
Dr. Abdul Ameer M.
Hussein
Lec. 2
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Tues. 9 / 12 / 2014
Published by : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2014 – 2015
Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
2
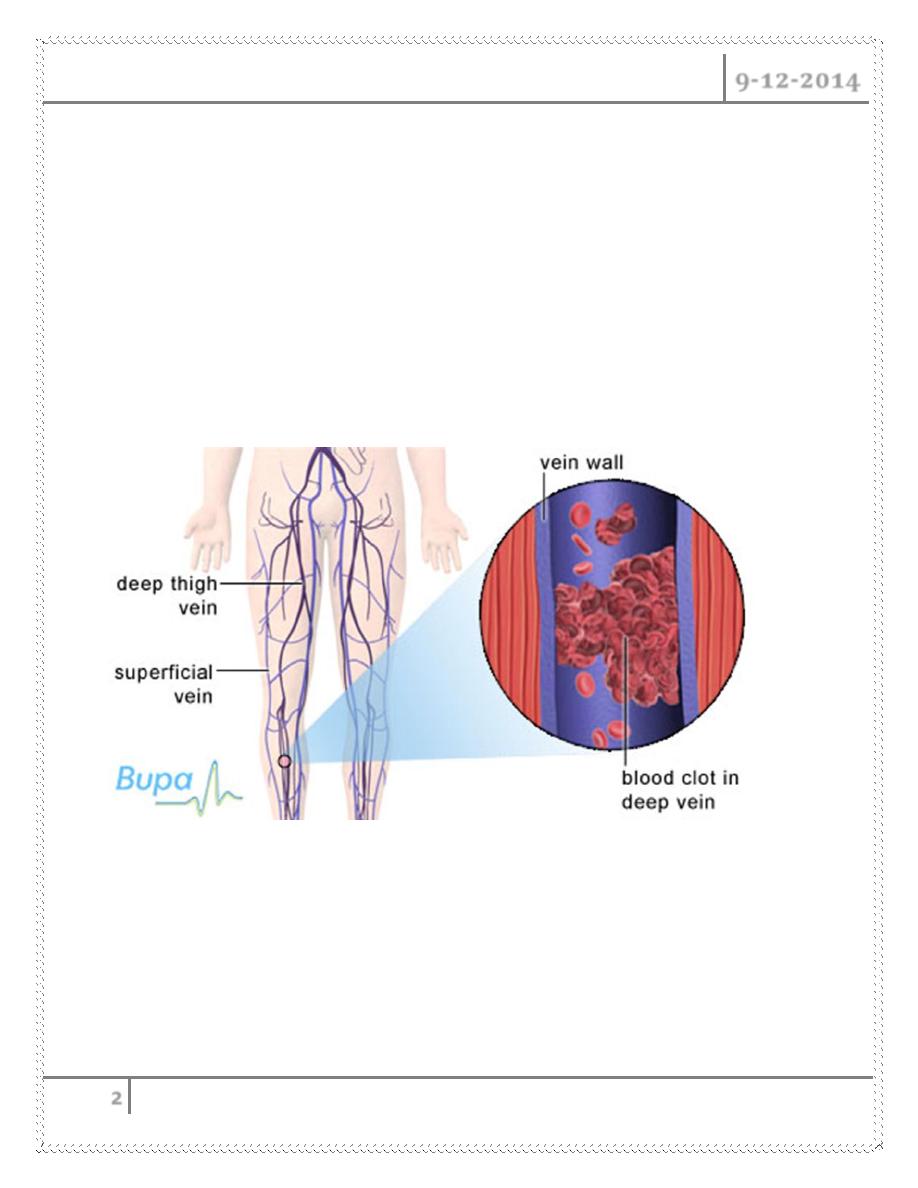
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Composite term for DVT &PE
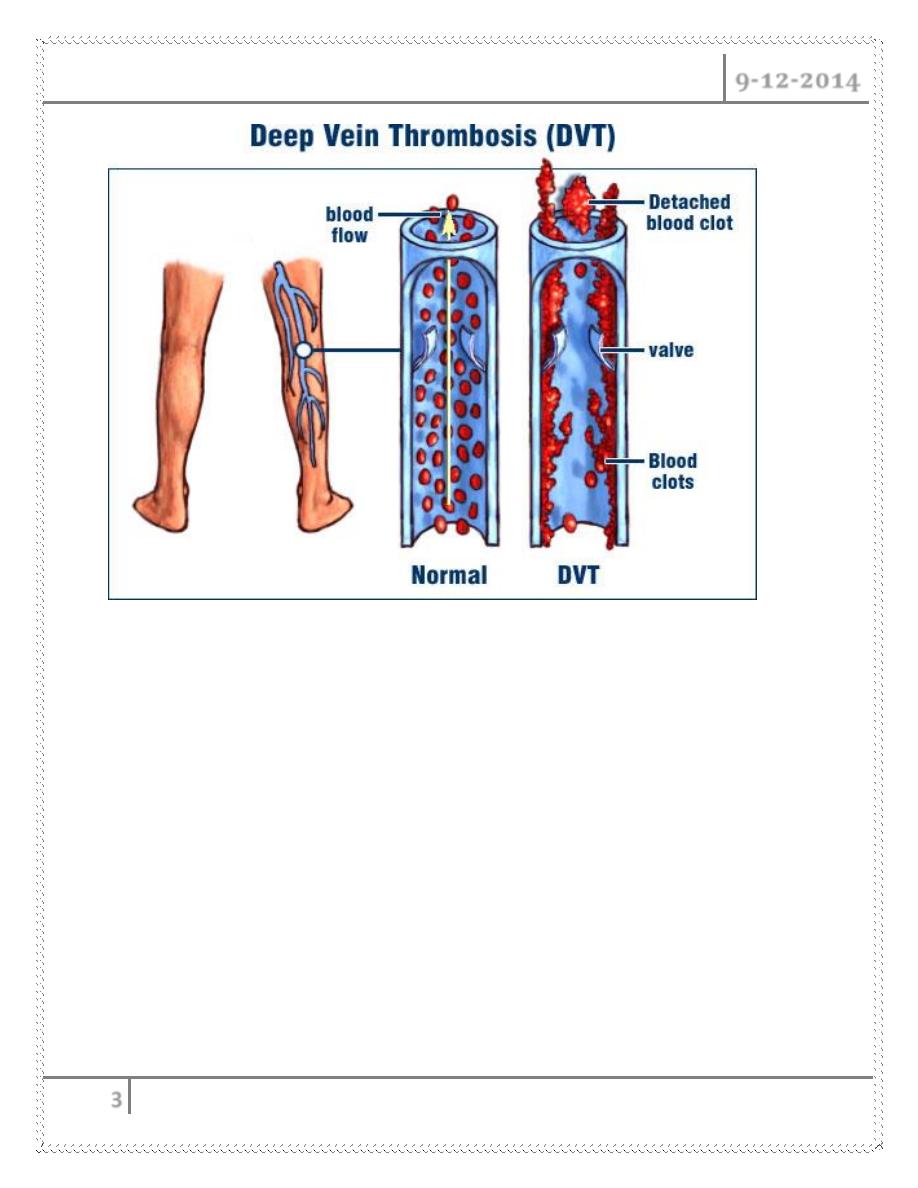
The presence of thrombus with in deep veins is termed as deep vein
thrombosis
It is a life threatening condition that may lead to sudden death in the short
term or long term
Morbidity due to the development of post thrombotic limb and venous
ulceration
Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
3
CLASSIFICATION
PROXIMAL DVT : thrombus formed in veins above the knee joint (femoral,
iliac, popliteal)
DISTAL DVT : those formed below the knee joint (calf veins)
Venous thrombosis are difficult to recognize clinically. The documented
cases probably represent only tip of the Ice Berg ( SILENT KILLER )
EPIDEMIOLOGY
M:F 1.2:1
Age more than 40 years
VT occur in more than 50% of patient’s having orthopaedic surgical
procedures

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
4
10 to 20% of patient with idiopathic DVT have or develop cancer
1/3
rd
to 1/4
th
patient having proximal DVT may develop PE
About 10% of hospital deaths attributable to PE (from DVT)
AIR TRAVEL AND DVT
Up to 1 out of 10 air line passengers develop small asymptomatic blood
clots
Due to hypoxia and reduced cabin pressure
VT occurs in patients regularly without any damaged to the blood vessels
Calf vein - most common
Ilio femoral - most symtomatic
IVC - most lethal
Paralysis of lower limbs
Polycythaemia
Medical illness
o stroke
o MI
o CHF
o Pneumonia
o COPD
o Infections
o Nephrotic syndrome
o Inflammatory bowel disease
Oral contraceptives
Varicose veins

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
5
VTE Risk Patient Factors
Age
Previous VTE
Malignancy
Obesity
Prolonged immobility
Trauma
Surgery
Pregnancy/ postpartum
Indwelling central venous catheter
Deficiency of anti-thrombin III, Protein C or S
PATHO-PHYSIOLOGY
VIRCHOW`S TRIAD
Predisposing Factors
1- Stasis
2- Vascular damage
3- Hyper coagulability
Imbalance between thrombogenesis & thrombolytic agents
FATE OF THROMBUS
1- Propagation
2- Embolization
3- Dissolution
4- Organization & recanalization
ORGIN
DVT usually originates from veins of calf around the valve cusps or with in
soleal plexus

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
6
A minority of cases occurs directly in ilio femoral veins
In practical terms the development of VT is best understood as activation of
coagulation in areas of reduced blood flow
Majority of calf vein thrombus dissolve completely
Only 20% progress proximally
Propagation occurs before embolization
The process of adherence and organization of venous thrombus does not
begin until 5 to 10 days after thrombus formation
This non adherent thrombus may propagate or embolise
Propagation or organization of venous thrombus
destruction of valves &
varying degree of venous outflow obstruction
chronic venous
insufficiency
VTE Results in :
1- Fatal PE
2- Non-fatal PE
3- Post-thrombotic syndrome
POST-PHLEBETIC SYNDROME
Consequence of recanalization of major venous thrombus
Due to incompetence of valves
Long term morbidity
Causes chronic edema &venous ulcers
CLINICAL FEATURES
Swelling/edema
most specific sign
unilateral
Leg pain (50%)
non specific

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
7
Redness/erythema
over the thrombus
Tenderness(75%)
calf or along the involved veins
does not correlate size, site, extent
Low grade pyrexia
Signs and symptoms of PE
HOMAN`S SIGN
Pain or discomfort in leg on forceful dorsiflexion of foot with knee straight
Present only in 10% of confirmed DVT
Highly non-specific
Present in 50% of cases with out DVT
Misleading sign
No longer used
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
In approximately 70% of patients with clinically suspected DVT, alternate
diagnoses are ultimately found as follows :
Arthritis
Cellulitis, lymphangitis
Hematoma
Lymphedema
Muscle or soft tissue injury
Neurogenic pain
Postphlebitic syndrome
Ruptured Baker cyst
Stress fractures or other bony lesions
Superficial thrombophlebitis
Varicose veins

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
8
INVESTIGATION
DUPLEX ULTRASONOGRAPHY
MRI
CONTRAST C.T.
CONTRAST VENOGRAPHY
IMPEDANCE PLETHYSMOGRAPHY
D- dimer level
This cross-linked fibrin degradation product is an indication that thrombosis
is occurring , and that the blood clot is being dissolved by plasmin .
D-dimer is measured by latex agglutination or by an enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test that is considered positive if the level is
greater than 500 ng/mL
Other blood tests
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Primary coagulation studies (PT ,PTT ,Fibrinogen )
- Liver Enzymes
- Renal function and electrolytes
Protein S, protein C, antithrombin III, antiphospholipid antibodies and
homocysteine levels can be measured
investigations for these abnormalities are primarily indicated when DVT
is diagnosed in patients younger that 35 years or when venous thrombosis
is detected in unusual sites
TREATMENT
MEDICAL TREATMENT
Bed rest
Affected limb is elevated above the level of heart.
Anticoagulant prevent thrombus propagation and allow the endogenous lytic
system to operate
Pain relief

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
9
UNFRACTIONED HEPARIN
Initial bolus 7500 to 10000 IU followed by continuous in infusion to 1000 to
1500 IU/hr.
Infusion rate adjusted so that aPTT is approx twice the control value
Every 6 hrs aPTT monitered till therapeutic range is reached
Duration :5 days
Discontinue when platelet count <75,000
LOW MOLECULAR WT HEPARIN
Effective and better than conventional heparin.
Different preparations available.
Administered SC in fixed doses once or twice daily.
Duration -7 to 14 days
Anticoagulant effect by inhibiting the activated factor X.
Hemorrhagic complications doesn’t occur
WARFARIN
To be taken along with heparin for initial 4 to5 days.
Dose adj to maintain prothrombin time at INR 2.0 to3.0
Continued for 3 to6 months for pts with acute idiopathic DVT
For recurrent DVT/PE low intensity warfarin continued indefinitely
maintaining INR 1.5 to2.0
THROMBOLYTICS
Early administration
1- Prompt resolution of symptoms
2- Accelerate clot lysis
3- Preserve venous valves
4- Decrease the potential for developing post-phlebitic syndrome
Does not prevent clot propagation or rethrombosis
Heparin and oral anti coagulant therapy must follow a course of
thrombolysis

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
10
Haemorraghic complications reduced by regionally administering with
flouroscopic control
Streptokinase,urokinase
SURGICAL TREATMENT
1- Indicated when anticoagulant therapy is ineffective, unsafe or contraindicated
2- Major surgical procedures : clot removal and partial interruption of IVC to
prevent PE
THROMBECTOMY
o To restore venous patency and valvular function.
o Alone it is not indicated because rethrombosis is frequent.
o Heparin therapy is a necessary adjunct.
o Best reserved for patients with massive vein thrombosis when limb viability
is at risk
FILTERS FOR DVT
o First suggested by Trousseau in 1868.
o introducing intracaval devices percutaneosly and floating them into position
with fluoroscopy is the procedure of choice for filter placement
ACCEPTED INDICATION FOR FILTER PLACEMENT
Severe hemorrhage complications of anticoagulant therapy
Absolute contra indications to anticoagulation
Failure of anticoagulation such us new or recurrent VTE or PE
prophylaxis - yes or no?
YES - Overall reduction in DVT and PE is by 40% to 60%

Deep Vein Thrombosis Dr. Abdul Ameer M. Hussein
9-12-2014
11
PROPHYLAXIS
Usually combination of therapies
I.
EARLY MOVT & REHABLITATION
II.
MECHANICAL METHODS
Lower extremity exercises
Graded compression stockings
Intermittent pneumatic compression devices
PREVENTION OF TRAVELER`S THROMBOSIS
Graduated compression stockings
Exercise
Avoid alcohol &sleeping tablets
HIGH RISK PATIENTS
LMWH ,single dose SC before the flight
Complications
Early
Progression Pulmonary embolism
Paradoxical embolism
Acute compartment syndrome
venous gangrene
Late
Rec DVT
Post phlebitic syndrome
Done By
Ali Kareem
