
The Pancreas
After studying this lecture, you should be able to . . .
1.Knew the endocrine function of pancreas.
2.Understand the physiological effects of insulin on
different body parts.
3.Use your physiological knowledge to predict the
cause of signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus.

THAT CAUSE:………
(GLYCOGENOLYSIS AND LIPOLYSIS)
AND ALSO GLUCON
EO
GENESIS
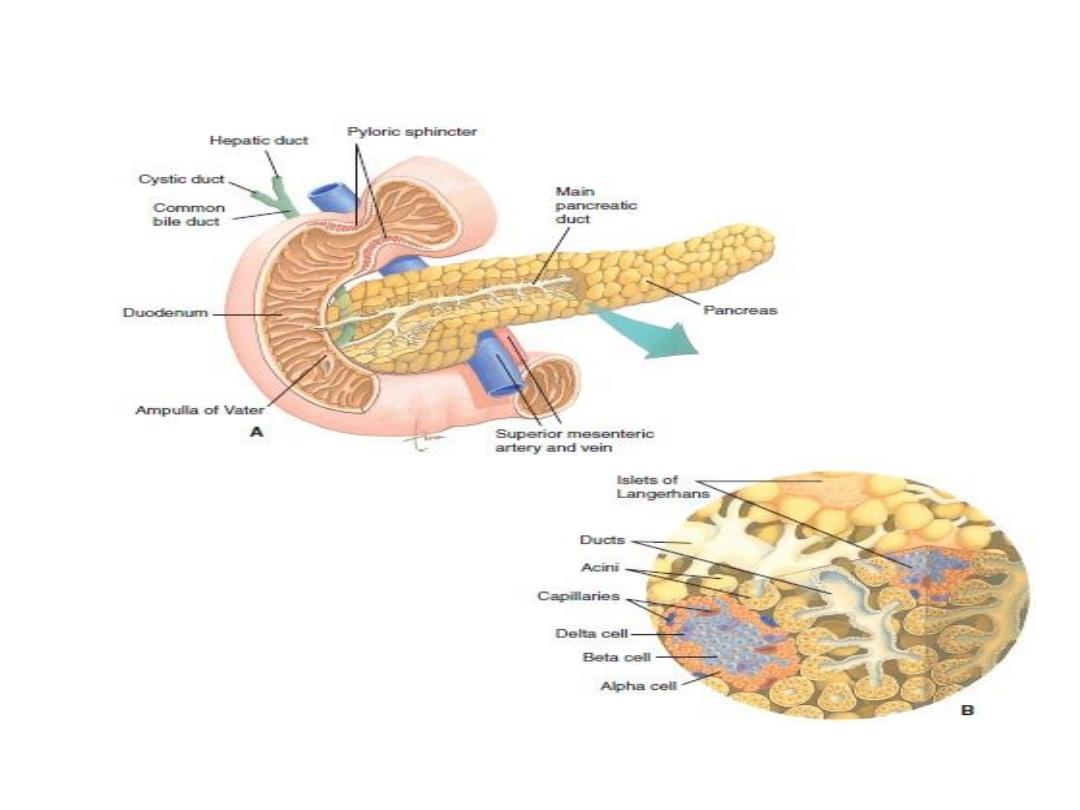
Alpha
cells
secrete
Glucagon

Delta cells secret Somatostatin

* CAUSE MOST OF THE GLUCOSE ABSORBED AFTER A MEAL
TO BE STORED ALMOST IMMEDIATELY IN THE LIVER IN THE
FORM OF GLYCOGEN.
*INSULIN PROMOTES THE CONVERSION OF ALL THIS EXCESS
GLUCOSE INTO FATTY ACIDS.
* INSULIN INCREASES GLUCOSE TRANSPORT INTO AND
GLUCOSE USAGE BY MOST OTHER CELLS OF THE BODY.
Beta cells secrete insulin

THE BRAIN CELLS ARE QUITE DIFFERENT FROM
MOST OTHER CELLS OF THE BODY IN THAT THEY
NORMALLY USE ONLY GLUCOSE FOR ENERGY.
with the exception of the brain cells

Insulin Promotes Protein Synthesis
and Storage:
*
Insulin stimulates transport of many of the
amino acids into the cells.
* Insulin inhibits the catabolism of proteins,
thus decreasing the rate of amino acid
release from the cells, especially from the
muscle cells.
* In the liver, insulin depresses the rate of
gluconeogenesis.
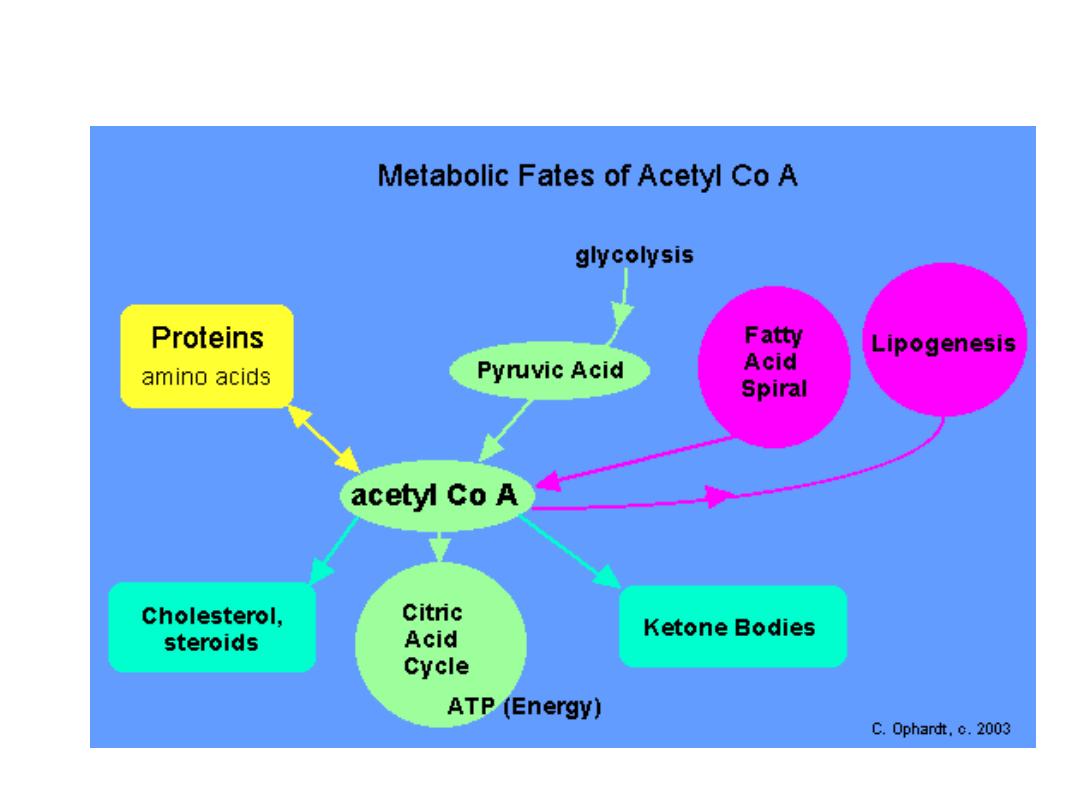
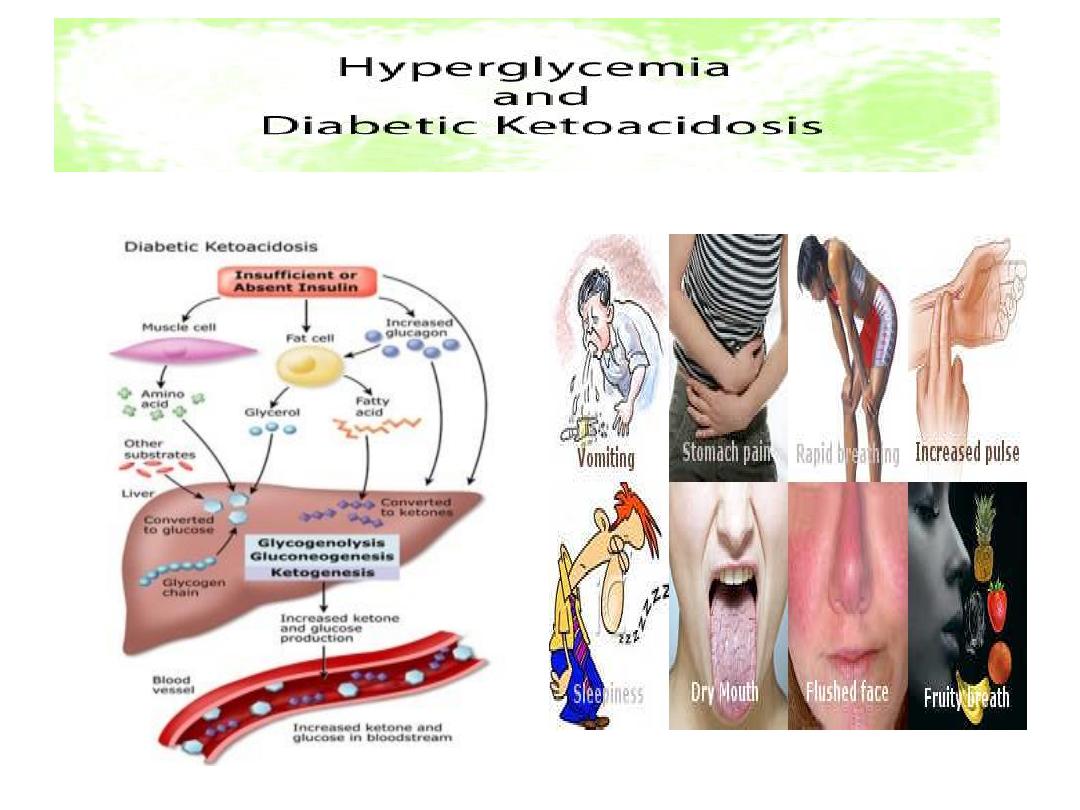
Ketosis
Insulin and Growth Hormone Interact
Synergistically to Promote Growth:

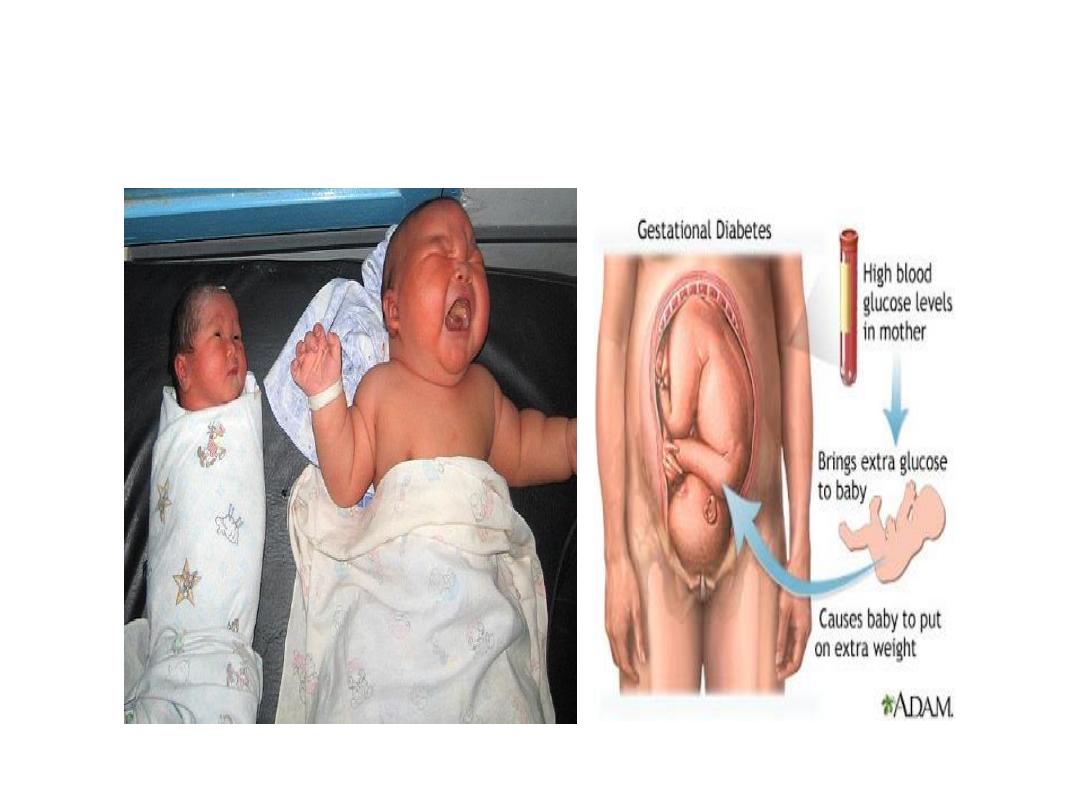
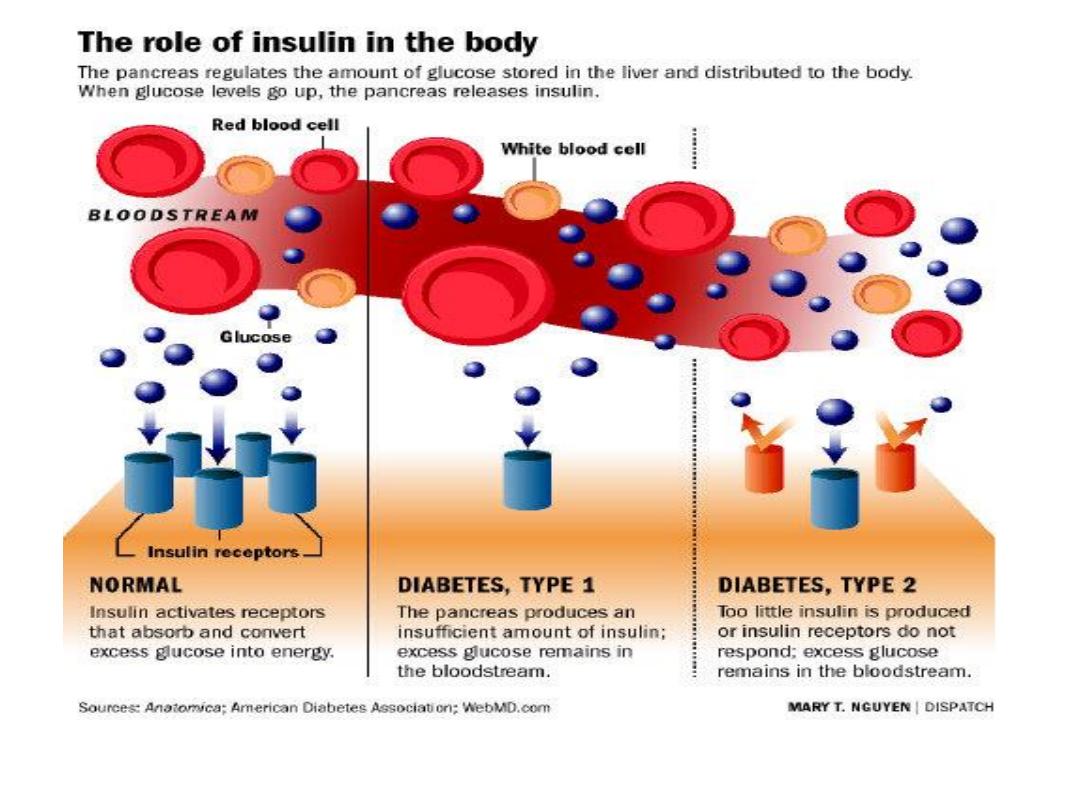
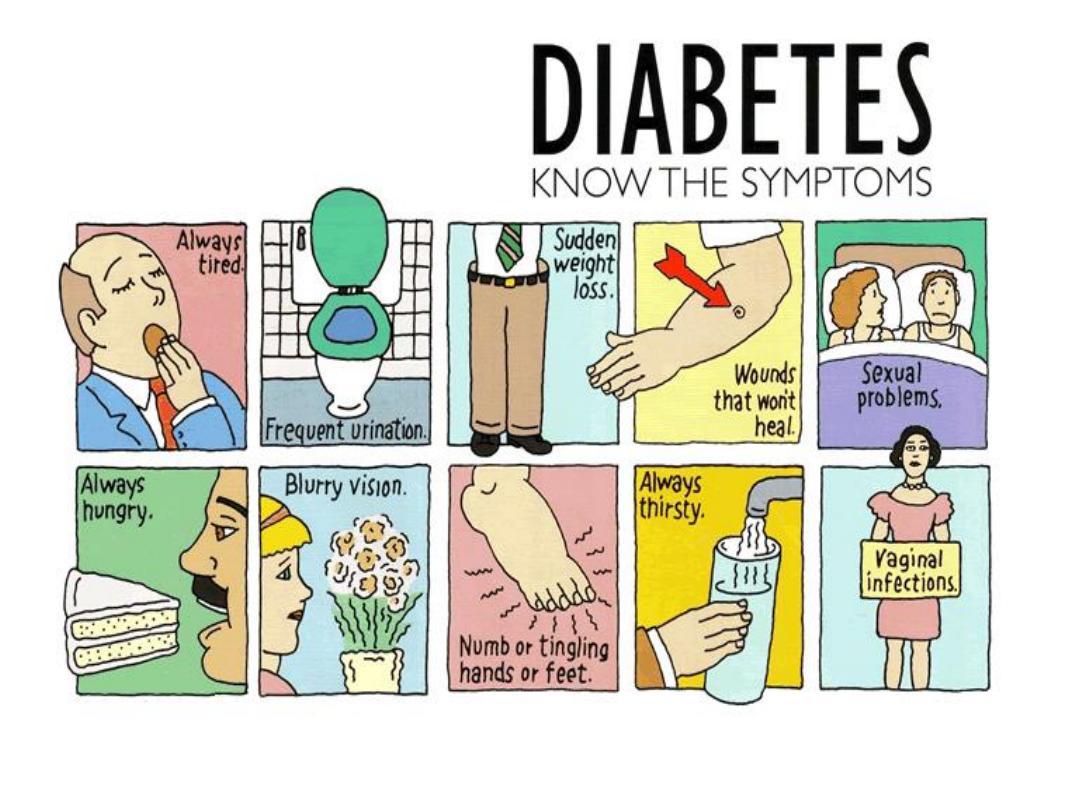
Diabetes Mellitus:

Type 1 D. M.

Bad Habits
Bad food
Overweight
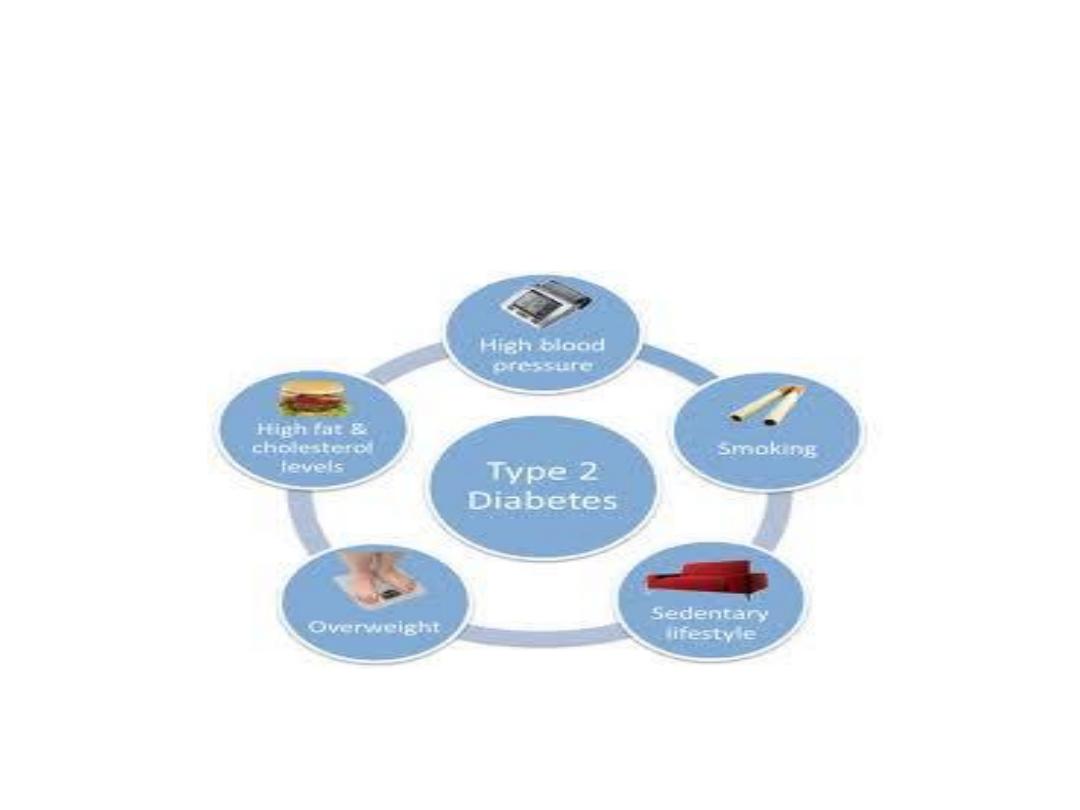
Type 2 Diabetes
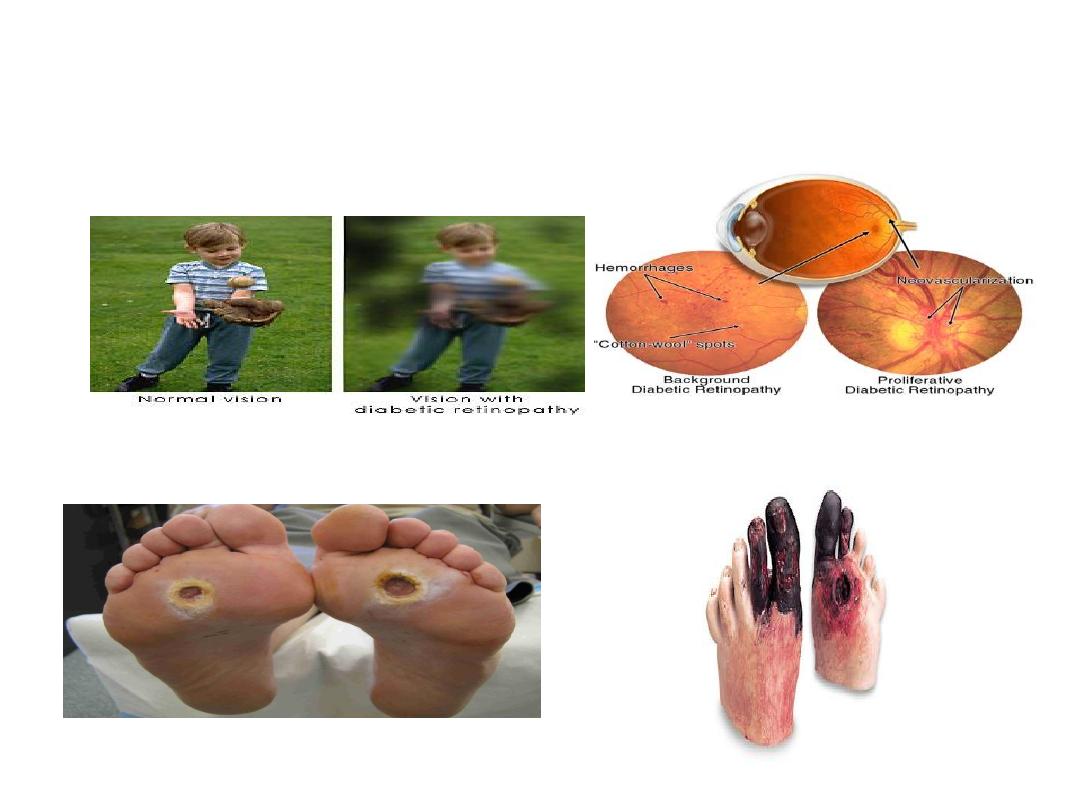
Complications of DM
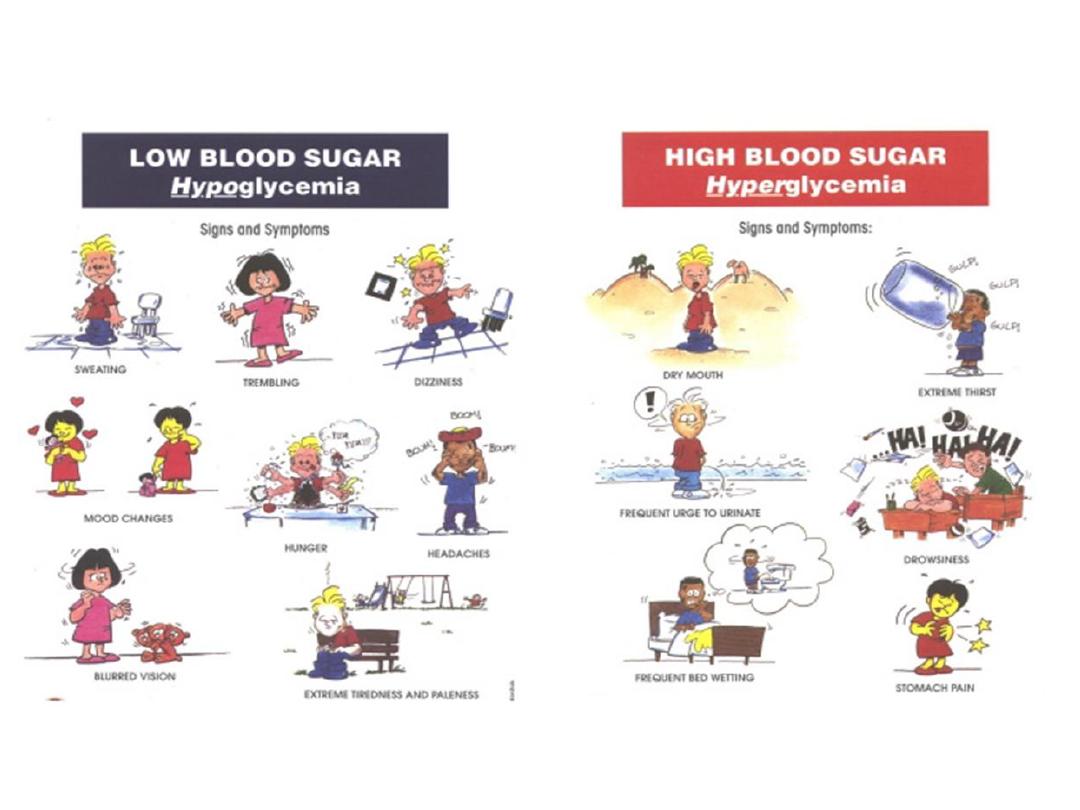
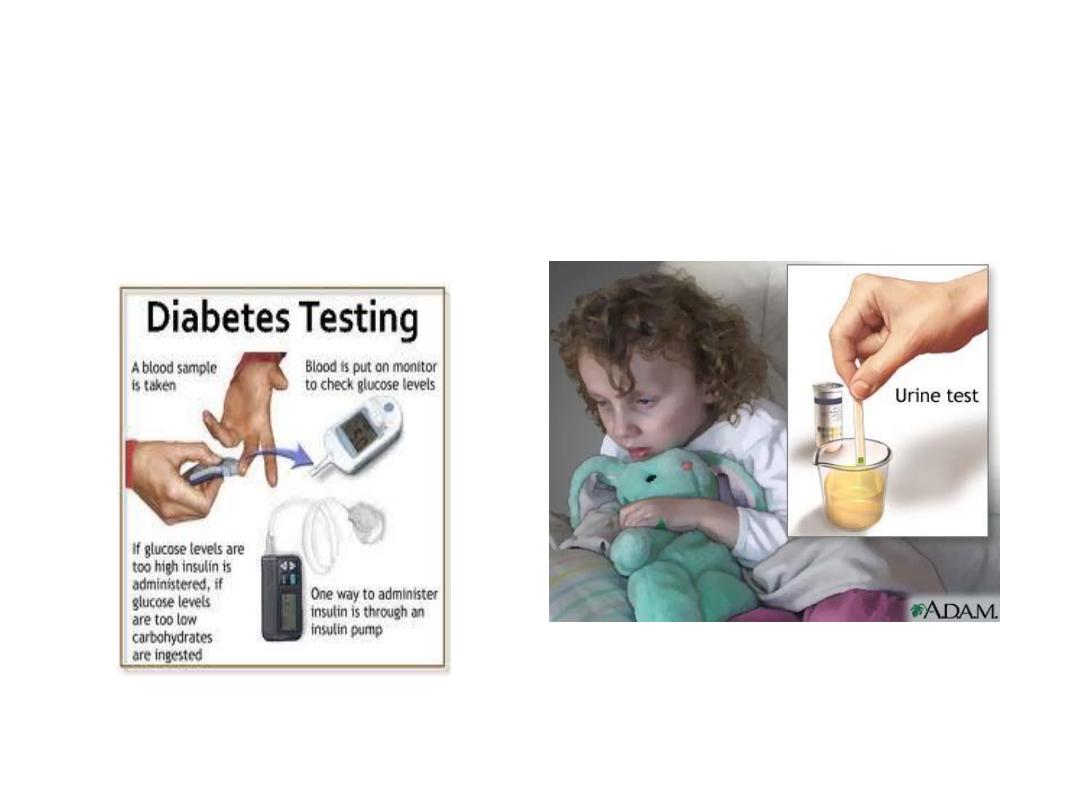
Physiology of Diagnosis of Diabetes
Mellitus

Thank You
