
BioChemistry
Dr.Munaf 3

Lecture 3
Electron Transport Chain ( ETC) &
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Ox.Phosph.):
Objectives:
●Describe the transport of electrons
through the respiratory chain.
● Explain how ATP is synthesized.
msd

●
ETC is the final common pathway in Aerobic
cells by which eˉ derived from various
substrates are transferred to O
2
to form H
2
O.
● Series of highly organized Ox.-Red.
enzymes & reactions represented as:
Red.A + Ox.B
↔ Ox.A + Red.B
the enzymes use NAD+ or FAD
as eˉ
acceptor cofactors ( Coenzymes ).
● Ox.Phosph. is the main source of E in
Aerobic cells , it is the process whereby free E
released
when eˉ are transferred along ETC ,
is coupled to form ATP from ADP + Pi.
MSD
● In intact mitochondria, eˉ transport & ADP
phosphorylation are tightly coupled reactions
But in damaged ones , these reactions may
occur unaccompanied and free E is released
as heat ( i.e. NO ATP production ).
● ETC & Ox.Phosph. Occur in the Inner
mitochondrial membrane (* Coupling
Membrane ). It has high selective
permeability for specific substances e.g.
ATP & other
nucleotides,pyruvate,succinate…etc MSD

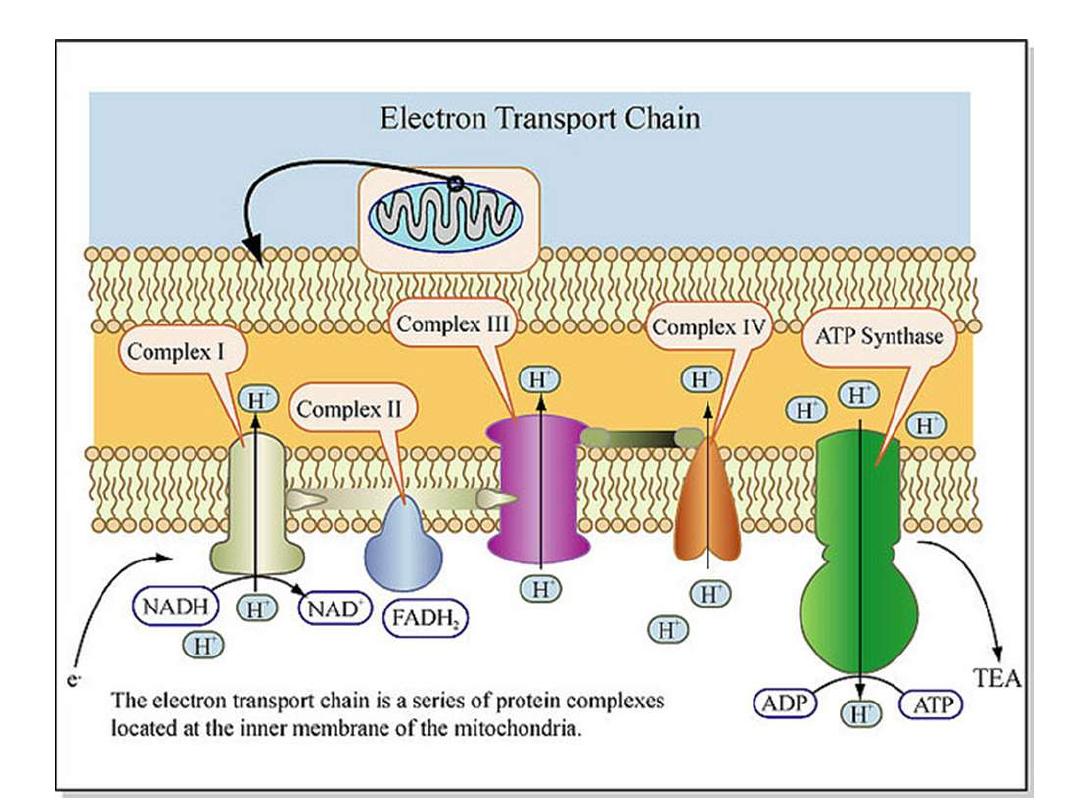
● Sources of eˉ are NADH ,FADH
2
. ETC is organized
into 4 complexes ( 9 reactions ):
Complex I
: Substrates → NADH→FMNH
2
→ Quinone ( Q ) by
NADH dehydrogenase
( inhibited by Rotenone - insecticide ).
Complex II
: Succinate → FADH
2
→ Q
by
Succ. DH
(inhibited by Carboxine ).
Complex III
: Q → Cytochromes b-c → Cyt.aa
3
by
Cyt.Reductase
(inhibited by Antimycin)
Complex IV
: Cyt. aa
3
→ O
2
→ H
2
O by
Cyt.
Oxidase
(inhibited by cyanide CN, Carbon
monooxide CO,Hydrogen Sulfide H
2
S , HN
3
Azide
).
MSD
● Phosphorylation occurs
in Complex V
& ATP is
formed as follows:
2 ADP + 2Pi + 2H
+
+ E → 2 ATP + 2H
2
O
by
ATP synthase ( ATPase )
… ( Oligomycin)
The most widely accepted theory of ETC &
Ox. Phosph. is the Chemiosmotic or
Mitchell ̛ s Theory.
●Control of Ox. Phosph. :
1- Availability of ADP , substrates & O
2
.
2- The capacity of ETC itself.
[ N.B. uncouplers of Ox. Phosph. are compounds
that cause normal ETC but NO production of ATP
e.g. 2,4 dinitrophenol & dicumarol ].
MSD

● Sites of coupling for ATP formation
Complex I , Complex III , Complex IV
NADH gives 3 or 2.5 ATP , FADH
2 ,
gives 2
or 1.5 ATP .
☻Several inherited defects
( NADH
dehydrogenase & Cyt. Oxidase
) of
Mitoch.occur and cause Myopathy &
Encephalopathy.
MSD

● The triglyceride(Fat) or TAG
hydrolyzed by
lipases
(Lipolysis) in
adipose tissue to give Glycerol & fatty
acids. Glycerol moves into the liver &
by
kinase
→ Glycerol 3-P then by
dehydrogenase
→ DHAP & by
isomerase
→ Glyceraldehyde 3-P ( triose 3-P )
then by reverse reactions of glycolysis
into Glc. to supply the brain. MSD
