
Bone marrow
Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer

Objectives
At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to
Identify the major site of hematopoiesis in the fetus and normal adult.
state the types of bone marrow
outline the compartments of red bone marrow
describe the types and distinctive characteristic of stem cells
Bone marrow
Is a soft connective tissue
occupies the medullary
cavity of long bones and
all the spaces between the
trabeculae of spongy bone
It accounts for
approximately
5%
of the
body weight in humans
Two varieties of marrow
are recognized
1.
Red marrow
2.
Yellow marrow
Red marrow
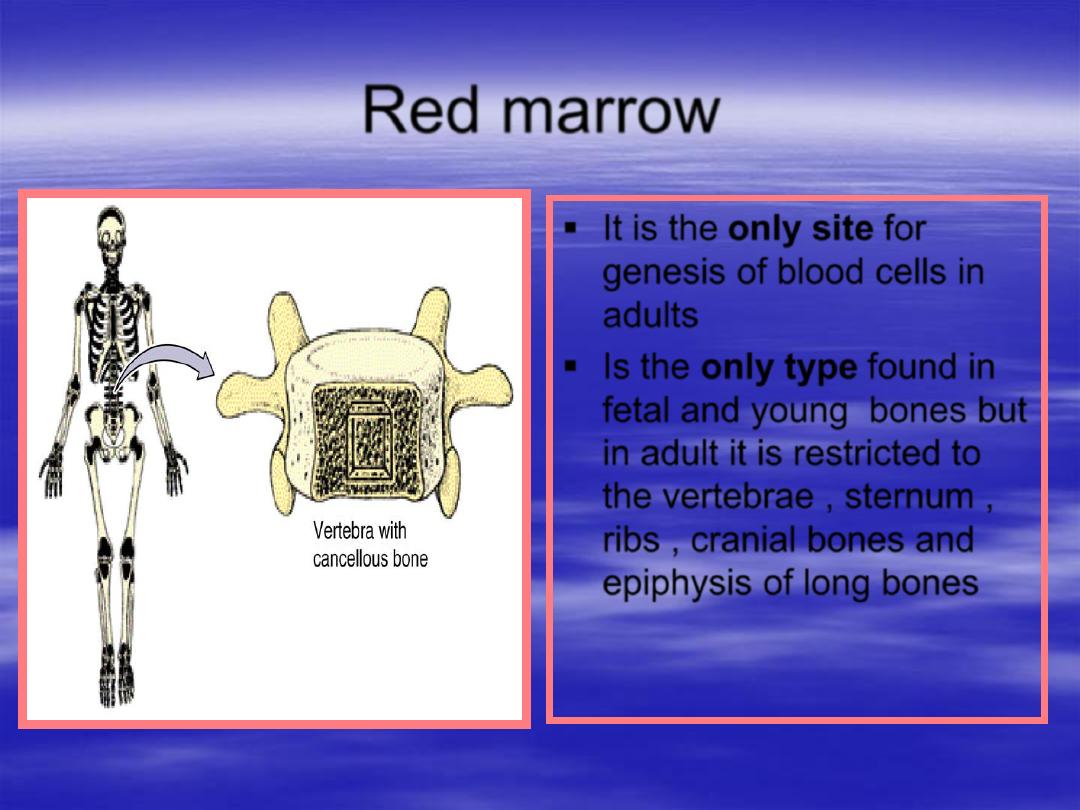
It is the
only site
for
genesis of blood cells in
adults
Is the
only type
found in
fetal and young bones but
in adult it is restricted to
the vertebrae , sternum ,
ribs , cranial bones and
epiphysis of long bones

Amount of red marrow varies with the age
Childhood
- red marrow is 100% of bone
marrow and present in virtually every bone.
Adults
- red marrow is 50% of bone marrow
presenting in sternum, ribs, pelvis and skull.
70 years
- red marrow reduced to 30% of the
bone marrow.

Yellow marrow
Consists in main of
fat cells
which have
gradually replaced the other marrow
elements .
With an adequate stimulus , yellow marrow
may resume the character of red marrow
and play an active role in the process of
blood development .
Red bone marrow has
1.
A vascular compartment
2.
An extravascular compartment
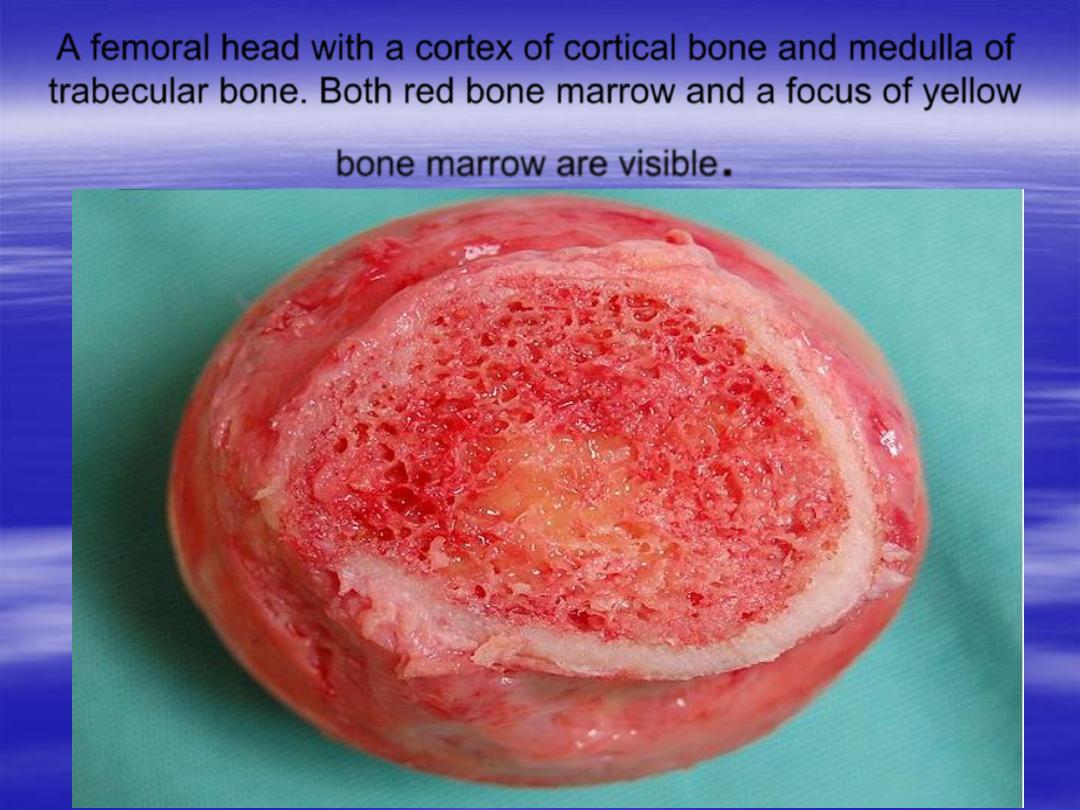
A femoral head with a cortex of cortical bone and medulla of
trabecular bone. Both red bone marrow and a focus of yellow
bone marrow are visible
.
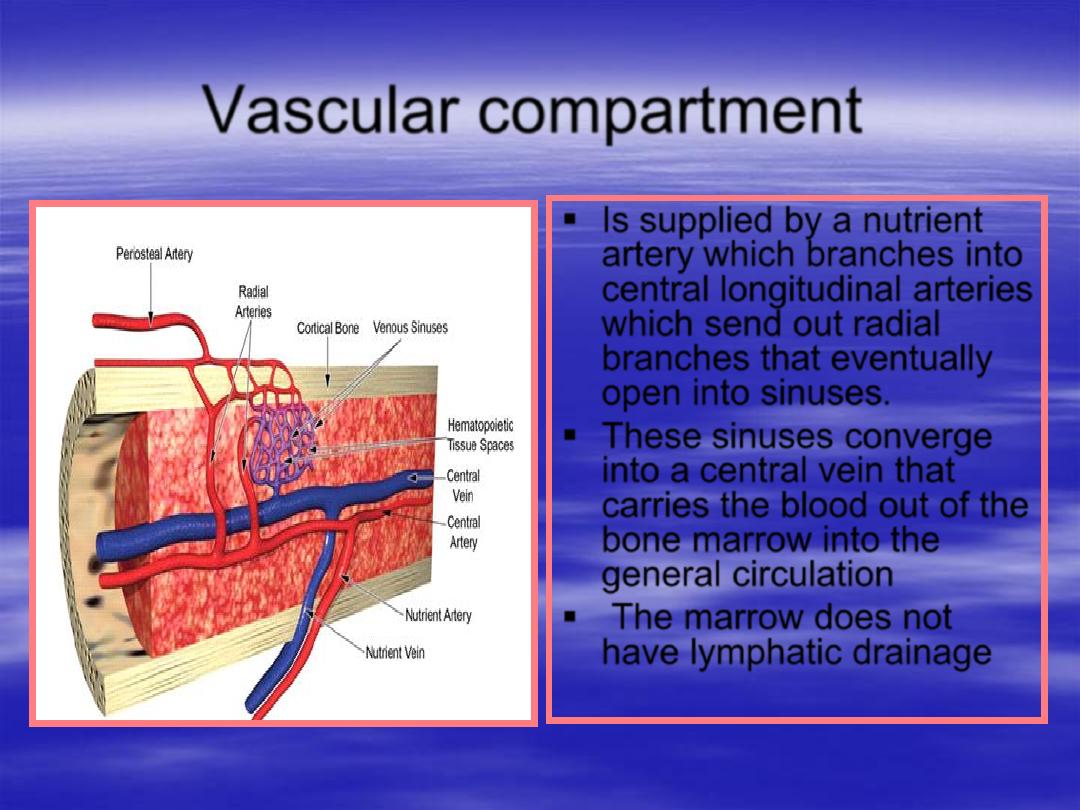
Vascular compartment
Is supplied by a
nutrient
artery
which branches into
central longitudinal arteries
which send out
radial
branches
that eventually
open into
sinuses
.
These
sinuses
converge
into a
central vein
that
carries the blood out of the
bone marrow into the
general circulation
The marrow does not
have lymphatic drainage
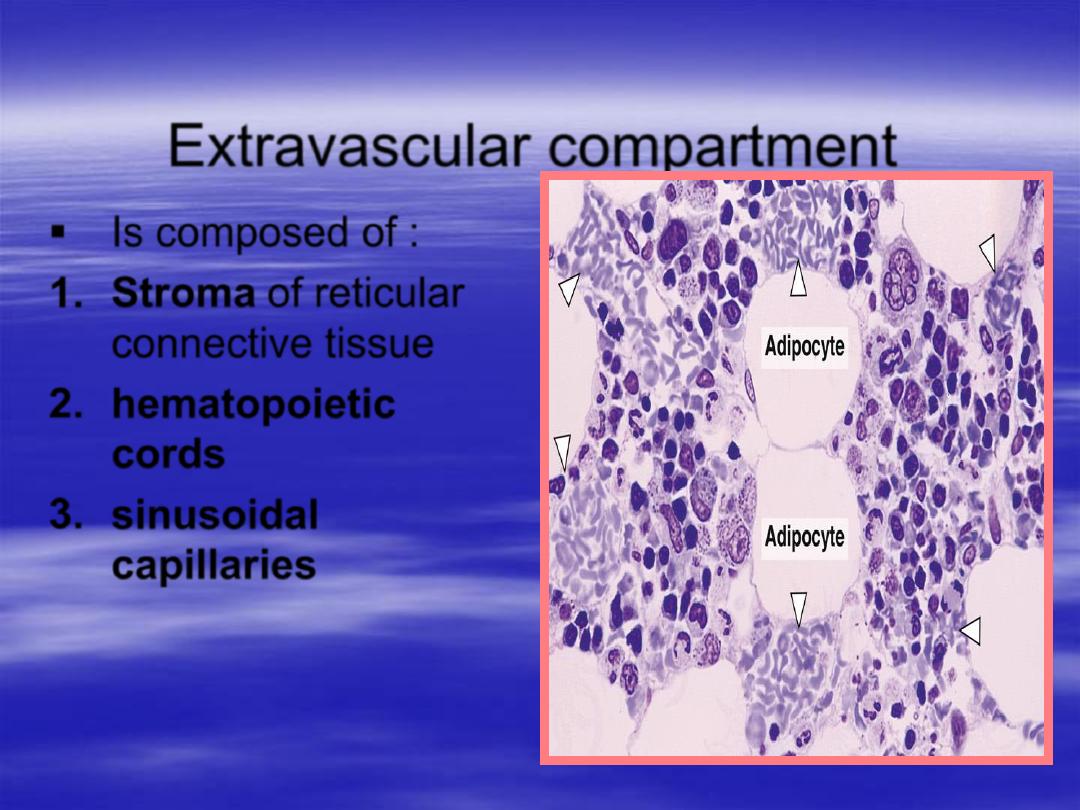
Extravascular compartment
Is composed of :
1.
Stroma
of reticular
connective tissue
2.
hematopoietic
cords
3.
sinusoidal
capillaries

Stroma is composed of
reticular tissue
1. reticular cells
2.Reticular fibers
macrophages and adipose cells
Matrix

Reticular cells
Stellate
in shape
and are
in contact with each other
along extended cellular
processes.
Function of reticular
cells
:
1.
Act as a meshwork to
support and protect the
haemopoietic cells
2.
Formation of reticular
fibers
3.
Phagocytosis
4.
They transfer to
adipocytes by
accumalating lipid in their
contents
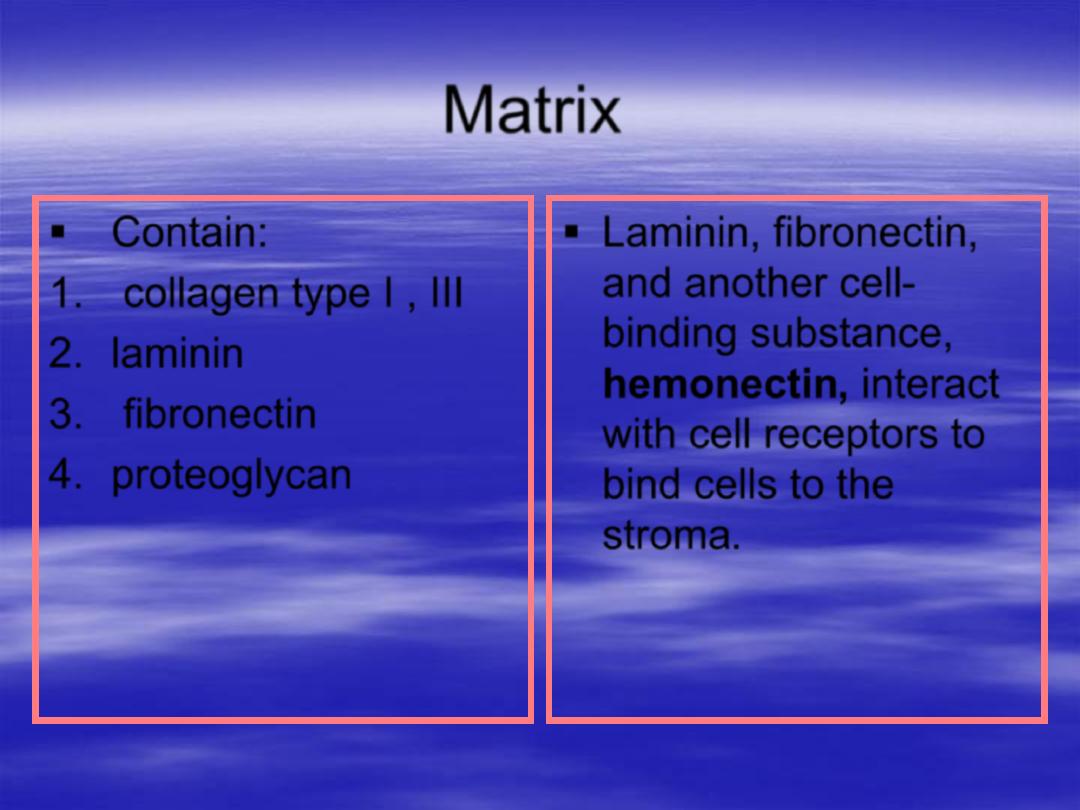
Matrix
Contain:
1.
collagen type I , III
2.
laminin
3.
fibronectin
4.
proteoglycan
Laminin
,
fibronectin
,
and another cell-
binding substance,
hemonectin
, interact
with cell receptors to
bind cells to the
stroma.
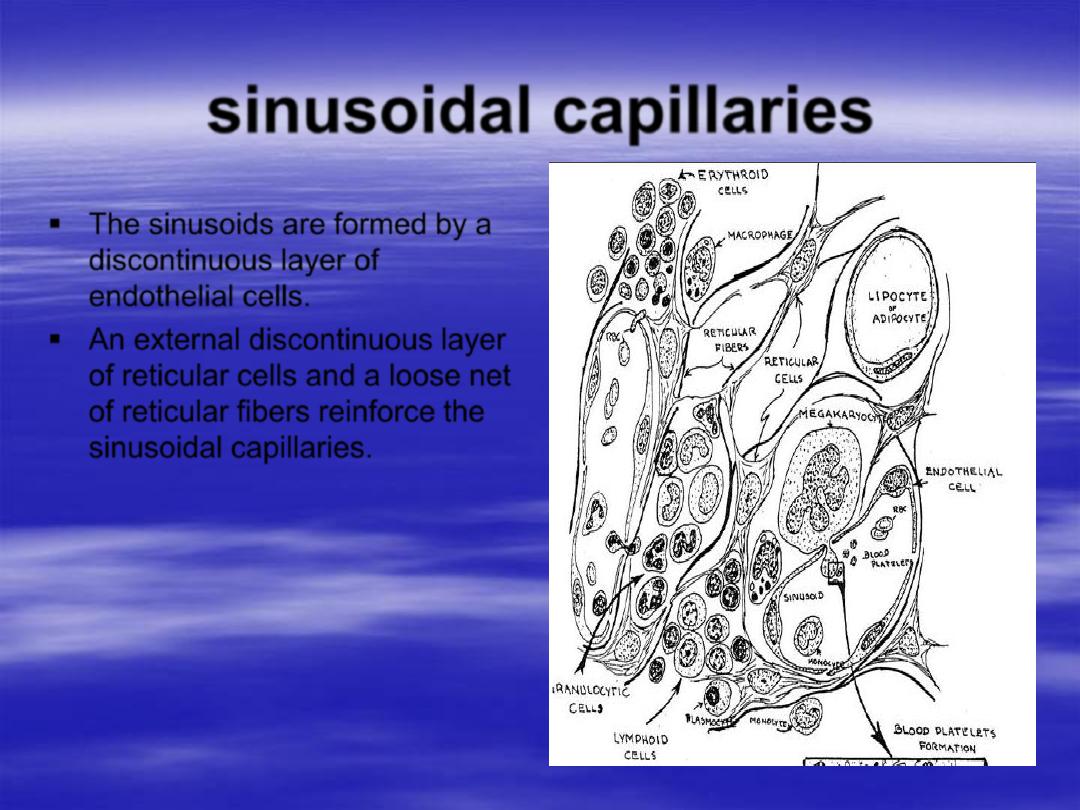
sinusoidal capillaries
The sinusoids are formed by a
discontinuous layer of
endothelial cells.
An external discontinuous layer
of reticular cells and a loose net
of reticular fibers reinforce the
sinusoidal capillaries.
Bone marrow barrier
The blood vessels of the bone marrow constitute a
barrier, inhibiting immature blood cells from
leaving the marrow.
Only mature blood cells contain the membrane
proteins required to attach to and pass the blood
vessel endothelium. Hematopoietic stem cells may
also cross the bone marrow barrier, and may thus
be harvested from blood
.

Stem cells
are pluripotential cells capable of self-renewal.
Some of their daughter cells form specific, irreversibly
differentiated cell types, and other daughter cells remain
stem cells.

Stem cells
They retain the ability
1.
to
renew
themselves through mitotic cell
division and
2.
can
differentiate
into a diverse range of
specialized cell types.
They found in all multi-cellular organism .

Two broad types of mammalian
stem cells
1.
Embryonic stem cells
that are found in
blastocysts
2.
Adult stem cells
that are found in adult
tissues

Embryonic Stem Cells
are derived from the inner cell mass of the
embryo.
Because these cells are
pluripotent and can
virtually form any cell or tissue type, they
have the potential for curing a variety of
diseases, including diabetes, Alzheimer and
Parkinson diseases, anemias, spinal cord
injuries, and many others.
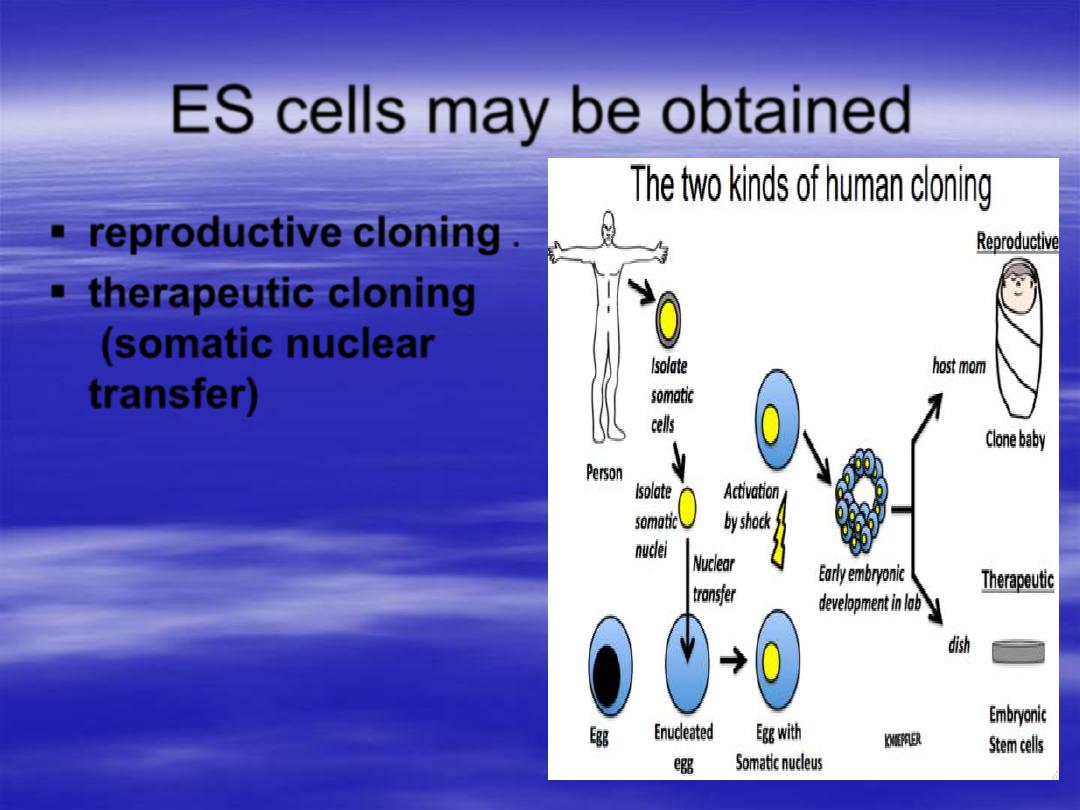
ES cells may be obtained
reproductive cloning
.
therapeutic cloning
(somatic nuclear
transfer)

Reproductive cloning
ES cells may be obtained
from embryos
after
in
vitro fertilization
This approach has the
disadvantage that
1.
the cells may cause
immune rejection
, since
they would not be
genetically identical to their
hosts.
2.
Another issue with this
approach is based on
ethical considerations,
since the cells
are derived
from fertilized viable
embryos
.
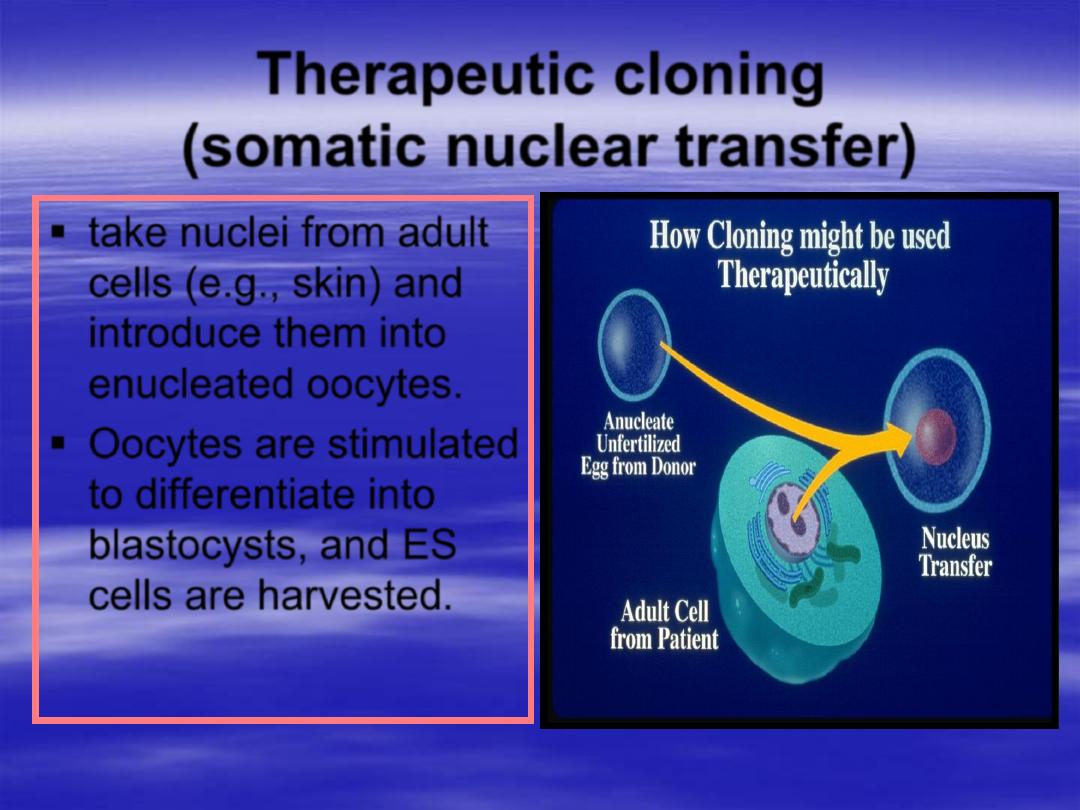
Therapeutic cloning
(somatic nuclear transfer)
take nuclei from adult
cells (e.g., skin) and
introduce them into
enucleated oocytes.
Oocytes are stimulated
to differentiate into
blastocysts, and ES
cells are
harvested
.

Therapeutic cloning
(somatic nuclear transfer)
Since the cells are derived from the host,
they are
compatible genetically
and
since fertilization is not involved, the
technique is
less controversial

Adult Stem Cells
Adult tissues contain stem cells
that also may prove valuable in
treating diseases.
These cells are restricted in
their ability to form different cell
types and, therefore,
are
multipotent
,not pluripotent.
Adult stem cells isolated from
rat brains have been used to
cure Parkinson disease in rats,
suggesting that the approach
has promise.
Disadvantages of the approach
include
1.
the
slow rates of cell division
characteristic of these cells and
2.
their scarcity
, which makes
them difficult to isolate in
sufficient numbers for
experiments
.
