
Q 1. A 60 year old man was presented to
emergency clinic unit because of tight
chest pain that had occurred 3 days
previously. The following laboratory test
results
were
found:
serum CK 235 u/l (NR less than 250)
serum cTnT 0.15 µg/L (0.1). Answer the
following
questions:
1.
What
is
the
diagnosis
2.
what
is
the
difference
in
these
biomarkers
patterns
3. is there is need for measurement of Ck-
MB?why.

Q2.
A 21 year old female complaining of a flu-like
illness for 2 days. She had fever, vomiting, abdominal
tenderness and the her doctor found that she was
jaundiced and she had returned recently from a long
holiday
in
Asia.
Laboratory
enzymes
were:
S.ALT
activity
560
U/L
(10-50)
S.AST
activity
600
U/L
(10-40)
S.ALP
activity
190
U/L
(40-125)
1.What
is
the
diagnosis
2. which is the specific test for such diagnosis
3.In case of marked elevation of ALP and moderate
increase
in
aminotransferase,
what
is
your
interpretation.


Q: Select the best enzyme for evaluation
of each of the following conditions:
.1
Prostatic carcinoma
.2
Muscle dystrophy
.3
Bony tumour with ESR 100 mm3/h.pre
`
2

●
Iron
deficiency
anemia
- blood haemoglobin concentration falls
below
the
lower
limit
of
normal
▪
Hb
(
),
MCV
(
),
TIBC
(
),
serum ferritin (
),
marrow iron (absent)

Iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia
•
The characteristic sequence of events ensues
when the total body iron level begins to fall:
1. decreases the iron stores in the
macrophages of the
liver, spleen and
bone marrow
2. increases the amount of free erythrocyte
protoporphiryn (FEP)
3. begins the production of microcytic
erythrocytes
4. decreases the blood haemoglobin
concentration

Iron deficiency anemia
Definition and etiologic factors
Definition: The end result of a long period of
negative iron balance
Etiologic causes of IDA
∆ Decreased iron intake
◄inadequate diet, impaired absorption,
gastric surgery, celiac disease

∆ increased iron loss
◄gastrointestinal bleeding (haemorrhoids,
salicylate ingestion, peptic ulcer, neoplasm,
ulcerative colitis)
◄excessive menstrual flow, blood donation,
disorders of hemostasis
∆ increased physiologic requirements for iron
◄infancy, pregnancy, lactation
◄cause unknown (idiopathic hypochromic
anemia)

Symptoms of anemia
•
Fatigue
•
Dizziness
•
Headache
•
Palpitation
•
Dyspnea
•
Lethargy
•
Disturbances in menstruation
•
Impaired growth in infancy

Symptoms of iron deficiency
•
Irritability
•
Poor attention span
•
Lack interest in surroundings
•
Poor work performance
•
Behavioural disturbances
•
Pica
•
Defective structure and function of epithelial
tissue
–
especially affected are the hair, the skin, the
nails, the tongue, the mouth, the
hypopharynx and the stomach
•
Increased frequency of infection

Pica
•
The habitual ingestion of unusual substances
–
earth, clay (geophagia)
–
laundry starch (amylophagia)
–
ice (pagophagia)
•
Usually is a manifestation of iron deficiency
and is relieved when the deficiency is treated

Abnormalities in physical examination
•
Pallor of skin, lips, nail beds and conjunctival
mucosa
•
Nails - flattened, fragile, brittle, koilonychia,
spoon-shaped
•
Tongue and mouth
–
glossitis, angular cheliosis, stomatitis
–
dysphagia (Peterson-Kelly or Plummer-Vinson
syndrome
(carcinoma in situ)

Laboratory findings (1)
•
Blood tests
–
erythrocytes
•
hemoglobin level
•
the volume of packed red cells (VPRC) ↓
•
RBC
•
MCV and MCH
•
Hypochromia
–
platelets
•
usually thrombocytosis

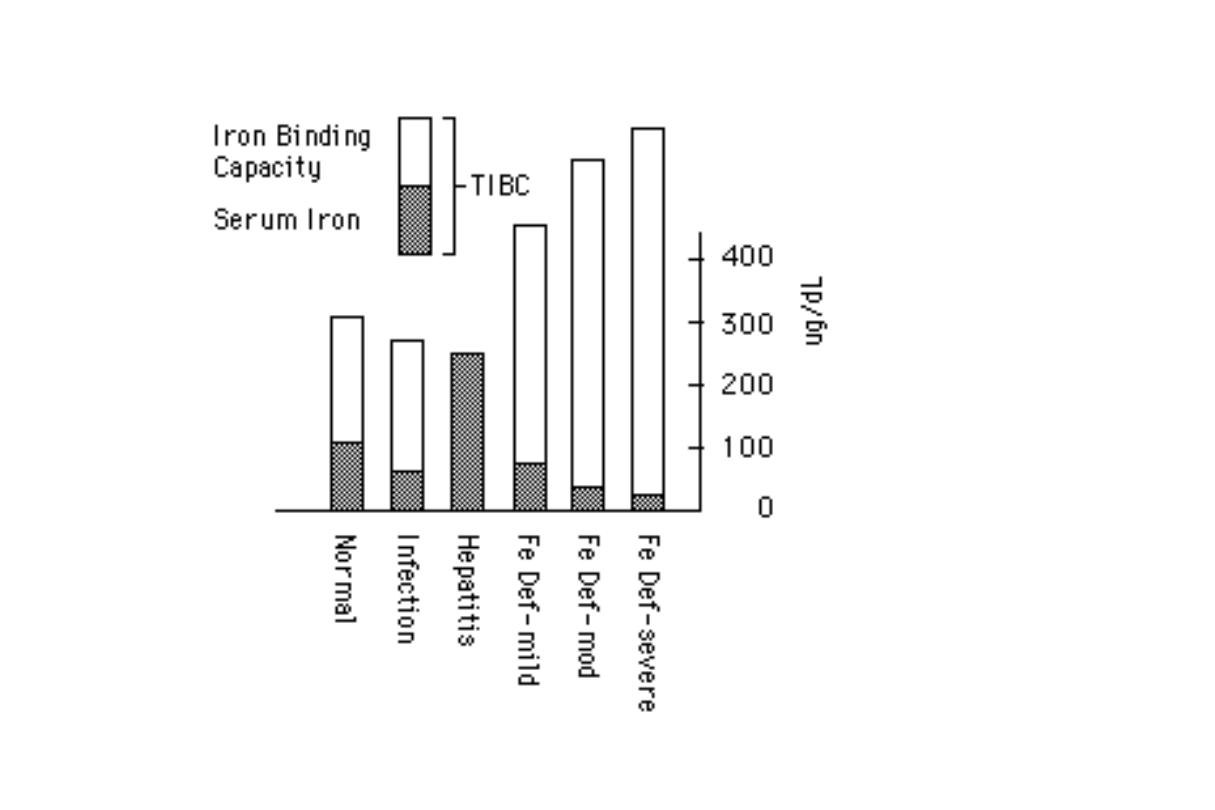
Biochemical Laboratory findings (2)
•
Iron metabolism tests
–
serum iron concentration ↓
–
total iron-binding capacity TIBC
–
saturation of transferrin ↓
–
serum ferritin level
–
serum transferrin receptors

The plasma or serum ferritin concentration
declines very early in the development of
IDA, long before changes are observed in
blood Hb concentration, RBC size, TIBC or
serum
iron
concentration.
Thus
measurement
of
serum
ferritin
concentration is used as a very sensitive
indicator of IDA that is uncomplicated by
other
concurrent
disease

When ID is developing, the RE stores
(hemosiderin
and
ferritin)
become
completely
depleted
before
anemia
occurs.
At
an
early
stage,
no
clinical
abnormalities.
Later, patient may develops general
symptoms
and
signs
of
anemia.
In severe case of IDA ridged or spoon
nails.

Summary
◄ IDA is the end result of a long period of
negative iron balance
◄ Decreased iron intake, increased iron loss,
and increased physiologic requirements for iron
◄ Measurement of serum ferritin concentration
is used as a very sensitive indicator of IDA that
is uncomplicated by other concurrent disease
