Lecture 2
2 – Tricarboxylic acid Cycle (TCA) or Citric
acid Cycle or Kreb ̛ s Cycle
Objectives:
a- Outline the intermediates and enzyme
activities .
b- State which steps produce reduced
coenzymes and high energy phosphate
compounds.
c- Explain its regulation and the link with other
pathways through intermediate compounds.

▪
The link between glycolysis & TCA cycle
Pyruvate ( cytosol) enters the mitochondria
( matrix)and irreversibly converts into Acetyl CoA.
2 pyruvate + CoASH + 2NAD→2 AcetylCoA +
2 NADH + 2 CO
2
by
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Enzyme (
PDC or PDH )
an enzyme of 4 distinct enzymatic
activities & 5 coenzymes namely;
[Thiamine pyrophosphate(TPP), Coenzyme A (
CoA), NAD, FAD & lipoic acid].
PDH
is inhibited
by dietary deficiency of Thiamine(vit.B1),
arsenite,mercuric ions.

☻
PDH
genetic defect ( inborn error ) leads to
↑[pyruvate] & [lactate] i.e. Lactic Acidosis &
Neurological disorders .
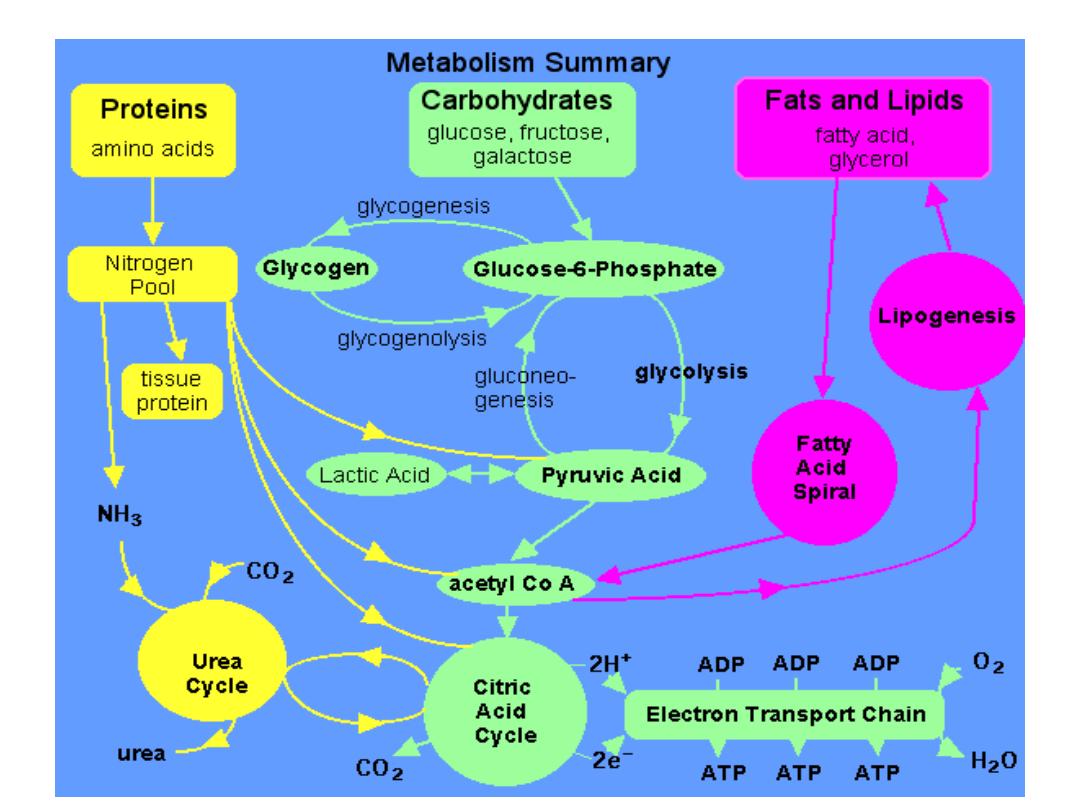
The TCA cycle;
●Series of 9 enzymatically catalyzed
mitochondrial reactions that form a common
pathway for the final oxidation of all
metabolic fuels ( CHO,lipids, &
proteins)giving Glc.,free fatty acids ( FFAs
also called unesterified FAs) and amino
acids(AAs) which are catabolized to
AcetylCoA ( the substrate of TCA ). msd
●TCA cycle reactions are both Catabolic &
Anabolic & so called Amphibolic pathway.
Oxidation of Acetyl CoA to form intermediate
compounds, E & CO
2
is catabolic reactions.
Citrate formed can move out of mitochondria
when there surplus excess of E & Glc as in
cases of ↑ Eating & ↓ physical activities ( sitting
all the time) with no exercises or sport, this
Citrate can be reconverted into Acetyl CoA
( a precursor of FAs synthesis that is esterified
with glycerol forming Triglycerides ( Fat) in
lipogenesis pathway in liver to go into adipose
tissues to be stored causing Obesity.Lipogenesis
is Anabolic pathway. msd

●TCA cyle provides much of the E for
respiration .The elecrtrons generated by this
cycle in the form of reducing equivalents
(reduced coenzymes) like NADH & FADH
2
are transferred to the ETC & produce ATP
by Ox. Phosph..
● Net Reaction :
AcetylCoA + 3 NAD + FAD +GDP + Pi +
2H
2
O → 2CO
2
+ 3 NADH + FADH
2
+ GTP
+ 2H
+
+ CoA .
msd
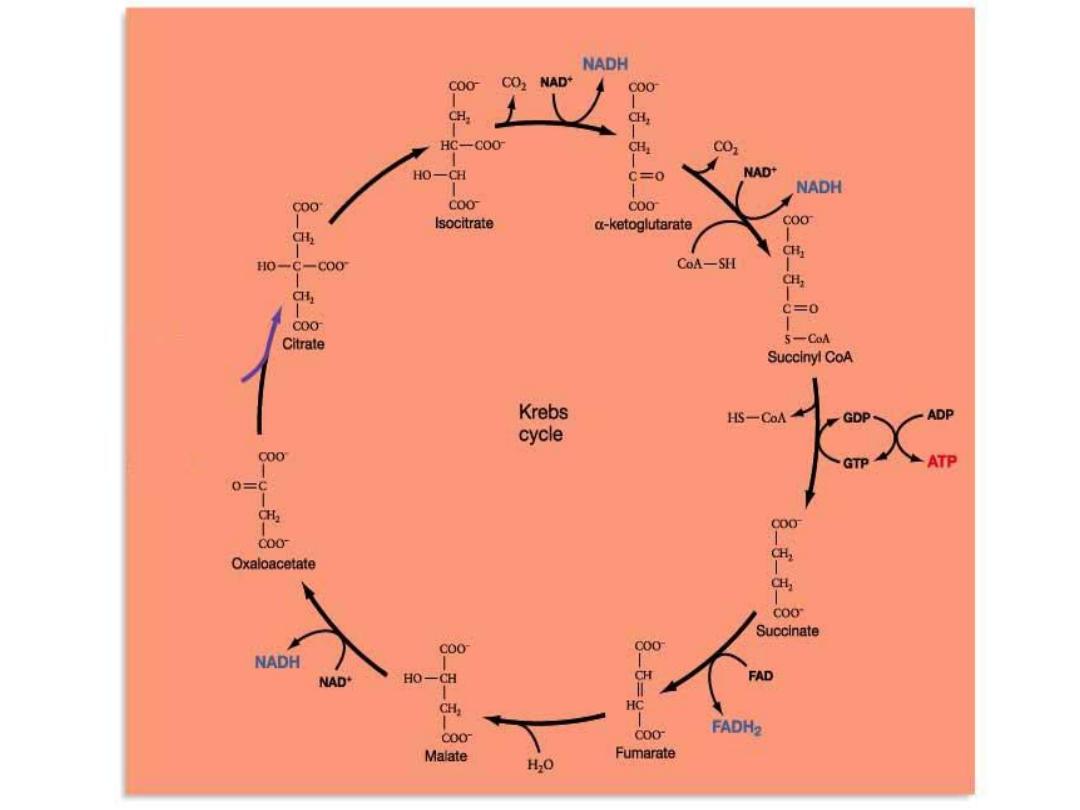

1- Acetyl CoA + OAA → Citrate
by
Synthetase
& recycle in the 9 reactions.
2- Isocitrate by
its dehydrogenase
→
α KG + NADH + CO
2
3-
α KG by
its dehydrogenase
→
Succinyl CoA + NADH + CO
2
4- Succinyl CoA by
its thiokinase
→
Succinate + 1 GTP
5- Succinate by
its dehydrogenase
→
Fumarate + 1 FADH
2
6- Fumarate by
fumarase
( hydration)→
Malate
msd
7- Malate by its
dehydrogenase
→
OAA + NADH
OAA recycle to produce E as follows :
3
NADH → 9ATP ( or 7.5 ATP )
1 FADH2
→ 2 ATP ( or 1.5 )
1
GTP → 1 ATP
i.e. 1
Acetyl CoA → 12 ATP ( or10 ATP )
2 = = = 24 ATP ( or 20 )
●
Regulation : The 3 important regulatory
enzymes are;
1-
Citrate Synthase
2
-
Isocitrate DH
3-
α KG DH
are inhibited in E sufficieny when ATP , NADH
Succinyl
CoA are ↑ . ADP act as Activator.
msd

☻Genetic defects of enzymes are
associated with severe Neurological
damage due to ↓↓ ATP formation in CNS.
msd
