Lecture 1
ORGANS & Cells OF
IMMUNE SYS.
Antigen Presenting Cells
Dr. Mohammed M. al Ani

OBJECTIVES ;
by the end of this lecture you will be able to
Define the
Primary (central) & the Secondary (peripheral)
Lymphoid organs
Asses the function of the thymus
Explain the T cell education
State the
Antigen Presenting Cells (APC)
Analyze the function of Ag presenting cell
Differentiate the Super Ag from other Ag
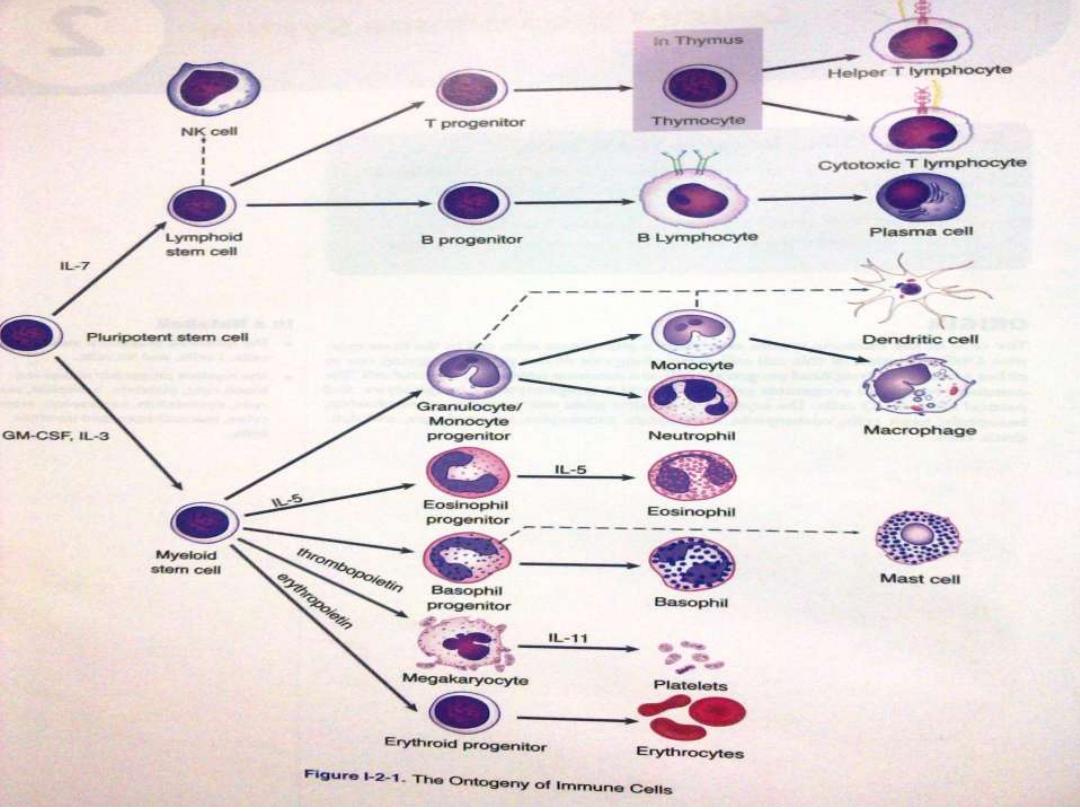
Stem cells originate from the
yalk sac
in the 1
st
6 wks of gestation
Then the
LIVER
for the next few month
Then the
BONE MARROW
will be resp. for origination &
proliferation of stem cells under control of diff, hormones
, enzymes & interleukin like IL3 ,
IL7
,MG CSF Macrophage
granulocyte colony stimulating factor
IL7
Stem cell
IL3
Lymphoid series
(Lymphocyte & Nk
cell)
MYELOID SERIE
(RBC Granulocyte
Monocyte)

Organs of Immune System
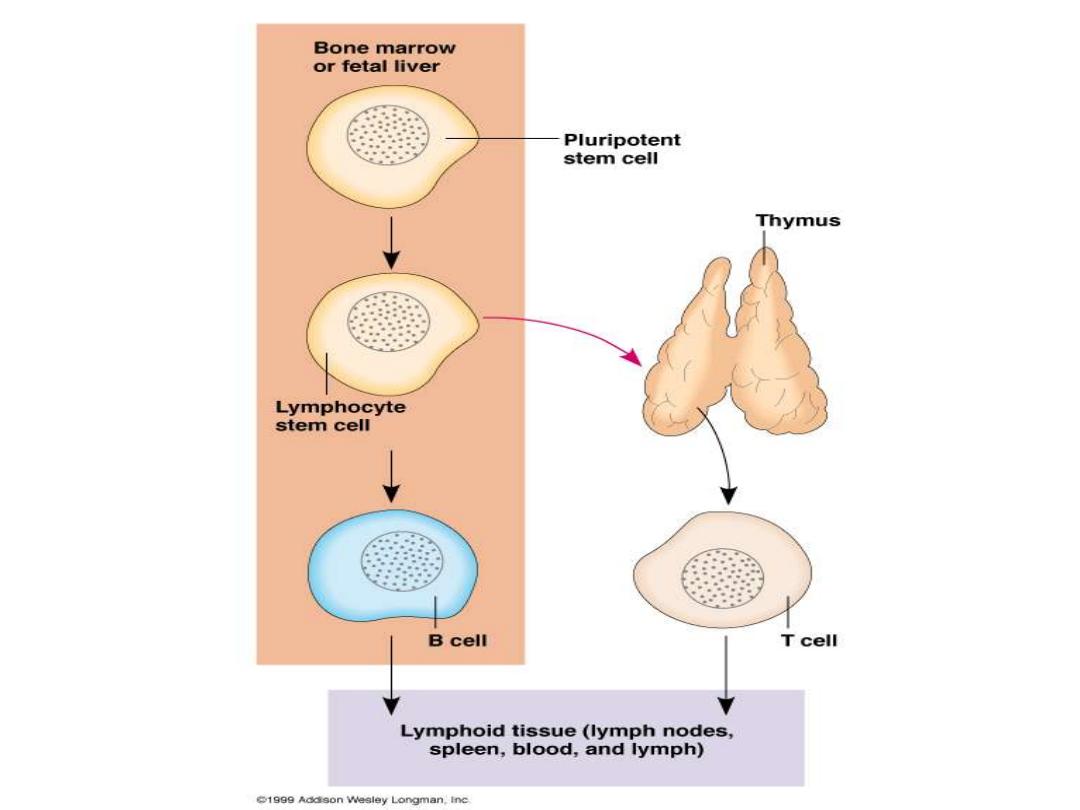
Primary (central)
Thymus
for T cells &
bone
marrow
for B cells
Site where lymphocyte
maturation
Secondary (peripheral) encapsulated (spleen &
lymph node) and Unencapsulated (Mucosa
associated lymphoid tissue M.A.L.T.)
Site
where Lymphocyte interact with Antigens &
other cells
Naïve (virgin ) lymphocyte
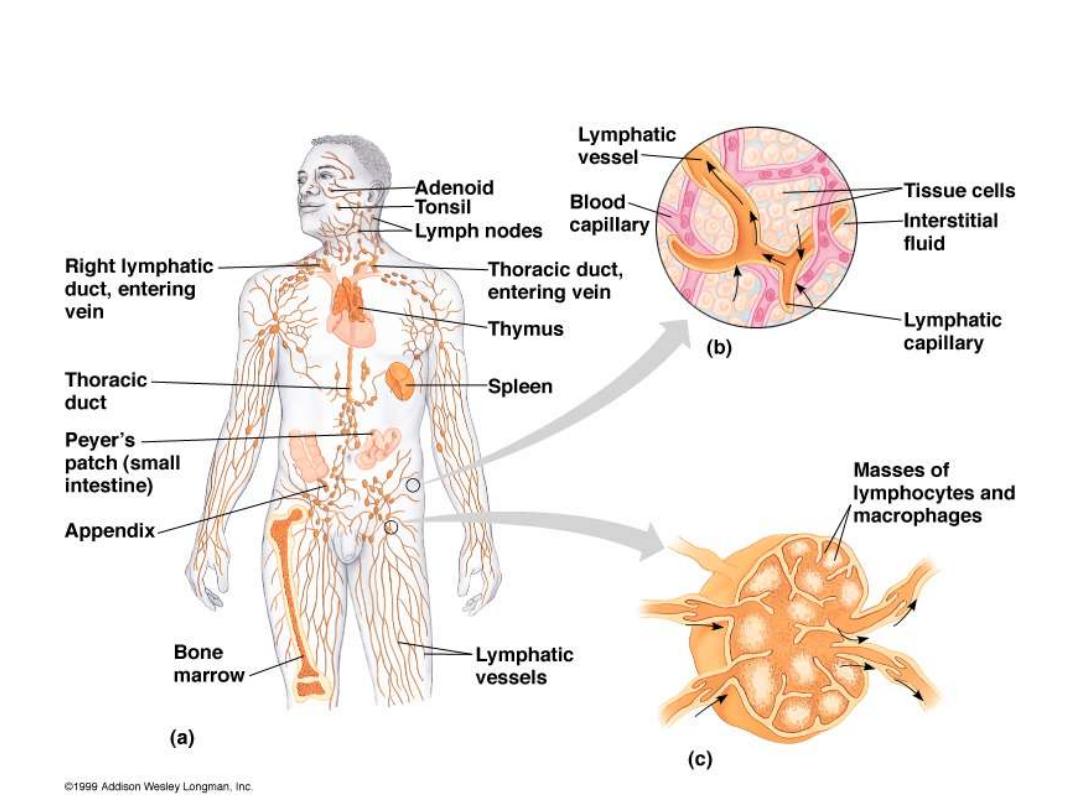
Components of Human Immune System

Thymus
2 lobs each with Cortex & medulla
T Lymphocyte Education
Cortex: T cells are Immature Highly dividing
,Highly dying (95%)die by Apoptosis because
Auto-reactive cells (
Negative selection
)
Medulla less dividing less dying cells , only that
recognize self MHC ( by CD4 or CD8 ) will
expand(
positive selection
)

Cells of the thymus
Epithelial cells
secrete thymic hormones as
thymopoietin ,Thymoline &Thymosine also
Enzymes as ADA(adenosine deaminase) & PNP
(purine necleoside phosphorylase) which help
in differentiation & maturation of Tcells
Inter –digitating dendritic cells
they are rich
in class II Ag & teach T cells how to deal with
an Ag

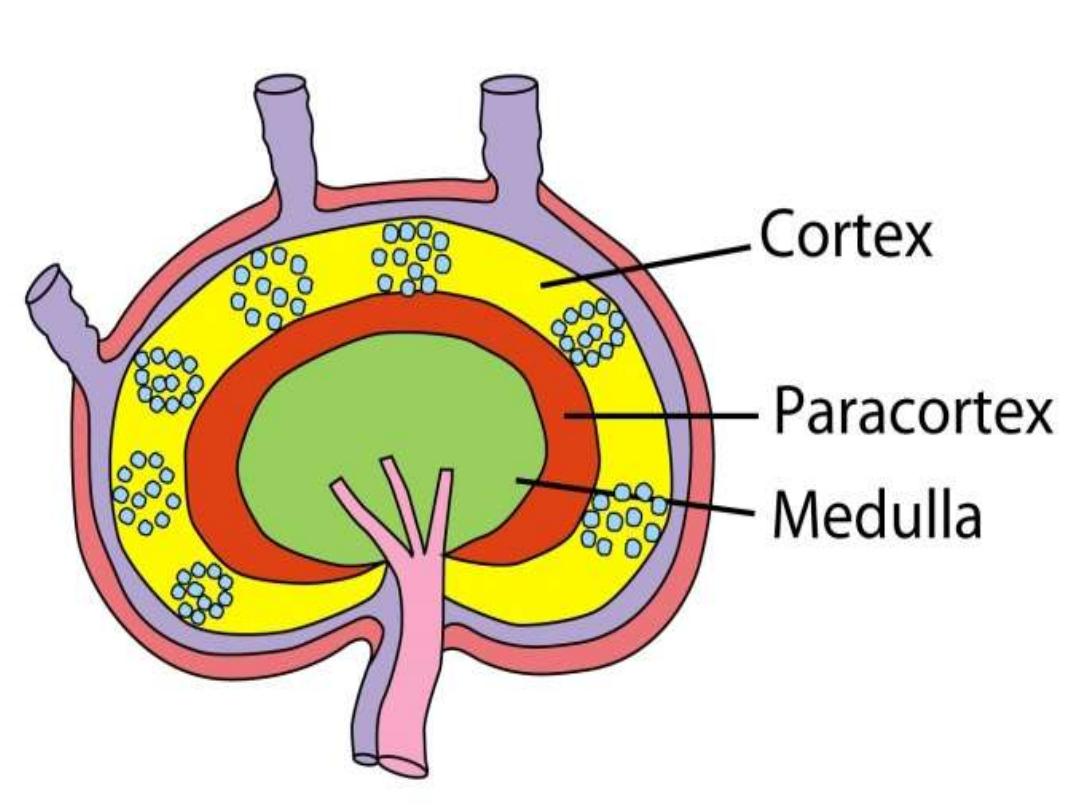
Lymph node
• Filters Ag from the lymph
Cortex containing aggregations of B
lymphocytes as a primary follicles after Ag
stimulation become secondary follicles
containing large dividing B lymphocytes ( blast
cells & plasma cells
Para cortex contains T lymphocytes

spleen
Red palp site where old RBCs are destroyed
White palp
surrounds the spleenic arteries
forming Peri-arteriolar lymphoid sheath (
area
for T lymphocytes)
Between red & white palp the
Marginal Zone
which is
( area for B lymphocytes)
Inter-digitating cells will take the
Blood born Ag
to the peri arteriolar
lymphoid sheath

ANTIGEN PRESENTIG CELL
(APC)
• Monocyte in the blood(1-6% of WBC) circulate
for 3 days Tissue as a Macrophage
Like alveolar cell,kupffer cell in the liver & glail
cell in the Brain where they live for months &
when activated they become APC where they
have B7 molecule & Class II MHC
Activation by
phagocytosis, Gamma-interferon &
cytokines from T helper cells as IL2,IL12
While IL 8 is a chemotactic

APC
Include(any cell have B7 mol.& class II MHC)
• Dendritic cells
• Inter-digitating cells
• B lymphocytes
• Macrophages
• Langerhans cell
They process the Ag & present it to T lymphocytes
with
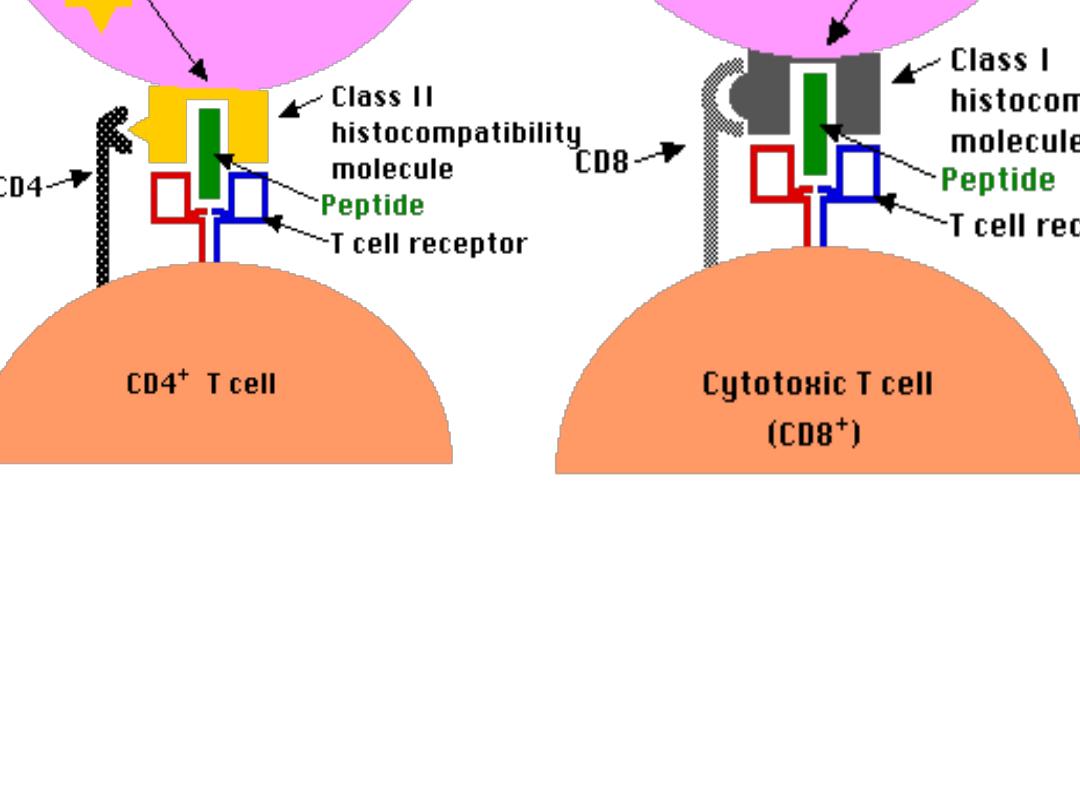
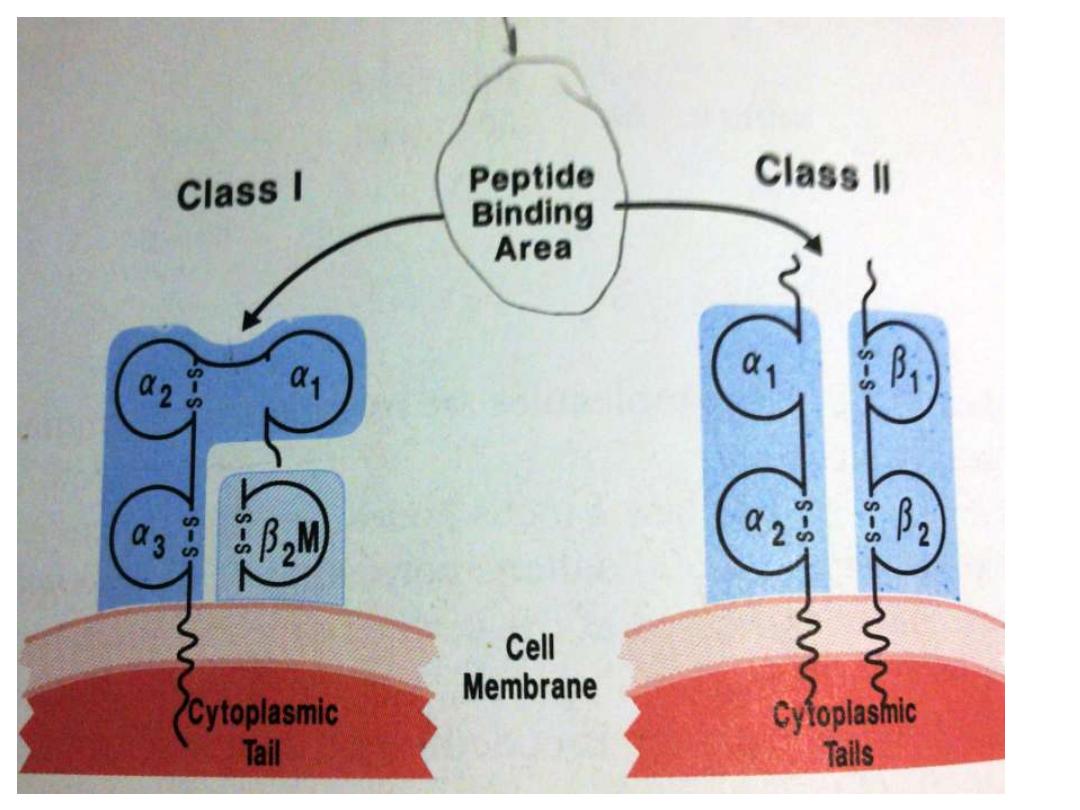
class I
for CD8+ cells or
Class II
for CD4+
cells
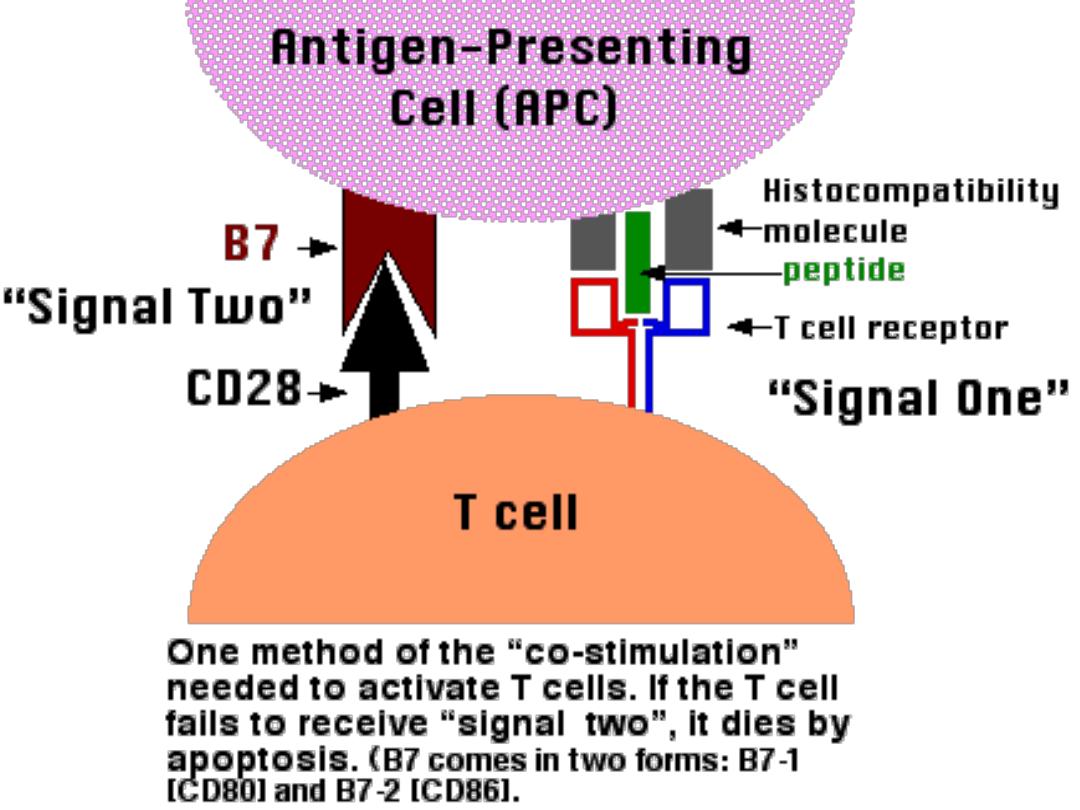
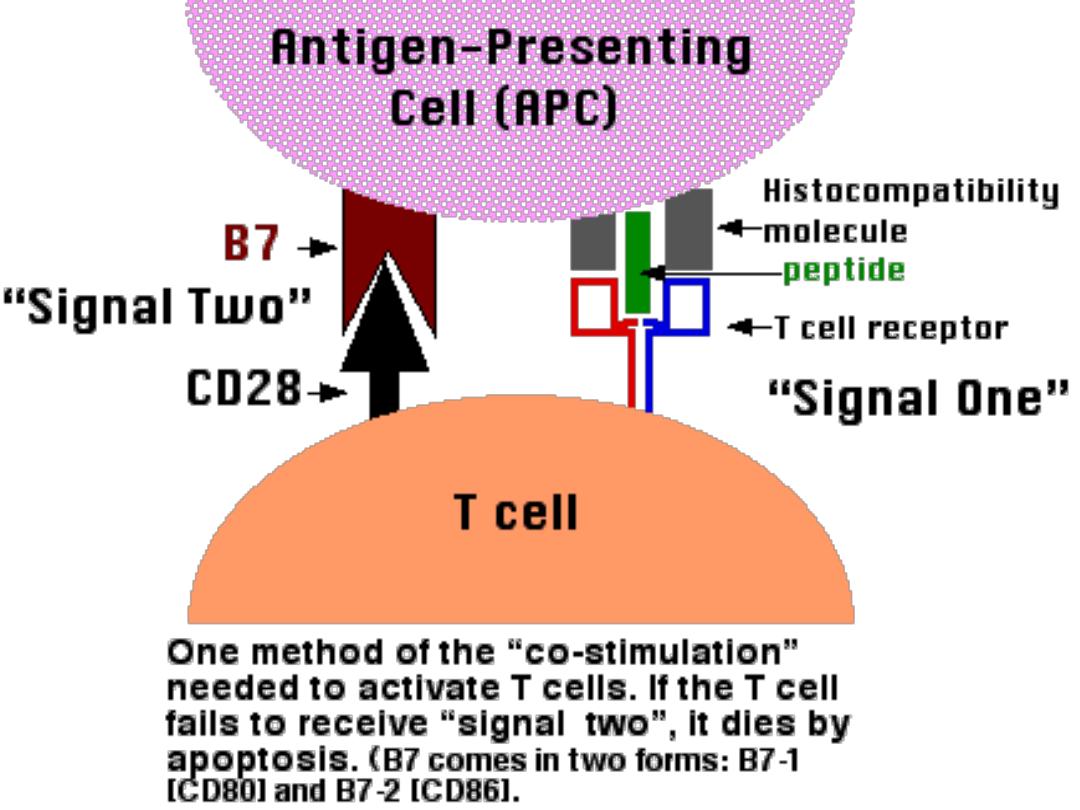
Also they deliver
B7 Mol
. To react with CD28 on T
helper cells

APC
APC secretes ;
• IL1, TNF, (both are endogenous
• pyrogen) also IL12 which activate T cells
•
IFN α ( Anti-virus)
• Hydrolytic Enz., nitric oxide H2O2 , Super
oxide
• Lysozyme

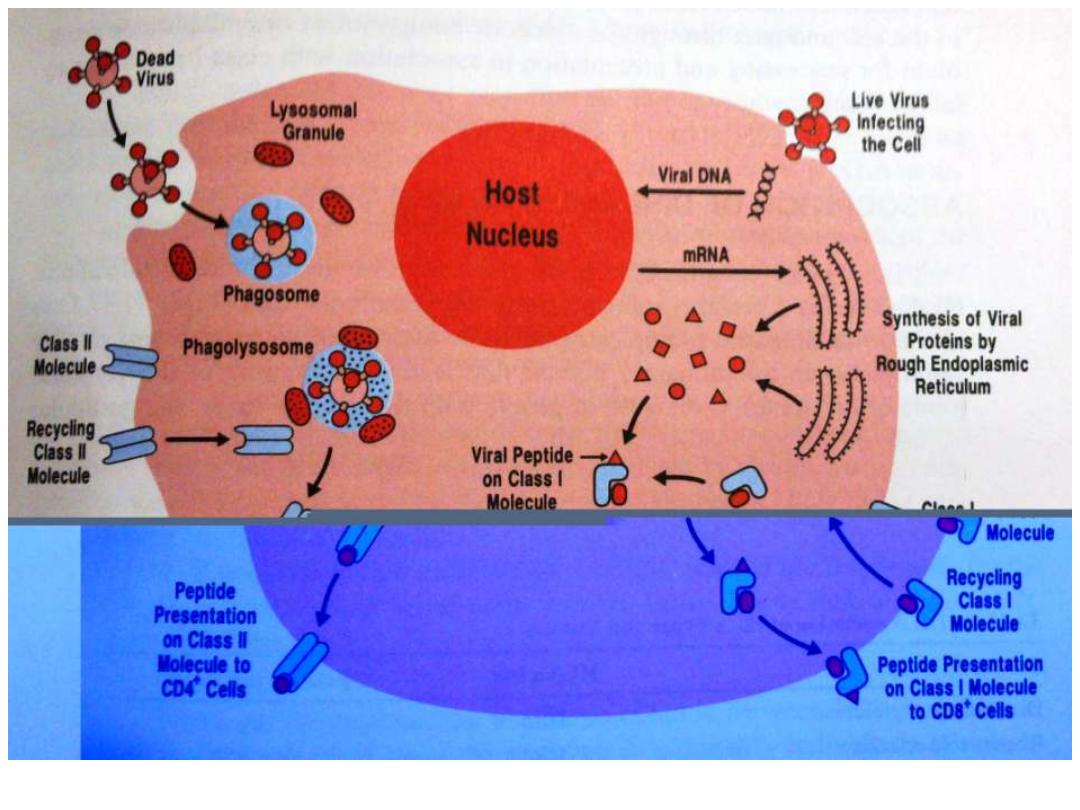
Functions of APC
-Identifications of Microbes (Ag) by
recognition
Recptor as TL R
-Engulfment (
Phagocytosis
) into phagosomes
-
Lysosomes
which are filled with digestive enz. Fuse
with phagosome to form
phagolysosome
Which will digest the Ag with
preserving
the Epitope
-
Presents
the epitope in the groove of MHC class I or
class II on their surface for CD8 &CD4
respectively in association with
B7
molecule
.
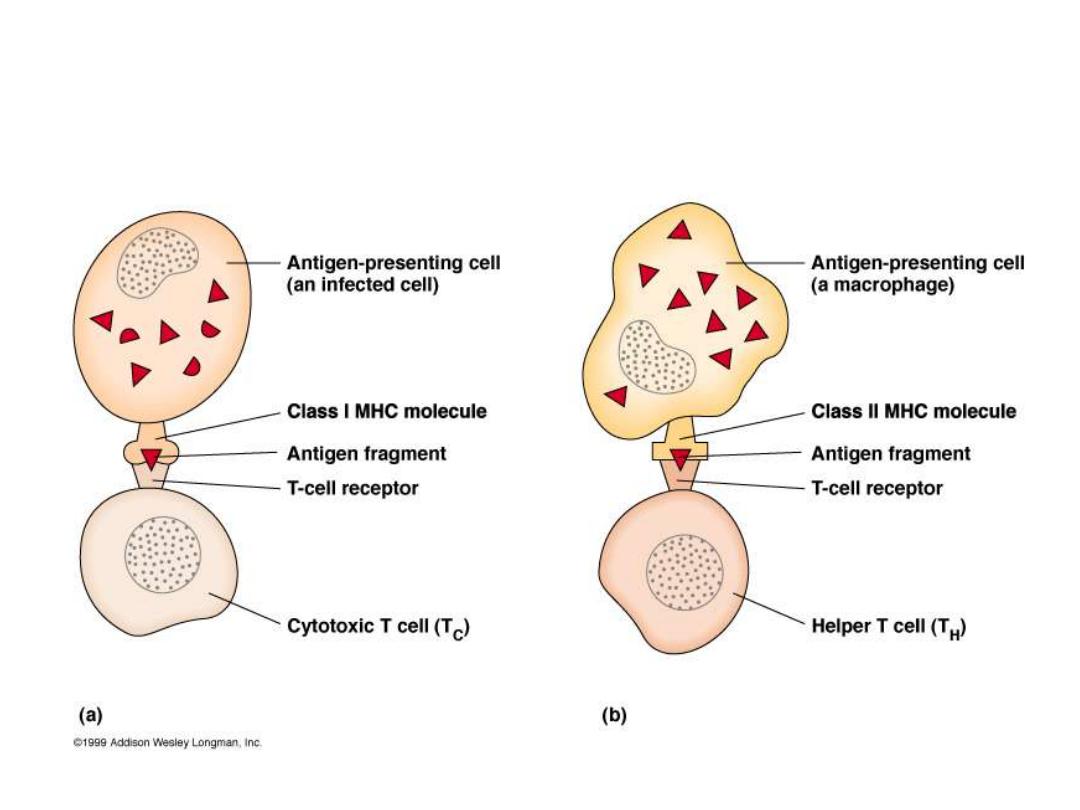
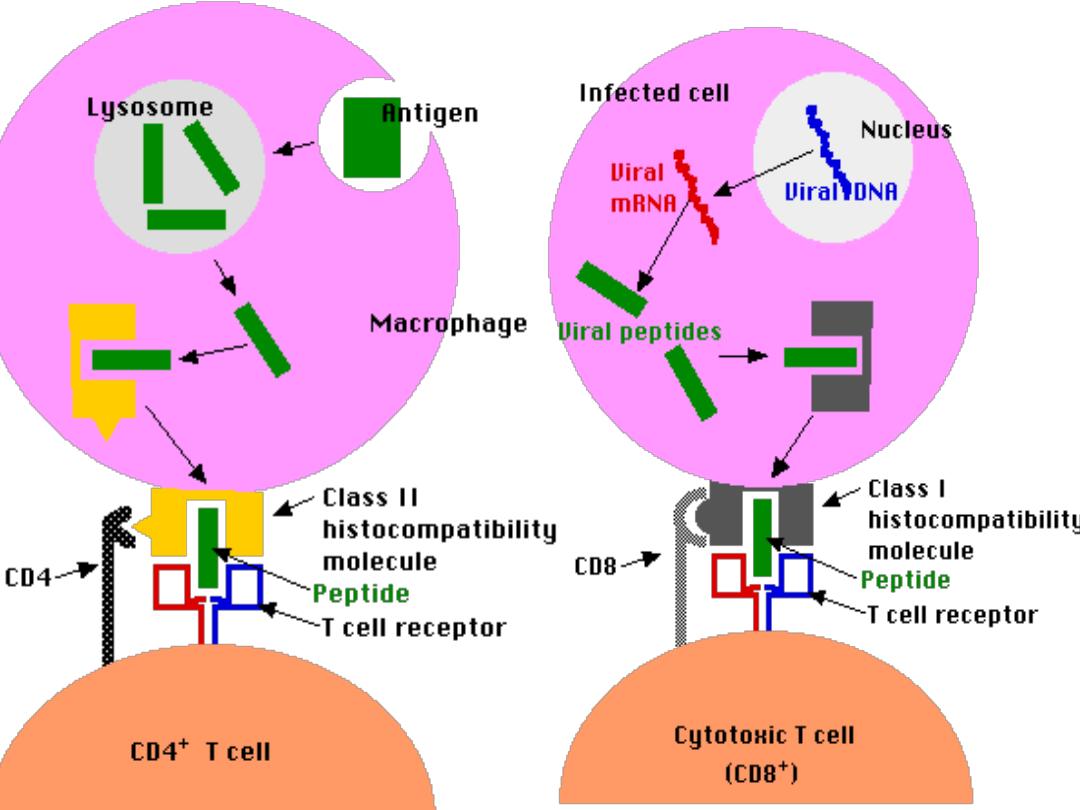
T Cells Only Recognize Antigen Associated
with MHC Molecules on Cell Surfaces
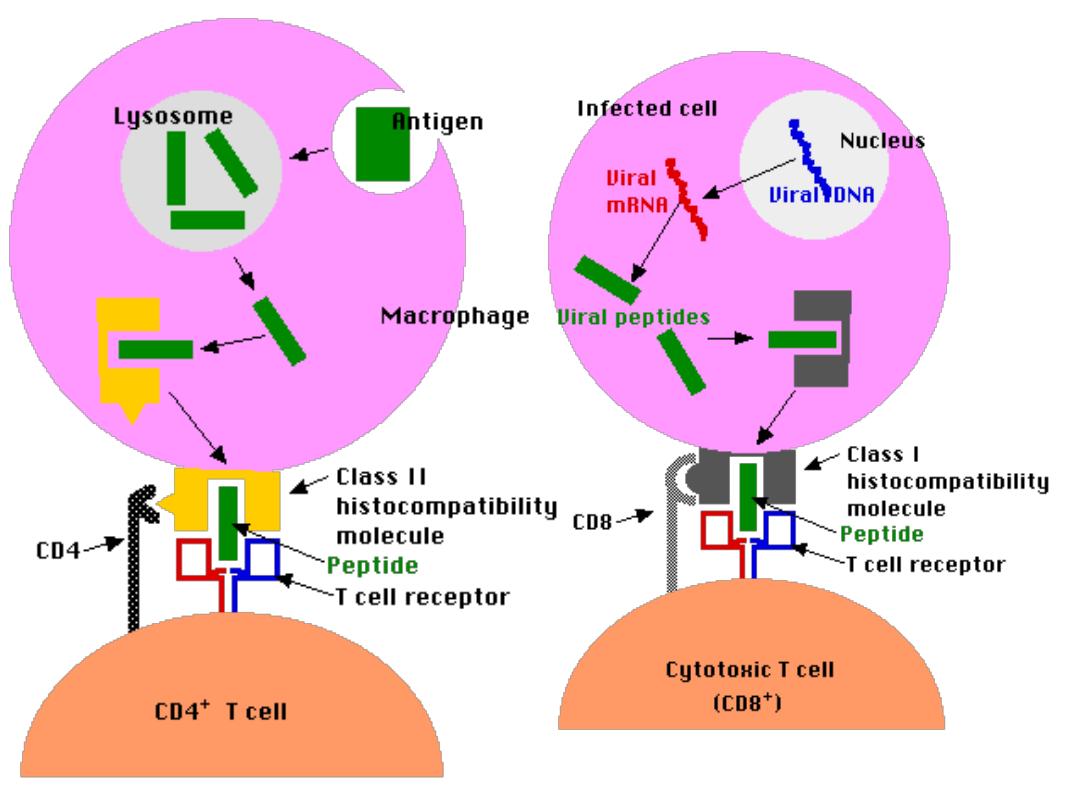

Activation of T helper Lymphocyte
T h cells can not recognize & react with an Ag
unless presented by APC in association with class
II MHC for activation of Th (CD4+) cells
Class II presented only on the surface of APC
So APC focus & engulf the Ag,(
usually Exogenous
)
slice it through lysozomal enz. With preservation of
its epitops which will be coupled with class II
through the endocystic pathway then distributed
on the surface of APC
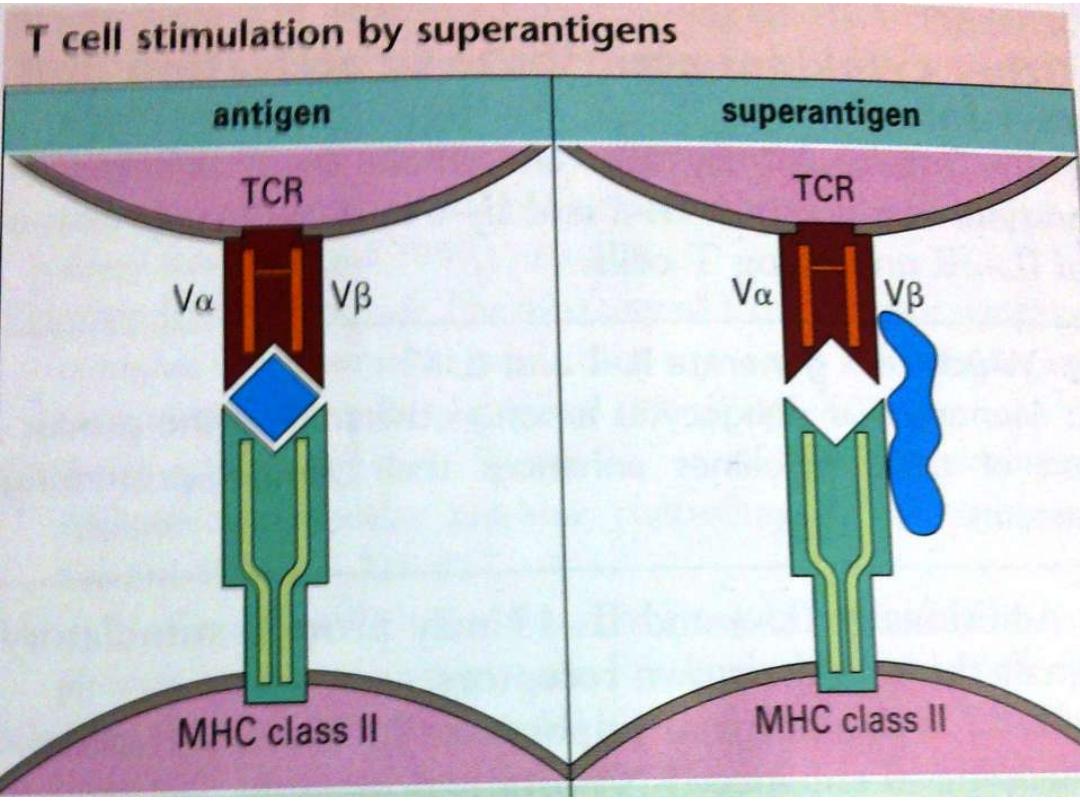
Super Ag
Potent T cell Mitogen trigger mitosis of CD4+
cells in the absence of Ag processing . It is able
to activate a large population of T h cells up to
20% of all peripheral blood Th
cells, so
realizing a large quantity of cytokines as
TNF
toxic shock syndrome(Staph. Toxin)
(toxins, Mycoplasma some viruses)

Summery
Primary lymphoid organ (central)
Thymus
for T cells &
bone
marrow
for B cells
Site where lymphocyte maturation
Secondary lymphoid organ : Lymph node Filters Ag from the
lymph ,while Spleen Filters Ag from the Blood
Ag presenting cells Include(any cell have B7 mol.& class II
MHC) like
Langerhans cell
Dendritic cells
B lymphocytes
Macrophages
Function of APC Identifications of Microbes (Ag) by
recognition
Recptor as TL R
-Engulfment (
Phagocytosis
) into phagosomes
- Distraction of the Ag by
Lysosomes
with
preserving of
the
Epitope
-
Presents
the epitope in the groove of MHC class I or class II
on their surface for CD8 &CD4 respectively in association with
B7
molecule
.

Quiz choose the most appropriate answer;
1-CD4 molecule on the T helper cells
recognizes
a- Self Class I HLA
b- Self Class II HLA
C- Non self Class I HLA
d- a+b

2-Primary Lymphoid organs include
a- Thymus
b- Lymph node
c- Bone Marrow
d- a +c

Ref.
Jawedez microbiology
Hide
