Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 1
Bilaminar germ disc:
(2
nd
week of development) ( week of complete implantation of
blastocyst):
Here we will discuss changes occur day by day
Day 8 :
1- Blastocyst starts.. to embedded partially in the endometrial stroma.
2- At the site of the embedding , the blastocyst differentiated into 2 types of
cells:
a) Cytotrophoblast : which is inner layer of mono nucleated cells, whose
cells have clear boundaries.
b) Syncytiotrophoblast : which is outer layer of multinucleated cell, with
ill-defined cell boundary.
3- Cytotrophoblast reveals active mitotic division with increased number of cell,
this lead to migration of cytotrophoblast cell into Syncytiotrophoblast, fuse
with its cells & lose their cell membrane.
Mitotic division is absent in Syncytiotrophoblast.
In the inner cell mass, 2 layers will be appear due to differentiation of its cell,
these layers are:
a) Hypoblast layer: whose cells are cuboidal, small & adjacent to
blastocyst cavity.
b) Epiblast layer: whose cells are tall columnar cells &adjacent to the
amniotic cavity.
Hypoblast & epiblast together form a flat disc. A small cavity appears between
the cells of epiblast. This cavity enlarges in size & called amniotic cavity.
The cell that is originated from epiblast, lies adjacent to the cytotrophoblast is
called amnioblast.

Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 2
The epiblast , weither in its own area or become amnioblast is in same continuity
& lining the amniotic fluid .
This change regarding the dividing future embryo. Regarding the uterus, at the
site of implantation site, it becomes edematous, highly vascular with large ,
tortuous glands that secret mucous & glycogen .(i.e. preparation of the uterus ,
mainly at implanted site, to receive the implanted embryo.
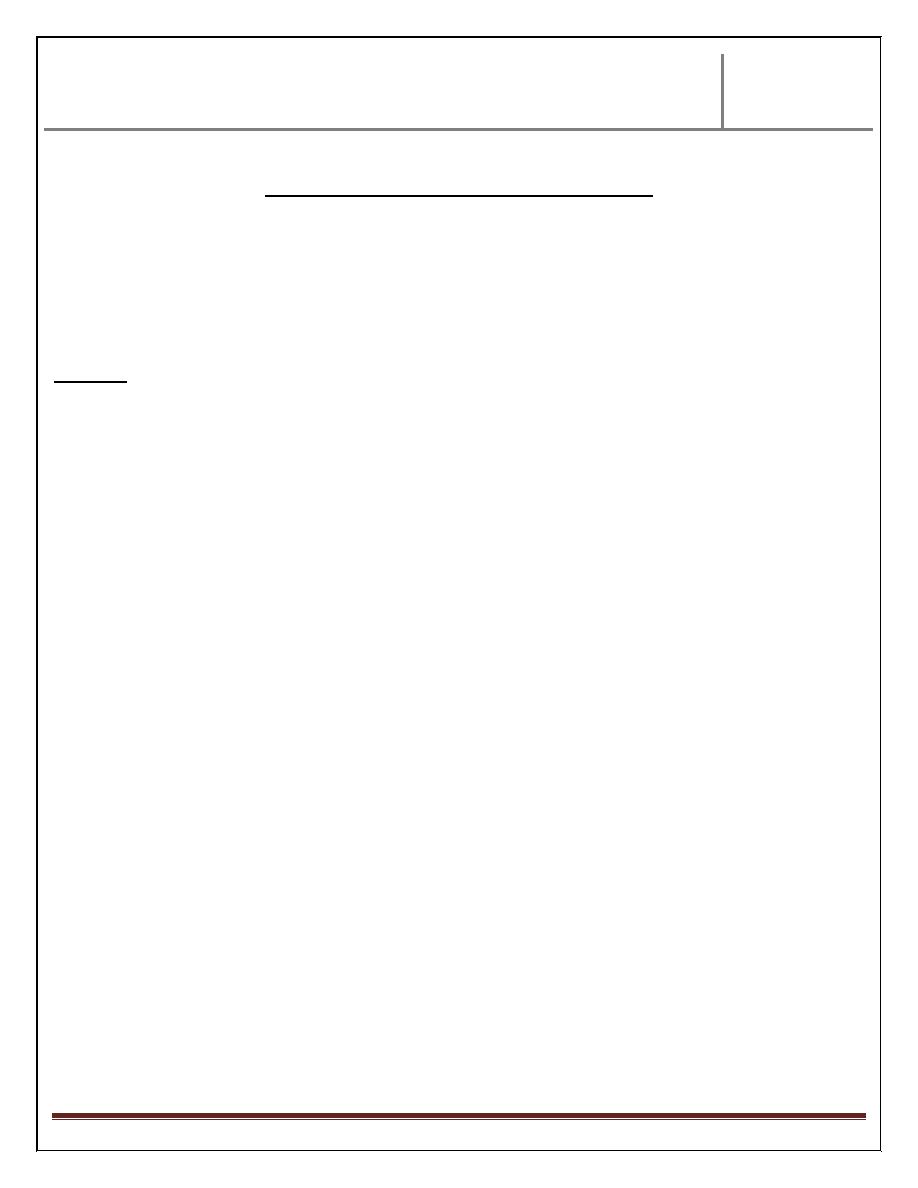
Day 9 :
Changes occur in this stage are:
- Blastocyst, more deeply implanted in the uterus & penetration defect is closed
by fibrin coagulum.
- Appearance of vacuoles in the syncytium, these vacuoles fused together
forming lacune. This stage called lacunar stage. This change occurs at
embryo pole.
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 3
At the abembryonic pole, from the hypoblast, flat cells arise forming thin
membrane surrounding a cavity called exocoelomic cavity (primitive yolk
sac).
This flat membrane called exocoelomic (Heuser’s) membrane. Outer to thin
membrane single layer of trophoblast cells.
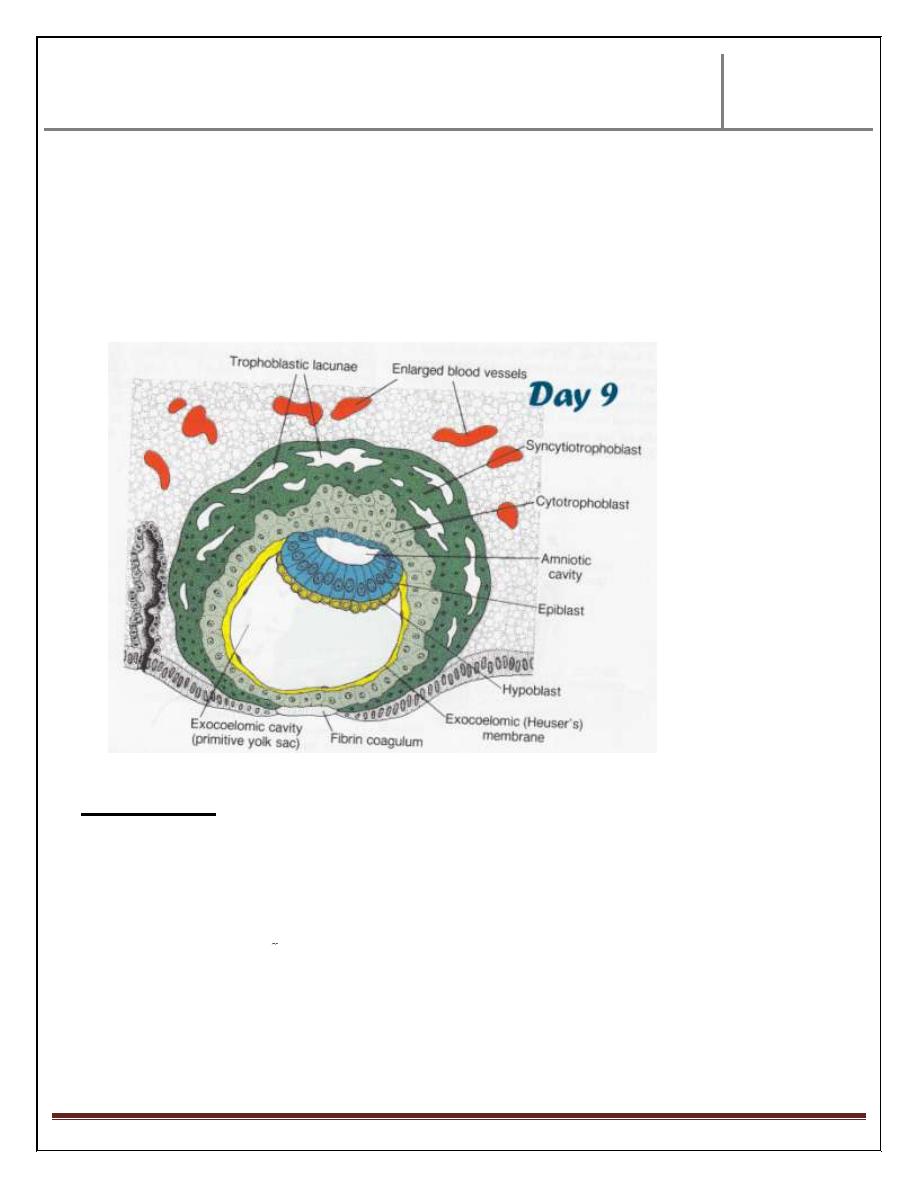
Day 11 & 12:
At these stages, changes occur in the endometrium of uterus, & changes occur in
the blastocyst.
At maternal side, the capillaries will be congested & dilated forming what is
known as sinusoids.
At embryonic side, the blastocyst is completely embedded inside endometrium
uterus leaving small fibrin area covering the entry area.
The syncytium reveals more & more lacunae which increased in size & no. , &
form an intercommunicating network inbetween .
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 4
The syncytial lacuanae become continuous with sinusoids i.e. maternal blood
will enter the lacunar system.
This lacunar system with maternal sinusoids will form what is called utero
placental circulation .
At this time, a fine, loose connective tissues originate from yolk sac cell,
distributed between the inner surface of trophoblast & outer surface of
exocoelomic cavity. These tissues called extraembryonic mesoderm.
Later on, extraembryonic mesoderm revealed so many cavities located between
the two layers of this mesoderm, the inner one called extraembryonic somatic
mesoderm, & the inner called extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm.
These cavities united together forming big single cavity called extraembryonic
cavity or chorionic cavity.
This cavity will surround the primitive yolk sac & lined by extraembryonic
somatic mesoderm.
The primitive yolk sac will be covered by extra embryonic splanchnic
mesoderm.

Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 5
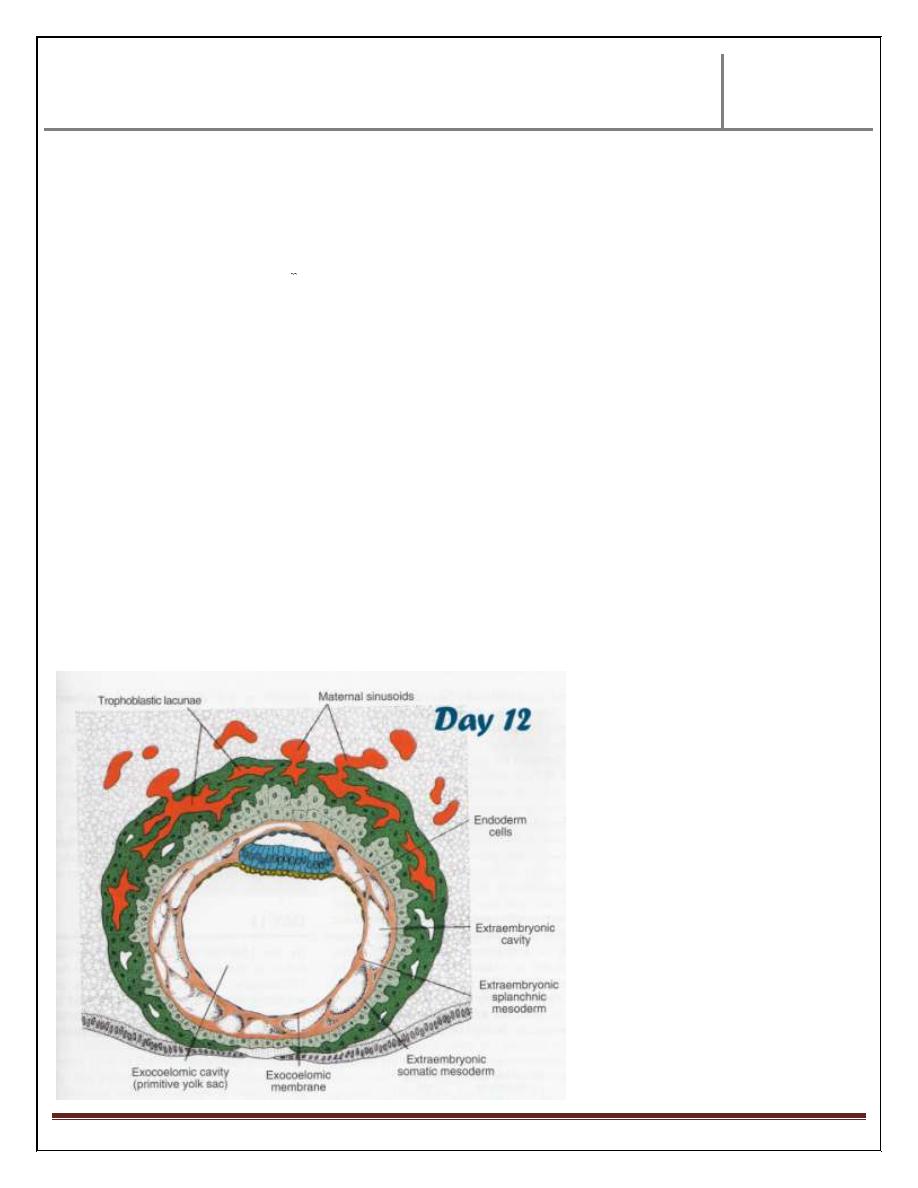
Day 13:
At this day, the defect in the endometrium due to implantation of ovum is
disappeared by continuous endometrial lining, except bulging of the blastocyst
toward uterine cavity.
IMP
At the site of implantation; the blood flow increased & area of
implantation becomes so delicate that bleeding from one of congested lacunae
could occur. This bleeding occur at same time of expected menstrual cycle,
therefore some or most of females think that bleeding is a menstrual cycle
which lead to mistaken in calculation the delivery date.
Trophoblast shows villi penetrating Syncytiotrophoblast. This is called
primary villi. The hypoblast produce additional cells that migrate along the
inside of the exocoelomic membrane forming new cavity called secondary
yolk sac. The yolk sac is smaller than original exocoelomic cavity (primitive
yolk sac) but large portion of the exocoelomic cavity are pinched off, forming
exocoelomic cyst.
later on, the extracoelomic cavity expands & forms large chorionic cavity.
The bilaminar layer with amniotic cavity & secondary yolk sac has been
attach only to the inner surface of 14 days blastocyst only through the
connecting stalk (which originate from extraembryonic somatic mesoderm)
& this is the future umbilical cord.
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 6
Clinical notes:
Sometimes the fertilized ovum failed to implant in its normal place in uterus.
This condition called ectopic pregnancy. the abnormal sites for abnormal
implantation could be:
1- Ovaries (0.2%).
2- Abdominal cavity (1.4 %) mostly in the douglus pouch.
3- Ampullary region of fallopian tube( 80%).
4- Tubal implantation (12%) .
5- Interstitial implantation (0.2%).
6- At the internal os & called placenta brevia (0.2%).

Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Lec.1
2013-
2014
Embryology
Page 7
THE END
