Lecture 6
Hexose Monophosphate Shunt( HMP) or
Pentose Phosphate Pathway ( PPP) &
Uronic Acid pathway.
Objectives:
a - Evaluate the importance of HMP shunt in
cells of certain tissues particularly erythrocytes.
b- Describe the Uronic Acid pathway and its
involvement in synthesis of some
mucopolysaccharide & detoxification of bilirubin
, steroids & some drugs.
c- Identify the inherited disorders in both
metabolic pathway.
MSD

HMP shunt or PPP
●
Location:
liver, lactating mammary glands, adipose
tissue,adrenal cortex,gonads,RBCs…etc
but not in skeletal muscle.
●Functions:
1- Provides NADPH an important reduced &
phosphorylated coenzyme used in Reductive
Biosynthesis reactions of FAs , steroids,
glutathione..etc.
2- Provides Ribose5-P( used in the synthesis of
nucleotides & nucleic acids).
MSD

3- Provides a route for the use of Pentose &
their conversion to intermediates of glycolysis
namely Glycerald.3-P (triose-P) & Frc6-P
( hexose-P) .
4- NADPH is essential in RBCs to keep the
antioxidant Glutathione ( Glycine-Cysteine-
Glutamate) ; tripeptide (Gly-Cys-Glu) in the
reduced state (GSH) important to prevent cell
hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
) toxicity from oxidizing
the membrane component causing lysis (
hemolysis ) → Hemolytic Anemia.
MSD

NADPH + GSSG → NADP + GSH by
Glutathione Reductase
GSH + H
2
O
2
→ GSSG + H
2
O by
Glutathione Peroxidase
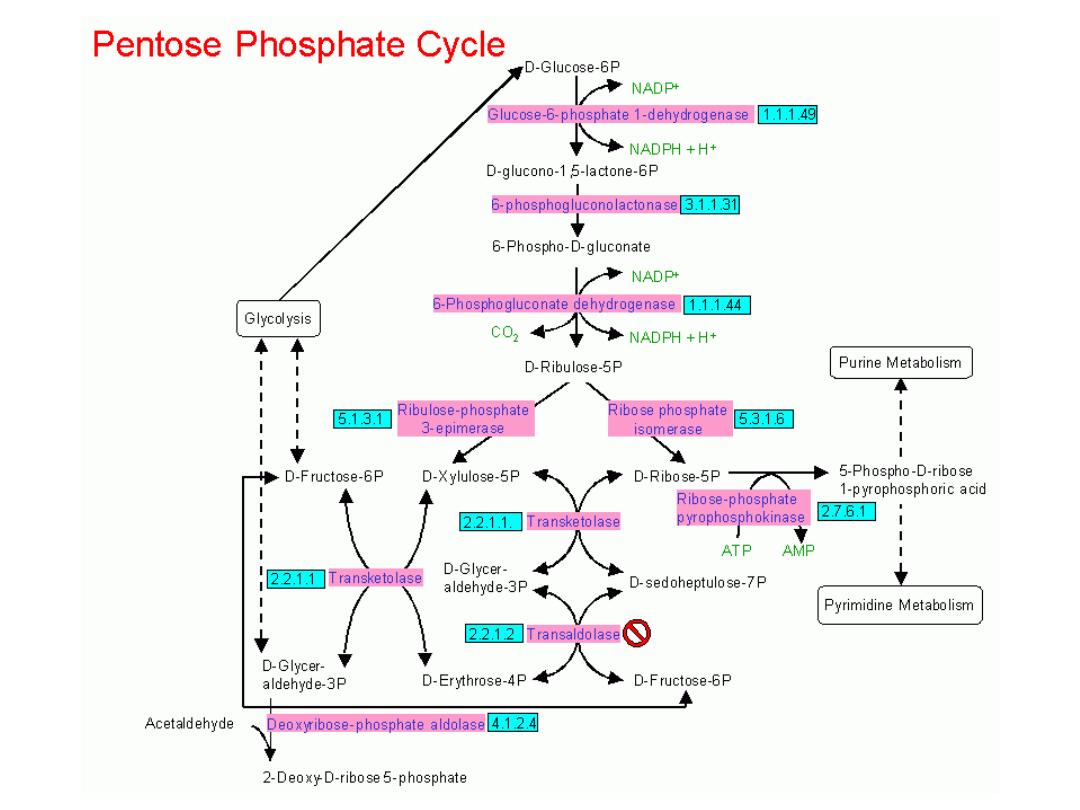
● Reactions:
1- 3 Glc6-P + 6
NADP →→→ 6 NADPH +
3CO
2
+ Ribulose5-P
Three oxidative, irreversible reactions result in
NADPH & CO
2
& Ribulose 5-P by
glucose 6-P
dehydrogenase ( G6PD)
2- Ribulose5-P ( 5-
C) → Ribose5-P ( 5-C )
( nucleotides & nucleic acid )by
isomerase
MSD

3- Ribulose5-P enters in non-oxidative , reversible
( interconversion ) of sugar phosphate to give
Frc6-P & Glycerald.3-P
Ribulose5-P ↔ Xylulose5-P by
Epimerase
4- Xylulose 5-P + Ribose 5-
P ↔
Sedoheptulose7-P ( 7-C) + Glycerald.3-P(3-C)
by
Transketolase
& Thiamine pyrophosphate
( TPP) an active Vit.B1 as a coenzyme.
Glycerald. 3-P is an intermediate of glycolysis
and this point is a link between HMP shunt &
glycolysis . MSD
5-
Sedo.7-P + Glycerald.3-P ↔
Erythrose-P ( 4-C) + Frc6-P ( 6-C) by
Transaldolase
6- Xyl.5-P( 5-C) + Eryth.4-P ( 4-
C) ↔
Frc6-P ( 6-C) + Glycerald.3-P ( 3-C)
by
Transketolase
& TPP.
● Regulation :
1- availability of NADP
2-
G6PD
is activated by CHO feeding &
inhibited by starvation & DM.
3-
G6PD
is activated by TPP.
MSD

☻Genetic defect ,deficiency of
G6PD
in
some people in the Mediterranean region
lead to Hemolytic Anemia. This is due to
drugs like Aspirin,antimalarial primaquine or
food ( Fava Beans ) causing Favism.
Chronic deficiency of thiamine lead to
Wernicke ̛s Korsakoff Syndrome.
MSD

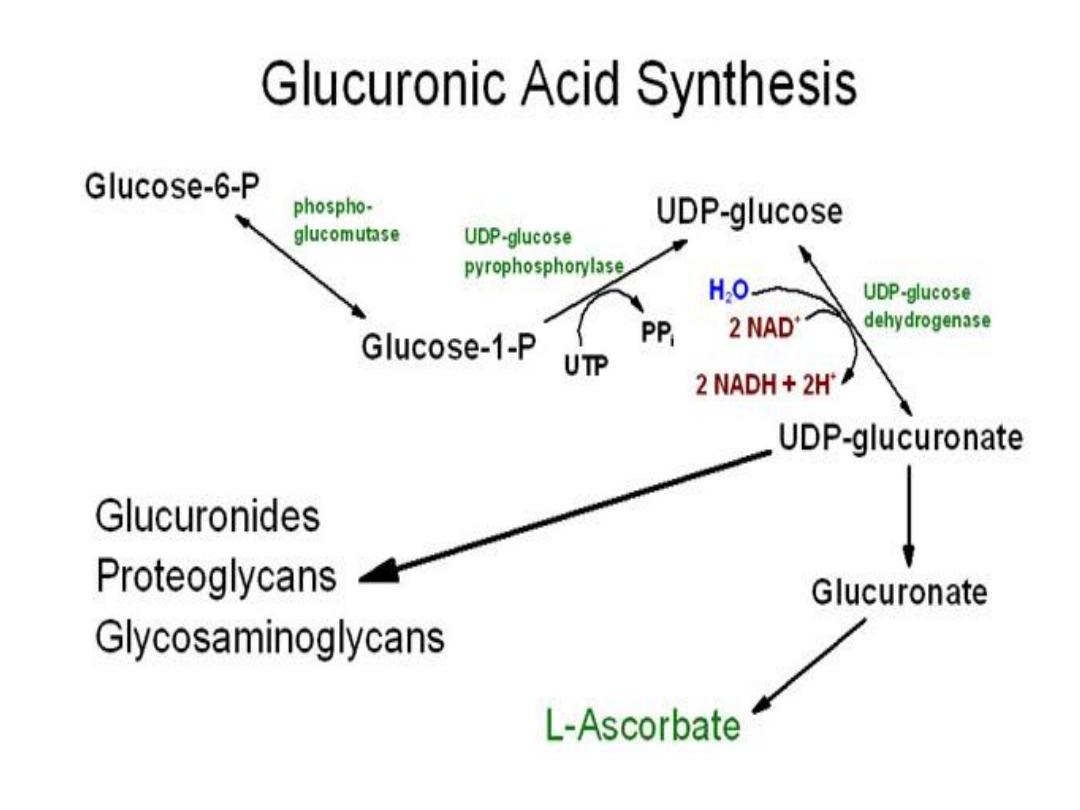
Uronic Acid ( uronate ) pathway
●In liver, Glc is converted to Glucuronic acid or
Glucuronate (GluUA), Ascorbic acid
( vit.C)
but not in human , and Pentoses .
● Like HMP shunt NO ATP is produced.
● Reactions:
1- Glc6-
P → Glc1-P by mutase then + UTP
→ UDP-Glc by pyrophosphorylase
2- UDP-Glc +
NAD → NADH +
UDP-Glucuronate by dehydrogenase
MSD

3- UDP-Glucuronate is used for conjugation with
the aminosugars ( Glucosamine& Galactosamine)
in the synthesis of Mucopolysaccharides (MPS) or
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) having various
functions in the body e.g. Hyaluronic acid (HA)
found in eye , Synovial fluid,Placenta ; Chondroitin
sulfate (CS) found in cartilage; and Heparin found
in blood .
4- UDP-Glucuronate is also used for conjugation
with steroid hormones, bilirubin & a number of
drugs that are excreted in urine or bile as
glucuronide conjugates.
MSD
5- L – Xylulose is a pentose sugar that is
accumulated in the blood .
☻In the genetic defect the Inherited
disorder ( Inborn error ) of Essential
Pentosuria due to deficiency of its
Reductase enzyme.
6- This pathway is linked to HMP shunt by
formation of Xylulose5-P & Glycolysis by
formation of Frc6-P.
MSD

☻7- Mucopolysaccharidoses ( another inborn
error)
A group of 10 related disorders due to
inherited defect of
Lysosomal hydrolases
enzymes
that degrade MPs ( GAGs ). Hurler &
Hunter Syndromes due to deficiency of
Iduronidase & Sulfatase
, respectively. MPs are
accumulated in tissues & excess are excreted in
urine.
MSD

Abbreviation:
CHO – carbohydrate
ATP – adenosine triphosphate
ADP – adenosine diphosphate
Pi – inorganic phosphate
E – energy
ETC – electron transport chain
Ox.Phosph. – oxidative phosphorylation
TCA cycle- tricarboxylic acid cycle
CAC – citric acid cycle
~P
– high-energy phosphate bond
UTP
– uridine triphosphate
GTP
– guanosine triphosphate
CTP
– cytidine triphosphate MSD

HMP shunt – hexose monophosphate shunt
PPP – pentose phosphate pathway
UA – uronic acid pathway
Glc or G – glucose
Frc – fructose
Glc 6-P – glucose 6- phsphate
Glc 1-P – glucose 1-phosphate
Frc 6-P – fructose 6 phosphate
Frc I,6 bisP – fructose 1,6 bisphosphate
Frc 2,6bisP – fructose 2,6 bisphosphate
Glycerald.3-P – glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
DHAP – dihydroxyacetone phosphate
1,3 bisPG – 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate
2,3 bisPG – 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate
MSD

3 PG – 3 phosphoglycerate
2PG – 2 phosphoglycerate
PEP – phosphoenolpyruvate
HK – hexokinase
GK – glucokinase
PFK – phosphofructokinase
1,6bisPase – 1,6 bisphosphatase
PK – pyruvate kinase
PC – pyruvate carboxylase
PDC or PDH – pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Glc6Pase or G6Pase – glucose 6 phosphatase
NADH – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide(reduced)
NAD – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( oxidized)
MSD

NADPH – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate ( reduced )
NADP - nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate ( oxidized )
FADH
2 -
Flavine adenine dinucleotide ( reduced )
FAD - Flavine adenine dinucleotide ( oxidized )
AA – amino acid
FA – fatty acid
cAMP – cyclic adenosine monophosphate
TPP – thiamine pyrophosphate
CoA – coenzyme A
TAG or TG – triacylglycerol or triglyceride
DM – Diabetes mellitus
MSD

UDP-Glc – uridine diphosphate glucose
UDP-GluUA - uridine diphosphate glucuronate (
glucuronic acid )
α-KG – alpha ketoglutarate
OAA
– oxaloacetic acid or oxaloacetate
Rib.5P
– ribose 5 phosphate
Ribul. 5P
– ribulose 5 phosphate
Xylul.5P
– xylulose 5 phosphate
Sedoheptul.7P
– sedoheptulose 7 phosphate
Eryth.4P
– erythrose 4 phosphate
GSH
– glutathione (reduced)
GSSG
– glutathione ( oxidized )
H
2
O
2
–
hydrogen peroxide
MSD
