LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
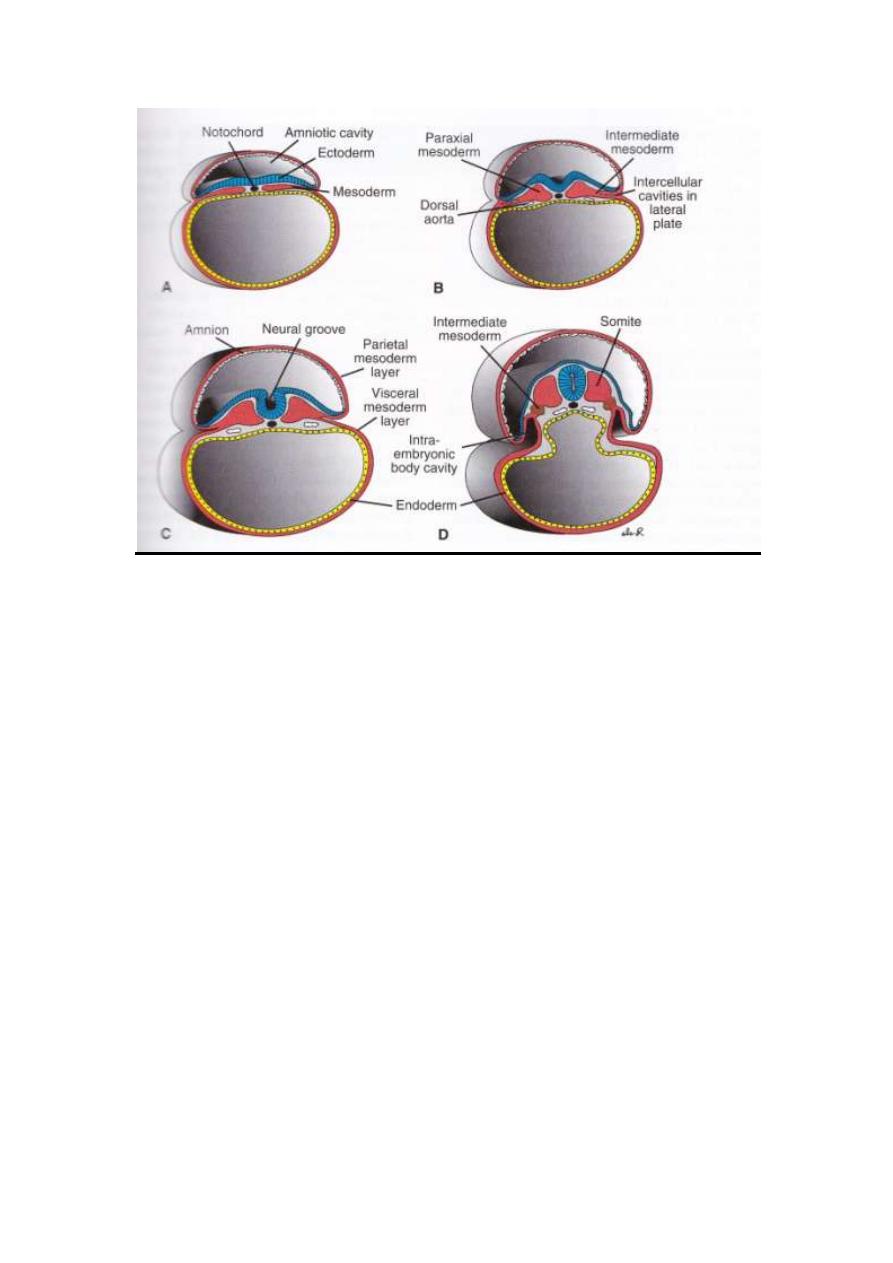
Section in the embryo showing.
A- 17
th
day embryo
-Three germinal layers
-Notocord
-Amniotic cavity
-Yolk sac lined by endoderm
B- 19
th
day embryo
-Crest formation at the tip of neural fold
-Dorsal aorta
-Paraxial &intermediate mesoderm
-Notocord
-Neural groove begin

LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
-Yolk &amniotic cavity is present
C-20
th
day embryo
-
Parietal mesoderm layer covering the amniotic cavity
-Visceral mesoderm layer covering yolk cavity
-Somites begin to appear
D-21
st
day embryo
-Paraxial mesoderm appear which become somites
-Intermidiate mesoderm appear
-Lat. plate become obvious
20
th
days embryo showing somites formatin
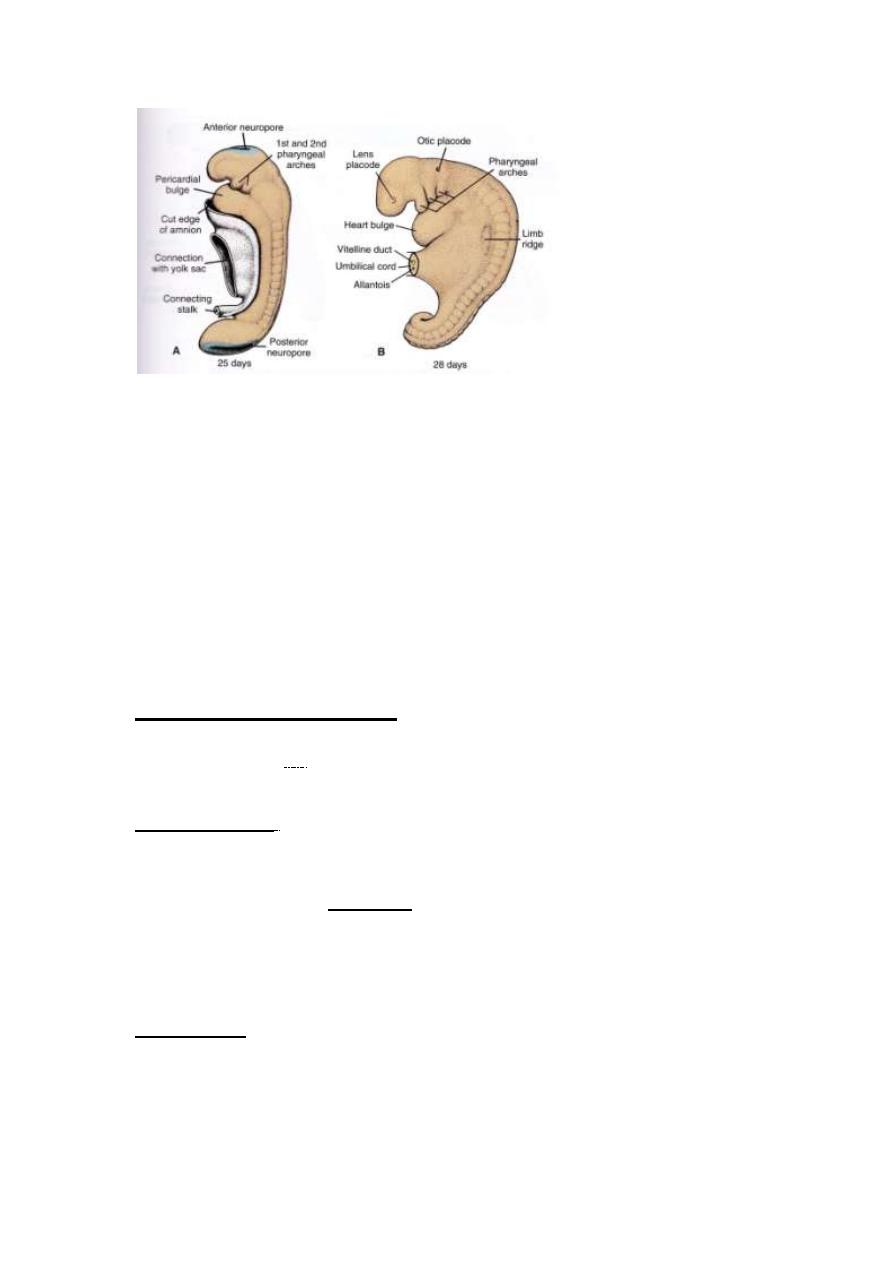
LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
25
th
days embryo showing ant.&post. neuropore
28
th
days embryo showing otic placod ,lens placode &umbilical cord
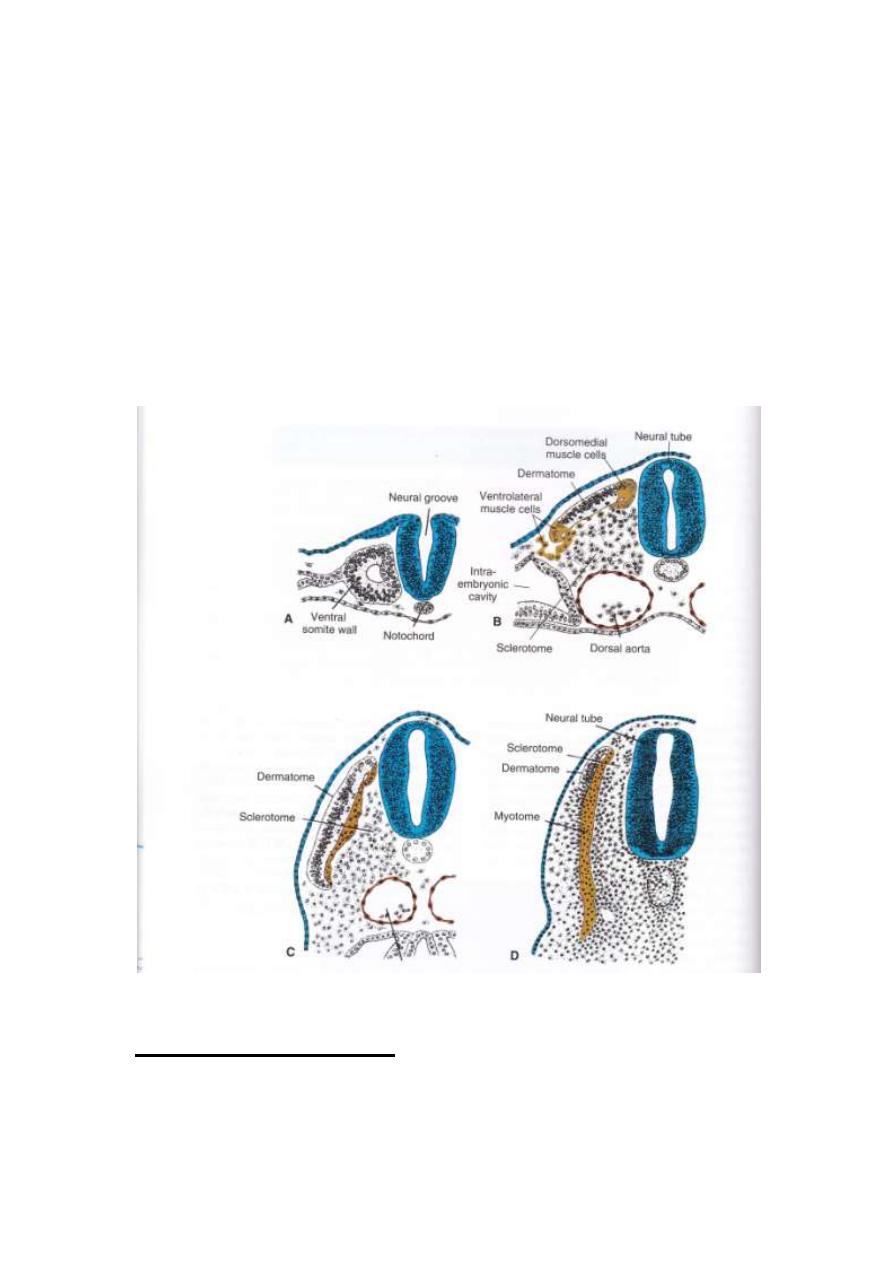
Somite differentiation:
When somites, 1
st
formed, they exist as a ball of mesoderm
(fibro-blast like).These cells then undergo process of
epithelization & arrange in a shape of donut surrounding small
lumen.
At the beginning of 4
th
week , the ventral & medial cells of
somite lose its epithelial characters, & become mesenchymal
(fibro-blast like) again, & its position shifted surrounding
notochord & neural tube.Collectively, these cells form the
sclerotome, which will be differentiated into vertebral column
& ribs.

LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
Cells at the dorsomedial & ventrolateral edge of the upper
region of somite form precursor for muscle cells, while the cells
between these two groups form the dermatome.
Cells from both muscle precursor groups become mesenchymal
again & migrate beneath the dermatome to create
dermomyotome.
Besides, cells from ventrolateral edge migrate into the parietal
layer of lateral plate mesoderm to form most of the musculature
for the body wall ( external, internal oblique & transversus
abdominus, & the most of limb muscles).
Cells in the dermatomyotome ultimately form dermis for skin of
the back & muscles for the back , body wall (intercostal
muscles) & some of limb muscles.
Imp Notes:
1- Each dermatome & myotome retains its innervation from
its segment of origin , no matter how far it migrates.
2- Each somite forms:
a) Its own sclerotome ( tendon & cartilage & bone
components).
b) Its own myotome(providing segmental muscle
component).
c) Its own dermatome which form the dermis of the
back.
LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
Lateral plate mesoderm:
Lateral plate mesoderm splites into parietal (somatic) &
visceral (splanchnic) layers, which line inter embryonic cavity
(parietal layers) & surround the organs (visceral layer).
Mesoderm from parietal layer, together with ectoderm, forms
lat. Body wall folds. These folds, together with head (cephalic
fold) & tail (caudal folds), close the ventral body wall.
Imp: the parietal layer of lateral plate mesoderm forms the
following:
- Dermis of the skin in the body wall & limbs.
- Bones & connective tissue of the limbs & sternum.
Besides, sclerotome & muscle precursor cells that
migrate into the parietal layer of the lat. Plate of
mesoderms forming :
a) Costal cartilage.
b) Limb muscles.
c) Most of body muscles.
LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
Imp: the visceral layer of lat. Plate of mesoderms, together with
embryonic endoderm, form the wall of gut tube.
Mesoderm cells of parietal layer surrounding the inter-
embryonic cavity, form thin membrane called mesothelial or
serous membrane, which line peritoneum, pleural & pericardial
cavities & secrets serous fluid.
While mesoderm of visceral layer form a thin serous membrane
each organ.
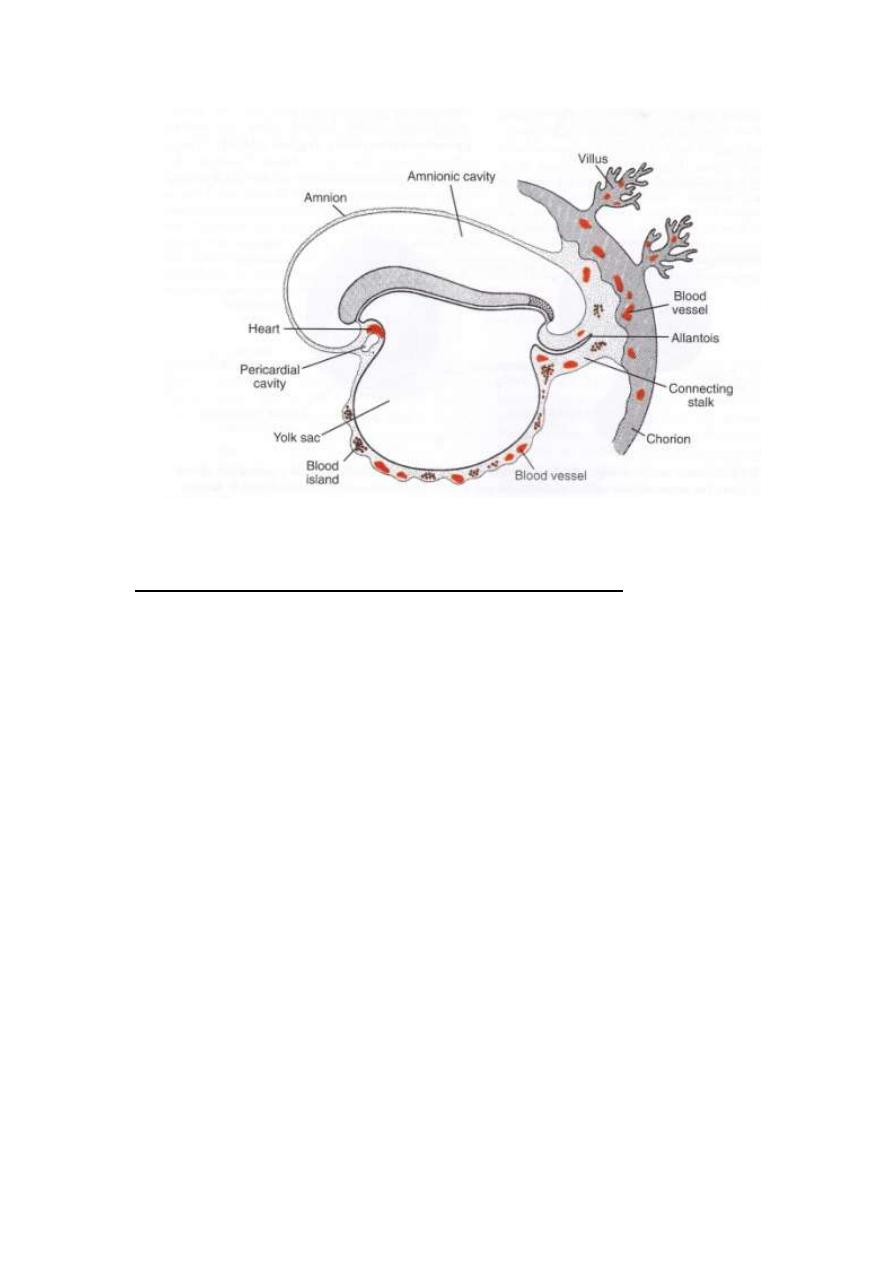
Blood & blood vessels:
One of derivatives of mesodermal germ layer is blood cells &
blood vessels.

LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
Blood vessels form in two ways:
1- Vasculogenesis: in this way the blood vessels arise from
blood islands.
2- Angiogenesis: which sprouts from existing vessels.
Hemangioblasts: is a common precursor for blood vessels &
blood cells formation. It originates from island of blood which
arise from mesodermal cells in the wall of yolk sac (3
rd
week) &
in lat. Plate mesoderm.
The first blood cell that arise in blood island, in the wall of yolk
sac is transitory .
While definitive hematopoietic stem cells are derived from
mesoderm surrounding aorta & from the area near developing
mesonephric kidney . This is called aorta-gonad-mesonephos
region (AGM). These cells will colonize the liver (which is
responsible for blood formation in embryo & fetus from
2
nd
– 7
th
months of development.
Then stem cell of liver will colonize bone marrow which is
definitive blood forming tissue, in the 7
th
months of gestation.
After that the liver loses its blood forming function.
LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
Derivatives of the endodermal germ layer:
One of the main organ forms from endoderm is gastro-intestinal
tract.
This germ layer lines the ventral surface of embryo forming the
root of yolk sac.
With formation of brain vesicles, the embryonic disc begin to
bulge into amniotic cavity. Lengthening of neural tube will
cause the embryo to curve into fetal position, so as head & tail
region move ventrally. Also the lateral body wall folds more
ventrally closing the ventral body wall.
In this way the whole embryo will pull the amnion down with
the embryo & so the embryo will be lie within amniotic cavity.
The ventral body wall close completely except at umbilical
region where the connecting stalk & yolk sac remain attached.
Failure of lateral body wall folds to close, this causes defect in
body wall called ventral body wall defect.

LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
The results of these growth cephalocaudally & lat. body wall,
gut will be form. It divided into foregut, midgut (which
communicates with yolk sac through vitelline duct) & hind gut.
Oropharyngeal membrane seperates the foregut, specifically,
pharynx from primitive oral cavity which called stomaderm.
In the 4
th
weeks, oropharyngeal membrane rupture & oral cavity
continue with the foregut.
Caudally, the hind gut, specifically the anal canal, separate from
primitive anus, which called proctodeum , by cloacal
membrane.
At the 7
th
week, this cloacal membrane rupture creating the
opening to the anus.
At this time allantois form the cloaca.
By the 5
th
week, cloaca, umbilical vessels & yolk sac duct are
incorporated in the umbilical region.
Endodermal germ layer also gives rise to:
1- Epithelial lining of respiratory tract.
2- Parenchyma of thyroid, parathyroid, liver & pancreas.
3- Reticular stroma of the tonsil & thymus.
4- Epithelial lining of urinary bladder & urethra.
5- Epithelial lining of tympanic cavity & auditory tube.
THE END

LEC4 EMBRYOLOGY 2013-2014
EMBRIONIC LAYER
PART(2)
تكملة محاضرة رقم
(
3
)
EMBRIONIC PERIOD
