
Dr. Ayad Abbas
Lec. 4
BLOOD TRANSFUSION
Tues. 11 / 11 / 2014
Published by : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
5102
-
5102
1
Lec.
4
Total
7
د.أياد عباس
Blood Transfusion
It is of two types:
Heterologous & Autologous.
1.Heterologous: transfusion of blood donated from person to another
person.
2.Autologous: transfusion of patient's own blood( by one of the following
3 methods) to avoid transfusion of infection and transfusion reaction.
a)Preoperative autologus donation(PAD): (2-6) units of blood taken from
the patient over a period of days or weeks before surgery with concurrent
iron treatment.
b)Intraoperative autologus donation(IAD):many devices are used to
collect blood from wound and filter it for retransfusion
c)Acute normovolaemic haemodilution:At start of surgery 1-2 bints of
blood drawn and replaced by fluid and retransfuse at the end of operation
Blood groups
RBC antigens (Ag) are of 2 types:
1.Ag with naturally occurring Ab: theses are A & B and their presence or
absence give rise to ABO groups.
O
AB
B
A
Group
None
A & B
B
A
Ag on RBC
Anti A, Anti B
None
Anti A
Anti B
Ab in serum
45%
4%
11%
40%
Frequency %
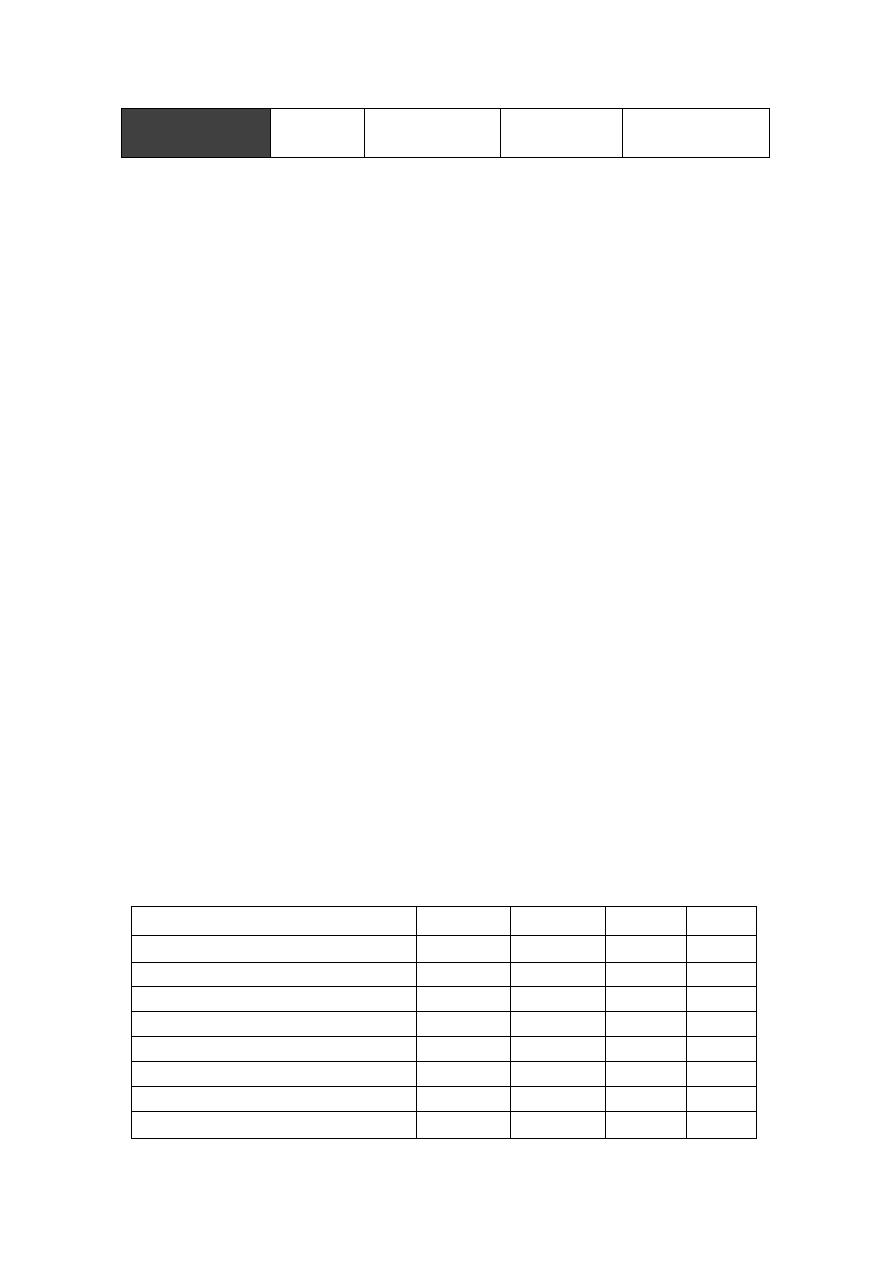
2
O only
A, B & O
B & O
A & O
Compatible
donor RBC
2.Resus grouping (Ag D) (Rh factor):
Unlike A & B Ag, the (Anti-D) Ab doesn't develop without exposure of
D -ve blood to D +ve RBC by blood transfusion or entrance of fetal
blood into the maternal circulation.
◊ 85 % of the caucasian's RBC has Ag D.
◊ 99% of Asian's RBC has Ag D.
Crossmatch:
Major: test if there is reaction between recipient serum against donor cells
Minor: test if there is reaction between recipient cells against donor
serum and now replaced by Ab screen on donor blood
The crossmatch take at least 45 min.because of incubation period and so
in so emergent case we can transfuse:
1)Type specific parcially crossmatched blood (last 5 min.)
2) Type specific uncrossmatched blood
3)O –ve blood
Anticoagulants needed for preservation of blood
1.C.P.D ( Citrate,phosphate, Dextrose)
Shelf life of RBC in such solution 21 days.
2.C.P.D.A (Citrate, Phosphate, Dextrose, Adenine)
Shelf life of RBC in such solution 35 days.
3.Heparin: shelf life of RBC is 4 hrs.
Changes in stored blood
21day
14 day
7 day
1 day
Days
6.9
7
7
7.1
pH
140
110
80
48
PCO
2
(mmHg)
179
145
101
41
B.lactate (mEq/L)
11
12
15
18
Plasma HCO
3
(mEq/L)
21
17
12
3.9
Plasma K
+
(mEq/L)
231
281
312
345
Plasma dextrose (mg/dl)
19
13
7.8
1.7
Plasma Hb (gm/dl)
<1
<1
1.2
4.8
2,3 DPG
*

3
0
0
0
10
Platelet %
20
40
50
70
Factor V & VIII %
* Note: 2,3 DPG: Diphosphate Glycerate which decreases the affinity of
RBC to O
2
and its ↓ → tissue hypoxia.
Indication of Blood Transfusion
1.Severe blood loss: trauma, GIT bleeding.
2.Following severe burn → RBC haemolysis.
3.During major surgery that associated with severe blood loss.
4.Anemic patient (severe).
5.Thrombocytopenia.
6.Bleeding due to clotting factor deficiency or dysfunction e.g.
haemophilia and liver disease.
Forms of blood may be obtained for blood
transfusion
1.Whole blood stores in CPD or CPDA or heparin.
These forms are stored in 4
○
C.
◊ Blood preserved with heparin used in open heart surgery:
● not diluted by ACD or CPDA volume
● given within 4 days
2.Fersh whole blood stored in ACD or CPDA.
Used within 24 hrs for:
● Thrombocytopenia
● Exchange transfusion of newborn
3.Concentarted RBC (plasma reduced blood).
Stored temperature: 4
○
, expiry:12 hrs
Indication:
● severe anemia
● patient with severe heart failure
● very young or very old patient
4.Fresh frozen plasma
● storage temperature: (-20)-(-30)
○
C
● separated immediately from RBC
● It is 225 ml and contain 1 U/Kg of all clotting factors and 3-4 mg/Kg
of fibrinogen
● could be stored for several months

4
Indication:
● Haemophilia or any isolated factor deficiency
● Massive blood transfusion(deficiency of facter 5 and 8
5.Platelet concentrate:50-70 ml
● storage temperature -20
○
● expiry: given within 12 hrs
Indication: thrombocytopenia or functional platelets disorder
6.Cryoprecipitate :it is white,cold,and insoluble precipitate results from
thawing of unit of fresh frozen plasma
It is 10 ml contains80-145U facter 8,250mg fibrinogen,andVonwillbrand
facter
Both have high concentration of anti haemophilic globuline
Indication:1) haemophilia (factor IIX deficiency).
2) fibrinogen deficiency
3)Facter 7 deficiency
4) Vonwillbrand disease
7)Clotting facter concentrate e.g facter 8 concentrate
Massive Blood Transfusion
Transfusion of half of blood volume within 1 hr (i.e. for adult ~ 5 bint =
2.5 L).
(or) Transfusion of an amountequals to or more than one blood volume
within 24 hr
Complication of Massive Blood Transfusion*
(very
important subject)
1.Coagulation disorder Treatment: FFP,platelet
2.Hypothermia Treatment: warming
3.Hypocalcaemia
4.Hyperkalaemia Treatment: Ca
+2
gluconate
5.Metabolic acidosis (early) followed by alkalosis when citrate
metabolized to HCO
3
.
6.Fluid overload
7. thrombosis air embolism
8.High O
2
affinity blood (tissue hypoxia)
9.Infection

5
Complication of Blood Transfusion**
(very important subject)
1.Immunological: Ag-Ab reaction
Haemolytic reaction
a.Immediate intravascular due toABO incompatibility
Symptoms:
Fever, chill, chest pain, hypotension,tachycardia, nausea, vomiting,
dyspnea, respiratory failure, haemorrhage.
Treatment:
● Take samples of recipient and donor blood for analysis
● i.v. fluid & O
2
● Adrenalin 0.5-1 ml of 1:1000 every 10 min. as required and may
followed by infusion
● Antihistamine e.g. chlorphenamin 10-20 mg
● hydrocortisone 100-500 mg i.v.
● NaHCO
3
may be required according to blood gas analysis
Treat renal vascular ischemia by:
1)crystalloid
2)diuretic e.g frusemide 20 mg
3)low dose dopamine 2-5Microgram/kg/min
b.Delayed extravascular :
● Occur due to reaction to minor blood group other than ABO.
● Occur 7-10 days
ms:
Sympto
Fever, anemia and jaundice
Treatment:
Conserative treatment
Non haemolytic reaction
(recipient Ab) in response to preveouse transfusion or pregnancy+ (
WBC, platelet or plasma protein) of donor. there are 4 types:
1)Febrile reaction:most common, about1-3%
2)Mild allergic reaction
3)Anaphlactic reaction
4)ARDS

6
2.Non-immunological
● Coagulopathy
● Metabolic acidosis
● Fluid overload
● Hyper K
+
● Hypo Ca
+2
● Thrombosis
● Air embolism
● Hypothermia
● High O
2
affinity Hb
● Infection: HIV, hepatitis, CMV, malaria and syphilis

7
