1
Immunology
_____________________________________
Lec. 5
د.عائدة الدرزي
Type IV hypersensitivity / Cell mediated (delayed) H.S.
- Inflammatory reaction occurs as a result of interaction between
actively sensitized T-Lymphocytes & specific Ag.
- The reaction is mediated by:
a. Lymphokines ( CD4
+
Th1
T
DTH
) *DTH delayed-type
hypersensitivity
The
effector
cells
that
are
responsible
for
delayed-type
hypersensitivity reaction are CD4+ Th1(T
DTH
). The Lymphokines
secreted by these cells recruit & activate macrophages and cause
tissue damage.
b. Cytotoxicity (CD8
+
CTLs) * CTLs cytotoxic T
lymphocytes
The effector cells that are responsible for cell mediated cytotoxic
reaction are CD8
+
CTLs.
c. Both reactions.
- It is a delayed type reaction because it takes 24-72 hours to develop.
- The complement & antibodies play no role in this reaction.
- Delayed type H.S. is a major immune response to intracellular
microbes, including:
a. Bacteria
Mycobacterium T.B. , Mycobacterium Leprae
b. Viruses
Measles, chicken pox, herpes
c. Parasite
Leishmania species
d. Fungal
C. albicans, C. neoformans, H. capsulatum.

2
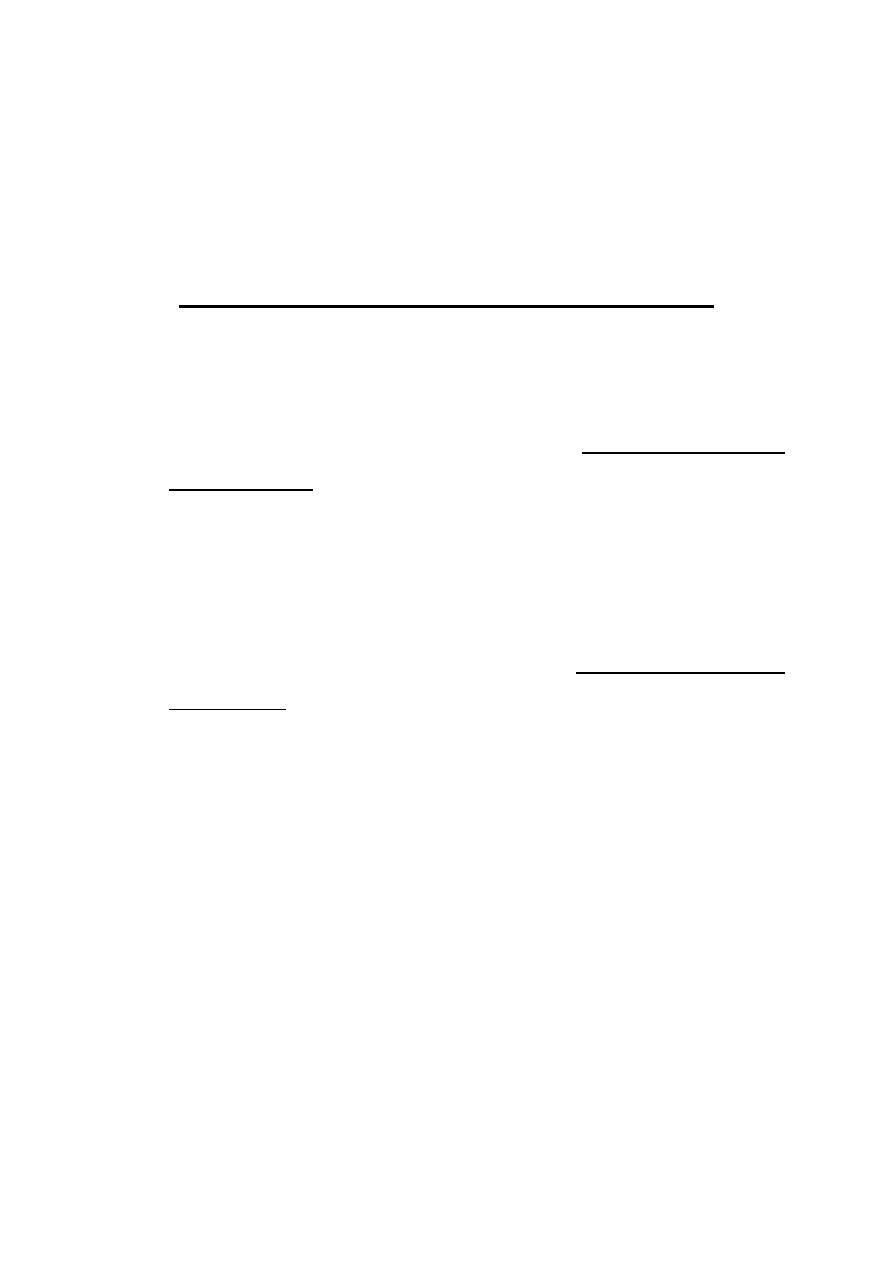
Mechanism of delayed type H.S.:
Antigens that induce type IV H.S. tend to activate Th lymphocytes of Th1
subset, which are often referred to as T
DT
H
cells.
The activated Th1 cells secret a number of Lymphokines including:
1. Migration-inhibition factor (MIF) inhibit migration of lymphocytes
2. Macrophage-activation factors (MAF) such as IFN-
Ү
, granulocyte
–
macrophage- colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and TNF-
α
enhance the microbicidal and cytolytic activity of macrophages.
3. Leukocyte inhibition factor inhibits random migration of neutrophils.
4. Macrophage chemotactic factor
5. IL 2 stimulates the growth of activated T cells & activates cytotoxic T
lymphocytes.
6. TNF-
β (lymphotoxin)
These cytokines lead to the recruitment of large number of monocytes
from the blood & to their activation when they become macrophages in
the tissues.
The activated macrophages phagocytose the Ag & release active O
2
metabolites, proteases &other lysosomal enzymes, some of which leak
out of the cells & damage the surrounding tissue.
3
4
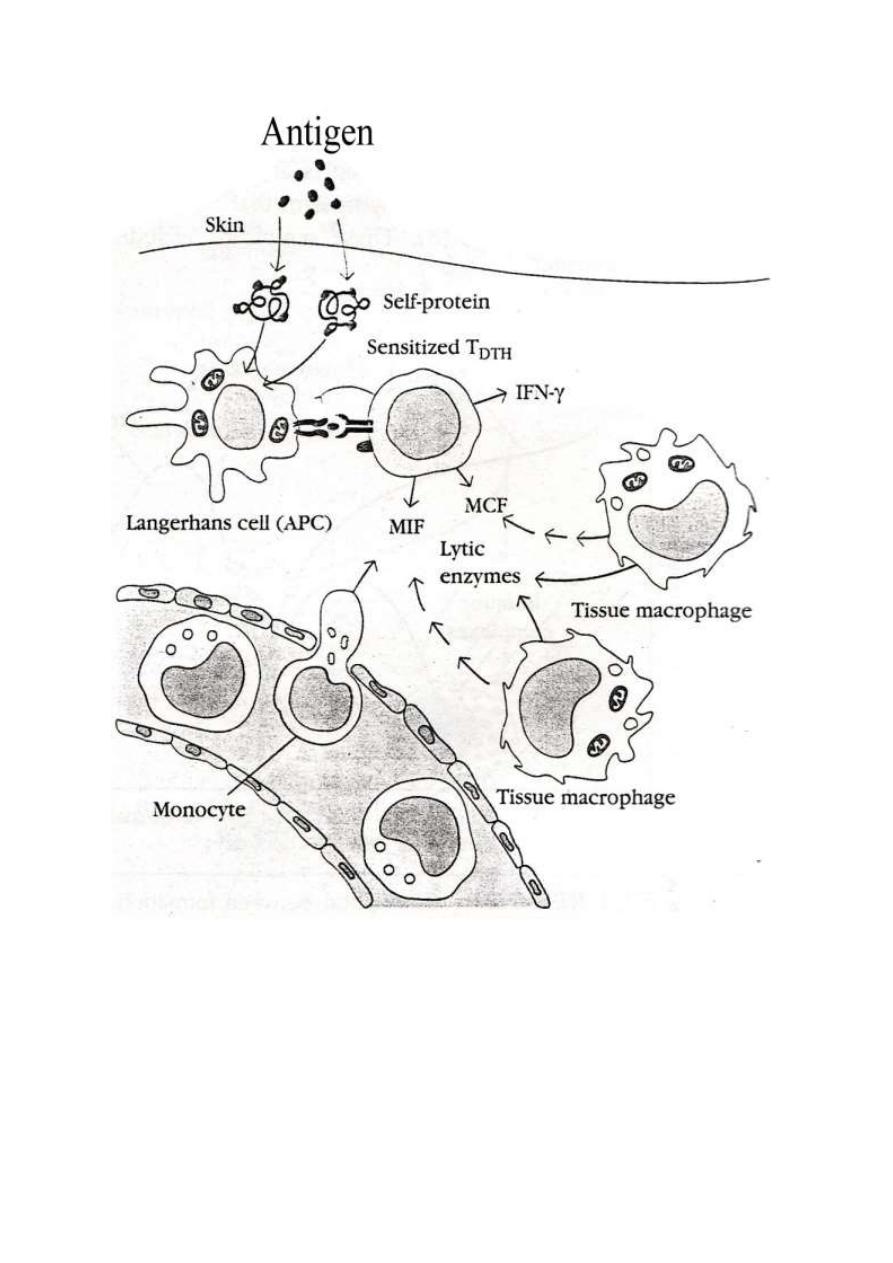
Mechanism of CTLs mediated cytotoxicity:
Plays a critical role in the host-cell mediated immune response against
viral infection, graft rejection ...etc
The CTLs recognize target cell following interaction between its TCR &
MHC class I antigens on surface of target cell. The CTLs kill their target
by delivery of toxic granule contents that induce the apoptosis of the cell
to which they attach. This process occurs in four phases:
1. Attachment to target
2. Activation ( Concentrate granules against attached target)
3. Exocytosis of granule contents (perforin & granzymes)
4. Detachment from the target
5
Clinical examples on delayed type H.S.:
Tuberculin skin test (TT):
- Positive TT indicates the presence of specifically sensitized T-lymph.
- Principles:
• The antigen is PPD (purified protein derivatives) of tuberculosis bacillus
Standardized to Tu (Todd units)
• 5-250 Tu of PPD are injected intrdermally
• The reaction appears slowly after 48-72 hours.
• In positive reaction, there is erythema & induration of > 10 mm in
diameter.
• Negative TT indicates:
1- No T.B. infection
2- Presence of Anergy (state of unresponsiveness) due to:
** Overwhelming infection
** Immunosuppressive illness
e.g. sarcoidosis, AIDS, Hodgkin's disease.
Positive tuberculin (Mantoux) test indicates:
1- Active T.B. infection
2- An unapparent (sub clinical) infection
3- Past history of the disease
4- Previous immunization
Allergic contact dermatitis:
- Due to contact with sensitizing substances or Ag including:
• Topically applied drugs (neomycin)
• Cosmetics, nickel & chromate (costume jewelers)
• Dyes, rubber compounds, preservatives ...etc.
Most of these substances are small molecules that can complex with
skin proteins & serve as haptens. This complex is internalized by APC in

6
the skin (Langerhans cells) , then processed & presented together with
MHC class II mol. causing activation of sensitized T
DTH
cells.
Immunological features:
-T-cell mediated eczematous disease
-Characterized by 48hrs delayed eczematous response to the
epicutaneous application of Ag.
Clinical features:
• Eczematous reaction.
• Acute form
erythema, oedema, vesiculation
• Chronic form
scaling
-The site of lesion is a clue for diagnosis:
• Ear lobes
earring
• Around neck
neck lacer
• Wrist
watch, bracelets, bands
Diagnosis:
- History
- Distribution of lesion
- In vivo diagnosis
- * patch test
Patch test:
A low dose of suspected Ag is placed on a patch of the patient's skin.
Eczema may develop 48-72 hrs later, indicative of type IV H.S.
7
NOTE: Penicillin can induce HS reaction by 4 mechanisms.
Penicillin-induced H.S. reactions:
Type of reaction
Ab or lymphocyte
induced
Clinical manifestation
I
IgE
- Urticaria
- Syst. Anaphylaxis
II
IgM IgG
- Haemolytic anemia
III
IgG
- Serum sickness
- G.N.
IV
TDTH cells
- Contact dermatitis
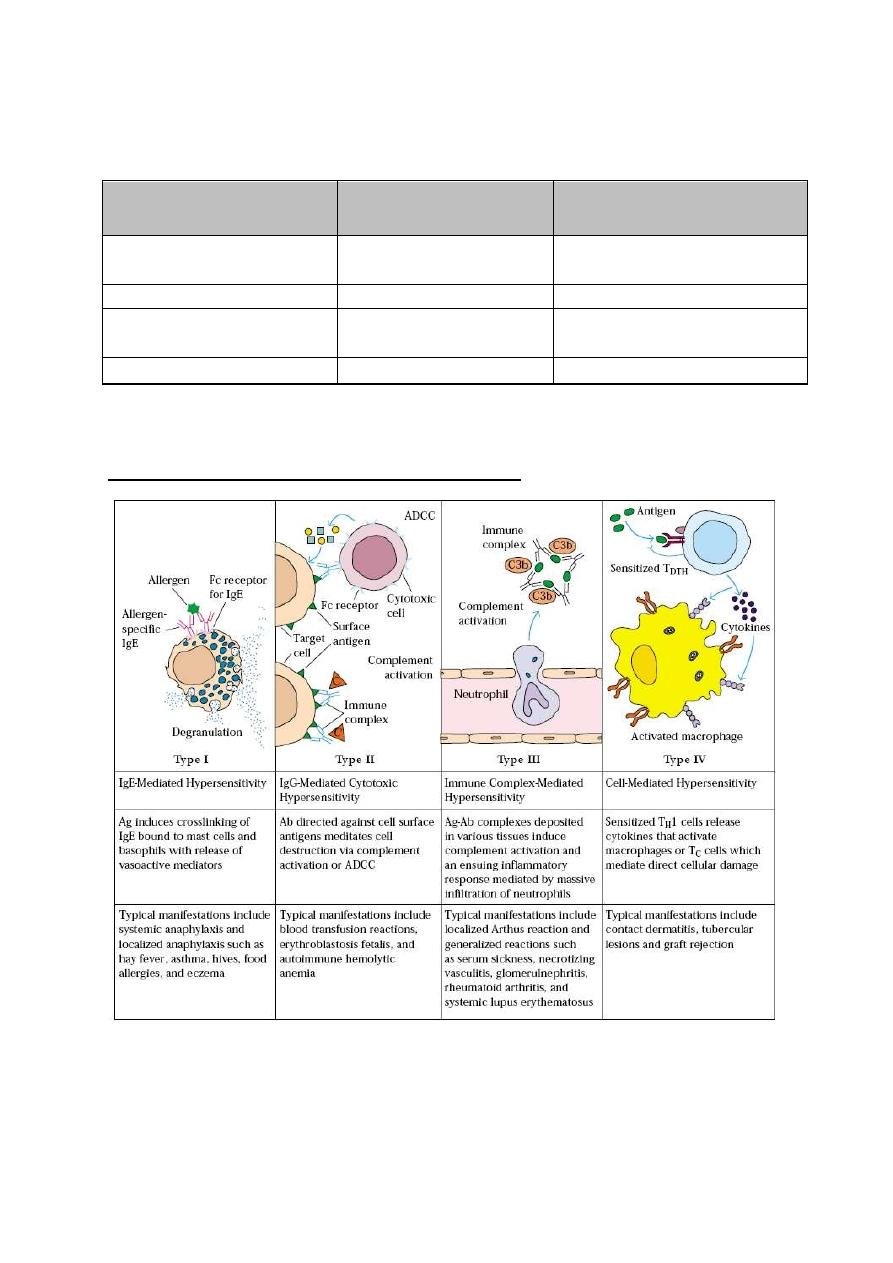
The 4 types of hypersensitivity reactions:
B
rought
t
o
y
ou
b
y :
A
li
K
areem
