The muscle

Objectives
1-Define simple muscle twitch?
2-Describe the sequential events in muscle
contraction according to the sliding filament
theory.
3- State the principles of walk along theory of
skeletal muscle contraction
4-Compare the two types of muscle contraction.
•

Electrical characteristics of skeletal
muscles:
1- The resting membrane potential is – 80 to – 90 mill volt in
skeletal muscle fiber (same as in large mylinated nerve fiber).
2- The electrical changes of the ion fluxes are similar to those of
the nerve fiber during action potential.
3- Duration of the action potential is 1 to 5 milliseconds (5 times
longer than that in mylinated nerve fiber).
4- The conduction velocity is 3 to 5 m/ second (less than that in
large mylinated nerve fiber).
5-Due to the slight difference in the threshold between muscle
fibers of the same muscle and the difference in the distance
between the stimulation site and different muscle fibers, the
action potential recorded from the whole muscle after direct
stimulation is proportional to the intensity of the stimulus
between threshold and maximum intensity (do not obey all or
none law).
6- Each single contraction is followed by a single relaxation in
response to a single action potential (simple muscle twitch).
•

Excitation contraction coupling
The process by which depolarization of the muscle fiber
initiates contraction is called excitation- contraction coupling.
1- Sliding filament theory
:
1 – The discharge of motor neuron.
2- An action potential travels along the motor
nerve to its ending in the muscle fiber.
3- Secretion of small amounts of
neurotransmitter substance Acetylcholine
(Ach) at the motor end plate.
4-Ach binds to nicotinic receptors on muscle
fiber membrane to open Ach gated channels.

5- Increase in Na and K ions conductance (Na ions
diffuse to the interior of the muscle fiber
membrane) and this will initiate a local end plate
potential, and when firing level is reached, action
potential is generated and spread along the
whole muscle fiber.
6- The inwards spread of the action potential by the
T system of tubules.
7- Release of calcium ions from the terminal
cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
8-Calcium will bind to Troponin C molecule this will
lead to conformational changes:
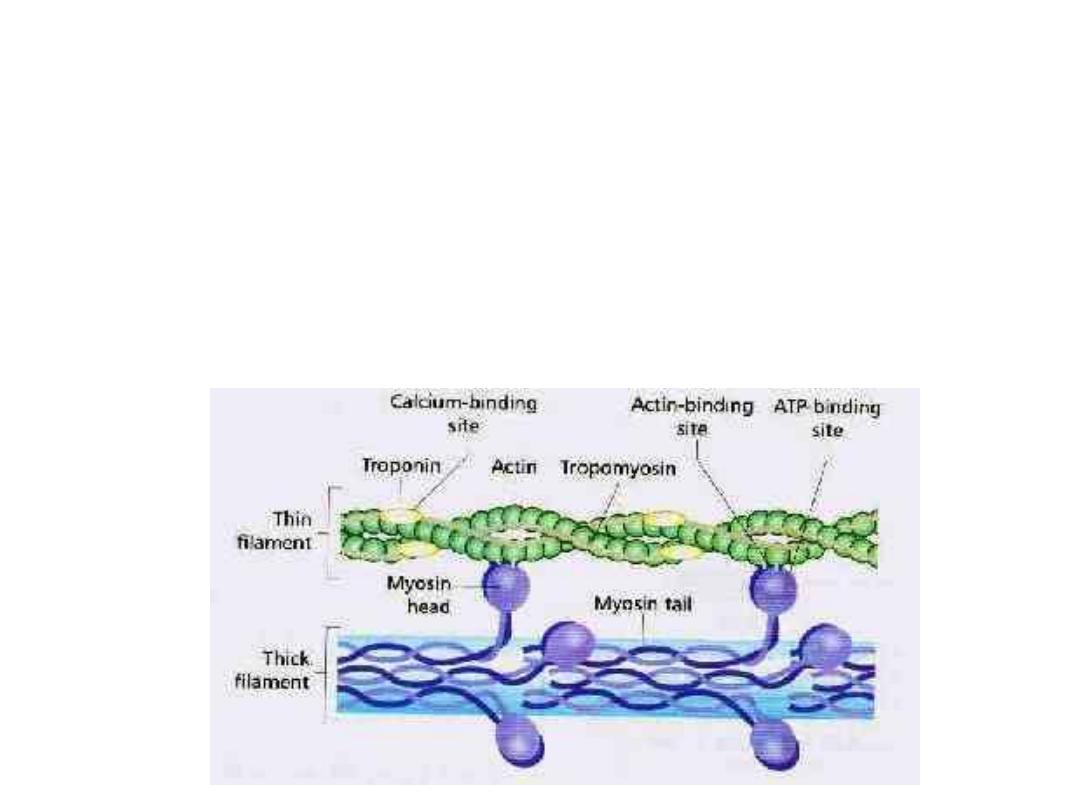
The binding of Troponin I to actin will be weakened.
This allows Tropomyosin to move laterally outside the groove
and uncover the binding sites for the myosin heads.
So Ca ions will act as an inhibitory factor on troponin –
tropomyosin attachment to actin.
The formation of cross bridges between actin and myosin heads
→ sliding of thin on thick filaments producing shortening (the
sarcomere will be shortened).
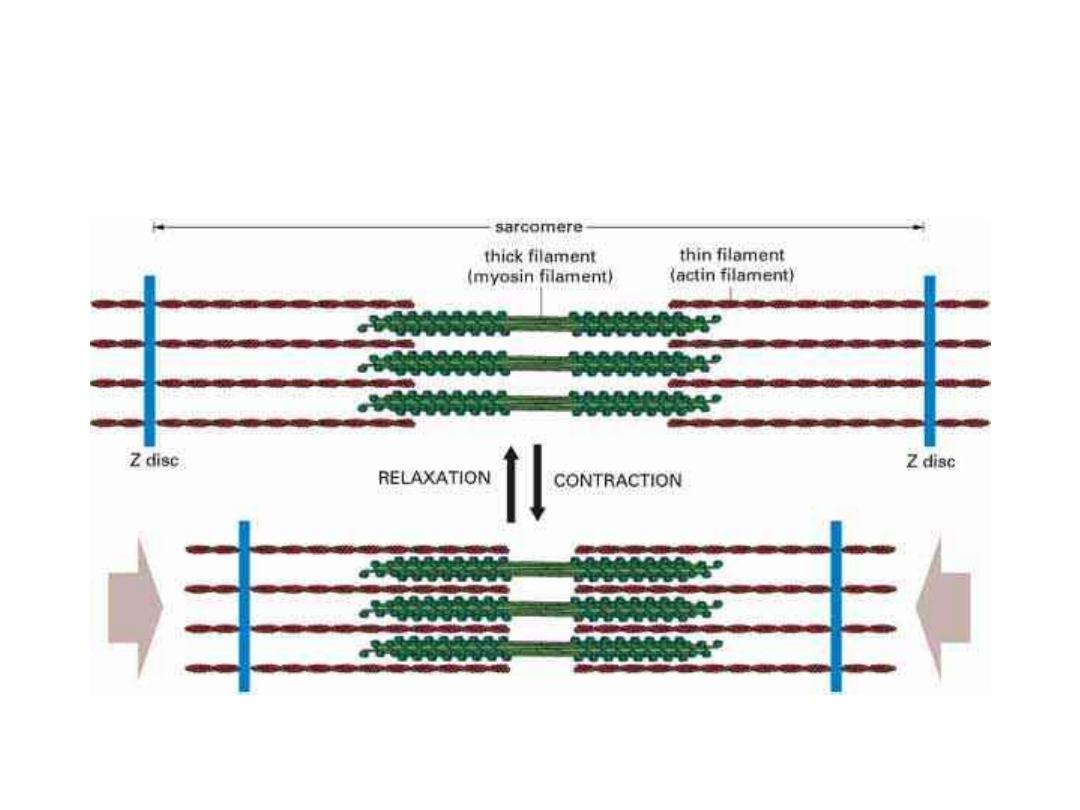
So during muscle contraction 1- the Z lines move closer to each
other, 2- the I band becomes shorter and 3- the A band stays at
the same length.

2- The walk- along or Rachet theory of
contraction:
This theory suggests that the sliding
during muscle contraction is produced by
attaching, breaking and reforming of the
cross linkages between actin and myosin
heads,
the intensity of the interaction
depends on the number of cross linkages .

-
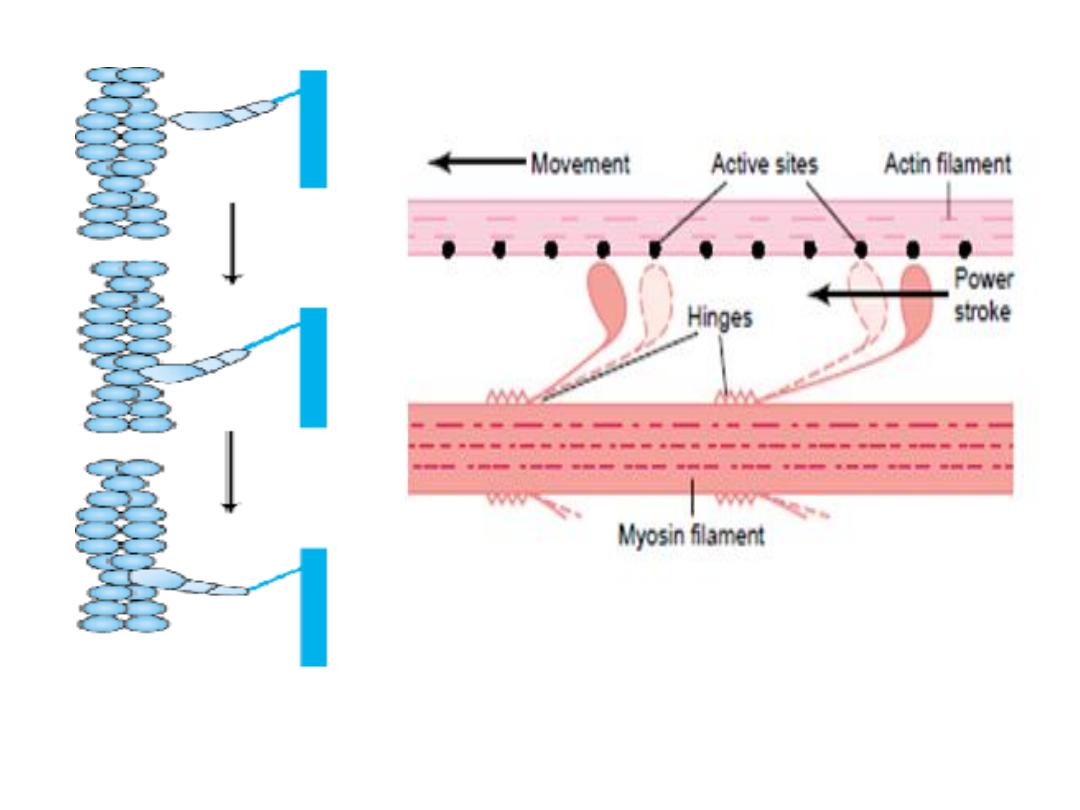
After uncovering of the active sites of the actin.
- Myosin head link to actin at 90 degrees angle, the
head tilts towards the arm to drag the actin filament
along with it,
- Producing movement by swiveling(pulling).
- Then disconnect(breaks away from the active site,
then the head returns to its extended direction , then
it combines with a new active site farther down along
the actin filament and the process is repeated).
The pulling of the heads of myosin to actin or
the tilt of the myosin head is called the
power
stroke.

Steps in relaxation:
1- After a fraction of a second, the calcium ions are pumped
actively back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by a Calcium
membrane pump
,
they are going to diffuse into the terminal
cisterns to be released by the next action potential.
2- The release of calcium ions from Troponin C,
3- Then cessation of binding between actin and myosin (i.e.
tropomyosin returns to its site.
4- Contraction stops.

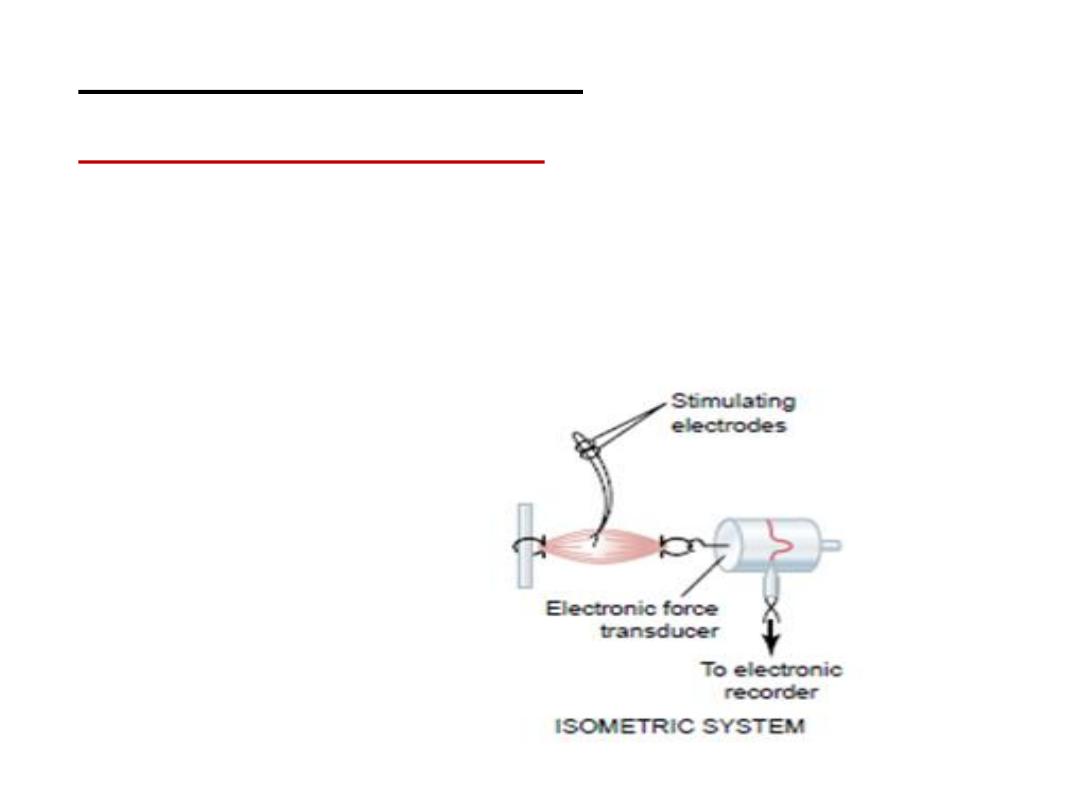
Types of contraction:
1- Isomertic contraction
:
is when the muscle does not shorten during
contraction i.e. no change in muscle length, but the
tension will increase.
e.g. trying to lift a heavy object. The work done here is zero,
because no movement.
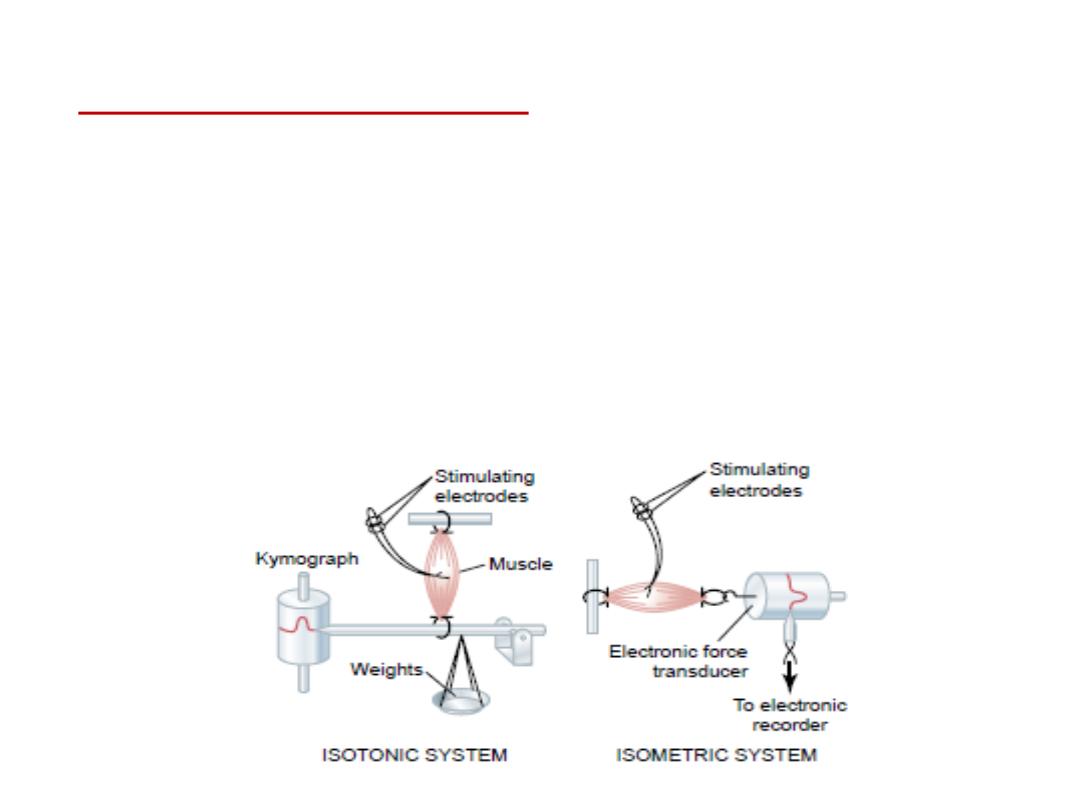
2- Isotonic contraction:
It is the contraction
that causes shortening of the muscle
length and the muscle has the same tension. e.g. lifting an object
by contracting the biceps muscle.
Here there is work done because there is movement.
The muscle shortens against a fixed load, and its characteristics
depends on the load against which the muscle contracts and on
the inertia of the load.
