
Lecture 2
CHOLESTEROL
Diagram the pathway of cholesterol biosynthesis and
define regulatory enzyme.
Observe the action of lipid lowering drugs like Statin
derivatives in decreasing blood cholesterol.
Group the vital compounds that are derived from
cholesterol like steroid hormones, vitaminD3.
Determine the functions of bile salts.

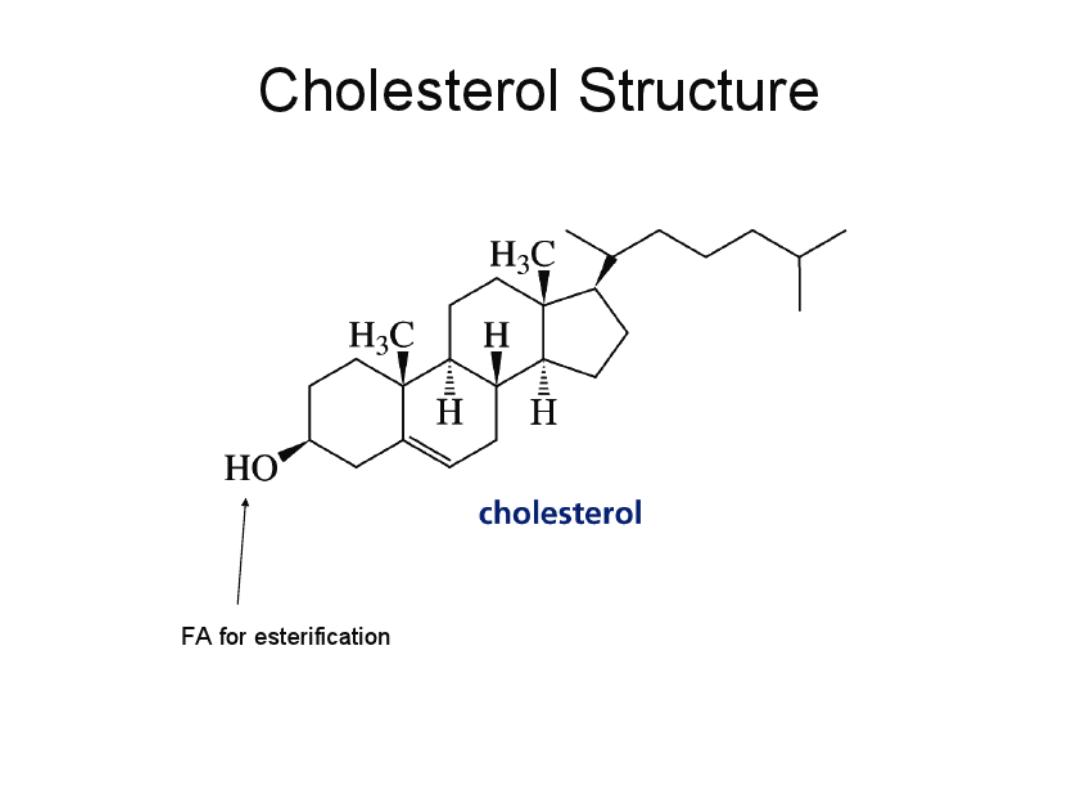
Cholesterol is a soft fatty(not solid) substance that is
produced endogenously in the body and also derived
from food materials such as dairy products, eggs (egg
yolk is rich in cholesterol), meat and poultry.
Cholesterol is a major sterol in animal tissues, in plant
is beta-sitosterol is poorly absorbed by humans and
appear to block the absorption of dietary cholesterol.
Cholesterol is vital substance in the body for the
normal functioning of various cells and tissues.

However,
cholesterol
in
high
amounts
(hypercholesterolemia) can get accumulated in the
blood vessels and disrupt their functions.
2/3 of
plasma cholesterol is esterified (OH at C3 is attached
with acyl group RCO- of fatty acid), the remainder
1/3 is free cholesterol. Free cholesterol (Fch) is more
polar than esterified cholesterol(Ech). Echs are
hydrophobic substances and are not found normally in
membranes ?.

Because of hydrophobicity of cholesterol is
transported in the blood after its association with
specific proteins (lipoprotein structure) and into bile
duct in association with phospholipids and bile salts.
Measurement of serum or plasma total cholesterol
involved both Fch & Ech.
Excess amounts of
cholesterol beyond the need of body cannot degraded
to CO2+H2O or other metabolites, but are; 50%
converted to bile acids and 50% are excreted as
unchanged cholesterol through the bile and intestine
into the feces.
Sources of body cholesterol
Diet
Hepatic Denovo Synthesis
Cholesterol synthesized in extrahepatic tissues
Liver cholesterol pool
secretion of HDL &VLDL
Free cholesterol in bile
conversion to bile salts/acids

Functions of Cholesterol
1.
Membrane component
2.Bile acids/salts
precursor
3.Vitamin D3 precursor
4
. Steroid Hormone
Precursors
Male & Female sex hormones(testosterone, other
androgens& Estrogens)
Adrenal cortex hormones (glucocorticoides&
Mineralocorticoides)

CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS
•
Occurs in cytoplasm
•
Requires NADPH & ATP
•Highly regulareted and the regulatory enzyme is
HMG-CoA* reductase
•
80% in liver, ~ 10% intestine, 10 %(skin, adrenal
cortex& reproductive tissues)
• precursors are Carbohydrate & fatty acids.
Note: *
HMG-CoA reductase;
Hydroxy methyl
glutaryl-CoA reductase
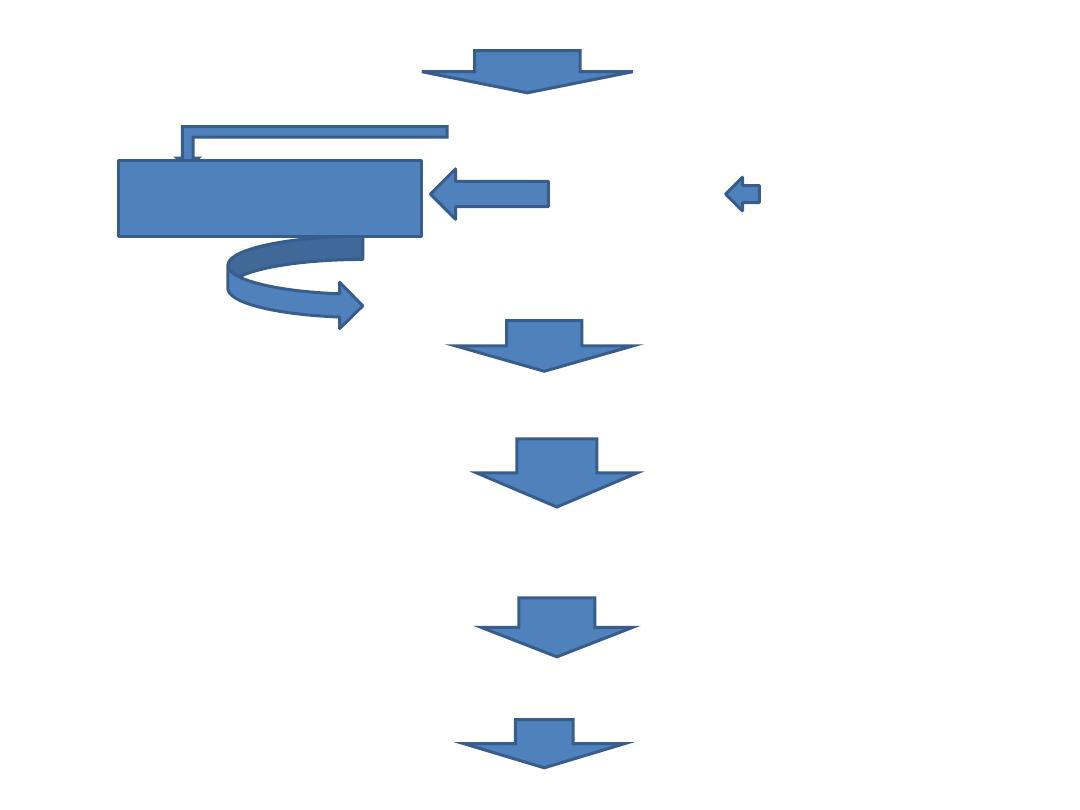
Glucose
Citrate
Acetyl-CoA
Acetate
Fatty acids
Acetacetate-CoA
HMG-CoA
*
HMG-CoA reductase NADPH as cofactor
Mevalonate
Sequalene
Cholesterol
Acetyl-CoA

The regulatory step is at HMG-CoA reductase enzyme.
This enzyme and so the cholesterol synthesis is
stimulated
post CHO diet and presence of insulin
, the
opposite for prolonged fasting and glucagon
. This
means that
high ATP stimulate the enzyme and the
pathway
and
low ATP inhibit both.
The pathway of
cholesterol synthesis is highly regularized, means it is
responsive to changes in cholesterol concentration
,
and regulatory mechanism (step of HMG-CoA
reductase)
exists to balance the rate of cholesterol

synthesis within the body (dietary cholesterol has
little effect) against the rate of cholesterol excretion
,
An imbalance in this regulation can lead to an
elevation in circulating levels of plasma or serum
cholesterol
(Hypercholesterolemia)
, with potential for
coronary artery disease(CAD). So, the increased
synthesis of cholesterol will inhibits the HMG-CoA
reductase regulatory enzyme and stop the pathway to
prevent normally the hypercholesterolemia. In
addition, those patients with hypercholesterolemia
are treated with drugs derivatives known-Statins such

as atorvastatin, pravastatin, and simvastatin- these
drugs regulate the blood levels of cholesterol by
inhibition of the same enzyme-HMG-CoA reductase
and so control blood and body cholesterol.
Cholesterol is the precursor of important
substance,
the
Bile
Acids.
Bile
Acids
and
Bile
Salts
These are organic compounds that involved two
types: Primary bile acids, cholic and chenodeoxycholic
acids, which are synthesized from cholesterol in the
liver by several steps of bile acids biosynthesis
pathway.

The regulatory enzyme of this pathway is cholesterol-
7-alpha-hydroxylase which stimulated by cholesterol
and inhibited by cholic acid. These bile acids
conjugated with glycine amino acid and taurine
derived from cysteine amino acid to form bile salts
with are more water solube. Bile salts are the most
important components of bile mixture of bile duct
(the duct involved in excretion of many substance
from the liver). Bile salts are either secreted into the
small intestine, the duodenum from liver or stored in
the gall blader when not needed for digestion.

In the small intestine, the intestinal flora convert the
primary bile acids into secondary bile acids, the
cholic=deoxycholic
and
chenodeoxycholic
acid=lithocholic
acid.
Bile salts are very important substance for digestion
and absorption of fat (lipid) diet and fat-soluble
vitamins (D, K, A, and E) BY acting as emulsifying
agents in the intestine and so helping in handling and
exposing the non polar lipid, the TG, to pancreating
enzymes. Moreover, bile acids and salts provide the
significant mechanism for excess cholesterol excretion
into bile duct, small intestine and finally in feces.
