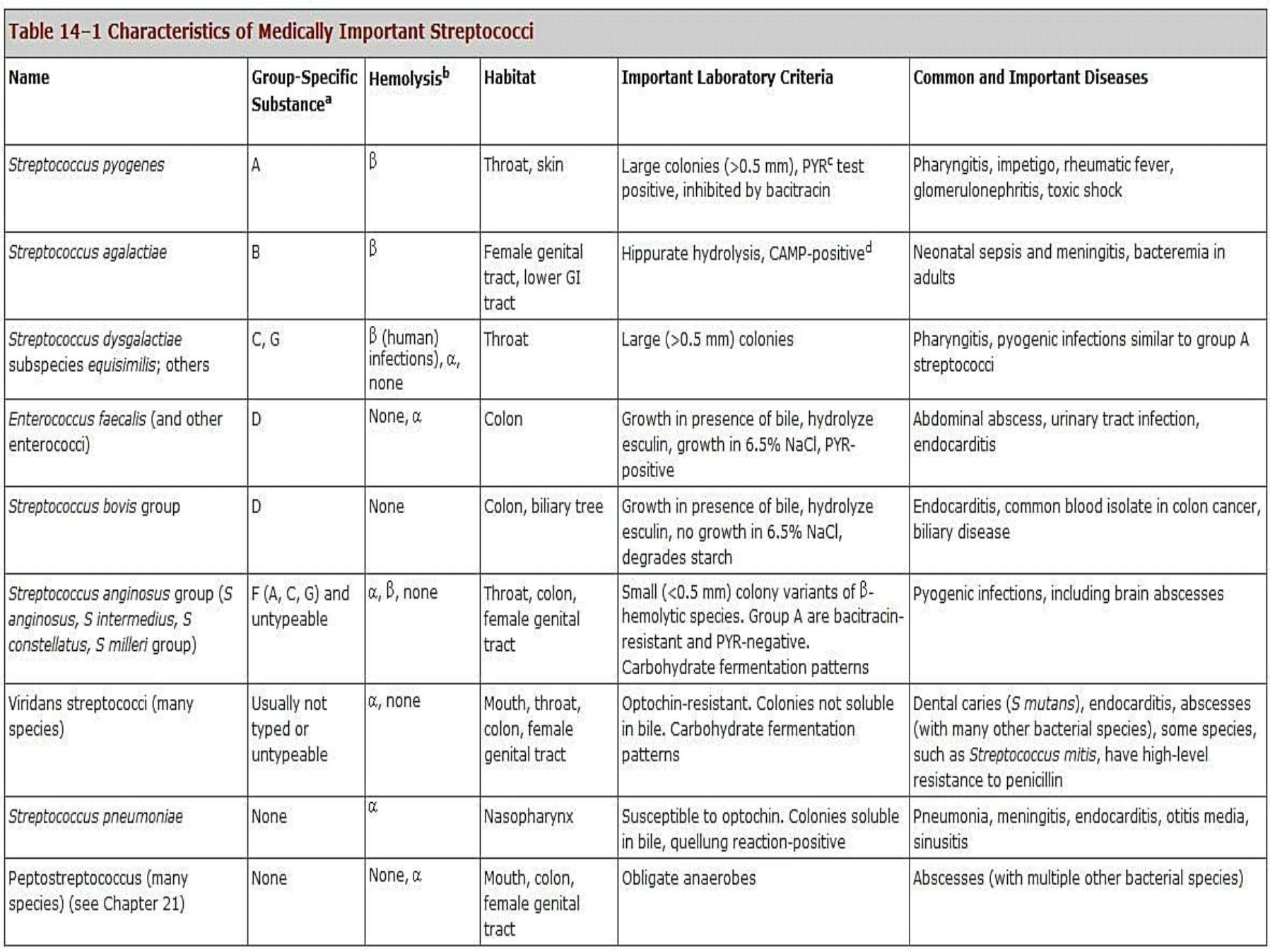

S
S
.
.
p
p
y
y
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
e
e
s
s
o
o
n
n
b
b
l
l
o
o
o
o
d
d
a
a
g
g
a
a
r
r
(
(
b
b
e
e
t
t
a
a
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
)
)
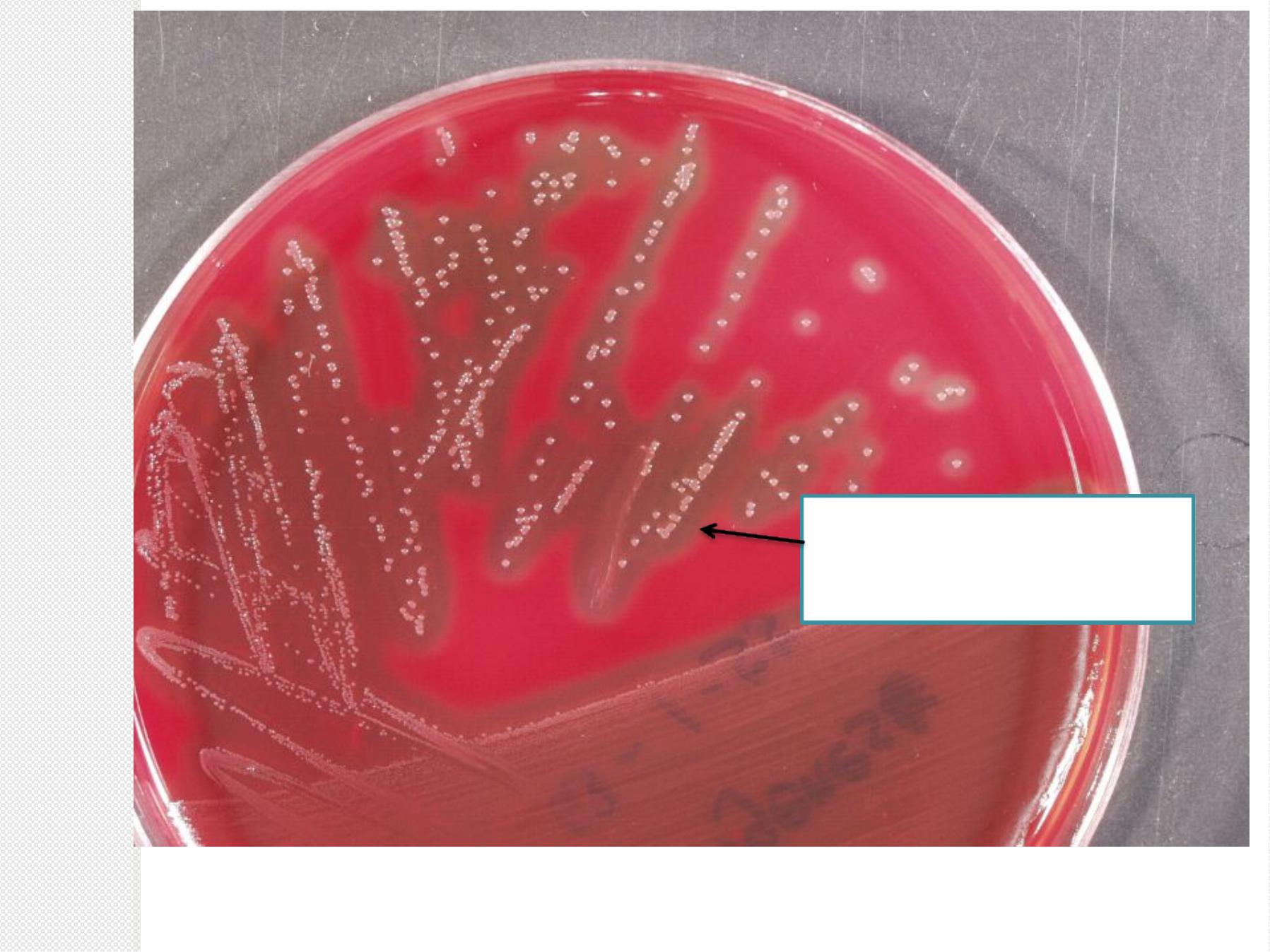
(Beta hemolysis)
clear zone around
colonies
A
A
l
l
p
p
h
h
a
a
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
(
(
g
g
r
r
e
e
e
e
n
n
d
d
i
i
s
s
c
c
o
o
l
l
o
o
r
r
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
)
)
S.pyogenes
(Group A β- hemolytic,GABH):
M
M
-
-
p
p
r
r
o
o
t
t
e
e
i
i
n
n
>
>
8
8
0
0
s
s
e
e
r
r
o
o
t
t
y
y
p
p
e
e
s
s
R
R
e
e
s
s
e
e
r
r
v
v
o
o
i
i
r
r
Human throat and skin
T
T
r
r
a
a
n
n
s
s
m
m
i
i
s
s
s
s
i
i
o
o
n
n
Spread by respiratory droplets or
direct contact
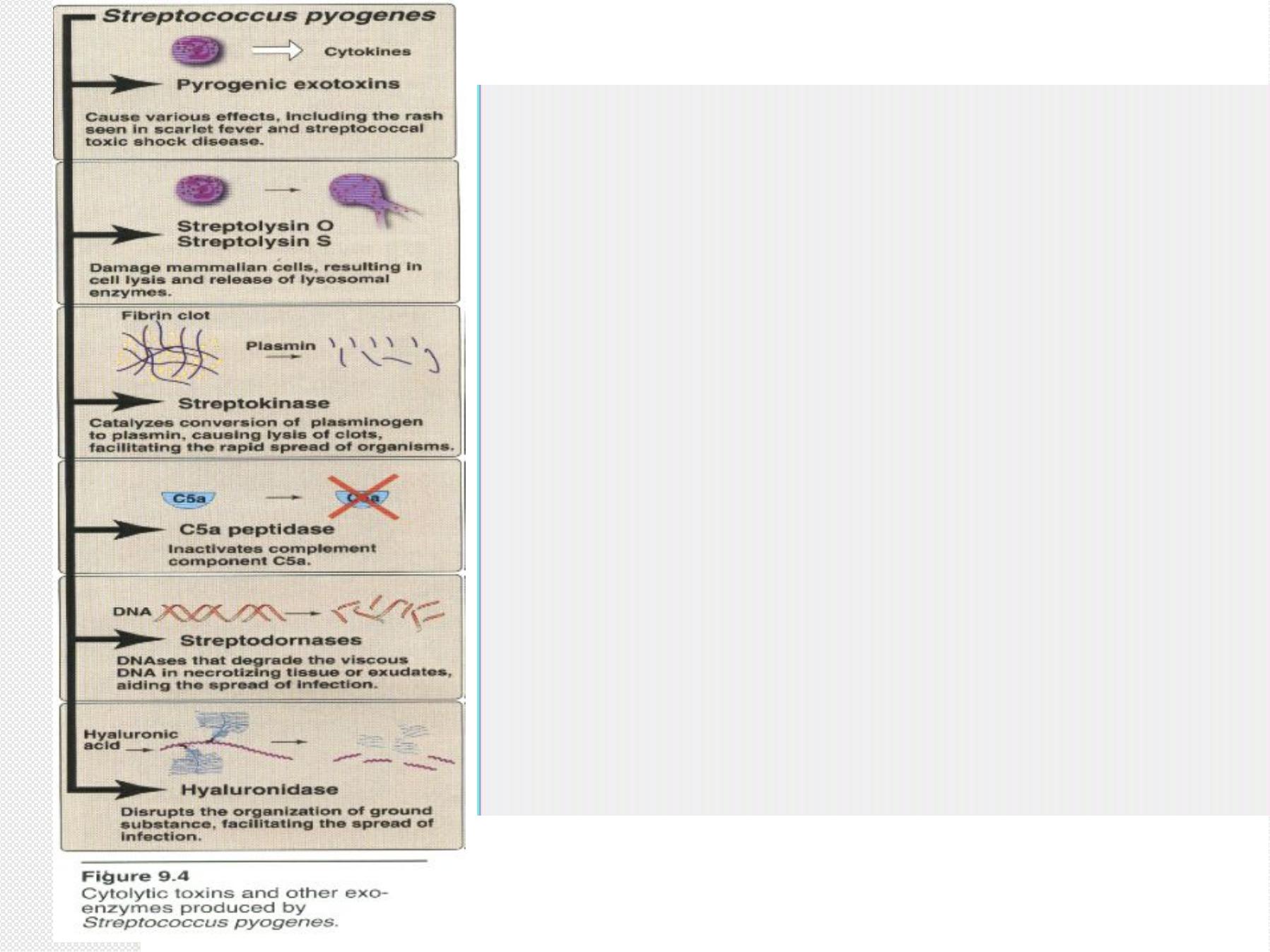
Virulence factors & Pathogenesis for S.pyogenes
1)
M protein and capsule.
2)
Streptolysin O:
destroys RBC & WBC, antigenic. anti-streptolysin O
(ASO) antibodies develop.
3)
Streptolysin S:
destroys RBC, not antigenic.
4)
Pyrogenic exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin):
few strains,
scarlet fever, few strains superantigens. streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
5)
Streptokinase
plasmin
breaks fibrin
spreading factor
6)
Hyaluronidase
spreading factor
7)
Streptodornases (DNAases)
spreading factor
8)
(Anti-C5a) peptidase
anti-inflammatory
9)
Diphosphopyridine Nucleotidase
à k i ll le u k o c y t e
DISEASES of
S.pyogenes
•
S
S
o
o
r
r
e
e
t
t
h
h
r
r
o
o
a
a
t
t
(
(
a
a
c
c
u
u
t
t
e
e
p
p
h
h
a
a
r
r
y
y
n
n
g
g
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
,
,
p
p
h
h
a
a
r
r
y
y
n
n
g
g
o
o
t
t
o
o
n
n
s
s
i
i
l
l
l
l
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
)
)
.
.
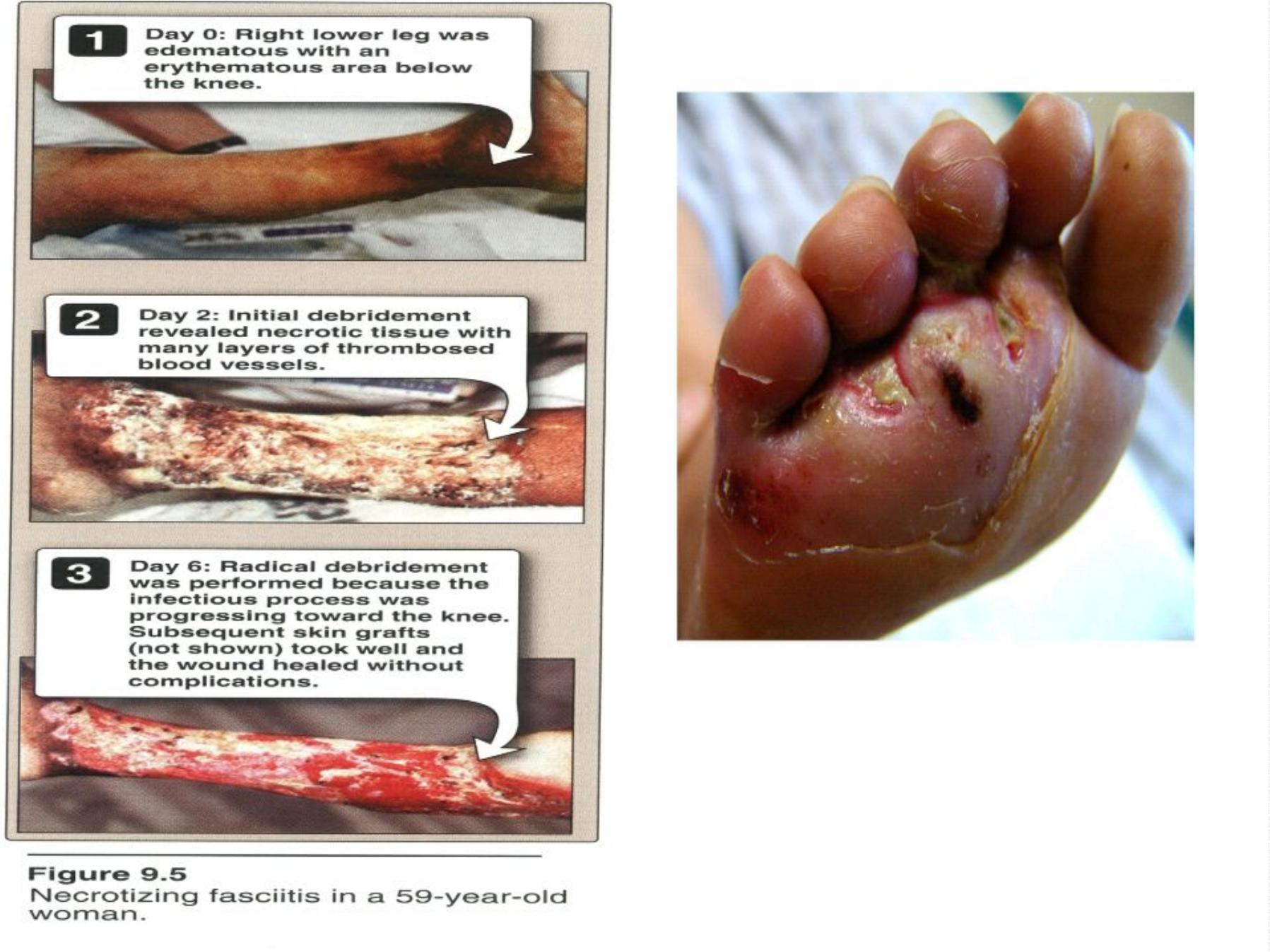
•
S
S
k
k
i
i
n
n
i
i
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
:
:
(
(
W
W
o
o
u
u
n
n
d
d
i
i
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
,
,
c
c
e
e
l
l
l
l
u
u
l
l
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
,
,
f
f
a
a
s
s
c
c
i
i
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
a
a
n
n
d
d
m
m
y
y
o
o
n
n
e
e
c
c
r
r
o
o
s
s
i
i
s
s
,
,
I
I
m
m
p
p
e
e
t
t
i
i
g
g
o
o
,
,
E
E
r
r
y
y
s
s
i
i
p
p
e
e
l
l
a
a
s
s
.
.
•
S
S
e
e
p
p
s
s
i
i
s
s
.
.
•
M
M
e
e
n
n
i
i
n
n
g
g
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
.
.
•
P
P
u
u
e
e
r
r
p
p
e
e
r
r
a
a
l
l
S
S
e
e
p
p
s
s
i
i
s
s
.
.
•
S
S
t
t
r
r
e
e
p
p
t
t
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
u
u
s
s
t
t
o
o
x
x
i
i
c
c
s
s
h
h
o
o
c
c
k
k
s
s
y
y
n
n
d
d
r
r
o
o
m
m
e
e
•
S
S
c
c
a
a
r
r
l
l
e
e
t
t
f
f
e
e
v
v
e
e
r
r
•
R
R
h
h
e
e
u
u
m
m
a
a
t
t
i
i
c
c
f
f
e
e
v
v
e
e
r
r
•
A
A
c
c
u
u
t
t
e
e
G
G
l
l
o
o
m
m
e
e
r
r
u
u
l
l
o
o
n
n
e
e
p
p
h
h
r
r
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
L
L
O
O
C
C
A
A
L
L
I
I
N
N
F
F
E
E
C
C
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
S
S
(
(
i
i
n
n
v
v
a
a
s
s
i
i
o
o
n
n
)
)
S
S
Y
Y
S
S
T
T
E
E
M
M
I
I
C
C
I
I
N
N
F
F
E
E
C
C
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
(
(
i
i
n
n
v
v
a
a
s
s
i
i
o
o
n
n
&
&
/
/
o
o
r
r
t
t
o
o
x
x
i
i
n
n
)
)
P
P
O
O
S
S
T
T
S
S
T
T
R
R
E
E
P
P
T
T
O
O
C
C
O
O
C
C
C
C
A
A
L
L
s
s
e
e
q
q
u
u
e
e
l
l
(
(delayed
antibody mediated diseases)
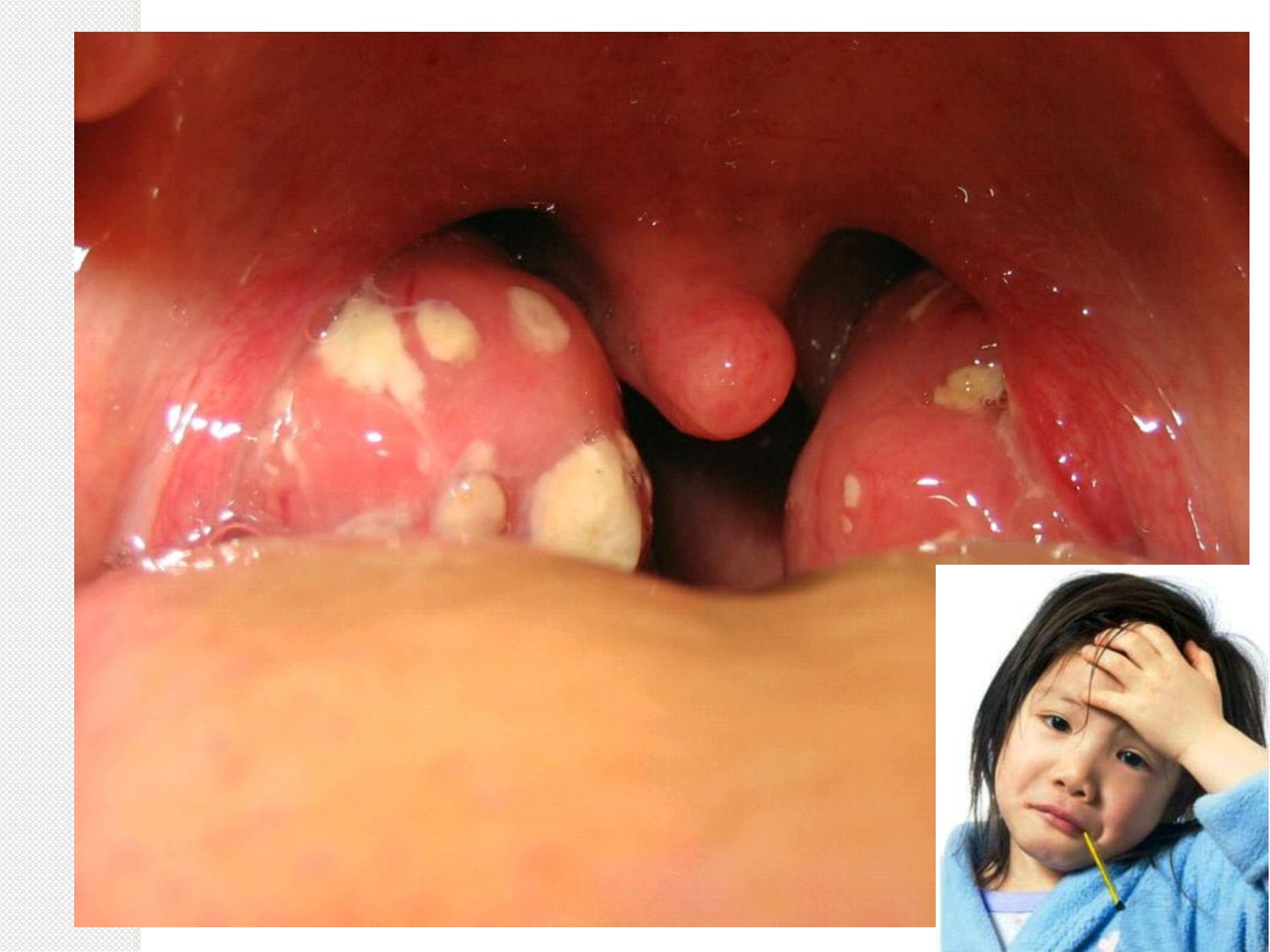
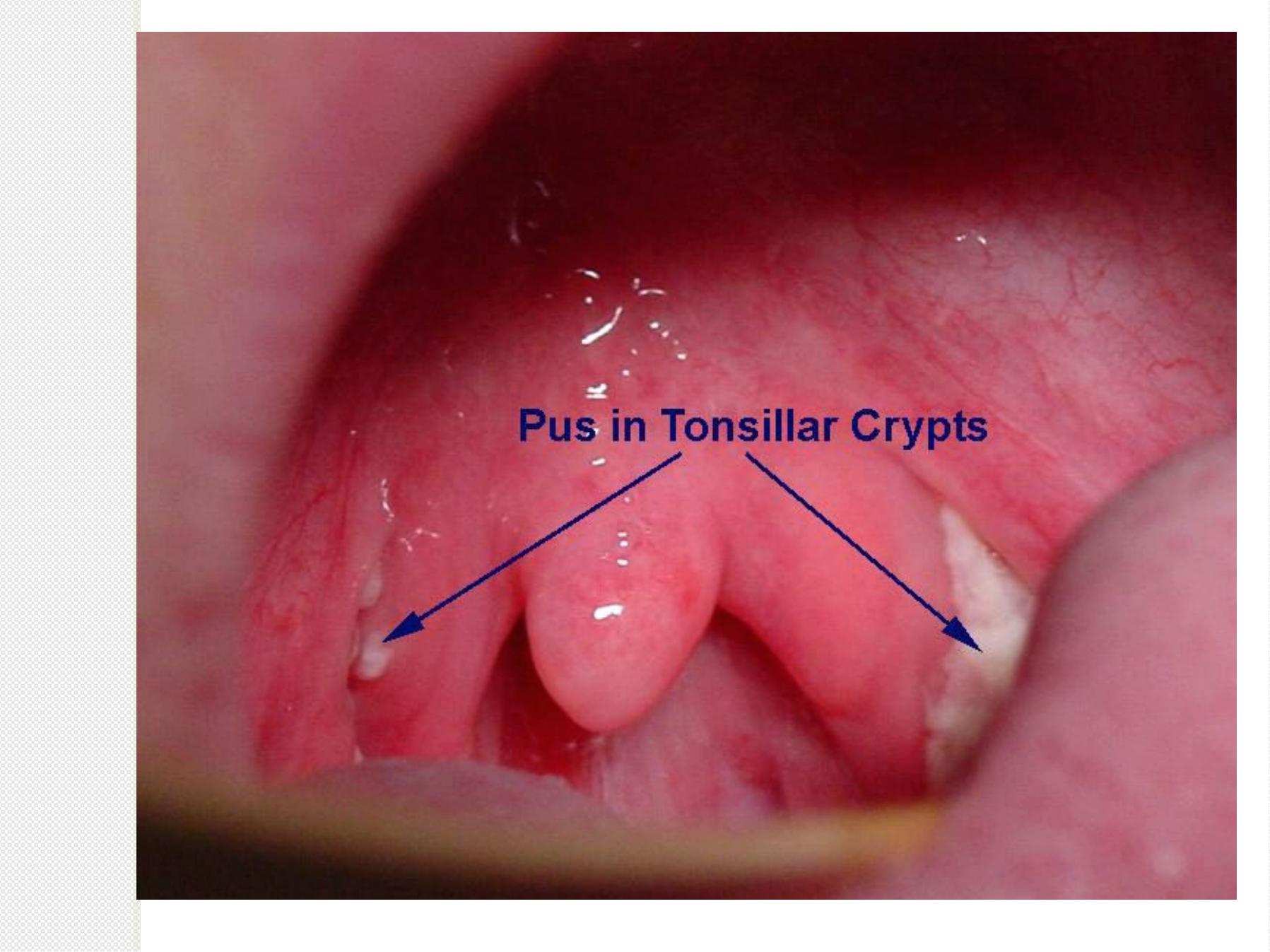
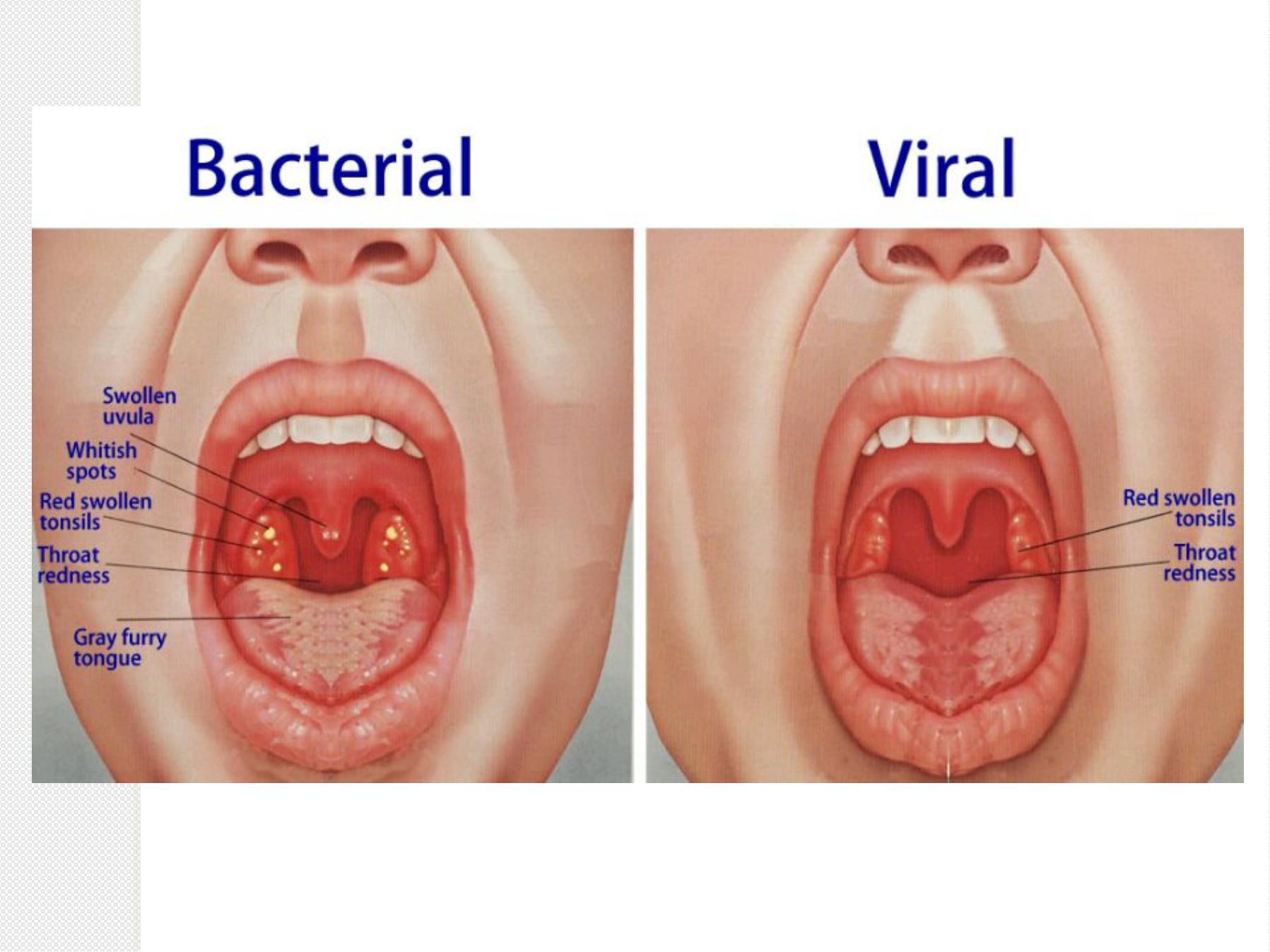
Acute Tonsillitis
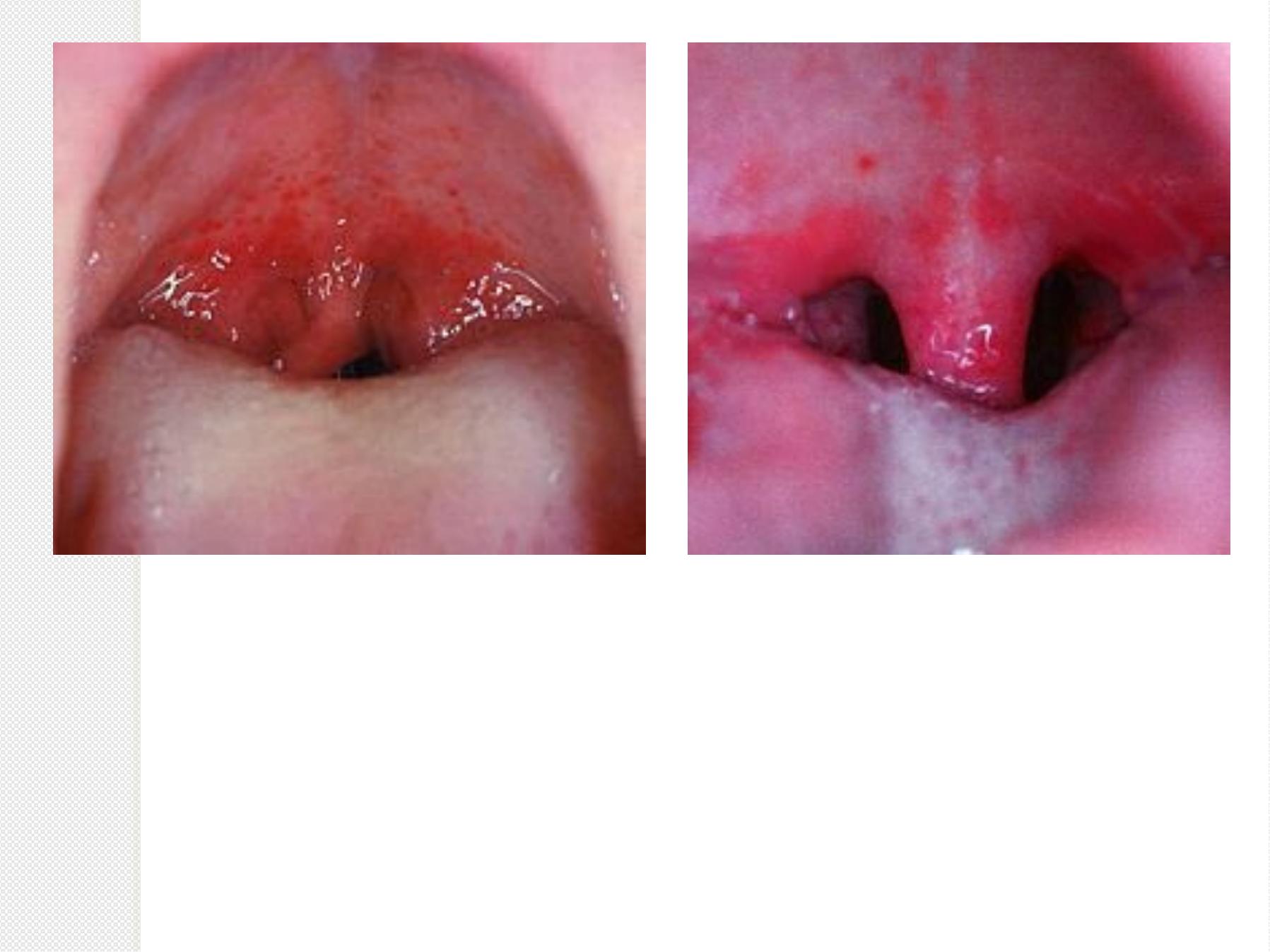
S
S
t
t
r
r
e
e
p
p
t
t
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
a
a
l
l
p
p
h
h
a
a
r
r
y
y
n
n
g
g
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
ASO te st:
—
Measure Ab against Streptolysin O
—
ASO test uses in poststreptococcal
infection. This test used to
determine
significance of current streptococcal
infection
by measuring the
A
A
S
S
O
O
T
T
:
—
ASOT (Ab Titer):
N
N
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
l
l
<
<
2
2
0
0
0
0
>
>
s
s
i
i
g
g
n
n
i
i
f
f
i
i
c
c
a
a
n
n
c
c
e
e
r
r
e
e
s
s
u
u
l
l
t
t
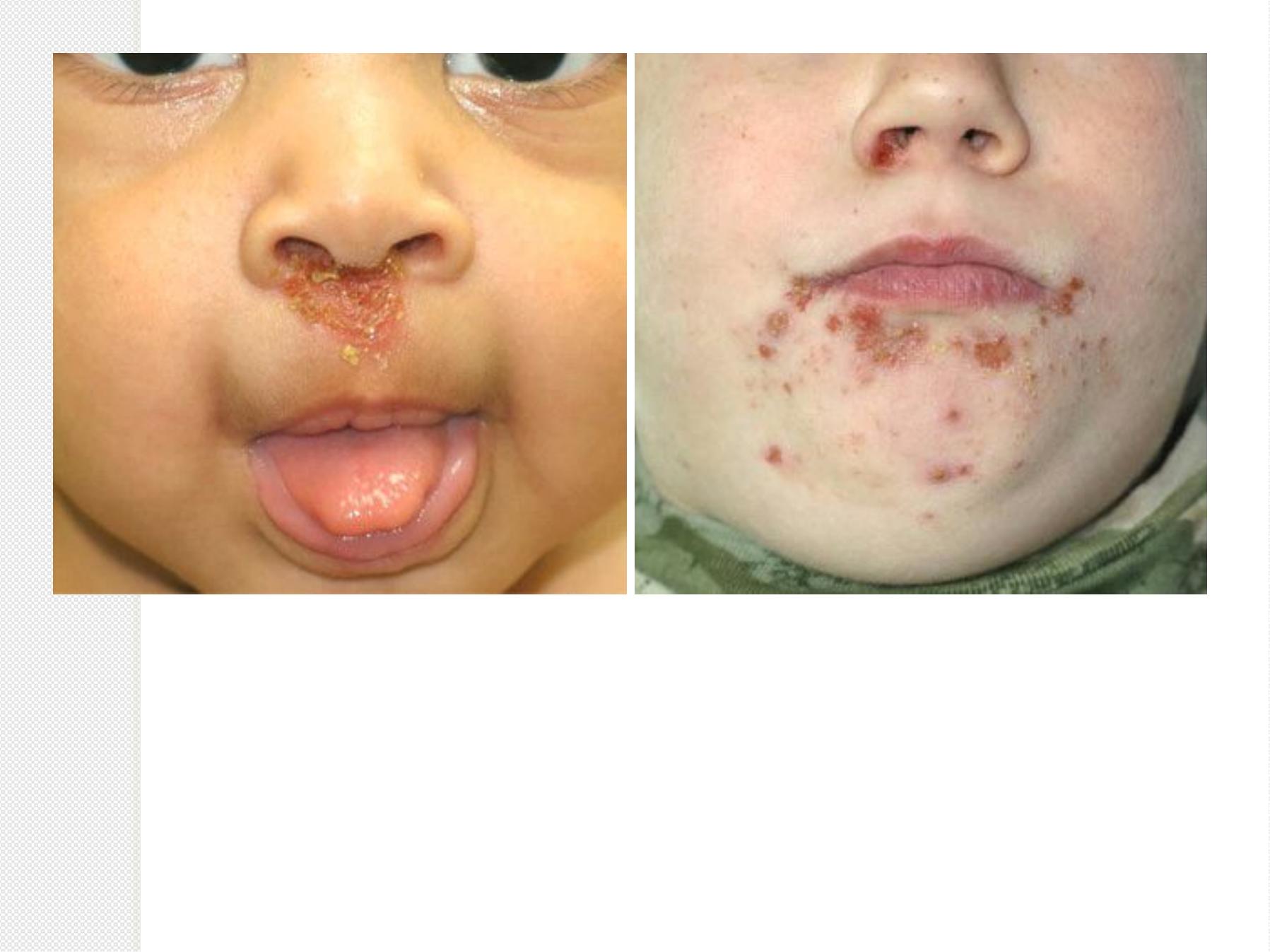
I
I
m
m
p
p
e
e
t
t
i
i
g
g
o
o
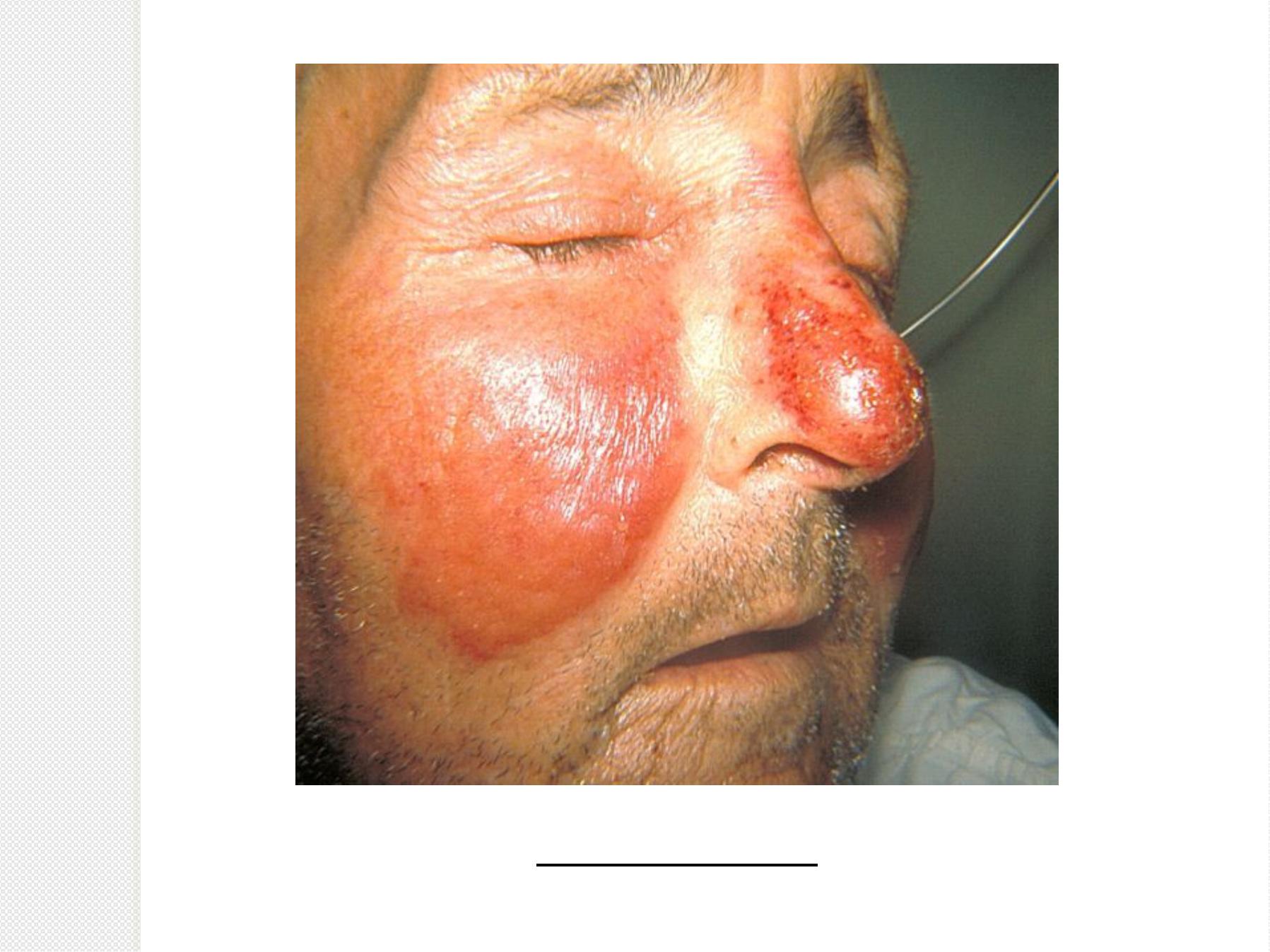
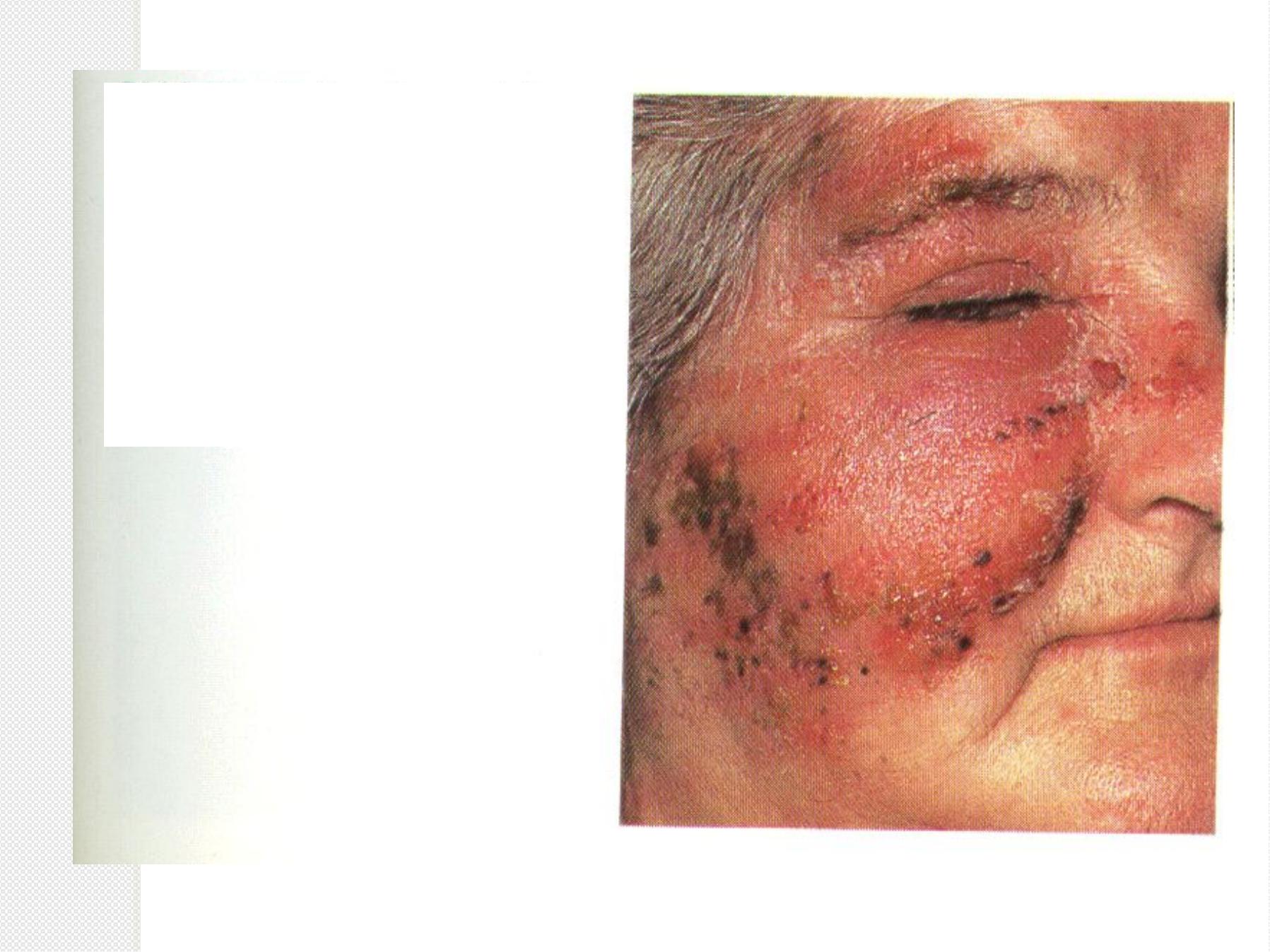
Erysipelas
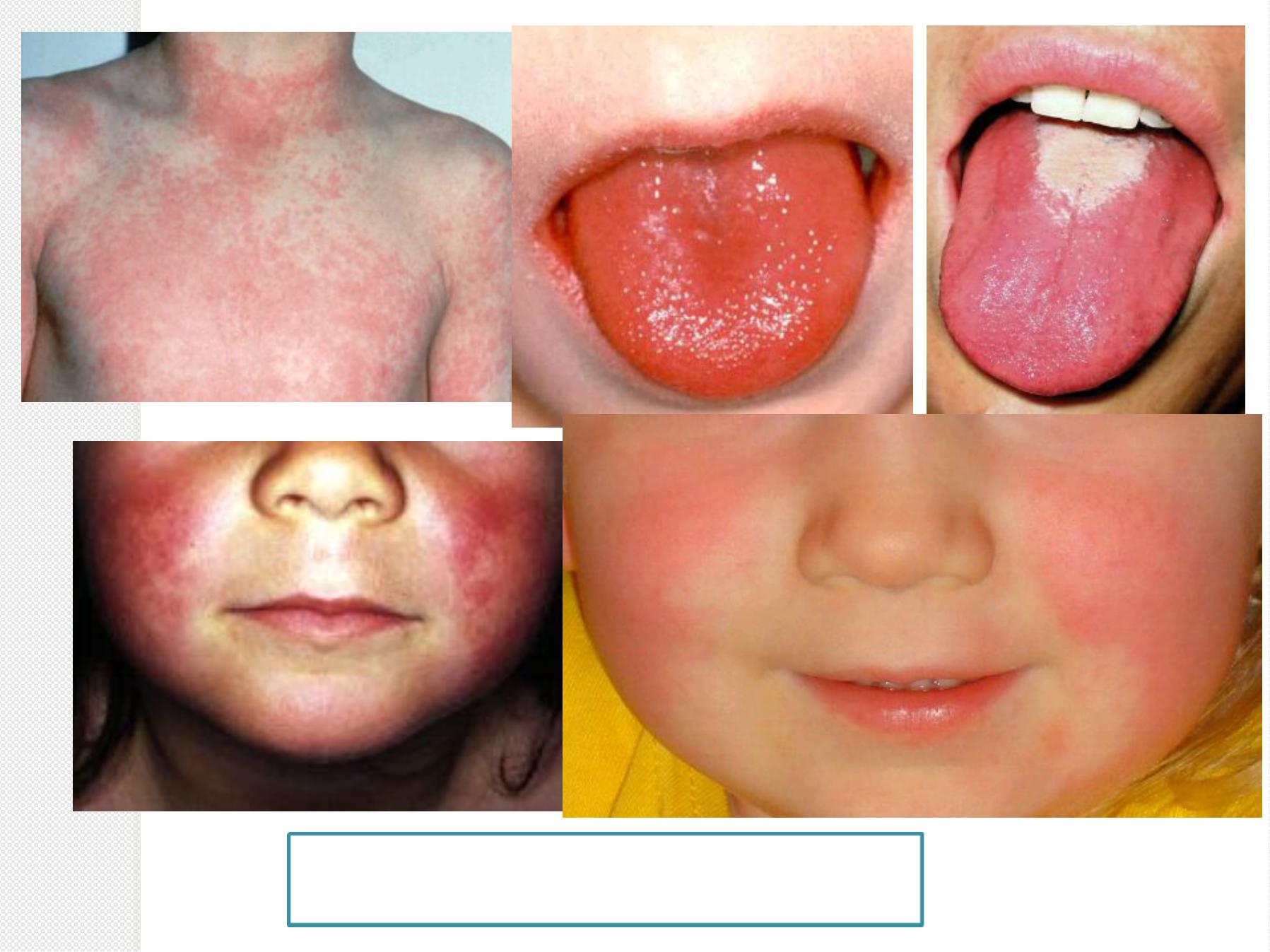
S
S
c
c
a
a
r
r
l
l
e
e
t
t
f
f
e
e
v
v
e
e
r
r
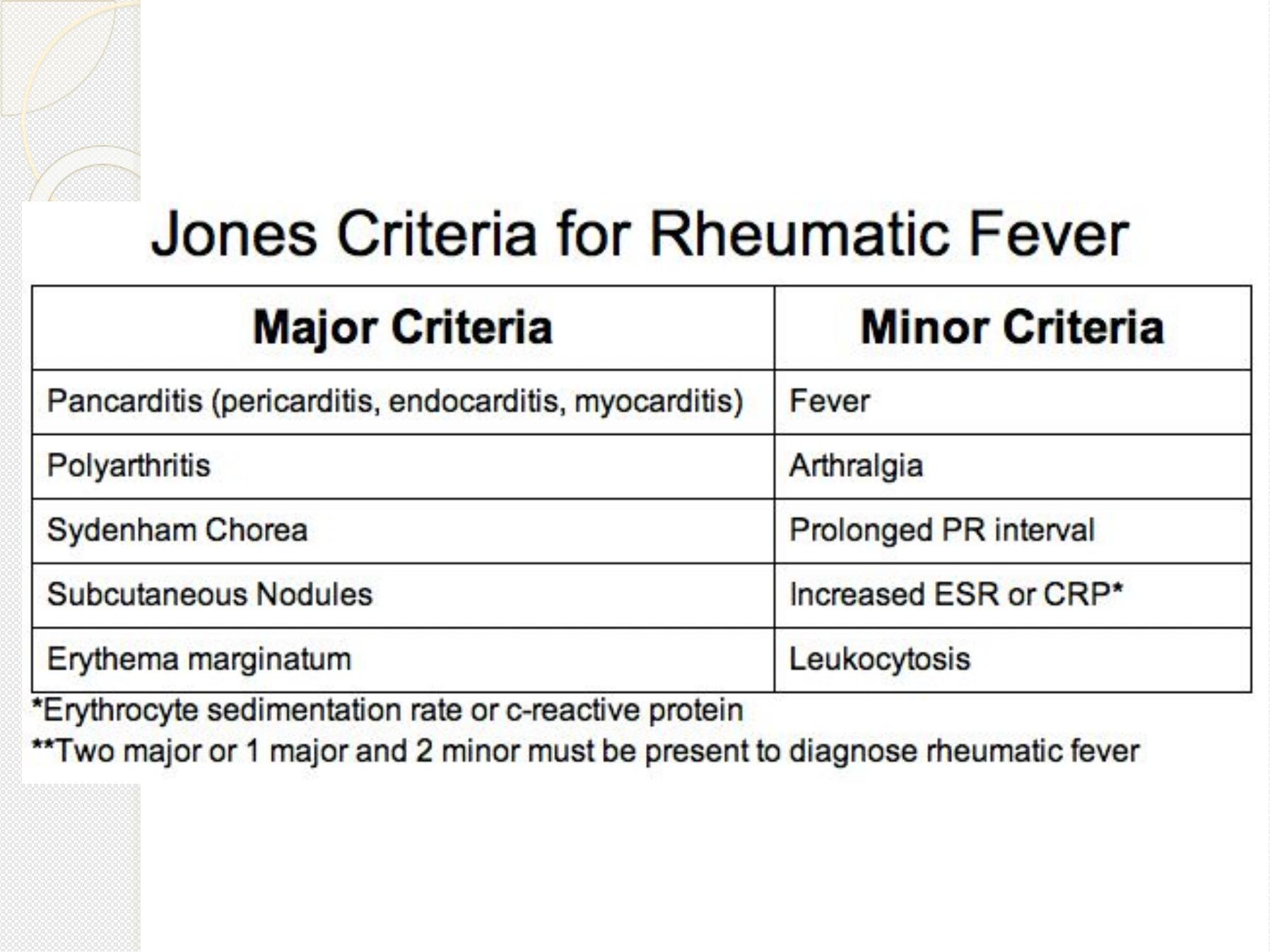
RHEUMATIC FEVER
Picture John Travolta in the movie Rheumatic Fever, the upcoming sequel to
Saturday Night Fever. His h eart is damaged from the stress of the hours of disco
dancing, his joints are aching from dropping to his knees, and his arms are
moving rhythmically in a disco ch oreiform jam.
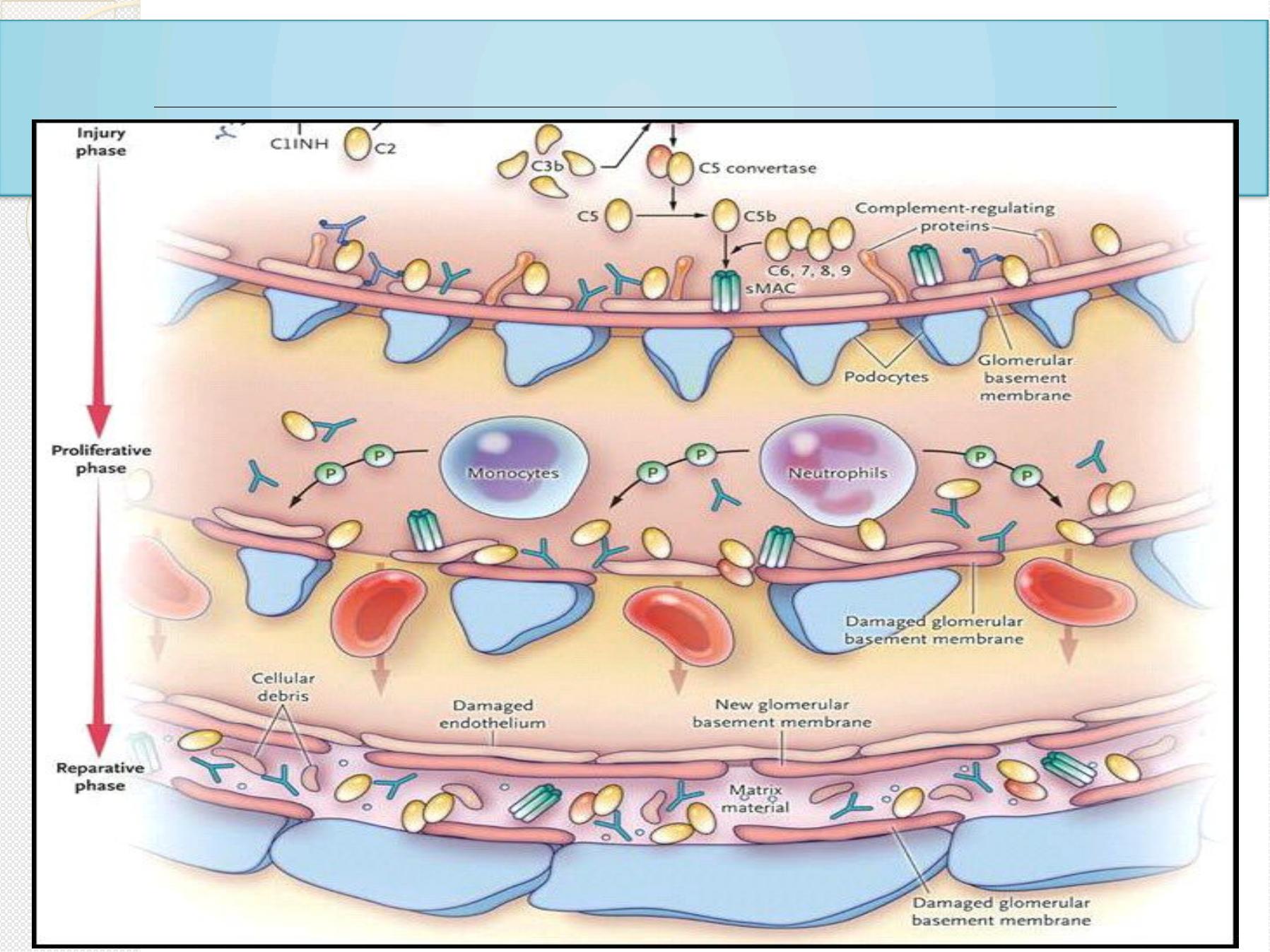
Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis:
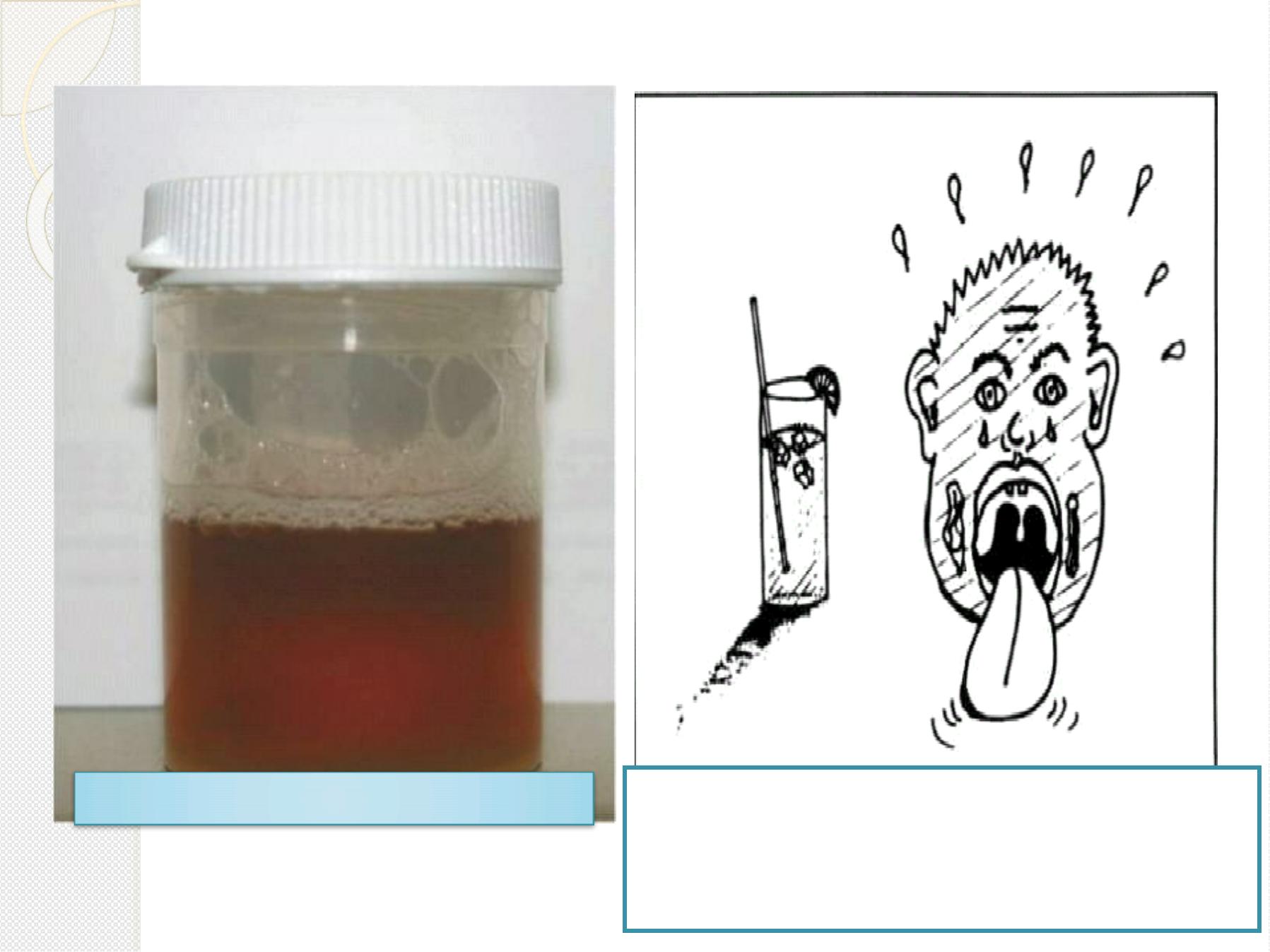
Tea colored urine
Acu t e p ost - st rept o coccal
g lom eru lon ep hr it is
cau ses Coca- Co la co lo red u r in e
( hem at u r ia) an d p u f f y f ace
Treatment
—
All S pyogenes
are susceptible to
penicillin G
,
and most are susceptible to
ery throm y cin
.
Some are resistant to tetracyclines.
—
Antimicrobial drugs have
no effect
on established
glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever.
—
In acute streptococcal infections, however, every
effort must be made to
rapid ly erad icate
streptococci
from the patient, eliminate the
antigenic stimulus (before day 8), and thus
prevent poststreptococcal disease.

Prevention, & Control
—
Detection and early antimicrobial therapy of
respiratory and skin infections with group A
streptococci. This requires maintenance of adequate
penicillin levels in tissues for 10 days
—
Antistreptococcal chemoprophylaxis in persons who
have suffered an attack of rheumatic fever.
—
Eradication of S pyogenes from carriers. This is
especially important when carriers are in areas such as
obstetric delivery rooms, operating rooms, classrooms,
or nurseries.

Quiz: T or F
—
Streptococci are Gram +ve cocci arranged in
chains.
—
All streptococci are beta hemolytic.
—
S.pyogenes classified according to N-protein.
—
S.pyogenes causes rheumatic fever within 72
hours of skin infections.
—
Acute S.pyogenes pharyngotonsillitis should be
rapidly eradicated from the patient to prevent
post-strepto complication.
Specimens
Direct Gram’
s
Slide
Culture
Biochemical
Serology
Antibiotics
sensitivity
L
L
a
a
b
b
o
o
r
r
a
a
t
t
o
o
r
r
y
y
D
D
i
i
a
a
g
g
n
n
o
o
s
s
t
t
i
i
c
c
s
s
t
t
e
e
p
p
s
s

Lab dx.:
—
S
S
p
p
e
e
c
c
i
i
m
m
e
e
n
n
s
s: sputum, throat swab, nasopharyngeal swab,
blood, CSF…etc.
—
G
G
r
r
a
a
m
m
s
s
t
t
a
a
i
i
n
n: G+ve cocci, arrange in chains.
—
C
C
u
u
l
l
t
t
u
u
r
r
e
e
:
: on blood agar àpinpointed, Grayish white,
translucent, matte or glossy colonies with large zone of β
-
hemolysis.
—
B
B
a
a
c
c
i
i
t
t
r
r
a
a
c
c
i
i
n
n
d
d
i
i
s
s
c
c (0.04 U) à sensitive àcauses zone of
growth inhibition.
—
P
P
Y
Y
R
R
+
+
v
v
e
e
:
: rapid test,
p
p
i
i
n
n
k
k is positive.
—
S
S
e
e
r
r
o
o
l
l
o
o
g
g
y
y:
1)
The rapid strep test (ELISA-based).
2)
Lancefield grouping, M-protein serotyping.
3)
ASO test (Antistreptolysin-O test): measure Ab titer.
ASO te st:
—
Measure Ab against Streptolysin O
—
ASO test used in suspected case of rheumatic
fever.
—
This test used to
determine significance of current
streptococcal infection
by measuring the
A
A
S
S
O
O
T
T
:
—
ASOT (Ab Titer):
N
N
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
l
l
<
<
2
2
0
0
0
0
>
>
s
s
i
i
g
g
n
n
i
i
f
f
i
i
c
c
a
a
n
n
c
c
e
e
r
r
e
e
s
s
u
u
l
l
t
t
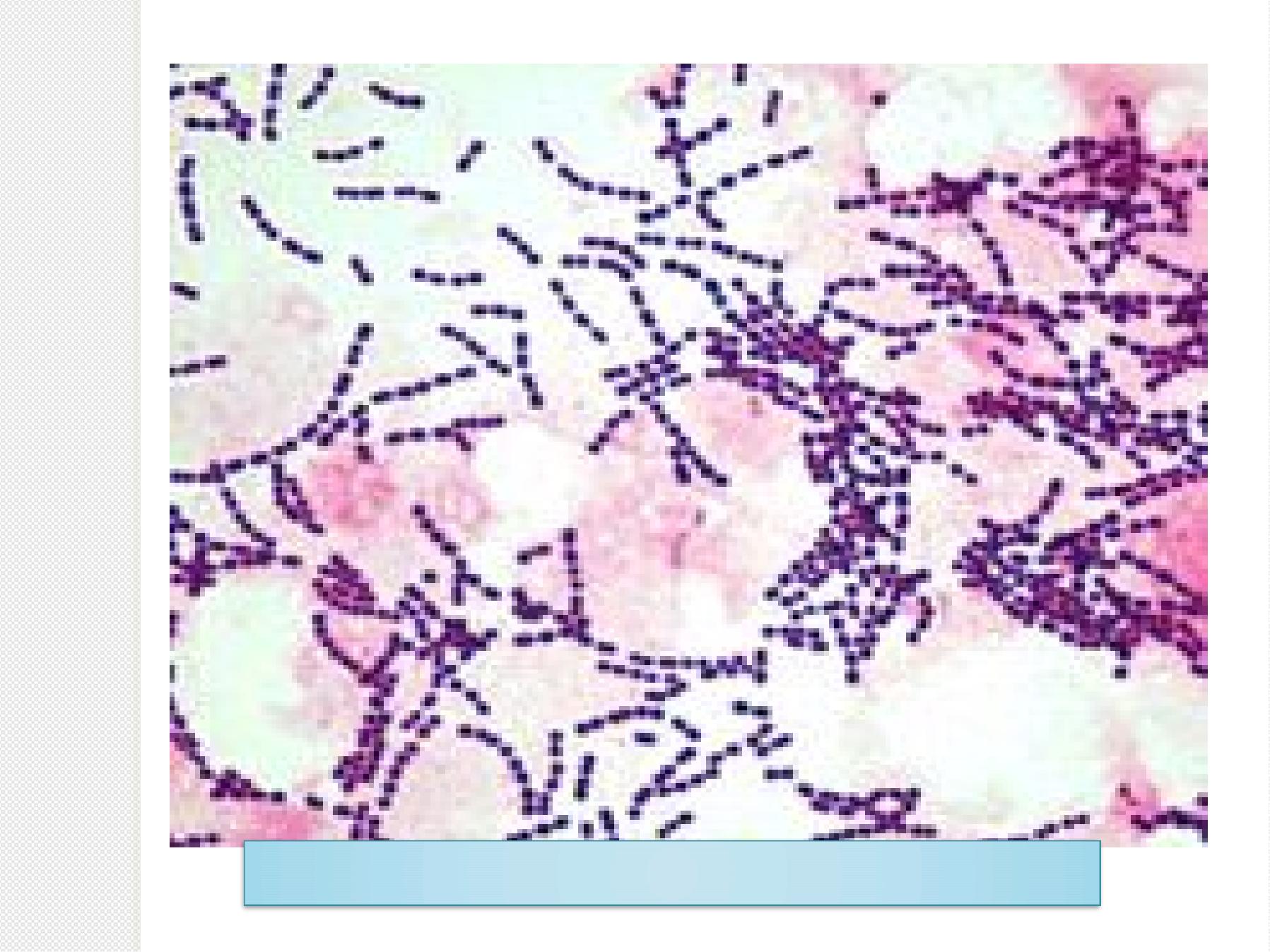
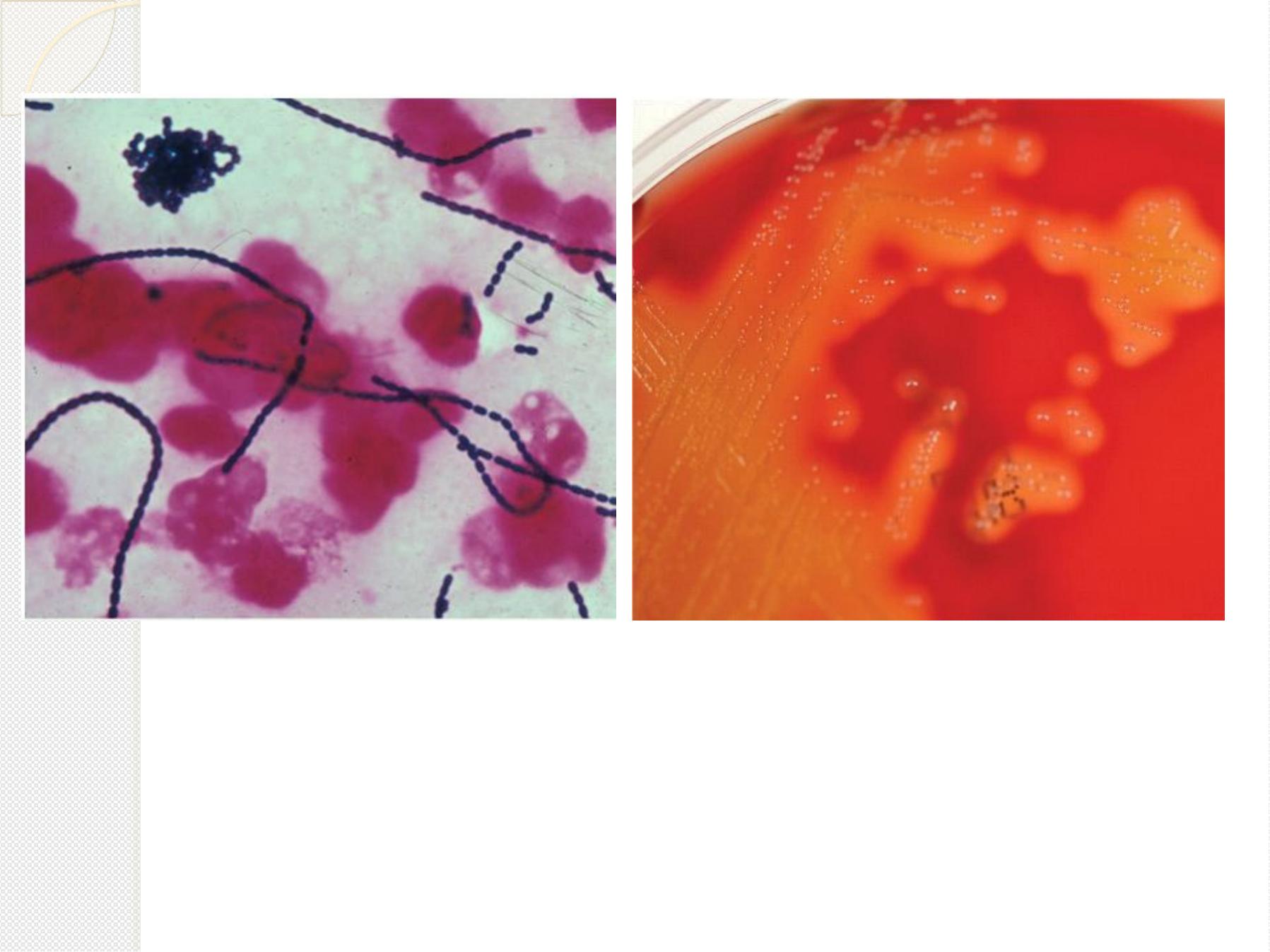
Gram stain: G+ve cocci, arrange in chains.
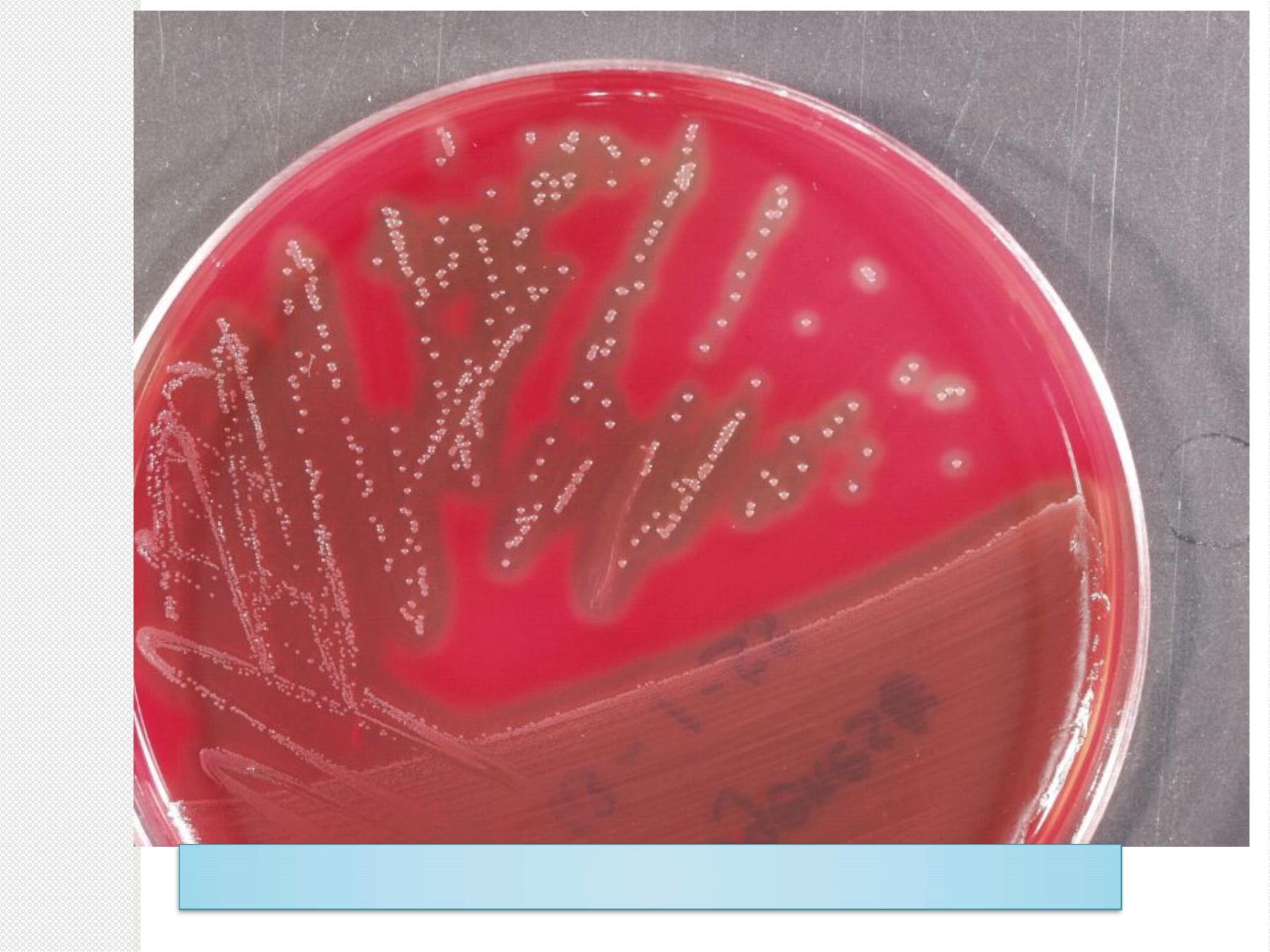
S
S
.
.
p
p
y
y
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
e
e
s
s
o
o
n
n
b
b
l
l
o
o
o
o
d
d
a
a
g
g
a
a
r
r
(
(
b
b
e
e
t
t
a
a
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
)
)
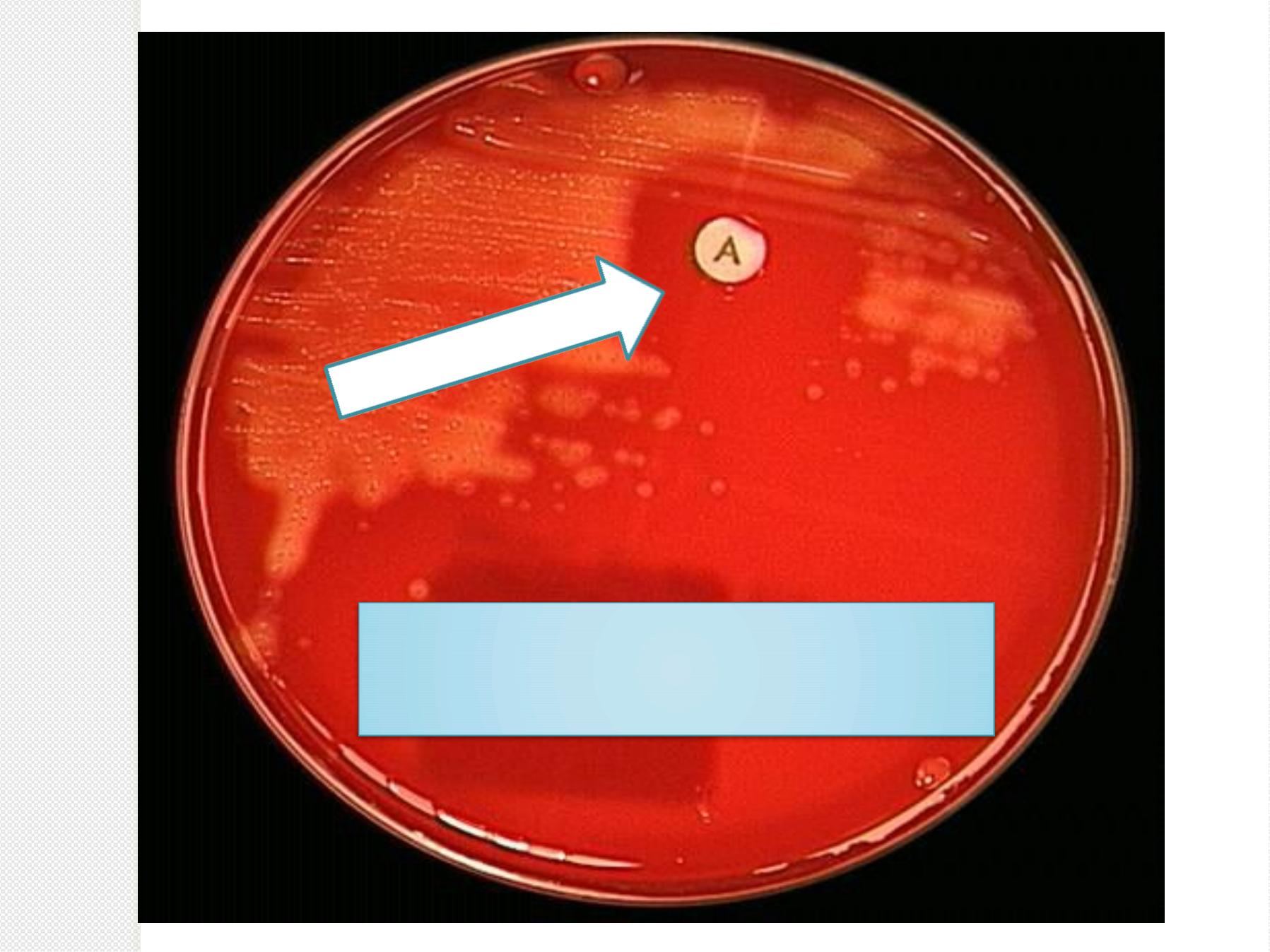
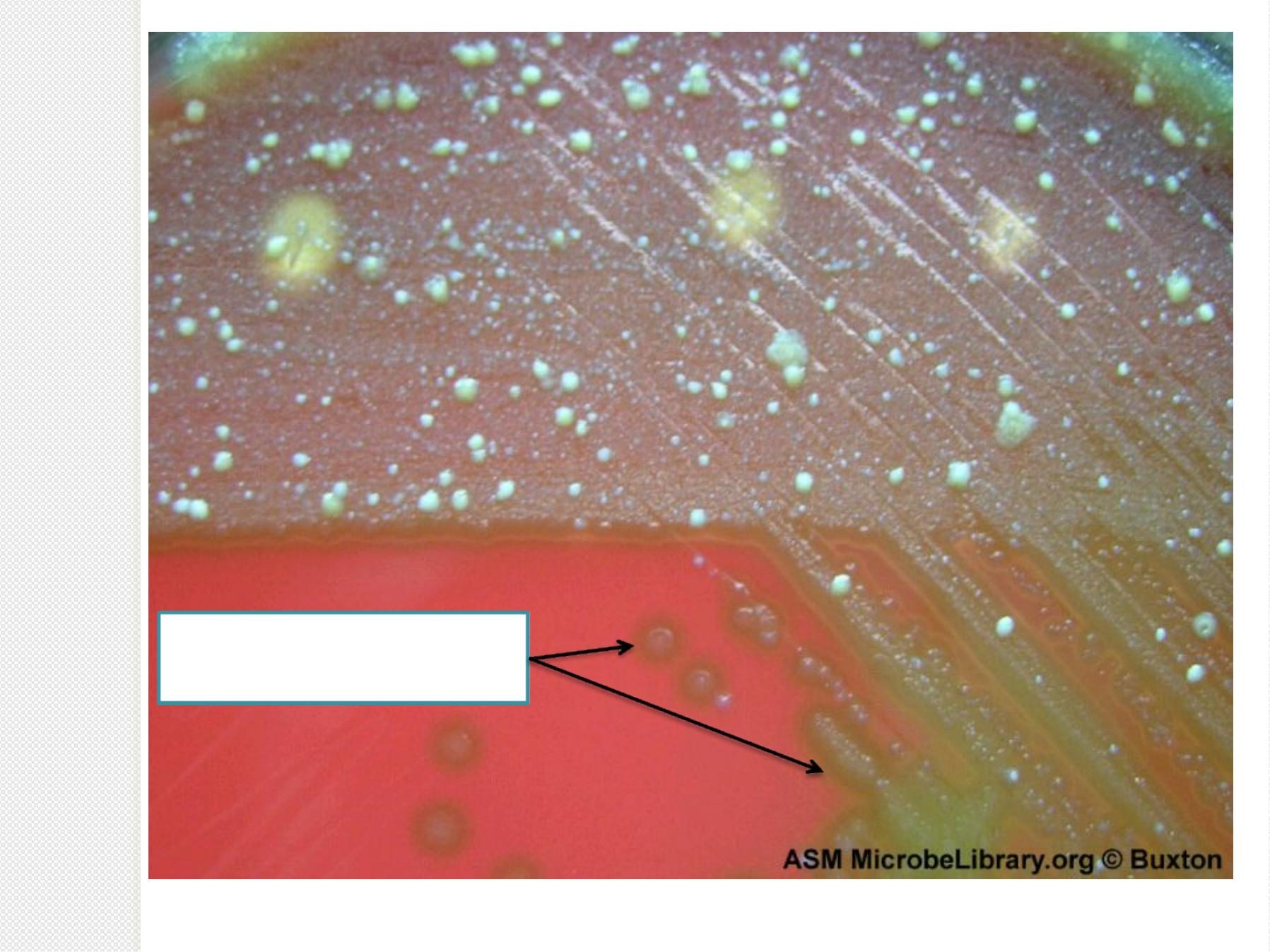
Bacitracin-disk-test-for-
Streptococcus-pyogenes
Zon
e of
inhi
bitio
n
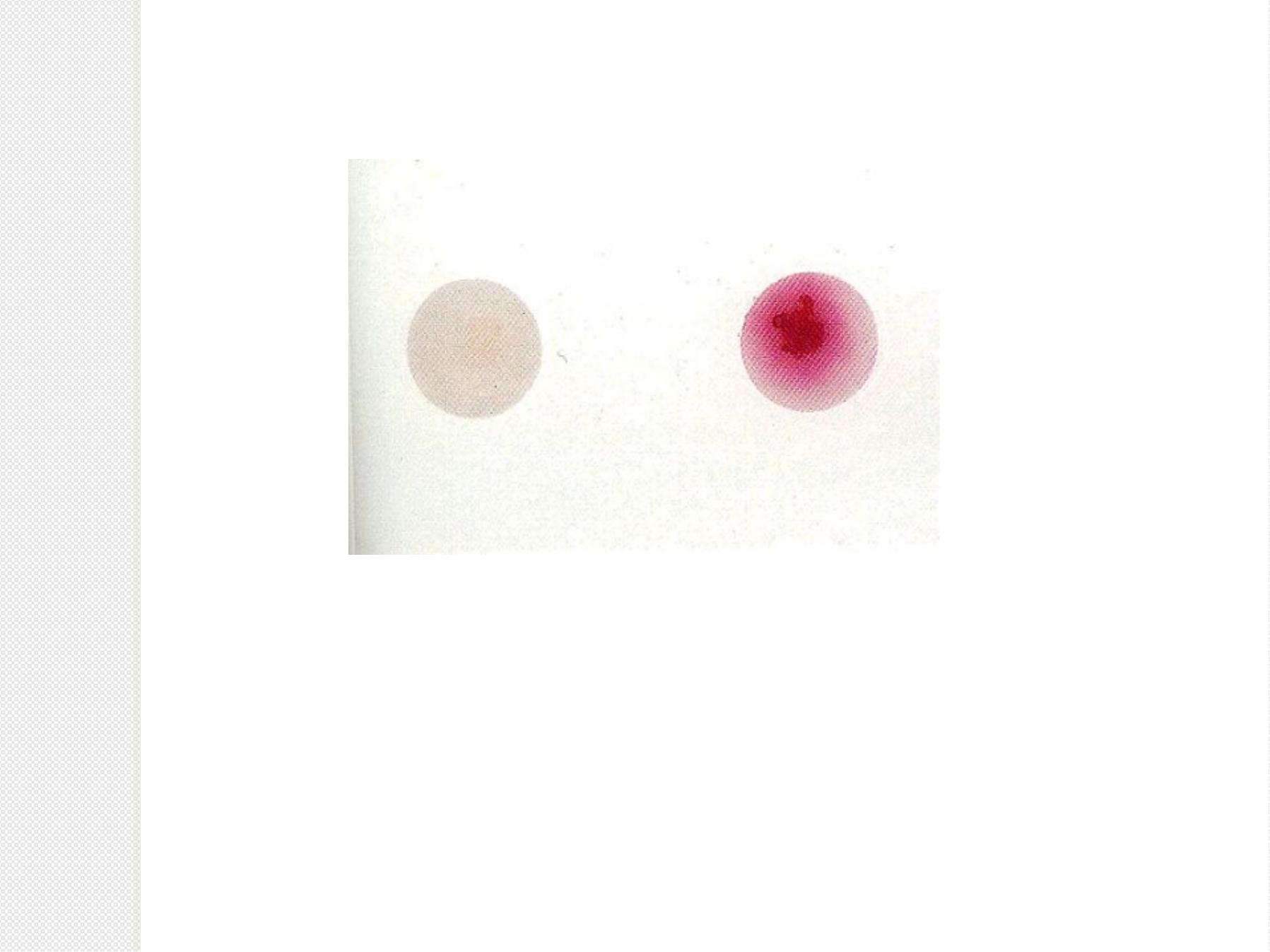
P
P
Y
Y
R
R
t
t
e
e
s
s
t
t
+
S
S
.
.
a
a
g
g
a
a
l
l
a
a
c
c
t
t
i
i
a
a
(
(
G
G
r
r
o
o
u
u
p
p
B
B
β
β
-
-
h
h
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
t
t
i
i
c
c
)
)
:
:
N
N
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
l
l
f
f
l
l
o
o
r
r
a
a
o
o
f
f
f
f
e
e
m
m
a
a
l
l
e
e
g
g
e
e
n
n
i
i
t
t
a
a
l
l
t
t
r
r
a
a
c
c
t
t
(
(
1
1
5
5
-
-
2
2
0
0
%
%
o
o
f
f
w
w
o
o
m
m
a
a
n
n
)
)
,
,
m
m
a
a
l
l
e
e
u
u
r
r
e
e
t
t
h
h
r
r
a
a
&
&
GIT.
L
L
e
e
a
a
d
d
i
i
n
n
g
g
C
C
a
a
u
u
s
s
e
e
f
f
o
o
r
r
n
n
e
e
o
o
n
n
a
a
t
t
a
a
l
l
s
s
e
e
p
p
s
s
i
i
s
s
,
,
p
p
n
n
e
e
u
u
m
m
o
o
n
n
i
i
a
a
&
&
m
m
e
e
n
n
i
i
n
n
g
g
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
.
.
(
acquire these bacteria during delivery
).
B
B
a
a
c
c
i
i
t
t
r
r
a
a
c
c
i
i
n
n
r
r
e
e
s
s
i
i
s
s
t
t
a
a
n
n
t
t
,
,
P
P
Y
Y
R
R
-
-
V
V
E
E
H
H
y
y
d
d
r
r
o
o
l
l
y
y
z
z
e
e
s
s
h
h
i
i
p
p
p
p
u
u
r
r
a
a
t
t
e
e
.
.
(
(
p
p
u
u
r
r
p
p
l
l
e
e
c
c
o
o
l
l
o
o
r
r
)
)
c
c
A
A
M
M
P
P
t
t
e
e
s
s
t
t
-
-
p
p
o
o
s
s
i
i
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
p
p
r
r
o
o
d
d
u
u
c
c
e
e
s
s
d
d
e
e
f
f
i
i
n
n
i
i
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
a
a
r
r
r
r
o
o
w
w
w
w
h
h
e
e
n
n
c
c
l
l
o
o
s
s
e
e
t
t
o
o
S
S
t
t
a
a
p
p
h
h
y
y
l
l
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
u
u
s
s
a
a
u
u
r
r
e
e
u
u
s
s
.
.
D
ia
g
n
o
st
ic
fe
a
tu
re
s
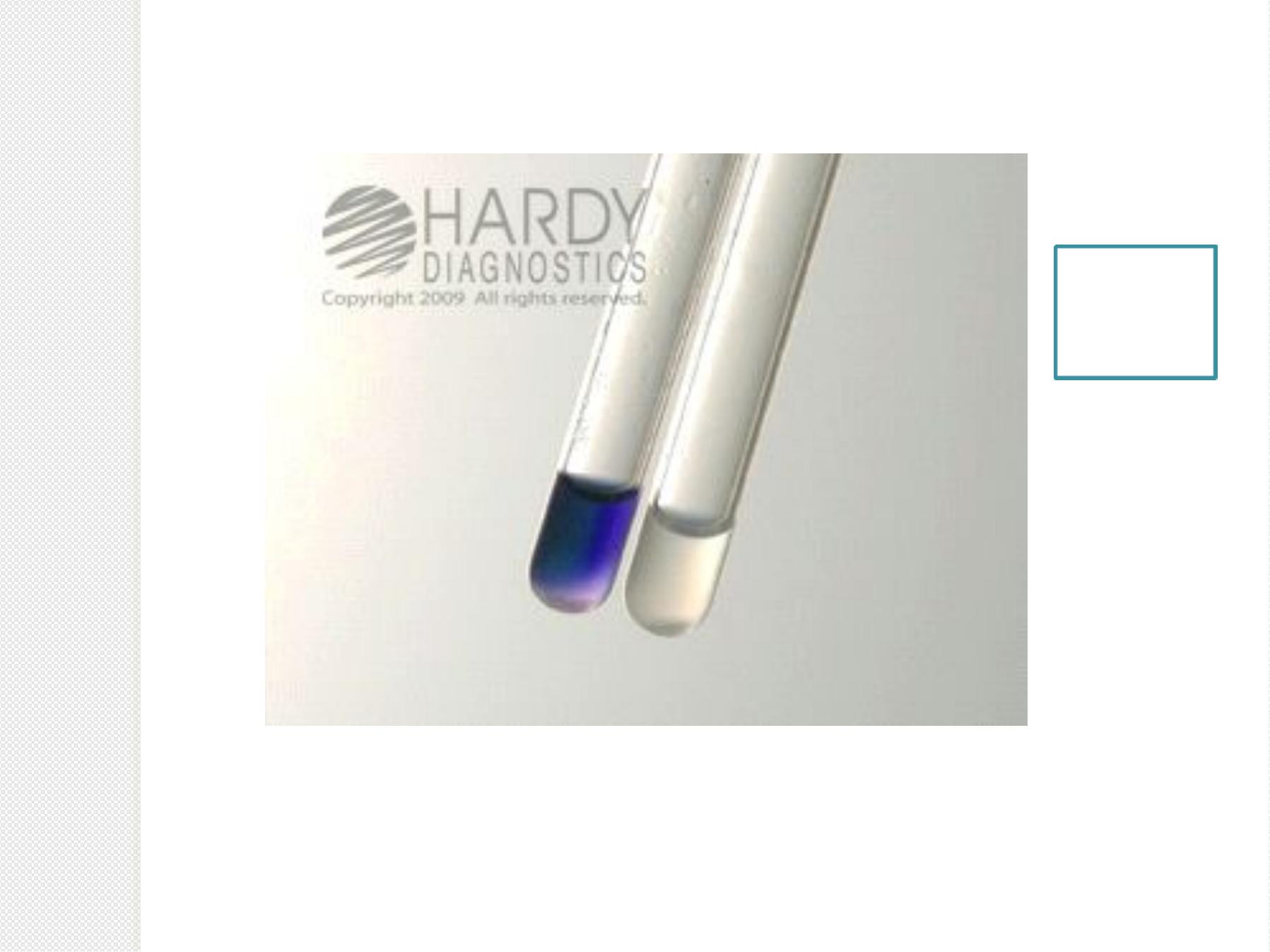

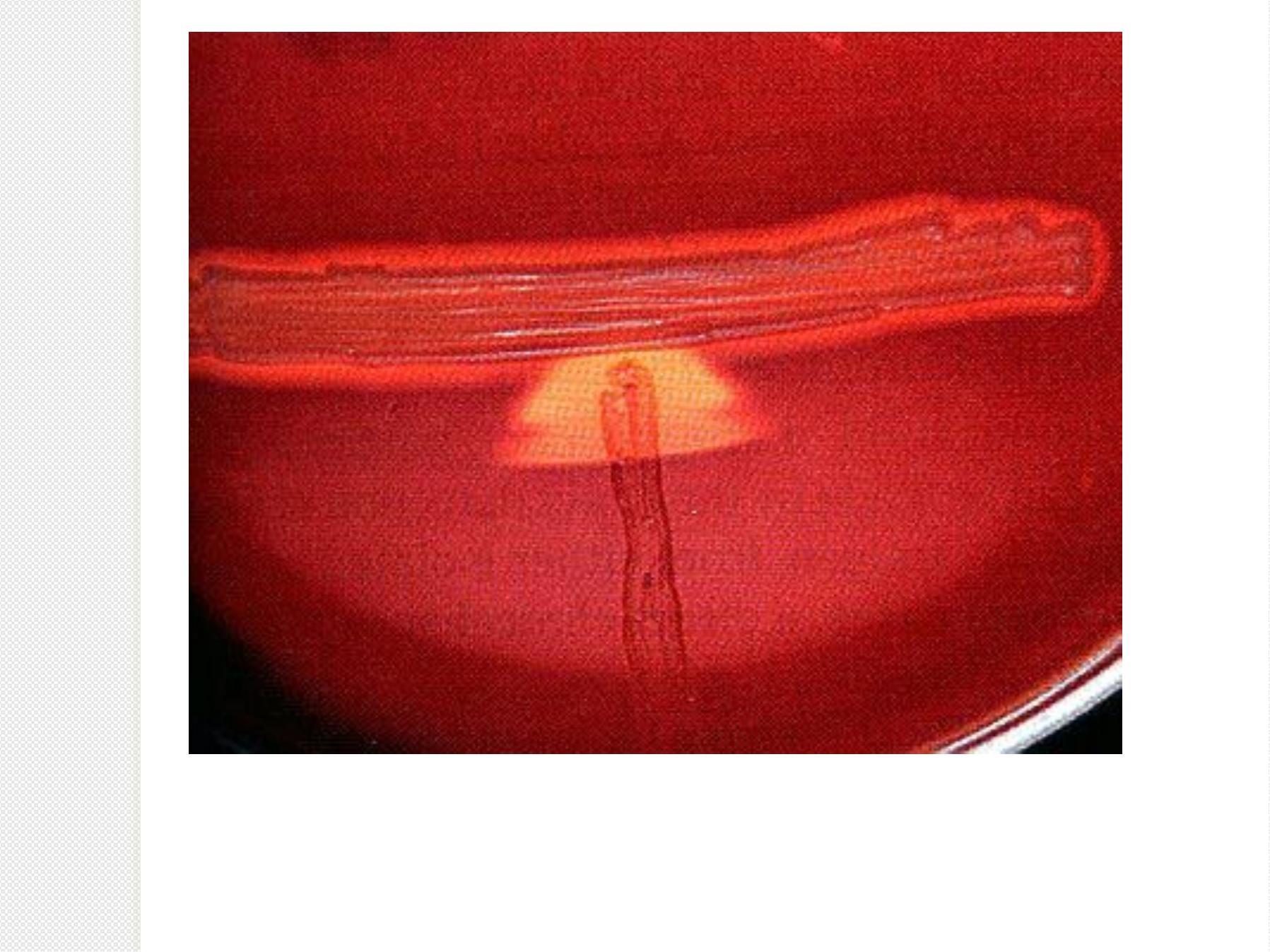
Hippurate Hy d roly ses
ﻟﻼﻃﻼ
ﻉ
c
c
A
A
M
M
P
P
t
t
e
e
s
s
t
t
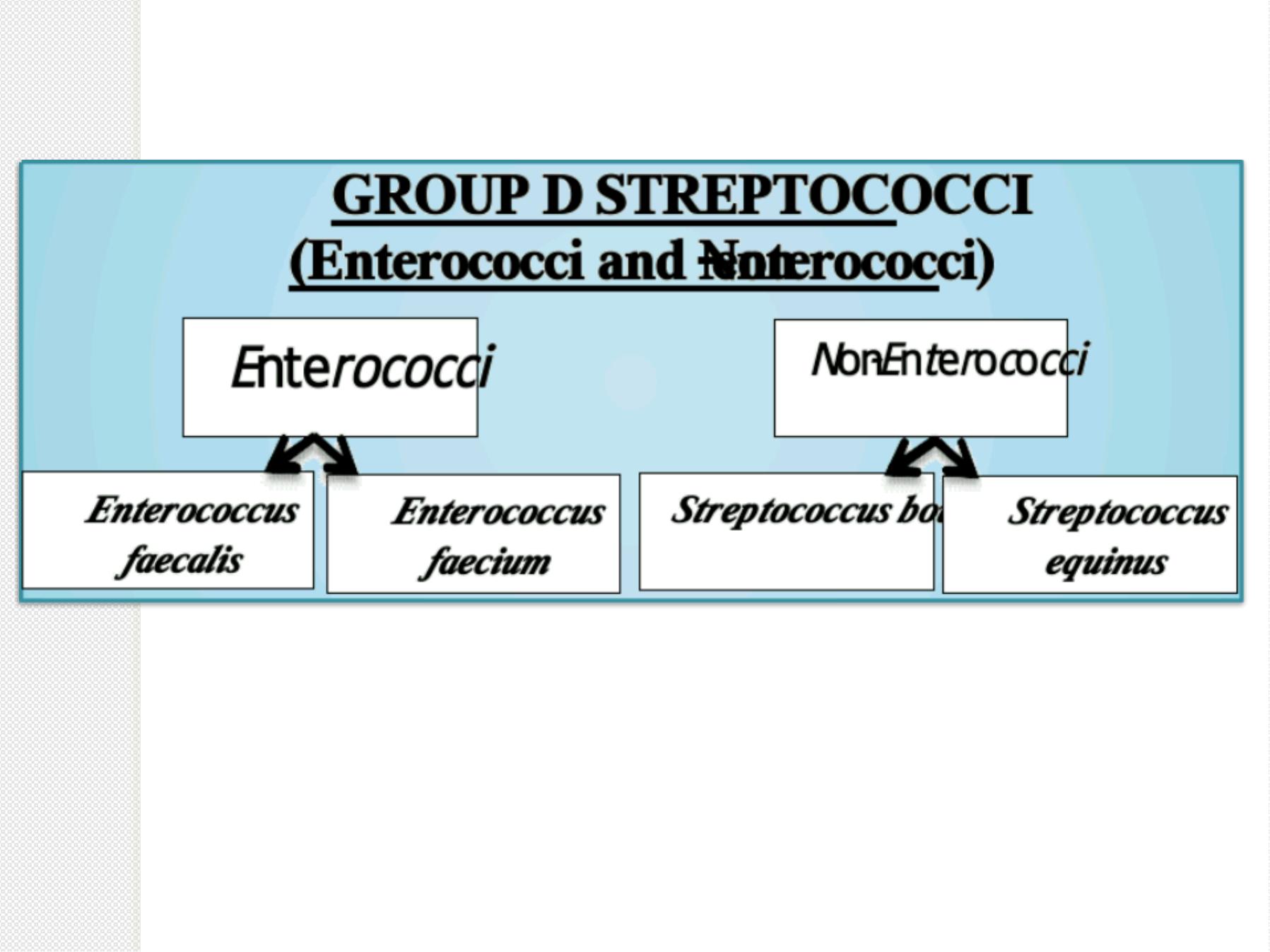

E
E
n
n
t
t
e
e
r
r
o
o
c
c
o
o
c
c
c
c
u
u
s
s
(
(
E
E
.
.
f
f
a
a
e
e
c
c
a
a
l
l
i
i
s
s
,
,
E
E
.
.
f
f
a
a
e
e
c
c
i
i
u
u
m
m
)
)
N
N
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
l
l
f
f
l
l
o
o
r
r
a
a
o
o
f
f
G
G
I
I
T
T
,
,
o
o
r
r
a
a
l
l
m
m
u
u
c
c
o
o
s
s
a
a
C
C
a
a
u
u
s
s
e
e
s
s
U
U
T
T
I
I
,
,
b
b
i
i
l
l
i
i
a
a
r
r
y
y
t
t
r
r
a
a
c
c
t
t
i
i
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
,
w
w
o
o
u
u
n
n
d
d
i
i
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
,
,
b
b
e
e
d
d
s
s
o
o
r
r
e
e
,
,
e
e
n
n
d
d
o
o
c
c
a
a
r
r
d
d
i
i
t
t
i
i
s
s
.
.
V
V
a
a
r
r
i
i
e
e
s
s
H
H
e
e
m
m
o
o
l
l
y
y
s
s
i
i
s
s
P
P
Y
Y
R
R
+
+
v
v
e
e
H
H
Y
Y
D
D
R
R
O
O
L
L
Y
Y
Z
Z
E
E
S
S
E
E
S
S
C
C
U
U
L
L
I
I
N
N
i
i
n
n
4
4
0
0
%
%
b
b
i
i
l
l
e
e
a
a
n
n
d
d
6
6
.
.
5
5
%
%
N
N
a
a
C
C
l
l
(
(
b
b
i
i
l
l
e
e
e
e
s
s
c
c
u
u
l
l
i
i
n
n
a
a
g
g
a
a
r
r
t
t
u
u
r
r
n
n
s
s
b
b
l
l
a
a
c
c
k
k
)
)
.
.
Vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE)
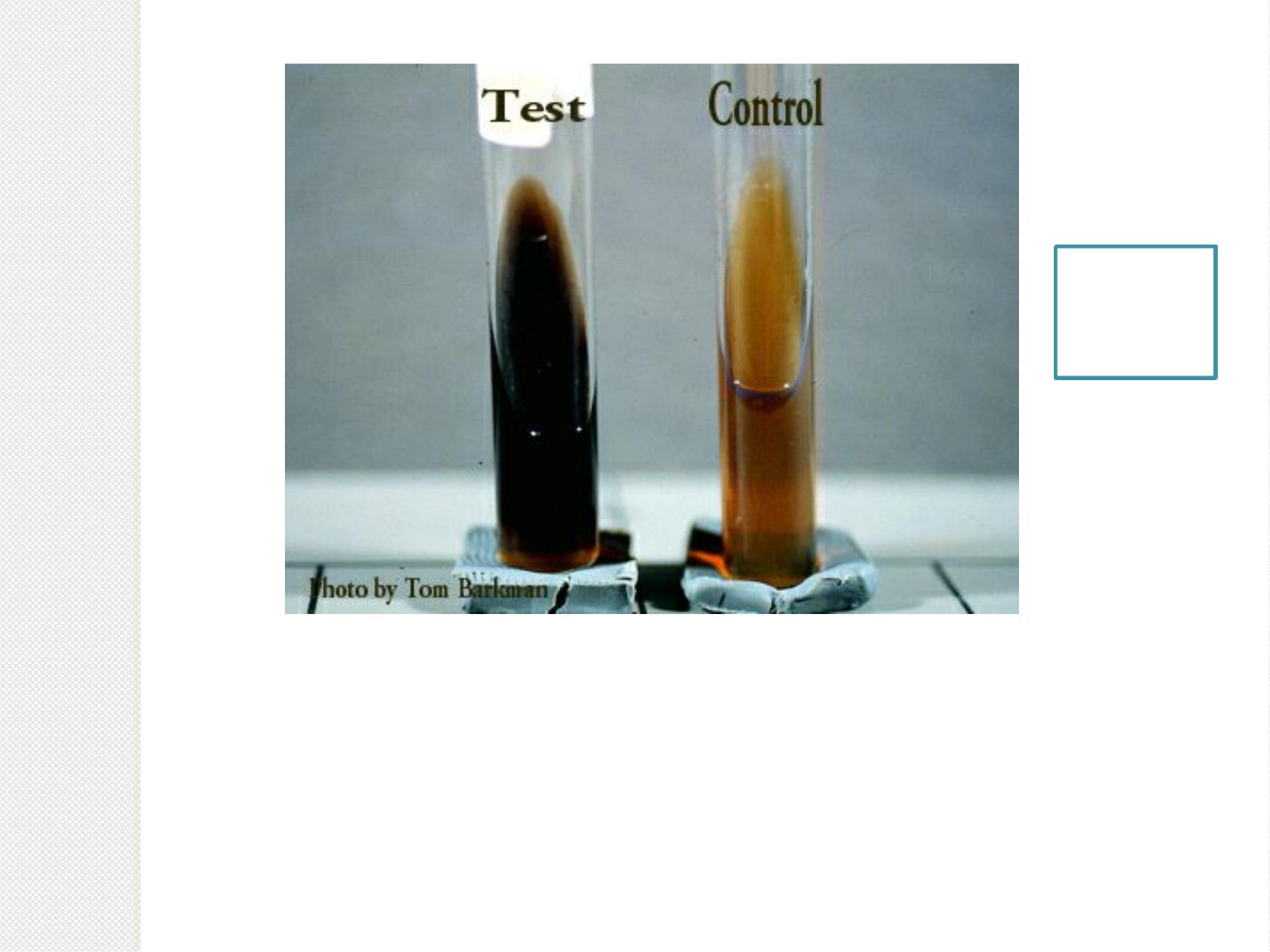

B
B
I
I
L
L
E
E
E
E
S
S
C
C
U
U
L
L
I
I
N
N
t
t
e
e
s
s
t
t
ﻟﻼﻃﻼ
ﻉ

Non-enterococcus
(Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus equinus ):
Like the enterococci, Streptococcus bovis is hardy,
growing in 40% bile (but not in 6.5% NaCl).
It lives in the G.I. tract, and it causes similar diseases.
Remarkable association between S. bovis infection
and colon cancer
Question?
Differentiate between Group B & Group A
Streptococci?
Q
Q
u
u
e
e
s
s
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
?
?
Give 2 organisms with PYR test positive.

summary
•
St rep tococci classified according to t he t ype of he molys is &
antigenic components .
•
S.pyogenes is the mo st pathoge nic spe cie s be cause of their
virulent factors.
•
S.pyogenes can cause post-infection se vere complications .
•
ASO test used in suspected case of rheumatic fever.
•
Streptococci easily diagnos ed in the lab. By using Gram’
s
staining, culture and bioche mical tests.
•
S.agalactia is t he leading Cause for neonatal se psis, p ne umonia &
meningit is.
•
Enterococcus Cause s UTI, biliary tract infect ion, wound infectio n,
be d sore, e ndo carditis.
•
streptococci infe ctions can be prevented by regular hygiene
precautions and by antibiotics, no vaccine .

Clinical Questions
?
?
Q
Q
u
u
i
i
n
n
s
s
y
y
(
(
p
p
e
e
r
r
i
i
t
t
o
o
n
n
s
s
i
i
l
l
l
l
a
a
r
r
a
a
b
b
s
s
c
c
e
e
s
s
s
s
)
)
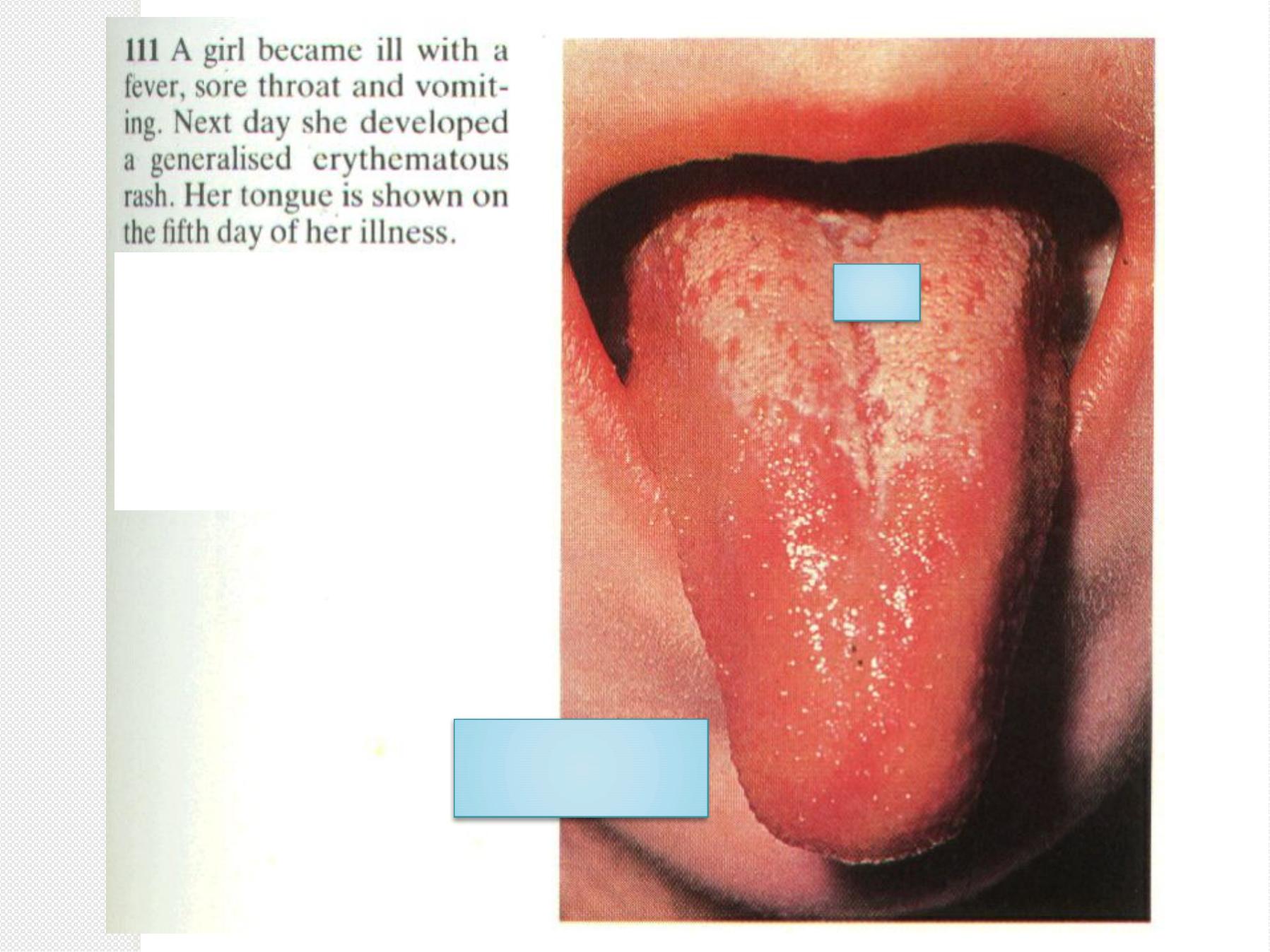
S
S
t
t
r
r
a
a
w
w
b
b
e
e
r
r
r
r
y
y
t
t
o
o
n
n
g
g
u
u
e
e
f
f
u
u
r
r

T
T
H
H
A
A
N
N
K
K
S
S
