
Learning objectives
-To understand the Specific Defenses
-To identify the Immune Responses.
-To delineate the forms of immunity and
Properties of each.
-To have an overview of immune responses:
*T cells and cell-mediated immunity
*B cells and antibody-mediated immunity
*classes of Antibodies(ImmunoglobulinsIgs)

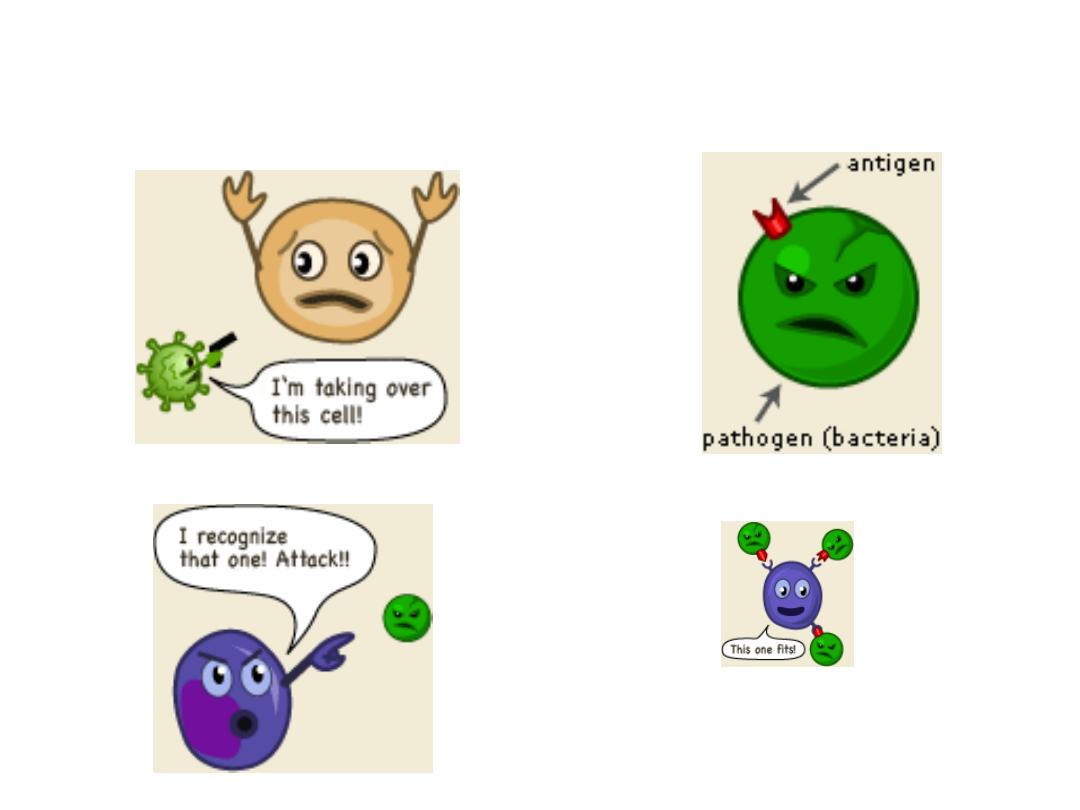
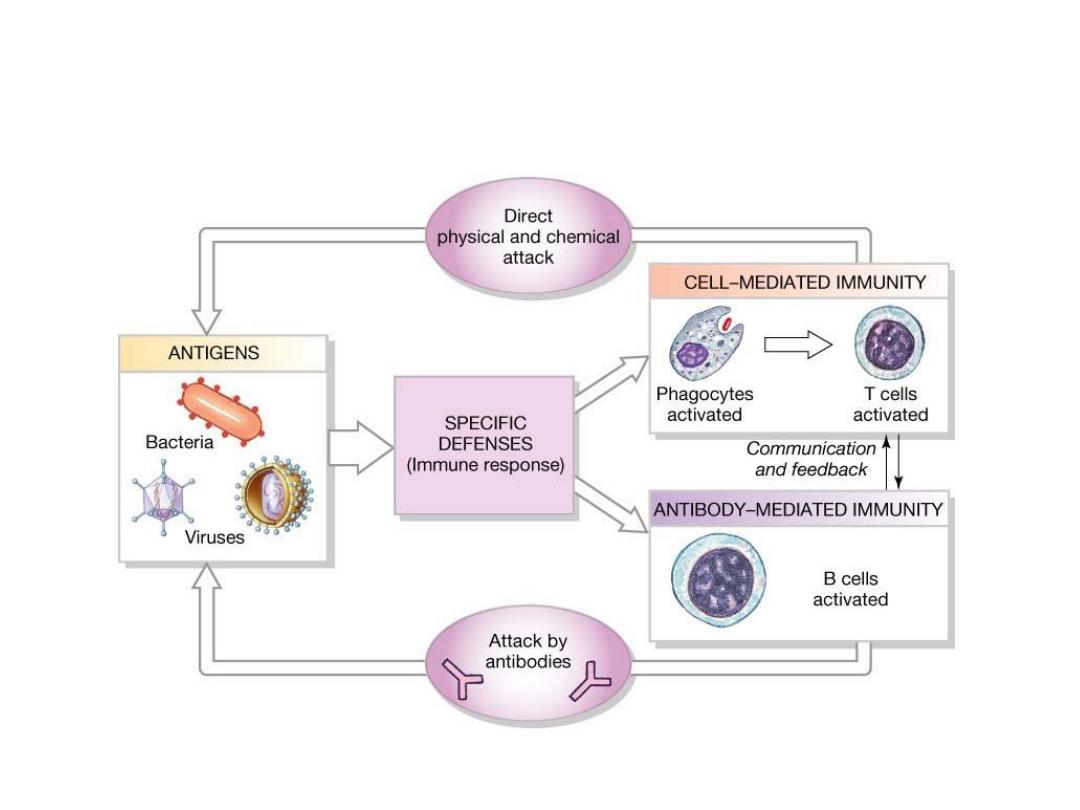
Specific Defense: The Immune Response
•
Respond to specific antigens
•
T cells
–
Cell-mediated immunity (cellular immunity)
–
Provide defense against abnormal cells and pathogens in
living cells
•
B cells
–
Antibody-mediated immunity (humoral immunity)
–
Provide a defense against antigens and pathogens in body
fluids
Immune System

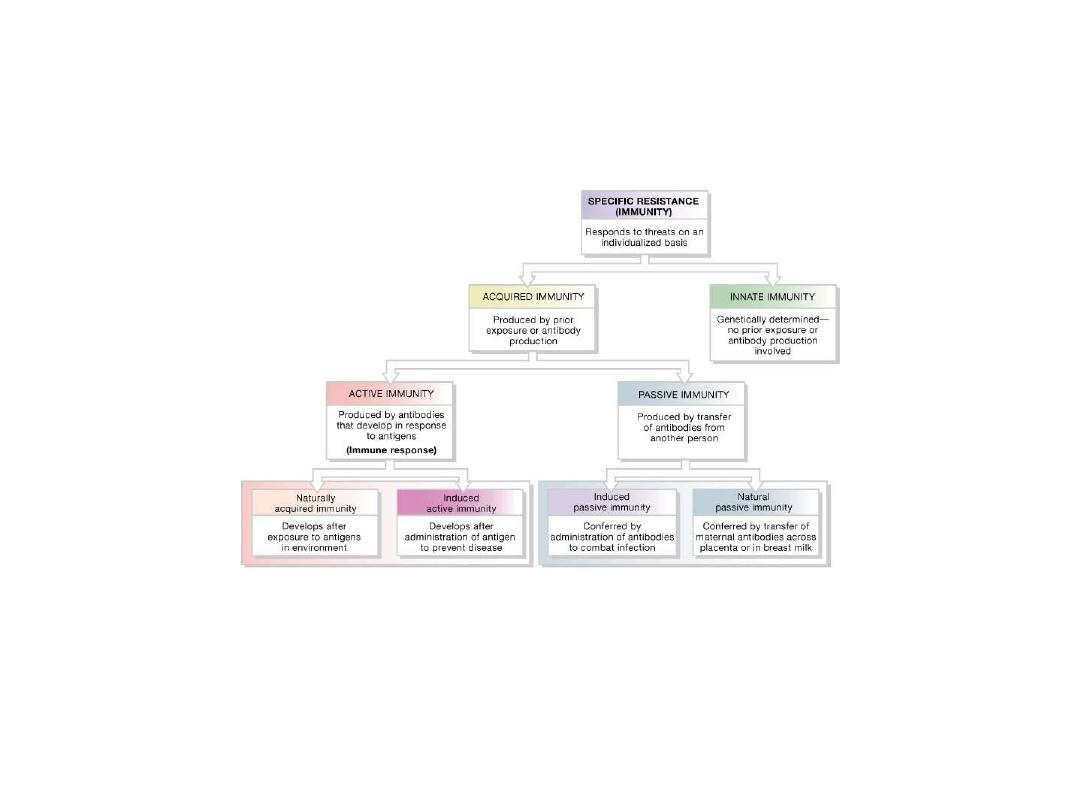
Forms of Immunity
•
Either innate or acquired
•
Innate
–
Genetically determined
•
Acquired
–
Active or Passive
•
Active Immunity
–
Naturally acquired immunity
–
Induced active immunity
•
Passive Immunity
–
Induced passive immunity
–
Natural passive immunity

Properties of Immunity
•
Specificity
•
Versatility
•
Memory
•
Tolerance
Overview of Immune Response

T Cells and Cell-Mediated Immunity
•
T cells recognize antigens when bound to
membranes of other cells
–
Membrane receptors called major
histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins
•
2 classes
–
Class I MHC proteins
–
Class II MHC proteins

Class I MHC Proteins
•
Found on the surfaces of all of our cells
•
MHC proteins bind small peptide molecules
normally present on cell membrane
–
Normal peptides: T cell ignores
–
Abnormal, virus, or bacteria (nonself): T cell
activated
•
Destroys abnormal/infected cell

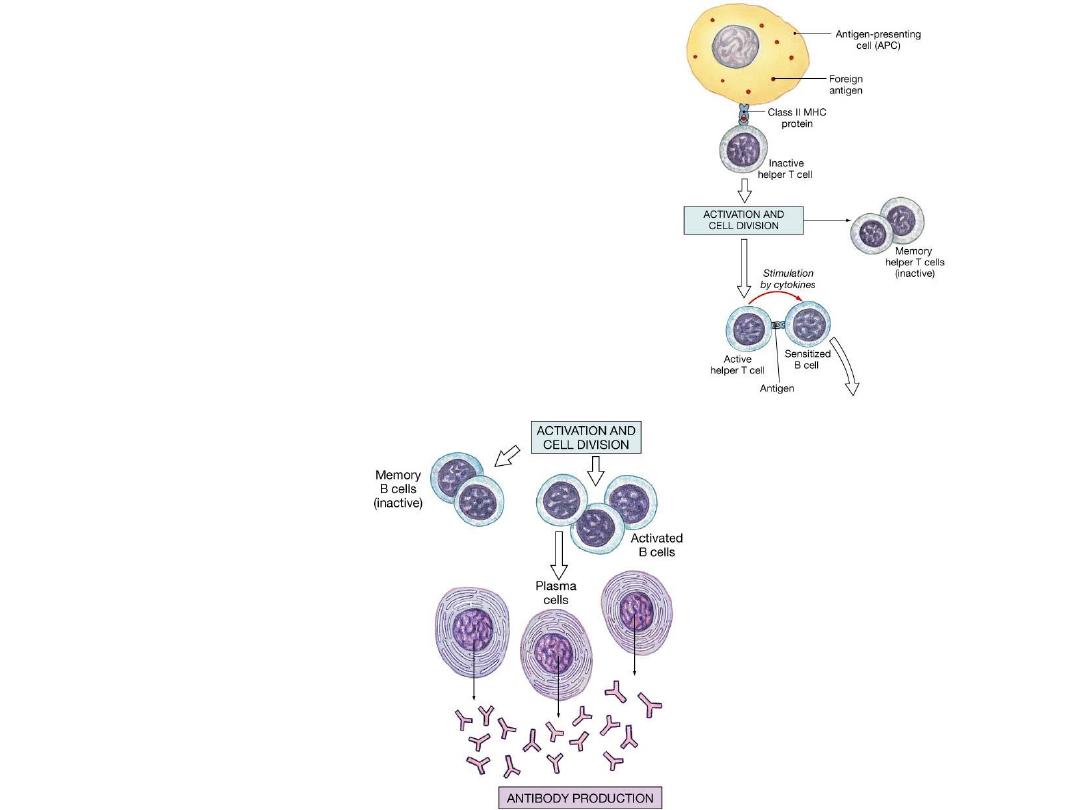
Class II MHC Proteins
•
Found only on membranes of lymphocytes and
phagocytic antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
–
Such as monocyte-macrophage group, free and fixed
macrophages
–
Specialized for activating T cells against foreign cells and
proteins
•
Phagocytic APCs engulf and break down foreign
antigens or pathogens
–
Fragments of foreign antigens displayed on phagocytic
cell’s membrane
•
Bind to Class II MHC proteins
•
T cells come in contact and become activated, starting the immune
response


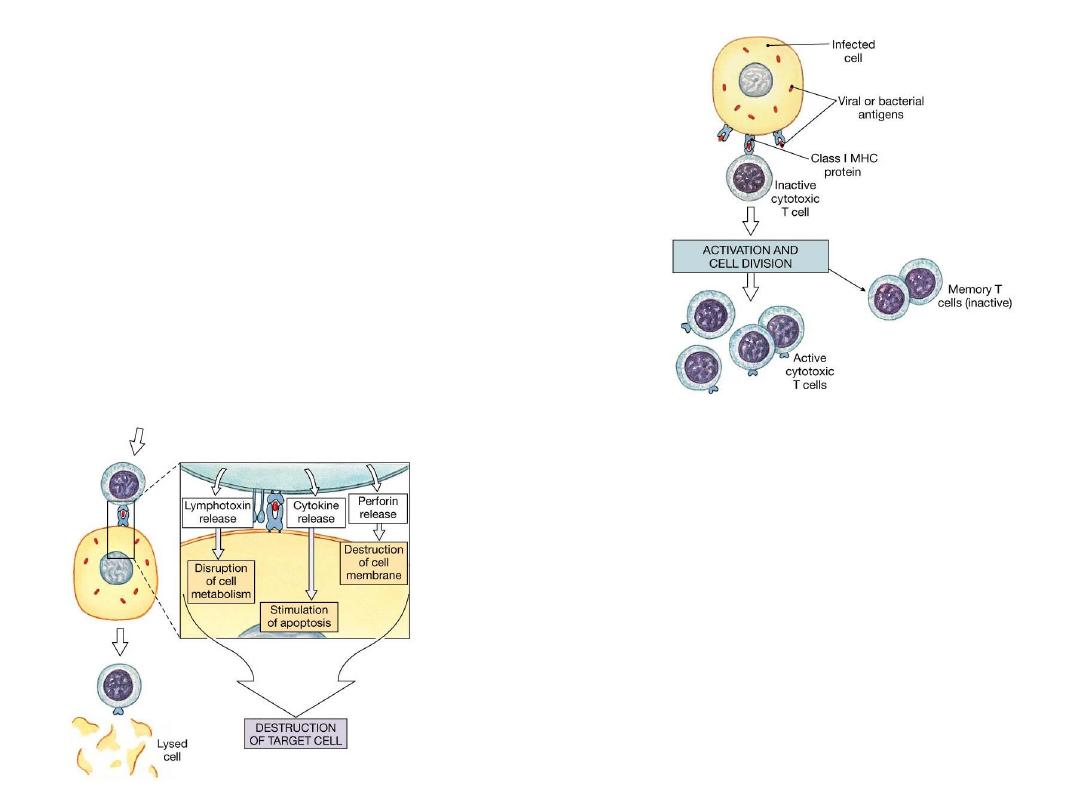
T Cells
•
T cell activation for both occur when MHC
protein contains specific antigen T cell
programmed to detect
–
Once activated, T cells divide and differentiate in
to cells with specific function in immune response
•
Cytotoxic T cells
•
Helper T cells
•
Memory T cells
•
Suppressor T cells

Helper T Cells
•
Activated by exposure to antigens bound to
Class II MHC proteins
•
Activated divide to produce
–
Active Helper T cells and memory cells
•
Release variety of cytokines that:
–
Coordinate specific and nonspecific defenses
–
Stimulate cell mediated and antibody-mediated
immunity

Memory T Cells
•
During cell division for both cytotoxic and
helper T cells, some develop into memory
cells
•
Remain in reserve
•
If same antigen attacks 2
nd
time, memory T
cells immediately differentiate into cytotoxic T
cells and helper T cells
–
Allows for more rapid and effective immune
response

Suppressor T Cells
•
When activated, depress responses of other T
and B cells
•
Does not occur immediately
–
Takes much longer for these cells to become
activated
–
Act after initial immune response

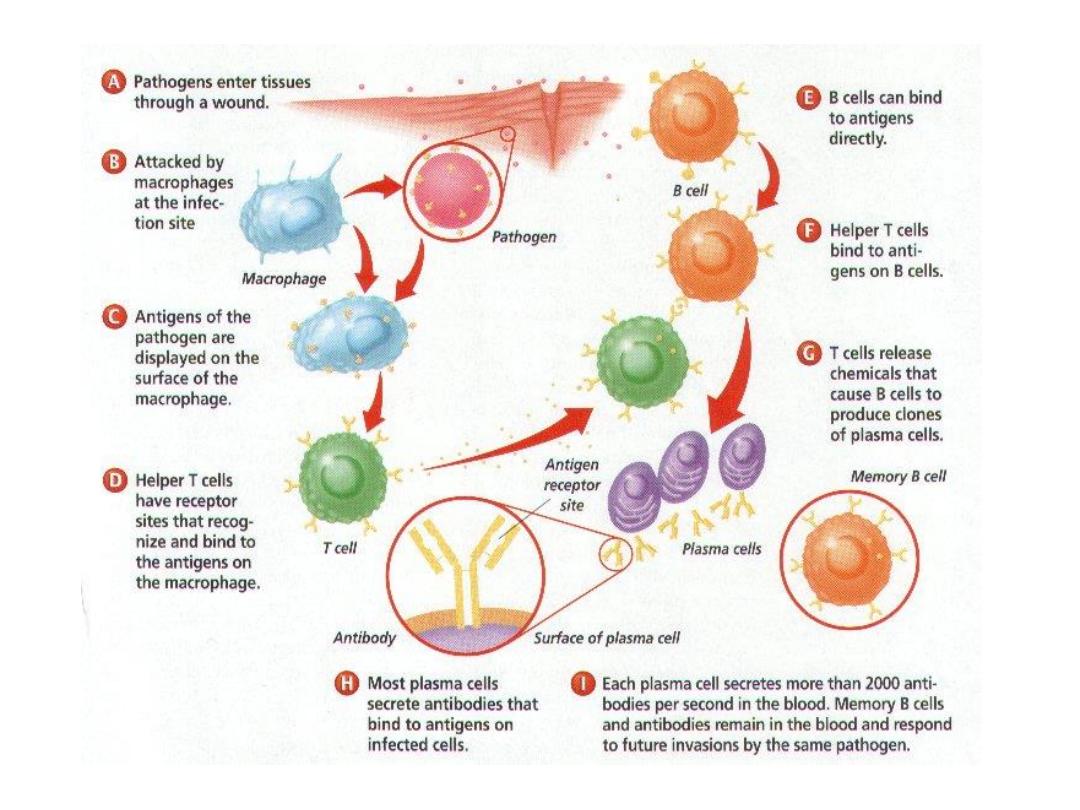
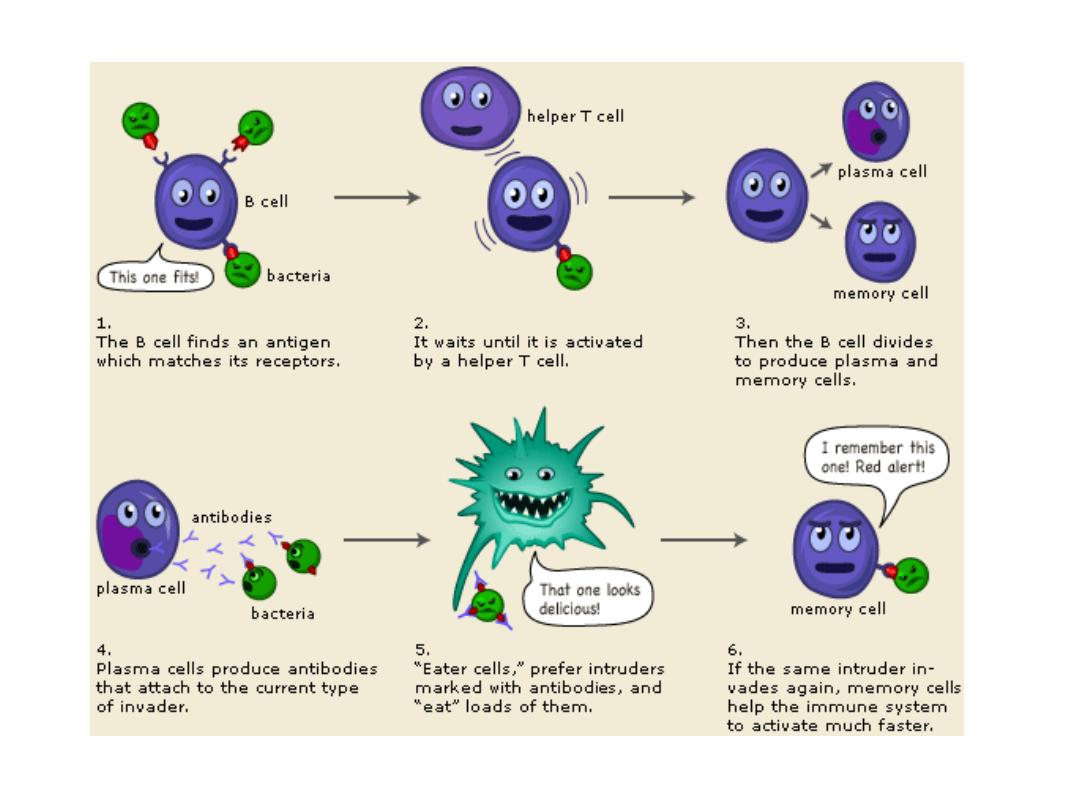
B Cells and Antibody-Mediated
Immunity: B Cell Activation
•
Each B cell carries its antibody molecules in its
cell membrane
–
If ISF contains antigens that can bind to
antibodies, B cells become sensitized
•
Antigens enter B cell and become displayed on Class II
MHC proteins on surface of B cell
–
Helper T cell activated by same antigen attaches to MHC
protein-antigen complex and secretes cytokines that:
»
Promote B cell activation
»
Stimulate B cell division
»
Accelerate plasma cell production
»
Enhance antibody production

B Cell Activation
•
Activated B cells divide several times
–
Produce daughter cells that differentiate into:
•
Plasma cells
–
Synthesize and secrete large numbers of antibodies on surface
of sensitized B cells
•
Memory cells
–
Similar to memory T cells
–
If exposed to same antigen, will differentiate into plasma cells


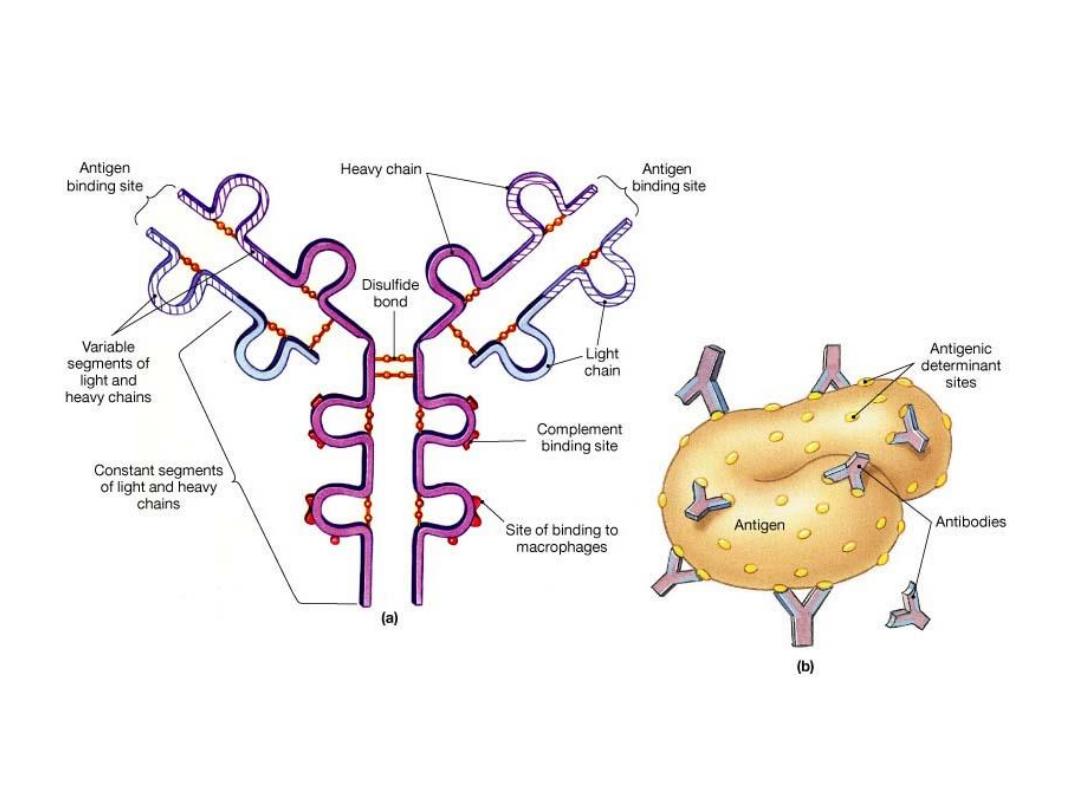
Antibody Structure
•
Consist of short and heavy chains of polypeptides
–
Each chain has constant and variable segments
•
Constant heavy chains form base of antibody molecule
–
B cells produce only 5 types of constant segments
–
Specificity depends on variable segments of light and
heavy chains
•
Free tips contain antigen binding sites (very specific for each type
of antigen)
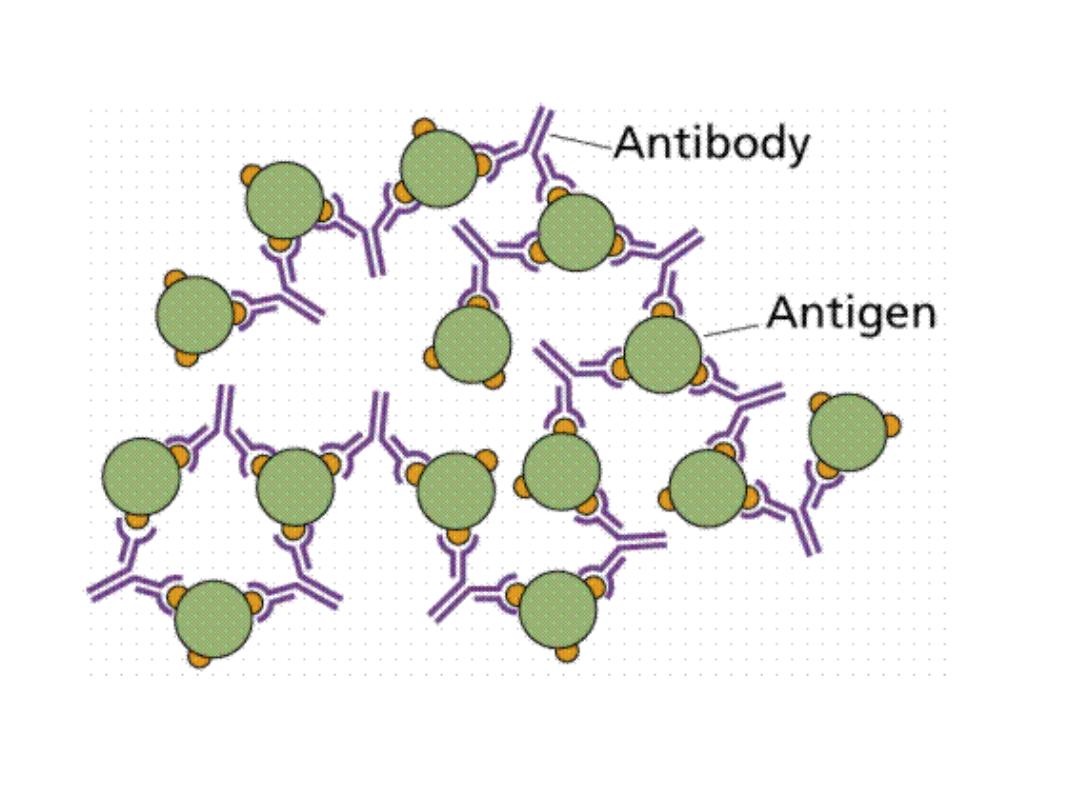
•
Antigen-antibody complex
–
Forms when antibody binds to proper antigen
–
Binds to sites and leads to B cell sensitization and an
immune response

Classes of Antibodies (Immunoglobins
Igs)
•
IgG
–
Largest and most diverse
–
Resist many viruses, bacteria, bacterial toxins
–
Can cross placenta
•
What type of immunity is that?
•
IgM
–
Circulate; attack bacteria
•
IgA
–
Found in exocrine secretions
•
Ex?
–
Attack pathogens before they enter the body
•
IgE
–
When bound to antigen, stimulates basophils and mast cells to release
chemicals to stimulate inflammation
•
IgD
–
Attached to B cell and involved in their activation

Antibody Function
•
Neutralization
•
Agglutination and Precipitation
•
Activation of a complement
•
Attraction of phagocytes
•
Enhancement of phagocytosis
•
Stimulation of inflammation
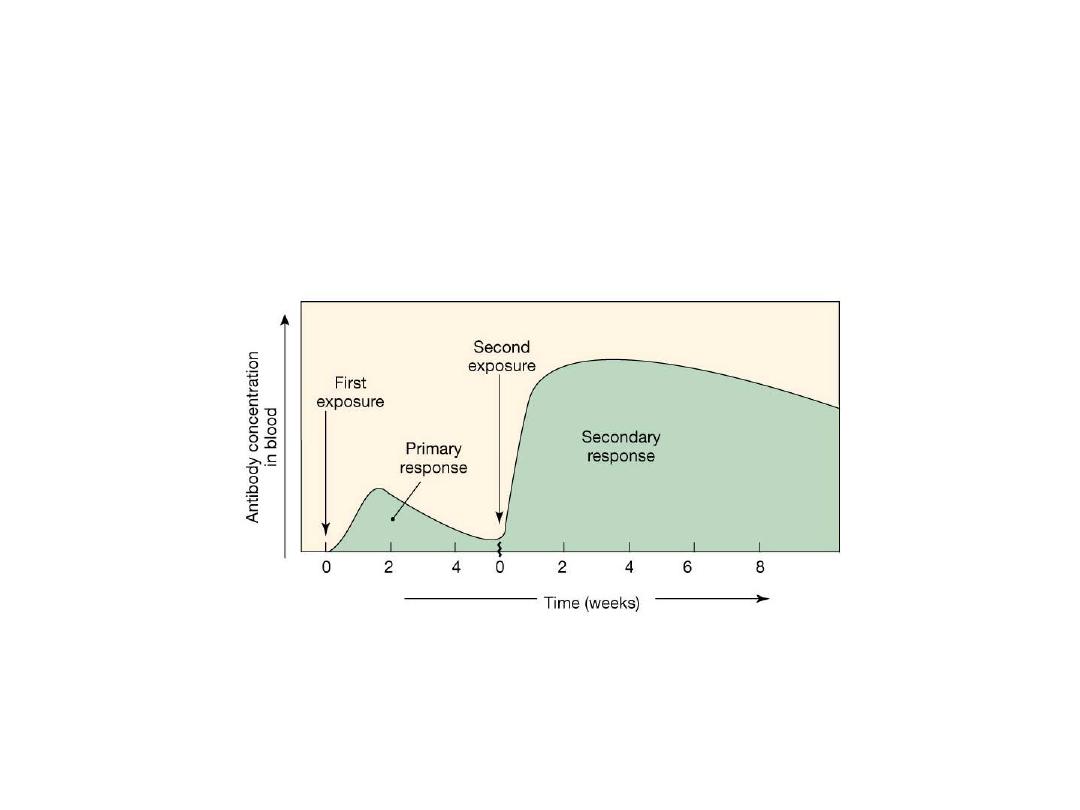
Primary and Secondary Responses to
Antigen Exposure
